请求参数处理
1.请求映射处理
Rest风格的请求,使用HTTP请求方式动词来表示对资源的操作。核心Filter,就是这个HiddenHttpMethodFilter。在SpringBoot中默认情况下表单的Rest风格默认没有开启
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter", name = "enabled")
public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter();
}
需要我们手动配置开启
spring:
mvc:
hiddenmethod:
filter:
enabled: true
但是表单默认情况下只支持POST和GET,那么SpringBoot如何处理呢?
通过查看HiddenHttpMethodFilter源代码可以看到
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取原始的request
HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request;
//判断这个请求是不是POST并且没有任何错误
if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) == null) {
//获取请求参数,默认定义为_method
String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) {
//不管前端定义的方法值是大写还是小写都转换成大写
String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
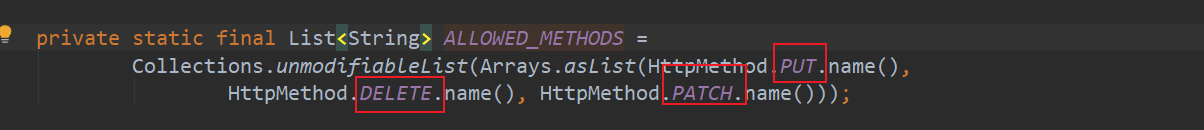
//查看比较SpringBoot能不能处理,默认能处理PUT,DELETE,PATCH
if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) {
//使用一个HttpMethodRequestWrapper类,包装模式来处理原始的Request
requestToUse = new HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method);
}
}
}
//如果本身就是REST风格直接跳过处理
filterChain.doFilter(requestToUse, response);
}
//使用到包装模式,HttpMethodRequestWrapper最终还是继承HttpServletRequest
private static class HttpMethodRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private final String method;
//重写了method方法的返回值
public HttpMethodRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request, String method) {
super(request);
this.method = method;
}
@Override
public String getMethod() {
return this.method;
}
}

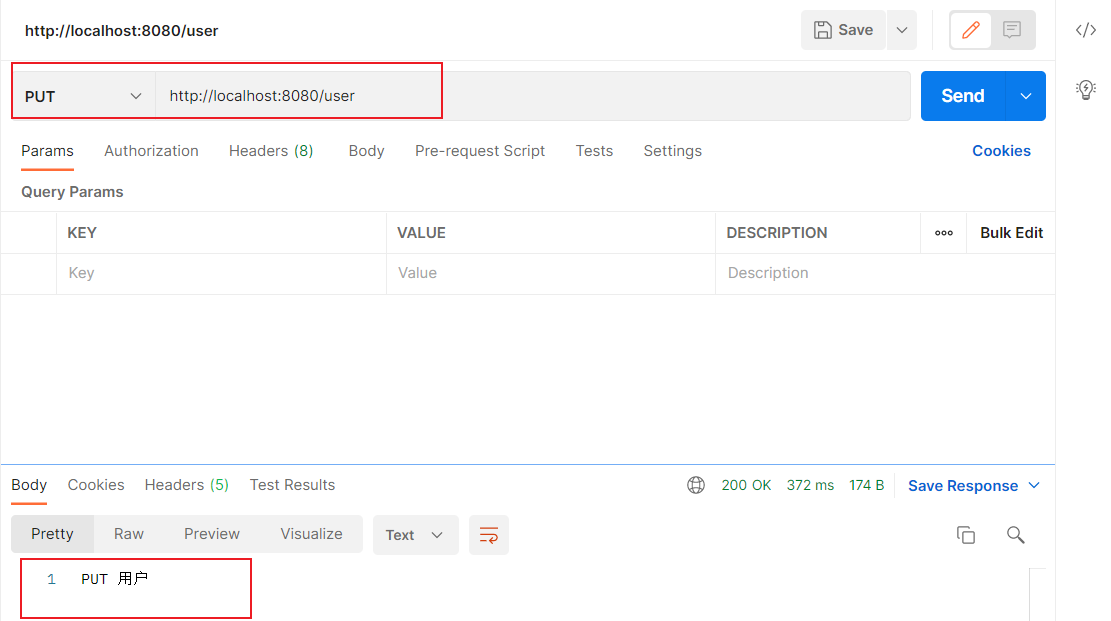
使用Postman测试
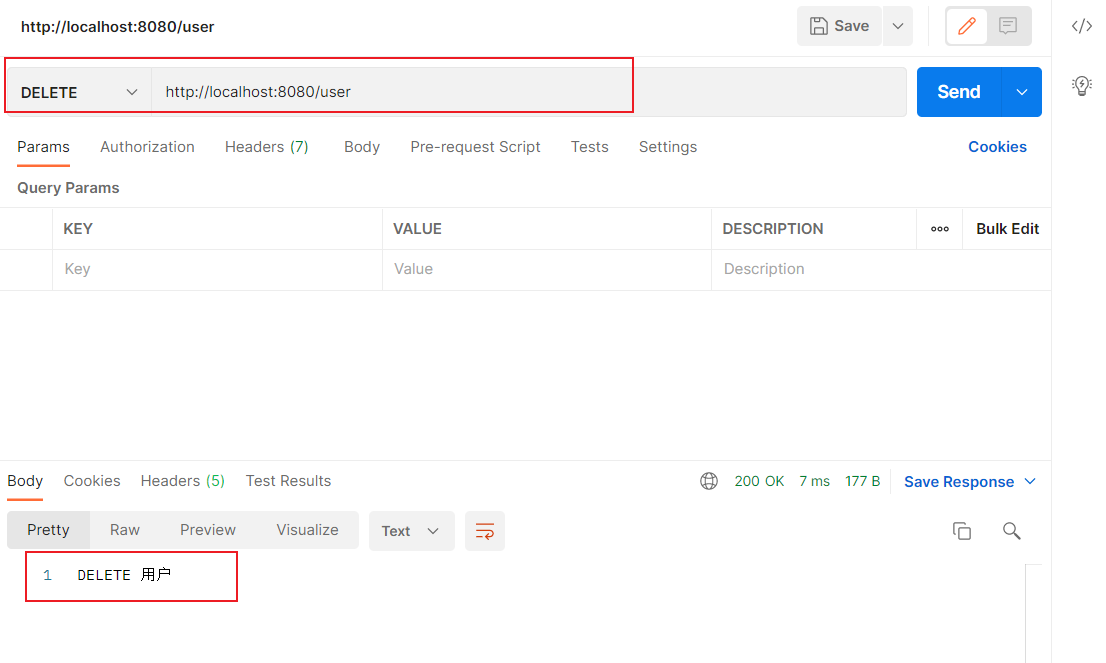
我们不能不想使用SpringBoot默认定义的_method,可以修改吗?
在WebMvcAutoConfiguration类的hiddenHttpMethodFilter方法上面有一个注解@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class),只有当我们容器中不存在HiddenHttpMethodFilter的时候,我们才会使用默认的,我们可以自定义一个HiddenHttpMethodFilter类。
@Configuration
public class WebConfig {
@Bean
public HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter(){
HiddenHttpMethodFilter methodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter();
methodFilter.setMethodParam("_m");
return methodFilter;
}
}
2.请求映射原理
我们知道在SpringMVC中最重要的一个类就是DispatcherServlet,我们使用IDEA继承树查看其继承关系:
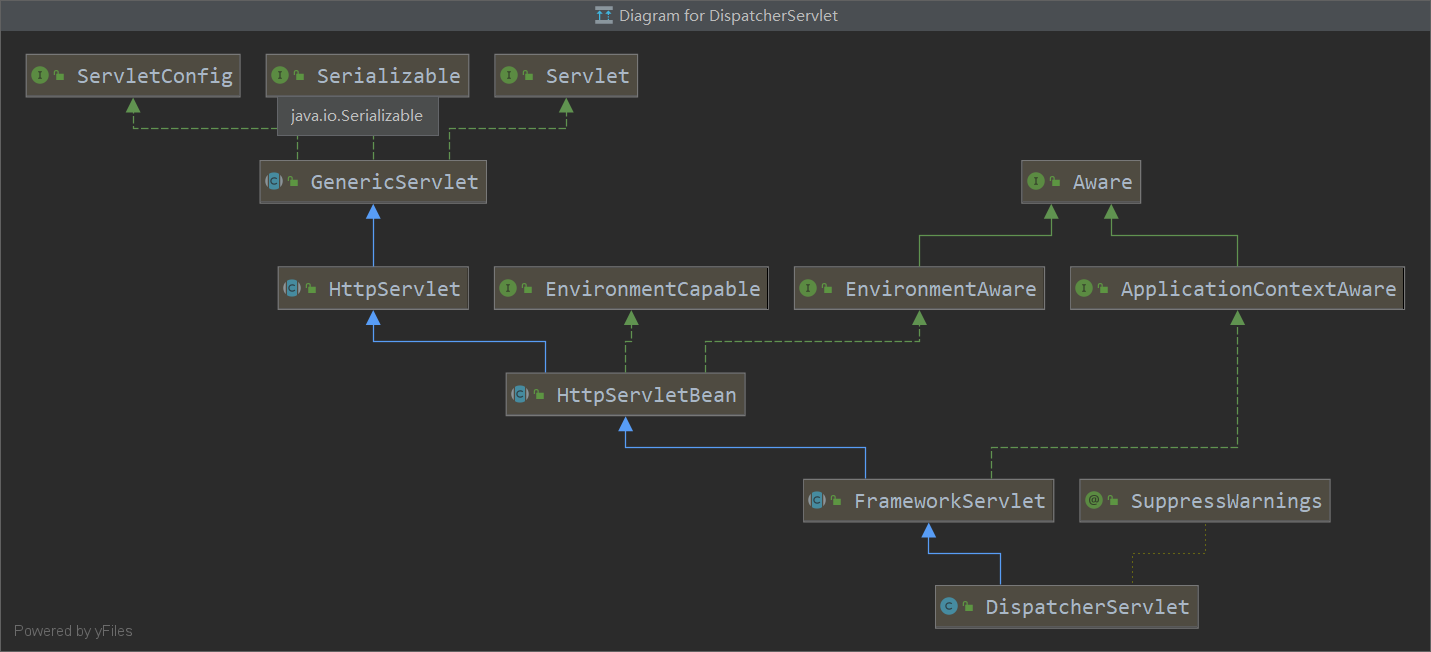
在HttpServlet中有两个非常重要的方法doGet和doPost,我们在原生的JavaWeb中一般通过继续HttpServlet重写doGet或者doPost来实现请求响应。那么我们在SpringMVC肯定也会重写这两个方法。我们顺着继续树查看在HttpServletBean有无重写,发现并没有重写,那么我们就继续看FrameworkServlet在这个类中,SpringMVC重写了doGet/doPost方法,我们查看源代码
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
/**
* Delegate POST requests to {@link #processRequest}.
* @see #doService
*/
@Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
都是调用processRequest来处理,我们继续看源码:
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
//前面都是一些Http请求设置,不重要,最重要的是下面这个方法doService
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
在这个方法里面出现了调用doService方法,我们进行看源代码:
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception;
我们发现这个方法在FrameworkServlet是一个抽象方法,那么就继续看继承树中的DispatcherServlet是否有实现,果然在DispatcherServlet中有相应的实现
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
}
这个方法里面最重要的就是一个调用doDispatch方法,我们继续看源代码:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
//异步管理
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
//视图设置
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//是不是文件上传
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//这里就是很重要的一个查看当前请求的处理器映射
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
getHandlerAdapter调用这个方法会去查找哪个处理器映射能够处理这个请求,在SpringMVC默认有五种类型的处理器映射:
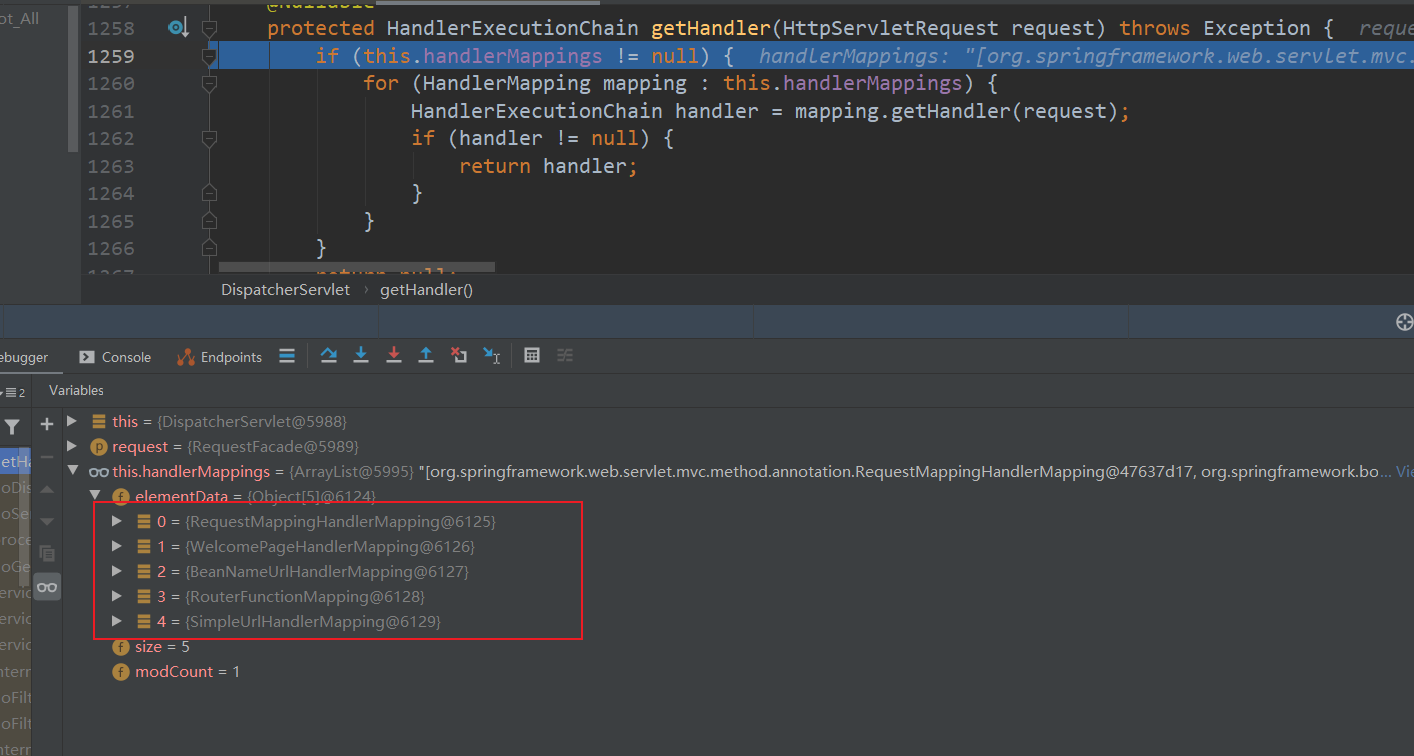
通过遍历对每一个处理器映射进行分析,是不是能够处理,找到一个能够处理的,在每一个处理器映射都记录了自己能够处理的映射,比如:
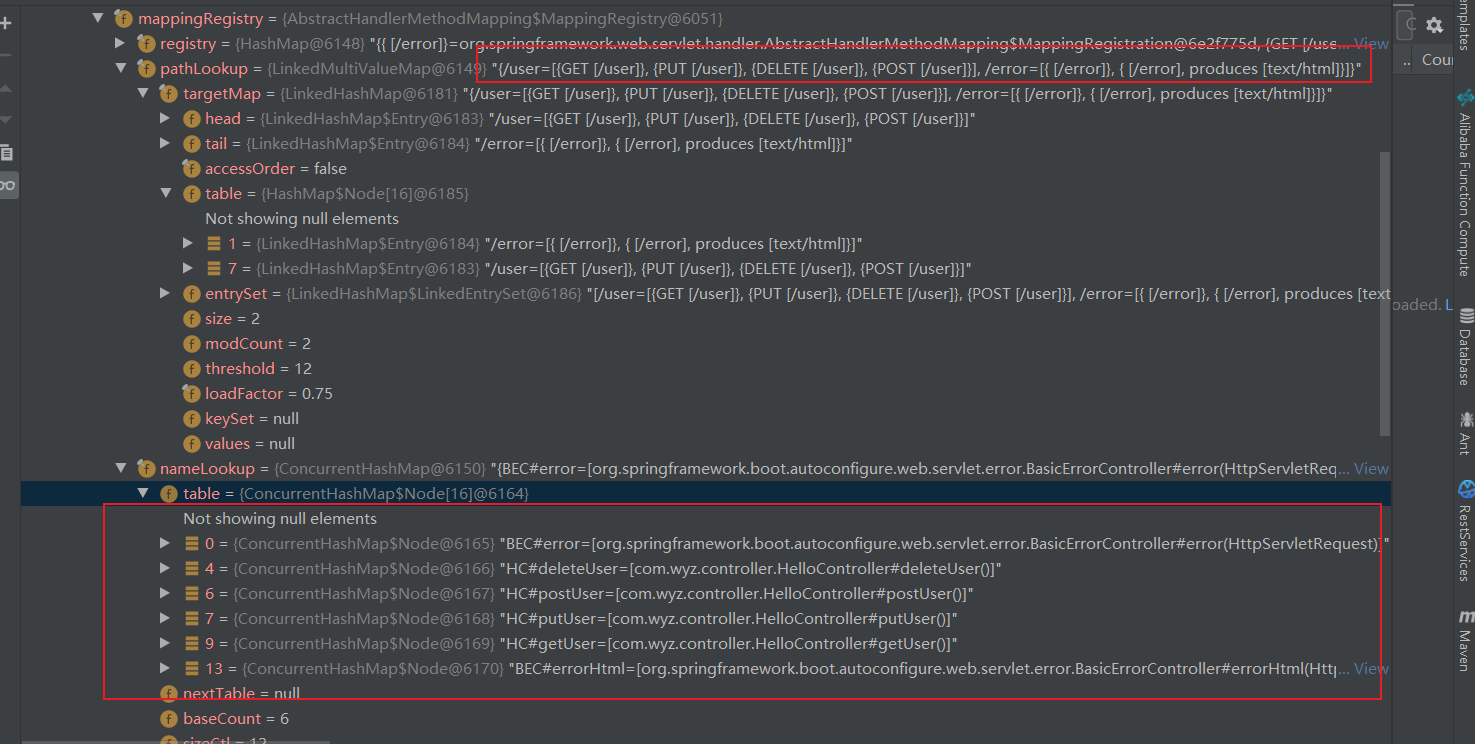
上面就是RequestMappingHandler能够处理的路径。在SpringBoot启动的时候这些映射路径都会注册到对应的处理器映射里面。找到之后就会返回,这样我们知道了请求映射是如何找到我们要处理的方法。在里面有一个处理器映射叫WelcomePage的请求处理器映射,这个就是欢迎页的处理,我们可以查看其代码看看
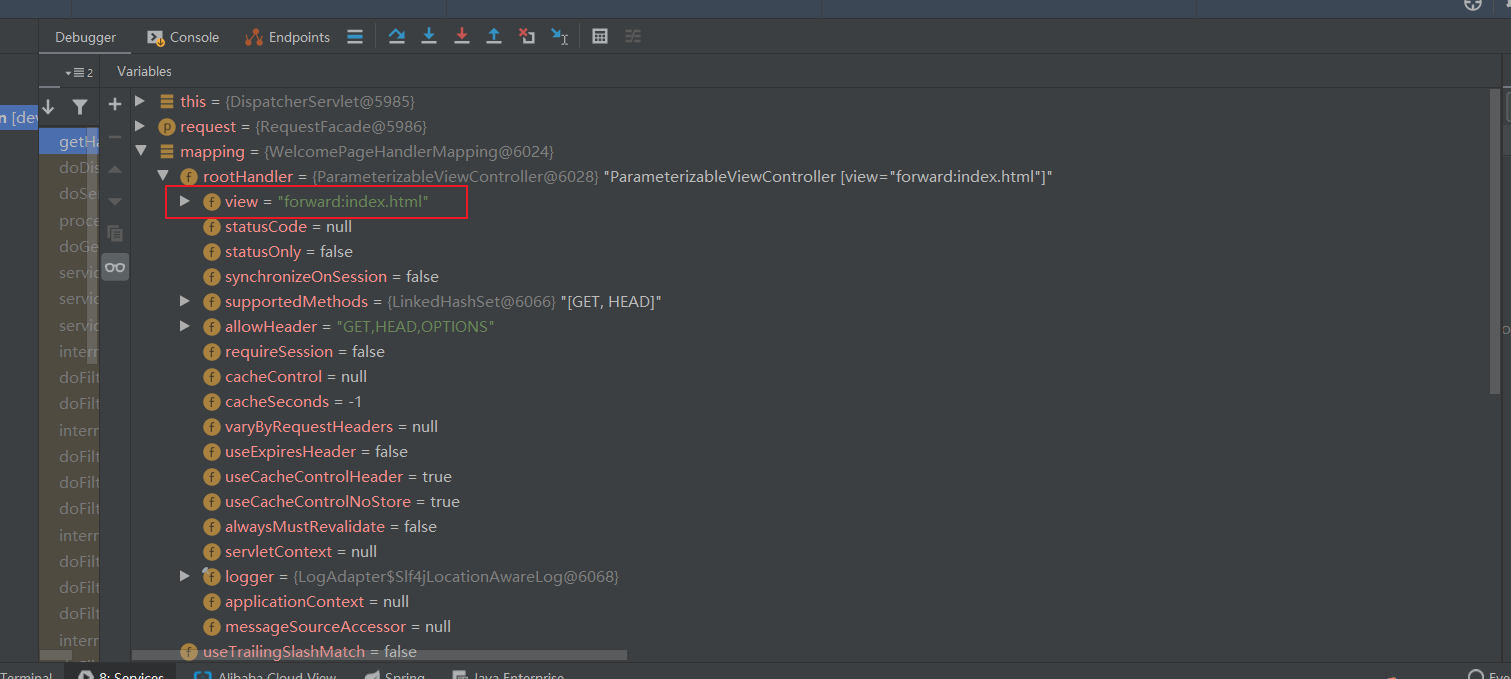
所有的请求映射都在HandlerMapping中。
-
SpringBoot自动配置欢迎页的 WelcomePageHandlerMapping 。访问 /能访问到index.html;
-
SpringBoot自动配置了默认 的 RequestMappingHandlerMapping
-
请求进来,挨个尝试所有的HandlerMapping看是否有请求信息。
-
- 如果有就找到这个请求对应的handler
- 如果没有就是下一个 HandlerMapping
-
我们需要一些自定义的映射处理,我们也可以自己给容器中放HandlerMapping。自定义 HandlerMapping


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号