CSS级联层叠样式
一、CSS:级联层叠样式简介
主要围绕三个方面进程阐述:
1、CSS样式分类
一般而言,所有的样式会根据下面的规则层叠于一个新的虚拟样式表中,其中数字 4 拥有最高的优先权(就近原则)。
浏览器缺省设置
外部样式表
内部样式表(位于 <head> 标签内部)
内联样式(在 HTML 元素内部)
2、CSS选择器:由一条多多条声明组成,selector {declaration1; declaration2; ... declarationN }
HTML元素选择器:*{}或p,a{}
类选择器:.info{}
ID选择器:#info{}
3、CSS属性
详情参考:http://www.w3school.com.cn/css/index.asp
二、HTML样式
共三种样式,均适用于就近原则。分别为直接应用外部样式文件,在HTML头head统一定义,和在各标签中单独定义三种。
1、外部样式表:在HTML外单独定义,直接引用。
当样式需要被应用到很多页面的时候,外部样式表将是理想的选择。使用外部样式表,你就可以通过更改一个文件来改变整个站点的外观。
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css">
</head>
2、内部样式表:在HTML文档头head统一定义
当单个文件需要特别样式时,就可以使用内部样式表。你可以在 head 部分通过 <style> 标签定义内部样式表。
<head> <style type="text/css"> body {background-color: red} p {margin-left: 20px} </style> </head>
3、内联样式:在单个标签内定义
当特殊的样式需要应用到个别元素时,就可以使用内联样式。 使用内联样式的方法是在相关的标签中使用样式属性。样式属性可以包含任何 CSS 属性。以下实例显示出如何改变段落的颜色和左外边距。
<p style="color: red; margin-left: 20px">
This is a paragraph
</p>
三、选择器
CSS选择器:由一条多多条声明组成,selector {declaration1; declaration2; ... declarationN }
1、HTML元素选择器:*{}或p,a{}
p { text-align: center; color: black; font-family: arial; }
h1 {color:red; font-size:14px;}
选择器分组:被分组的选择器就可以分享相同的声明。用逗号将需要分组的选择器分开。
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6 { color: green; }
2、类选择器:.info{}
.center {text-align: center} <h1 class="center"> This heading will be center-aligned </h1> <p class="center"> This paragraph will also be center-aligned. </p>
注意:类名的第一个字符不能使用数字!它无法在 Mozilla 或 Firefox 中起作用。
和 id 一样,class 也可被用作派生选择器:
.fancy td { color: #f60; background: #666; }
在上面这个例子中,类名为 fancy 的更大的元素内部的表格单元都会以灰色背景显示橙色文字。(名为 fancy 的更大的元素可能是一个表格或者一个 div) 元素也可以基于它们的类而被选择:
td.fancy { color: #f60; background: #666; } 在上面的例子中,类名为 fancy 的表格单元将是带有灰色背景的橙色。
<td class="fancy">
3、ID选择器:#info{}
#red {color:red;} #green {color:green;} <p id="red">这个段落是红色。</p> <p id="green">这个段落是绿色。</p>
id 选择器和派生选择器
#sidebar p { font-style: italic; text-align: right; margin-top: 0.5em; }
一个选择器,多种用法
即使被标注为 sidebar 的元素只能在文档中出现一次,这个 id 选择器作为派生选择器也可以被使用很多次:
#sidebar p { font-style: italic; text-align: right; margin-top: 0.5em; } #sidebar h2 { font-size: 1em; font-weight: normal; font-style: italic; margin: 0; line-height: 1.5; text-align: right; }
单独的选择器
id 选择器即使不被用来创建派生选择器,它也可以独立发挥作用:
#sidebar { border: 1px dotted #000; padding: 10px; }
4、属性选择器
[title] { color:red; } 下面的例子为 title="W3School" 的所有元素设置样式: [title=W3School] { border:5px solid blue; }
属性选择器在为不带有 class 或 id 的表单设置样式时特别有用:
input[type="text"] { width:150px; display:block; margin-bottom:10px; background-color:yellow; font-family: Verdana, Arial; } input[type="button"] { width:120px; margin-left:35px; display:block; font-family: Verdana, Arial; }
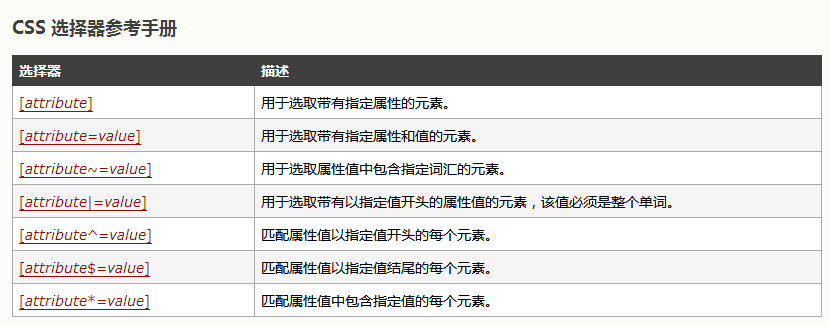
5、派生选择器:比方说,你希望列表中的 strong 元素变为斜体字,而不是通常的粗体字,可以这样定义一个派生选择器:
li strong { font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; } <p><strong>我是粗体字,不是斜体字,因为我不在列表当中,所以这个规则对我不起作用</strong></p> <ol> <li><strong>我是斜体字。这是因为 strong 元素位于 li 元素内。</strong></li> <li>我是正常的字体。</li> </ol>
如果您需要更深入地学习关于派生选择器的知识,请阅读 W3School 的高级教程中的以下内容:
CSS 后代选择器 http://www.w3school.com.cn/css/css_selector_descendant.asp
CSS 子元素选择器 http://www.w3school.com.cn/css/css_selector_child.asp
CSS 相邻兄弟选择器 http://www.w3school.com.cn/css/css_selector_adjacent_sibling.asp
四、CSS属性:字体、颜色、文本、位置、布局、边缘、列表、其他
标准属性:id, class, title, style, dir, lang, xml:lang
事件属性:onclick, ondblclick, onmousedown, onmouseup, onmouseover, onmousemove, onmouseout, onkeypress, onkeydown, onkeyup
<style> 定义样式定义。
<html> <head> <style type="text/css"> h1 {color:red} p {color:blue} </style> </head> <body> <h1>Header 1</h1> <p>A paragraph.</p> </body> </html>
<link> 定义资源引用。
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="theme.css" />
</head>
<div> 定义文档中的节或区域(块级)。
<div style="color:#00FF00">
<h3>This is a header</h3>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</div>
<span> 定义文档中的行内的小块或区域。
<p><span>some text.</span>some other text.</p>
<font> 规定文本的字体、字体尺寸、字体颜色。不赞成使用。请使用样式。
<basefont> 定义基准字体。不赞成使用。请使用样式。
<center> 对文本进行水平居中。不赞成使用。请使用样式。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号