跳转方式和数据处理
6.跳转方式
6.1 通过SpringMVC来实现转发和重定向 - 无需视图解析器
测试前,需要将视图解析器注释掉
@Controller
public class ResultSpringMVC {
@RequestMapping("/rsm/t1")
public String test1(){
//转发
return "/index.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping("/rsm/t2")
public String test2(){
//转发二
return "forward:/index.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping("/rsm/t3")
public String test3(){
//重定向
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
}
}
6.2 通过SpringMVC来实现转发和重定向 - 有视图解析器
重定向 , 不需要视图解析器 , 本质就是重新请求一个新地方嘛 , 所以注意路径问题.
可以重定向到另外一个请求实现 .
@Controller
public class ResultSpringMVC2 {
@RequestMapping("/rsm2/t1")
public String test1(){
//转发
return "test";
}
@RequestMapping("/rsm2/t2")
public String test2(){
//重定向
return "redirect:/index.jsp";
//return "redirect:hello.do"; //hello.do为另一个请求/
}
}
7. 数据处理
7.1 处理提交数据
1、提交的域名称和处理方法的参数名一致
提交数据 : http://localhost:8080/hello?name=wuyaz
处理方法 :
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(String name){
System.out.println(name);
return "hello";
}
2、提交的域名称和处理方法的参数名不一致
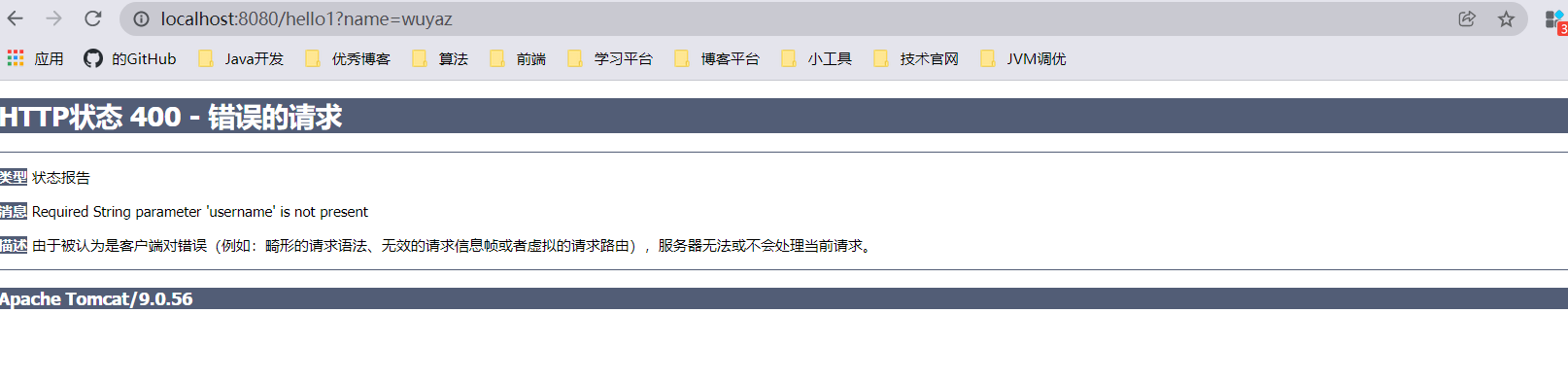
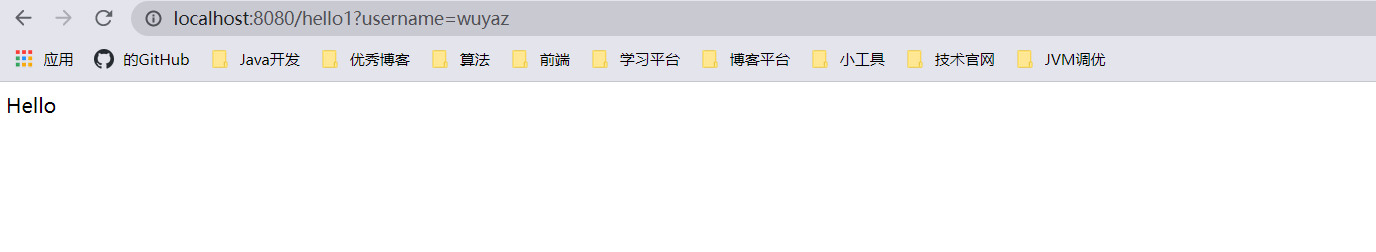
提交数据 : http://localhost:8080/hello?username=wuyaz
处理方法 :
@RequestMapping("/hello1")
public String hello1(@RequestParam("username") String name){
System.out.println(name);
return "hello";
}
3、提交的是一个对象
定义一个实体类
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public User(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
@RequestMapping("/hello2")
public String hello2(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "hello";
}
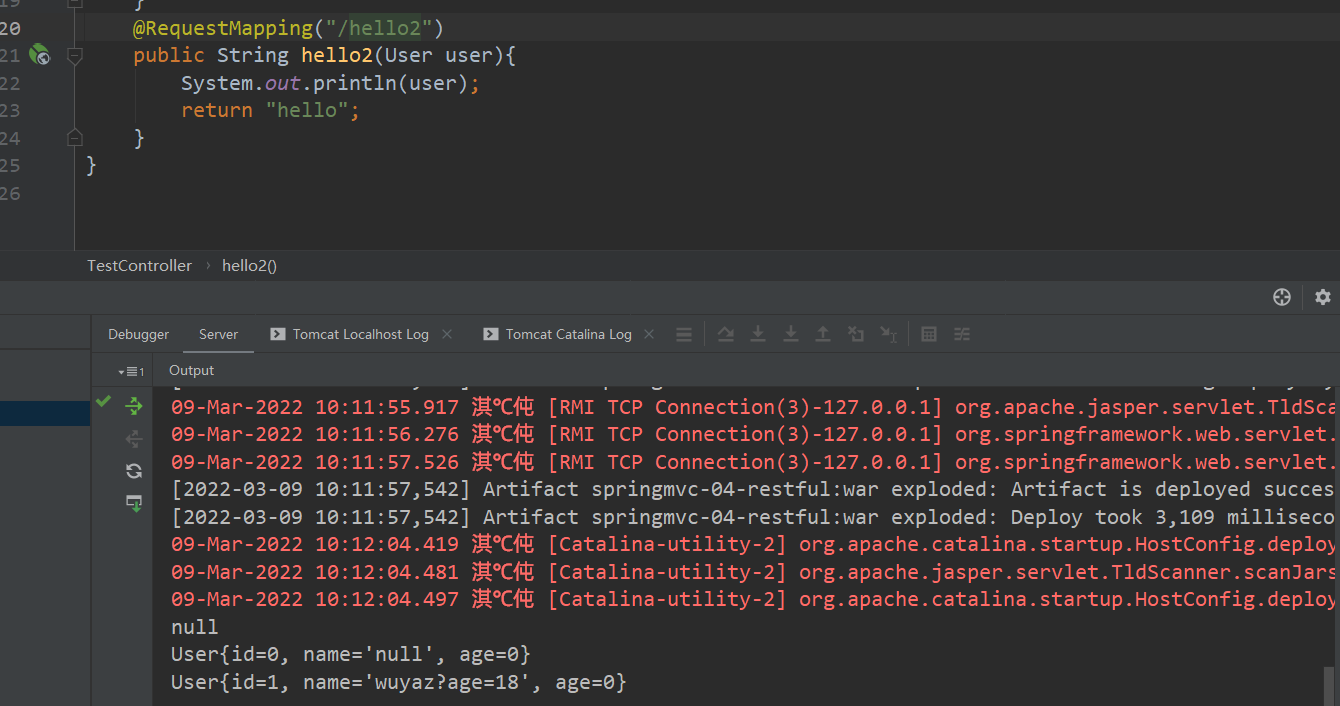
说明:如果使用对象的话,前端传递的参数名和对象名必须一致,否则就是null。
7.2 数据显示到前端
第一种 : 通过ModelAndView
我们前面一直都是如此 . 就不过多解释
public class ControllerTest1 implements Controller {
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws Exception {
//返回一个模型视图对象
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("msg","ControllerTest1");
mv.setViewName("test");
return mv;
}
}
第二种 : 通过ModelMap
ModelMap
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(@RequestParam("username") String name, ModelMap model){
//封装要显示到视图中的数据
//相当于req.setAttribute("name",name);
model.addAttribute("name",name);
System.out.println(name);
return "hello";
}
第三种 : 通过Model
Model
@RequestMapping("/ct2/hello")
public String hello(@RequestParam("username") String name, Model model){
//封装要显示到视图中的数据
//相当于req.setAttribute("name",name);
model.addAttribute("msg",name);
System.out.println(name);
return "test";
}
对比
就对于新手而言简单来说使用区别就是:
Model 只有寥寥几个方法只适合用于储存数据,简化了新手对于Model对象的操作和理解;
ModelMap 继承了 LinkedMap ,除了实现了自身的一些方法,同样的继承 LinkedMap 的方法和特性;
ModelAndView 可以在储存数据的同时,可以进行设置返回的逻辑视图,进行控制展示层的跳转。
当然更多的以后开发考虑的更多的是性能和优化,就不能单单仅限于此的了解。
7.3 乱码问题
编写表单测试文件
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/e/t1" method="post">
名字:<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
编写后台处理类
@RequestMapping("/e/t1")
public String Encoding(@RequestParam("username") String name, Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg",name);
return "test1";
}
中文测试
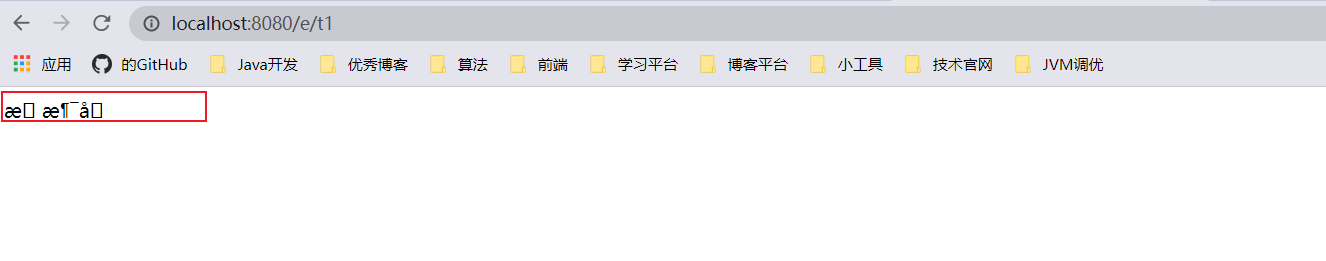
不得不说,乱码问题是在我们开发中十分常见的问题,也是让我们程序猿比较头大的问题!
以前乱码问题通过过滤器解决 , 而SpringMVC给我们提供了一个过滤器 , 可以在web.xml中配置 .
修改了xml文件需要重启服务器!
<filter>
<filter-name>encoding</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encoding</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
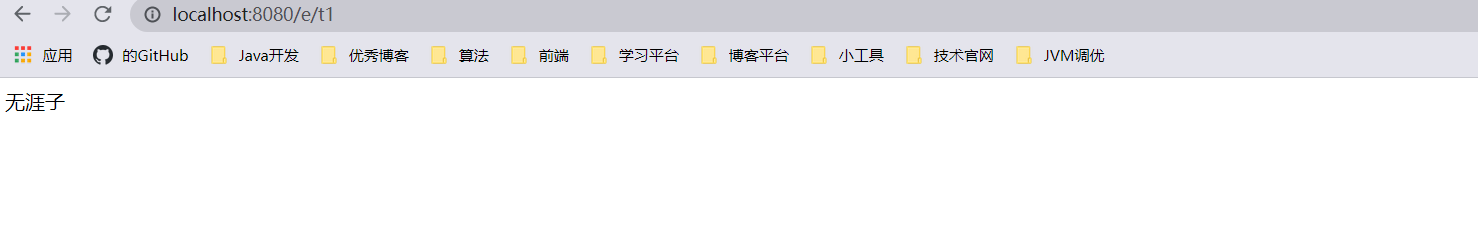
但是我们发现 , 有些极端情况下.这个过滤器对get的支持不好 .
处理方法 :
1、修改tomcat配置文件 :设置编码!
<Connector URIEncoding="utf-8" port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
2、自定义过滤器
package com.kuang.filter;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequestWrapper;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 解决get和post请求 全部乱码的过滤器
*/
public class GenericEncodingFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//处理response的字符编码
HttpServletResponse myResponse=(HttpServletResponse) response;
myResponse.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
// 转型为与协议相关对象
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;
// 对request包装增强
HttpServletRequest myrequest = new MyRequest(httpServletRequest);
chain.doFilter(myrequest, response);
}
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
}
//自定义request对象,HttpServletRequest的包装类
class MyRequest extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private HttpServletRequest request;
//是否编码的标记
private boolean hasEncode;
//定义一个可以传入HttpServletRequest对象的构造函数,以便对其进行装饰
public MyRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
super(request);// super必须写
this.request = request;
}
// 对需要增强方法 进行覆盖
@Override
public Map getParameterMap() {
// 先获得请求方式
String method = request.getMethod();
if (method.equalsIgnoreCase("post")) {
// post请求
try {
// 处理post乱码
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
return request.getParameterMap();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else if (method.equalsIgnoreCase("get")) {
// get请求
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap();
if (!hasEncode) { // 确保get手动编码逻辑只运行一次
for (String parameterName : parameterMap.keySet()) {
String[] values = parameterMap.get(parameterName);
if (values != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
try {
// 处理get乱码
values[i] = new String(values[i]
.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "utf-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
hasEncode = true;
}
return parameterMap;
}
return super.getParameterMap();
}
//取一个值
@Override
public String getParameter(String name) {
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = getParameterMap();
String[] values = parameterMap.get(name);
if (values == null) {
return null;
}
return values[0]; // 取回参数的第一个值
}
//取所有值
@Override
public String[] getParameterValues(String name) {
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = getParameterMap();
String[] values = parameterMap.get(name);
return values;
}
}
这个也是我在网上找的一些大神写的,一般情况下,SpringMVC默认的乱码处理就已经能够很好的解决了!
然后在web.xml中配置这个过滤器即可!
乱码问题,需要平时多注意,在尽可能能设置编码的地方,都设置为统一编码 UTF-8!



· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术