Entity Framework入门教程(14)---DbFirst下的存储过程
EF6中DbFirst模式下使用存储过程
我们已经知道EF可以将L2E或Entity SQL的查询语句自动转换成SQL命令,也可以根据实体的状态自动生成Insert/update/delete的Sql命令。这节介绍EF中使用预先定义的存储过程对一张或者多种表进行CURD操作。
EF API会新建一个function来映射数据库中的自定义函数或存储过程。下边讲解EF DbFirst模式下存储过程的用法,EF CodeFirst存储过程的用法会在以后的EF CodeFirst系列中介绍。
1.DbFirst模式——使用存储过程查询数据
第一步 在数据库新建存储过程
首先在数据库创建一个名为GetCoursesByStudentId的存储过程,这个存储过程返回一个学生的所有课程。
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[GetCoursesByStudentId] -- Add the parameters for the stored procedure here @StudentId int = null AS BEGIN -- SET NOCOUNT ON added to prevent extra result sets from -- interfering with SELECT statements. SET NOCOUNT ON; -- Insert statements for procedure here select c.courseid, c.coursename,c.Location, c.TeacherId from student s left outer join studentcourse sc on sc.studentid = s.studentid left outer join course c on c.courseid = sc.courseid where s.studentid = @StudentId END
第二步 生成EMD
这一步和普通生成EMD过程是一样的,值得注意的是在Choose Your Database Objects and Settings这一步勾选我们新建的存储过程(GetCoursesByStudentId)和下边的Import selected stored procedures and functions into the entity model ,如下图所示

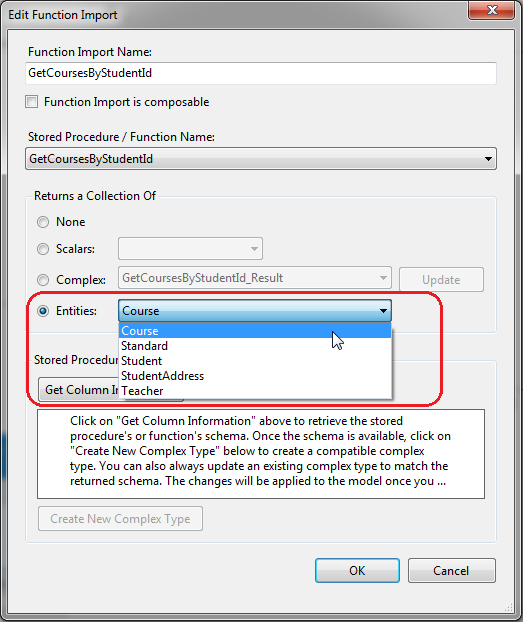
GetCoursesByStudentId()返回Course实体集合,所以我们不需要返回一个新的复杂类型。右键Function Imports下的GetCoursesByStudentId方法,选择Edit,出现以下界面,把Entities设置为Course即可
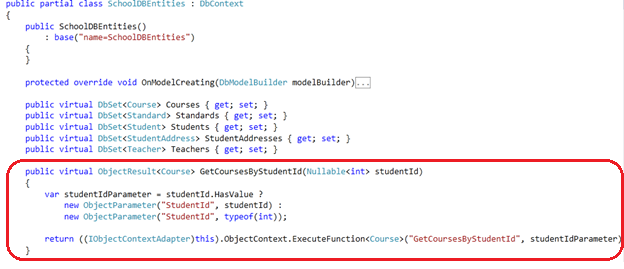
通过上边两步,在context中会生成一个GetCoursesByStudentId方法:
现在我们就可以愉快地使用context.GetCoursesByStudentId来执行存储过程了!如下:
using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities()) { var courses = context.GetCoursesByStudentId(1); foreach (Course cs in courses) Console.WriteLine(cs.CourseName); }
在数据库中执行的命令为: exec [dbo].[GetCoursesByStudentId] @StudentId=1
一点补充:EF中的表值函数和查询的存储过程使用的步骤是一模一样的(表值函数和存储过程本来就很类似,一个最重要的区别是EF中表值函数的返回值可用linq查询过滤)
2.DbFirst模式——使用存储过程执行CUD操作
这一部分介绍怎么通过存储过程来执行CUD(creat,update,delete)操作。
我们在数据库添加以下几个存储:
Sp_InsertStudentInfo(添加):
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_InsertStudentInfo] -- Add the parameters for the stored procedure here @StandardId int = null, @StudentName varchar(50) AS BEGIN -- SET NOCOUNT ON added to prevent extra result sets from -- interfering with SELECT statements. SET NOCOUNT ON; INSERT INTO [SchoolDB].[dbo].[Student]([StudentName],[StandardId]) VALUES(@StudentName, @StandardId) SELECT SCOPE_IDENTITY() AS StudentId END
sp_UpdateStudent(修改):
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_UpdateStudent] -- Add the parameters for the stored procedure here @StudentId int, @StandardId int = null, @StudentName varchar(50) AS BEGIN -- SET NOCOUNT ON added to prevent extra result sets from -- interfering with SELECT statements. SET NOCOUNT ON; Update [SchoolDB].[dbo].[Student] set StudentName = @StudentName,StandardId = @StandardId where StudentID = @StudentId; END
sp_DeleteStudent(删除):
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_DeleteStudent] -- Add the parameters for the stored procedure here @StudentId int AS BEGIN -- SET NOCOUNT ON added to prevent extra result sets from -- interfering with SELECT statements. SET NOCOUNT ON; DELETE FROM [dbo].[Student] where StudentID = @StudentId END
第一步:升级EDM
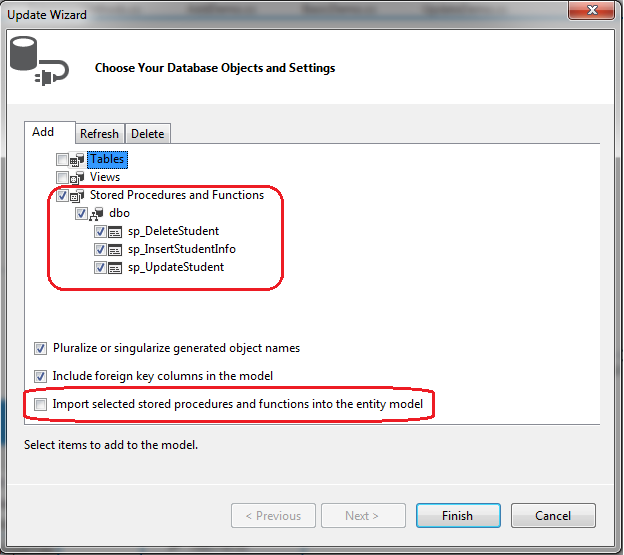
首先我们要升级EDM把这些存储过程添加当我们的EDM中。右键设计器,选择Update Model from Database,就出现了升级界面,如下图所示,展开Stored Procedure and Functions,勾选我们上边创建的三个存储过程,然后点击Finish。
这时模型浏览器中在Store Model中有了这三个存储过程,但是Function Imports中没有,如下所示:

打开模型设计器在Student实体上右键,选择Stored Procedure Mapping,来打开映射详情界面,如下图
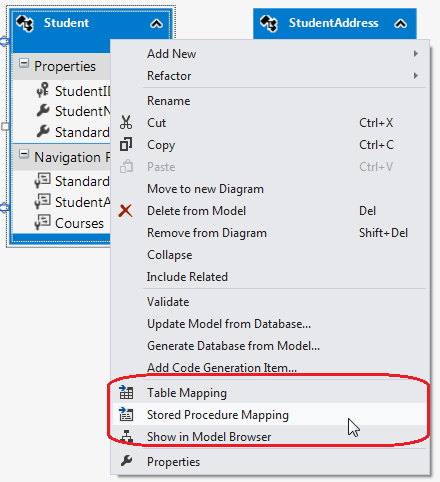
在下面的映射详细界面,我们看到<Select Insert Function>, <Select Update Function>, and <Select Delete Function>,给这些下拉菜单分别选择对应的存储过程,同时选择存储过程的输入输出参数,如下图所示:

右击Student实体,选择Validate,确保没有错误
现在我们执行add,update,或者delete时,EF不再执行自动生成的SQL命令,而是通过这些存储过程来执行,下面是一个栗子:
using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities()) { Student student = new Student() { StudentName = "New student using SP"}; context.Students.Add(student); //执行 sp_InsertStudentInfo context.SaveChanges(); student.StudentName = "Edit student using SP"; //执行 sp_UpdateStudent context.SaveChanges(); context.Students.Remove(student); //执行 sp_DeleteStudentInfo context.SaveChanges(); }
调用SaveChange()方法时,在数据库中执行的命令如下:
exec [dbo].[sp_InsertStudentInfo] @StandardId=NULL,@StudentName='New student using SP' go exec [dbo].[sp_UpdateStudent] @StudentId=47,@StandardId=NULL,@StudentName='Edit student using SP' go exec [dbo].[sp_DeleteStudent] @StudentId=47 go
注意:无论是使用存储过程还是默认生成的Sql命令,当插入一条记录并执行完SaveChange()方法后,这个新的实例会立即分配一个Id。这样设计是为了有效地追踪实体,让我们可以对实体执行进一步的操作(如没有id执行update会抛出异常),如下图:

EF系列目录链接:Entity Franmework系列教程汇总




· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决