进程间的管道通信
管道是进程间通信的一种工具。
1、管道是半双工的,建立管道后,只能由一个进程向另一个进程传数据。
2、管道只能在有公共祖先的两个进程之间使用。父进程建立管道后,fork,这个管道就能在父子进程之间调用了。
管道通过pipe函数创建。
pipe(int fd[2]);
要打开两个文件,文件描述符放在fd里面。写数据时往fd1里面写,读数据时从fd0里面读。
如果是父进程往子进程传数据,父进程的fd0关闭,写进fd1里面去。子进程的fd1关闭,从fd0里面读数据。
#include<unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include<memory.h> int main(){ int fd[2]; fd[0] = open("file0.txt",O_RDWR); fd[1] = open("file1.txt",O_RDWR); pipe(fd); pid_t pid; char buf[256]; pid = fork();//create child process if(pid<0){ printf("fork error\n"); } else if(pid>0){ memset(buf,'\0',256); close(fd[0]); write(fd[1],"from parent:Hello!\n",20); printf("In parent process and pid is %d\n",pid); } else{ printf("In child process and pid is %d\n",pid); close(fd[1]); read(fd[0],buf,256); printf("%s\n",buf); } }
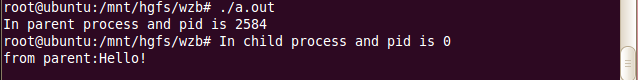
如果是子进程往父进程传数据,子进程的fd0关闭,写进fd1里面去。父进程的fd1关闭,从fd0里面读数据。
#include<unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include<memory.h> int main(){ int fd[2]; fd[0] = open("file0.txt",O_RDWR); fd[1] = open("file1.txt",O_RDWR); pipe(fd); pid_t pid; char buf[256]; pid = fork();//create child process if(pid<0){ printf("fork error\n"); } else if(pid>0){ printf("In parent process and pid is %d\n",pid); close(fd[1]); read(fd[0],buf,256); printf("%s\n",buf); } else{ memset(buf,'\0',256); close(fd[0]); write(fd[1],"from child:Hi!\n",15); printf("In child process and pid is %d\n",pid); } }

同时,打开的两个文件file1.txt 和 file0.txt里面根本木有东西残留的,只是拿去当管道而已,并没有写入文件里面去。




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步