NPOI使用教程附Helper
1 NPOI简介
1.1 NPOI是什么
NPOI是POI的.NET版本,POI是一套用Java写成的库,我们在开发中经常用到导入导出表格、文档的情况,NPOI能够帮助我们在没有安装微软Office的情况下读写Office文件,如xls, doc, ppt等。NPOI采用的是Apache 2.0许可证(poi也是采用这个许可证),这意味着它可以被用于任何商业或非商业项目,我们不用担心因为使用它而必须开放你自己的源代码,所以它对于很多从事业务系统开发的公司来说绝对是很不错的选择。
1.2 NPOI简单使用
NPOI的API十分人性化,使用起来非常容易上手。首先创建一个控制台应用程序,通过nuget获取NPOI,这里使用的是最新版本2.4.0,如下:
项目引入NPOI后就可以直接上手使用了,代码如下
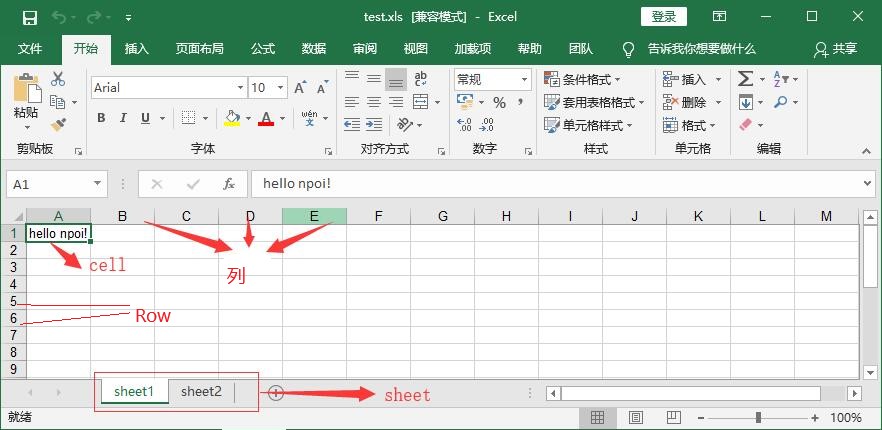
static void Main(string[] args) { //创建workbook,说白了就是在内存中创建一个Excel文件 IWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); //要添加至少一个sheet,没有sheet的excel是打不开的 ISheet sheet1 = workbook.CreateSheet("sheet1"); ISheet sheet2 = workbook.CreateSheet("sheet2"); IRow row1 = sheet1.CreateRow(0);//添加第1行,注意行列的索引都是从0开始的 ICell cell1 = row1.CreateCell(0);//给第1行添加第1个单元格 cell1.SetCellValue("hello npoi!");//给单元格赋值 //上边3个步骤合在一起:sheet1.CreateRow(0).CreateCell(0).SetCellValue("hello npoi"); //获取第一行第一列的string值 Console.WriteLine(sheet1.GetRow(0).GetCell(0).StringCellValue); //输出:hello npoi //写入文件 using (FileStream file = new FileStream(@"D:/TestFiles/test.xls", FileMode.Create)) { workbook.Write(file); } }
运行代码,结果如下,同时也在D盘的TestFiles文件夹下创建了test.xls文件

2 NPOI使用详解
2.1 单元格数据格式
用过Excel的人都知道,单元格是Excel最有意义的东西,我们做任何操作恐怕都要和单元格打交道。在Excel中我们经常要设置格式,比如说日期格式(2018-1-1)、小数点格式(1.20)、货币格式($2000)、百分比格式(99.99%)等等,这些东西在过去我们恐怕只能在服务器端生成好,不但增加了服务器端的代码量,还造成了不必要的字符串替换操作,如今NPOI将让服务器从这种完全没有必要的操作中解放出来,一切都将由Excel在客户端处理。
使用NPOI时要注意,所有的格式都是通过 CellStyle.DataFormat 赋给单元格的,而不是直接赋给单元格,设置单元格数据展示的格式有两种方法。
1.设置excel中内置的格式:
excel内部设置了很多格式,如下图所示:
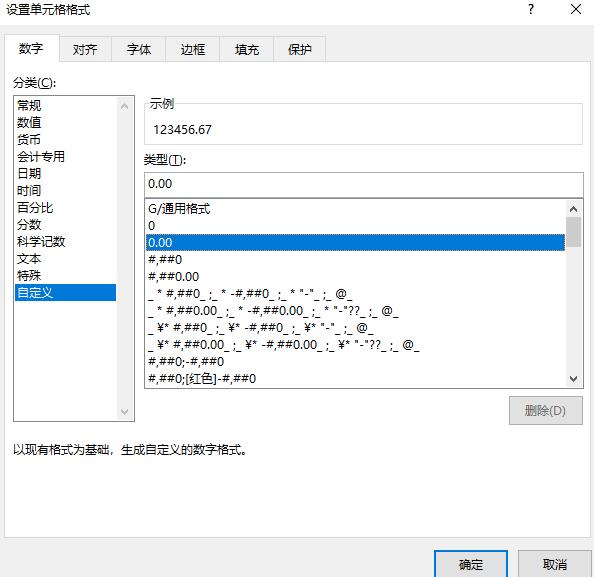
如果我们想使用这些内置的格式,可用通过 DataFormat.GetBuildinFormat('格式') 来使用,使用实例如下:
cellStyle.DataFormat = HSSFDataFormat.GetBuiltinFormat("0.00"); //两位小数,内置格式
2.设置自定义格式
有时候内置的格式不能满足我们的要求,这时候就可以使用 workbook.CreateDataFormat().GetFormat("格式") 自定义格式了,使用语法如下:
cellStyle.DataFormat= workbook.CreateDataFormat().GetFormat("yyyy年m月d日 hh时mm分ss秒");//显示中文日期和时间,自定义格式
下边的栗子展示了几种常用的数据格式用法:
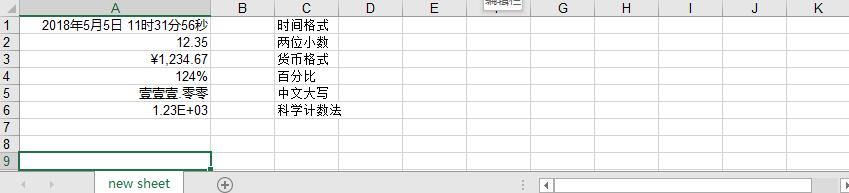
static void Main(string[] args) { IWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); ISheet sheet = workbook.CreateSheet("new sheet"); //设置日期格式,2018年5月5日格式 ICell cell = sheet.CreateRow(0).CreateCell(0); cell.SetCellValue(new DateTime(2018, 5, 5, 11, 31, 56)); ICellStyle cellStyle = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); cellStyle.DataFormat = workbook.CreateDataFormat().GetFormat("yyyy年m月d日 hh时mm分ss秒"); //cellStyle.DataFormat = workbook.CreateDataFormat().GetFormat("yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss"); cell.CellStyle = cellStyle; //保留2位小数 ICell cell2 = sheet.CreateRow(1).CreateCell(0); cell2.SetCellValue(12.346666); ICellStyle cellStyle2 = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); cellStyle2.DataFormat = HSSFDataFormat.GetBuiltinFormat("0.00"); cell2.CellStyle = cellStyle2; //货币格式 ICell cell3 = sheet.CreateRow(2).CreateCell(0); cell3.SetCellValue(1234.66666); ICellStyle cellStyle3 = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); cellStyle3.DataFormat = workbook.CreateDataFormat().GetFormat("¥#,##0.00");//美元的话格式为 $#,##0.00,其中#,##0表示千分号 cell3.CellStyle = cellStyle3; //百分比 ICell cell4 = sheet.CreateRow(3).CreateCell(0); cell4.SetCellValue(1.236666); ICellStyle cellStyle4 = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); //cellStyle4.DataFormat = HSSFDataFormat.GetBuiltinFormat("0.00%");//保留两位小数 cellStyle4.DataFormat = HSSFDataFormat.GetBuiltinFormat("0%"); cell4.CellStyle = cellStyle4; //中文大写数字 ICell cell5 = sheet.CreateRow(4).CreateCell(0); cell5.SetCellValue(111); ICellStyle cellStyle5 = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); cellStyle5.DataFormat = workbook.CreateDataFormat().GetFormat("[DbNum2][$-804]0.00");//不保留小数: [DbNum2][$-804]0 cell5.CellStyle = cellStyle5; //科学计数法 ICell cell6 = sheet.CreateRow(5).CreateCell(0); cell6.SetCellValue(1234.6666); ICellStyle cellStyle6 = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); cellStyle6.DataFormat = HSSFDataFormat.GetBuiltinFormat("0.00E+00"); cell6.CellStyle = cellStyle6; using (FileStream file = new FileStream(@"D:/TestFiles/test.xls", FileMode.Create)) { workbook.Write(file); } }
运行程序,生成的excel文件如下所示:
2.2 单元格合并及设置风格
单元格的合并和风格这部分内容比较多,但是Api十分的简单,为了看起来清晰,我们分成两个栗子来演示这部分的功能,代码中的注释很详细,这里就直接上代码了
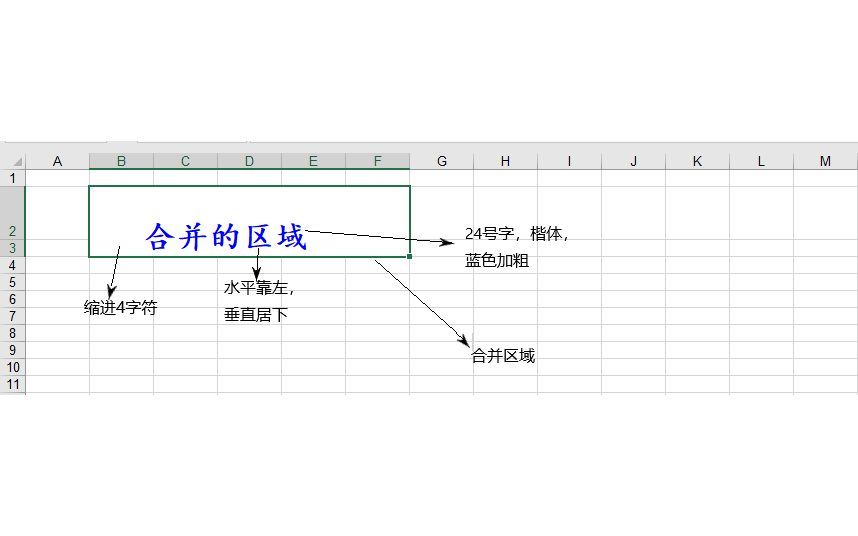
1.第一个栗子演示单元格合并,内容停靠,字体风格颜色大小等
static void Main(string[] args) { HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); ISheet sheet = workbook.CreateSheet("sheet1"); //------------------单元格合并 sheet.AddMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(1, 2, 1, 5));//合并单元格,4个参数依次为为startRow,endRow,startCol,endCol ICell cell = sheet.CreateRow(1).CreateCell(1); cell.SetCellValue("合并的区域"); cell.Row.HeightInPoints = 40;//行高 ICellStyle cellstyle = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); //----------------设置单元格常用风格 cellstyle.Alignment = HorizontalAlignment.Left;//水平居左,可选Right,Center cellstyle.VerticalAlignment = VerticalAlignment.Bottom;//垂直居中,可选Top,Center cellstyle.WrapText = true;//自动换行 cellstyle.Indention = 4;//缩进4个字节 //cellstyle.Rotation = 90;//字体旋转90度,取值范围是[-90,90] //---------------字体,字体大小、颜色 IFont font = workbook.CreateFont(); font.FontHeightInPoints = 24;//字号为24,可以用font.FontHeight = 24 * 20;FontHeight的单位是1/20点 font.FontName = "楷体";//字体 font.Boldweight = 700;//加粗 font.Color = HSSFColor.Blue.Index;//字体颜色 cellstyle.SetFont(font); cell.CellStyle = cellstyle; using (FileStream file = new FileStream(@"D:/TestFiles/test.xls", FileMode.Create)) { workbook.Write(file); } }
生成的excel文件如下图所示:
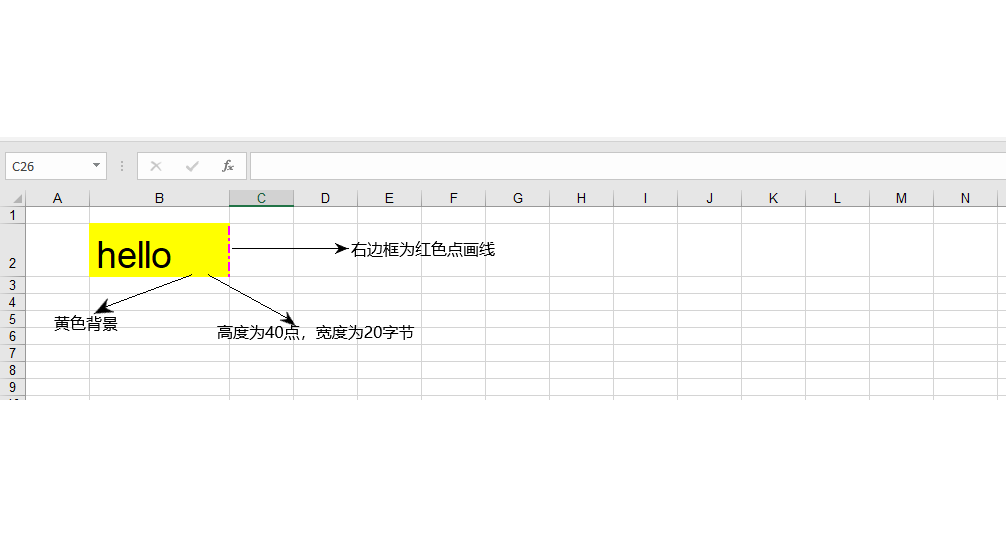
2.第二个栗子演示单元格的宽高、背景色、边框风格等
static void Main(string[] args) { IWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); ISheet sheet = workbook.CreateSheet("sheet1"); ICell cell = sheet.CreateRow(1).CreateCell(1); cell.SetCellValue("hello"); ICellStyle cellstyle = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); //设置宽度,把第2列设成20字节宽;参数1指定列的索引;参数2指定宽度,单位是1/256个字符宽度 sheet.SetColumnWidth(1, 20 * 256); //高度设成40,单位是点;也可以用cell2.Row.Height = 40 * 20;Height的单位是1/20点 cell.Row.HeightInPoints = 40; //右边框设置成点画线 cellstyle.BorderRight = BorderStyle.MediumDashDot; //右边框设成粉色 cellstyle.RightBorderColor = HSSFColor.Pink.Index; //前景色填充模式,实心 cellstyle.FillPattern = FillPattern.SolidForeground; //前景色填充颜色,黄色 cellstyle.FillForegroundColor = HSSFColor.Yellow.Index; //背景色 //cellstyle2.FillBackgroundColor = HSSFColor.Green.Index;//背景色设成green cell.CellStyle = cellstyle; using (FileStream file = new FileStream(@"D:/TestFiles/test.xls", FileMode.Create)) { workbook.Write(file); } }
运行程序,生成的excel文件如下:
其实在NPOI中除了操作单元格的内容和风格外,还提供了添加excel文件摘要,添加批注,画图,使用公式等功能,但是这些功能我们用的比较少,所以就不一一展示了,NPOI的公式我自己很少去使用,一般通过程序直接计算结果,个人感觉在程序中计算更加灵活,当excel的结构发生变化时修改起来也更方便些。
3.封装一个NPOI的helper类
我们先看一下这个helper的使用吧,先看从DataTable导出到excel,
首先使用Nuget添加几个包:NPOI,log4net(其他的日志记录组件也可以),System.Text.Encoding.CodePages(为了支持gb2312),具体代码如下:
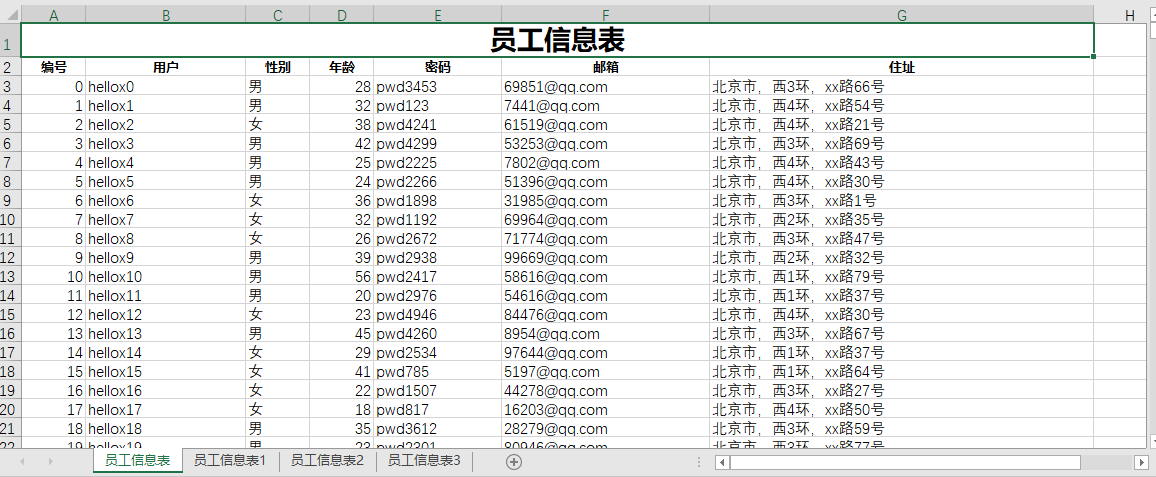
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { log4net.Config.XmlConfigurator.Configure(); //用于支持gb2312 Encoding.RegisterProvider(CodePagesEncodingProvider.Instance); //测试dataTable数据源 DataTable dataTable = new DataTable(); dataTable.Columns.Add("id", typeof(int)); dataTable.Columns.Add("uname", typeof(string)); dataTable.Columns.Add("sex", typeof(string)); dataTable.Columns.Add("age", typeof(int)); dataTable.Columns.Add("pwd", typeof(string)); dataTable.Columns.Add("email", typeof(string)); dataTable.Columns.Add("address", typeof(string)); Random r = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { DataRow row = dataTable.NewRow(); row["id"] = i; row["uname"] = "hellox" + i.ToString(); row["sex"] = r.Next(2) % 2 == 0 ? "男" : "女"; row["age"] = r.Next(40) + 18; row["pwd"] = "pwd" + r.Next(5000).ToString(); row["email"] = r.Next(100000) + "@qq.com"; row["address"] = $"北京市,西{r.Next(4) + 1}环,xx路{r.Next(100)}号"; dataTable.Rows.Add(row); } //DataTable的列名和excel的列名对应字典,因为excel的列名一般是中文的,DataTable的列名是英文的,字典主要是存储excel和DataTable列明的对应关系,当然我们也可以把这个对应关系存在配置文件或者其他地方 Dictionary<string, string> dir = new Dictionary<string, string>(); dir.Add("id", "编号"); dir.Add("uname", "用户"); dir.Add("sex", "性别"); dir.Add("age", "年龄"); dir.Add("pwd", "密码"); dir.Add("email", "邮箱"); dir.Add("address", "住址"); //使用helper类导出DataTable数据到excel表格中,参数依次是 (DataTable数据源; excel表名; excel存放位置的绝对路径; 列名对应字典; 是否清空以前的数据,设置为false,表示内容追加; 每个sheet放的数据条数,如果超过该条数就会新建一个sheet存储) NPOIHelper.ExportDTtoExcel(dataTable, "考勤信息表", @"C:\Users\ZDZN\Desktop/Hello.xlsx", dir, false, 400); } }
运行程序,当一个sheet的数目满了后会新生产一个sheet1来存储,效果如下:
接下来测试读取excel中的数据到datatable中,我们就读取刚才生成的excel中的数据到DataTable中去:
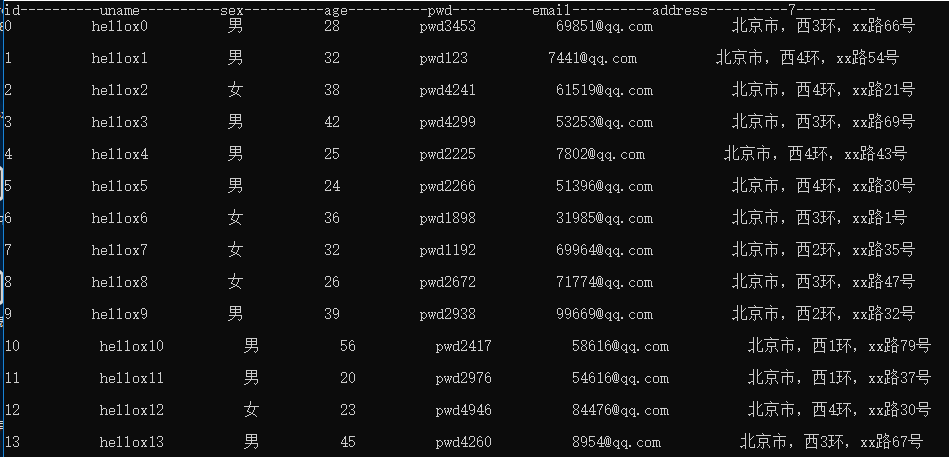
static void Main(string[] args) { log4net.Config.XmlConfigurator.Configure(); //用于支持gb2312 Encoding.RegisterProvider(CodePagesEncodingProvider.Instance); //DataTable的列名和excel的列名对应字典 Dictionary<string, string> dir = new Dictionary<string, string>(); dir.Add("id", "编号"); dir.Add("uname", "用户"); dir.Add("sex", "性别"); dir.Add("age", "年龄"); dir.Add("pwd", "密码"); dir.Add("email", "邮箱"); dir.Add("address", "住址"); //读取数据到DataTable,参数依此是(excel文件路径,列名对应字典,列名所在行,sheet索引) DataTable dt = NPOIHelper.ImportExceltoDt(@"C:\Users\ZDZN\Desktop/Hello11.xlsx", dir, 1, 0); //遍历DataTable--------------------------- foreach (DataColumn item in dt.Columns) { //显示dataTable的列名 Console.Write(item.ColumnName + new string('-', 10)); } Console.WriteLine(); //遍历DataTable中的数据 foreach (DataRow row in dt.Rows) { for (int i = 0; i < dt.Columns.Count; i++) { Console.Write(row[i].ToString() + new string(' ', 10)); } Console.WriteLine(); } Console.WriteLine("ok"); Console.ReadKey(); }
程序运行如下:
上边例子中的helper兼容了xls和xlsx两种格式,通过helper只需要一行代码就可以快速地进行excel和datatable间的数据转换,helper附件如下

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Data; using System.IO; using System.Text; using NPOI.HSSF.UserModel; using NPOI.SS.Formula.Eval; using NPOI.SS.UserModel; using System.Linq; using NPOI.SS.Util; using System.Text.RegularExpressions; using NPOI.XSSF.UserModel; using log4net; public class NPOIHelper { private static ILog loger = LogManager.GetLogger("myLogger"); #region 从DataTable导出到excel文件中,支持xls和xlsx格式 #region 导出为xls文件内部方法 /// <summary> /// 从datatable 中导出到excel /// </summary> /// <param name="strFileName">excel文件名</param> /// <param name="dtSource">datatabe源数据</param> /// <param name="strHeaderText">表名</param> /// <param name="sheetnum">sheet的编号</param> /// <returns></returns> static MemoryStream ExportDT(String strFileName, DataTable dtSource, string strHeaderText, Dictionary<string, string> dir, int sheetnum) { //创建工作簿和sheet IWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); using (Stream writefile = new FileStream(strFileName, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Read)) { if (writefile.Length > 0 && sheetnum > 0) { workbook = WorkbookFactory.Create(writefile); } } ISheet sheet = null; ICellStyle dateStyle = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); IDataFormat format = workbook.CreateDataFormat(); dateStyle.DataFormat = format.GetFormat("yyyy-mm-dd"); int[] arrColWidth = new int[dtSource.Columns.Count]; foreach (DataColumn item in dtSource.Columns) { arrColWidth[item.Ordinal] = Encoding.GetEncoding(936).GetBytes(item.ColumnName.ToString()).Length; } for (int i = 0; i < dtSource.Rows.Count; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < dtSource.Columns.Count; j++) { int intTemp = Encoding.GetEncoding(936).GetBytes(dtSource.Rows[i][j].ToString()).Length; if (intTemp > arrColWidth[j]) { arrColWidth[j] = intTemp; } } } int rowIndex = 0; foreach (DataRow row in dtSource.Rows) { #region 新建表,填充表头,填充列头,样式 if (rowIndex == 0) { string sheetName = strHeaderText + (sheetnum == 0 ? "" : sheetnum.ToString()); if (workbook.GetSheetIndex(sheetName) >= 0) { workbook.RemoveSheetAt(workbook.GetSheetIndex(sheetName)); } sheet = workbook.CreateSheet(sheetName); #region 表头及样式 { sheet.AddMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(0, 0, 0, dtSource.Columns.Count - 1)); IRow headerRow = sheet.CreateRow(0); headerRow.HeightInPoints = 25; headerRow.CreateCell(0).SetCellValue(strHeaderText); ICellStyle headStyle = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); headStyle.Alignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center; IFont font = workbook.CreateFont(); font.FontHeightInPoints = 20; font.Boldweight = 700; headStyle.SetFont(font); headerRow.GetCell(0).CellStyle = headStyle; rowIndex = 1; } #endregion #region 列头及样式 if (rowIndex == 1) { IRow headerRow = sheet.CreateRow(1);//第二行设置列名 ICellStyle headStyle = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); headStyle.Alignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center; IFont font = workbook.CreateFont(); font.FontHeightInPoints = 10; font.Boldweight = 700; headStyle.SetFont(font); //写入列标题 foreach (DataColumn column in dtSource.Columns) { headerRow.CreateCell(column.Ordinal).SetCellValue(dir[column.ColumnName]); headerRow.GetCell(column.Ordinal).CellStyle = headStyle; //设置列宽 sheet.SetColumnWidth(column.Ordinal, (arrColWidth[column.Ordinal] + 1) * 256 * 2); } rowIndex = 2; } #endregion } #endregion #region 填充内容 IRow dataRow = sheet.CreateRow(rowIndex); foreach (DataColumn column in dtSource.Columns) { ICell newCell = dataRow.CreateCell(column.Ordinal); string drValue = row[column].ToString(); switch (column.DataType.ToString()) { case "System.String": //字符串类型 double result; if (isNumeric(drValue, out result)) { //数字字符串 double.TryParse(drValue, out result); newCell.SetCellValue(result); break; } else { newCell.SetCellValue(drValue); break; } case "System.DateTime": //日期类型 DateTime dateV; DateTime.TryParse(drValue, out dateV); newCell.SetCellValue(dateV); newCell.CellStyle = dateStyle; //格式化显示 break; case "System.Boolean": //布尔型 bool boolV = false; bool.TryParse(drValue, out boolV); newCell.SetCellValue(boolV); break; case "System.Int16": //整型 case "System.Int32": case "System.Int64": case "System.Byte": int intV = 0; int.TryParse(drValue, out intV); newCell.SetCellValue(intV); break; case "System.Decimal": //浮点型 case "System.Double": double doubV = 0; double.TryParse(drValue, out doubV); newCell.SetCellValue(doubV); break; case "System.DBNull": //空值处理 newCell.SetCellValue(""); break; default: newCell.SetCellValue(drValue.ToString()); break; } } #endregion rowIndex++; } using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream()) { workbook.Write(ms); ms.Flush(); ms.Position = 0; return ms; } } #endregion #region 导出为xlsx文件内部方法 /// <summary> /// 从datatable 中导出到excel /// </summary> /// <param name="dtSource">datatable数据源</param> /// <param name="strHeaderText">表名</param> /// <param name="fs">文件流</param> /// <param name="readfs">内存流</param> /// <param name="sheetnum">sheet索引</param> static void ExportDTI(DataTable dtSource, string strHeaderText, FileStream fs, MemoryStream readfs, Dictionary<string, string> dir, int sheetnum) { IWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(); if (readfs.Length > 0 && sheetnum > 0) { workbook = WorkbookFactory.Create(readfs); } ISheet sheet = null; ICellStyle dateStyle = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); IDataFormat format = workbook.CreateDataFormat(); dateStyle.DataFormat = format.GetFormat("yyyy-mm-dd"); //取得列宽 int[] arrColWidth = new int[dtSource.Columns.Count]; foreach (DataColumn item in dtSource.Columns) { arrColWidth[item.Ordinal] = Encoding.GetEncoding(936).GetBytes(item.ColumnName.ToString()).Length; } for (int i = 0; i < dtSource.Rows.Count; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < dtSource.Columns.Count; j++) { int intTemp = Encoding.GetEncoding(936).GetBytes(dtSource.Rows[i][j].ToString()).Length; if (intTemp > arrColWidth[j]) { arrColWidth[j] = intTemp; } } } int rowIndex = 0; foreach (DataRow row in dtSource.Rows) { #region 新建表,填充表头,填充列头,样式 if (rowIndex == 0) { #region 表头及样式 { string sheetName = strHeaderText + (sheetnum == 0 ? "" : sheetnum.ToString()); if (workbook.GetSheetIndex(sheetName) >= 0) { workbook.RemoveSheetAt(workbook.GetSheetIndex(sheetName)); } sheet = workbook.CreateSheet(sheetName); sheet.AddMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(0, 0, 0, dtSource.Columns.Count - 1)); IRow headerRow = sheet.CreateRow(0); headerRow.HeightInPoints = 25; headerRow.CreateCell(0).SetCellValue(strHeaderText); ICellStyle headStyle = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); headStyle.Alignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center; IFont font = workbook.CreateFont(); font.FontHeightInPoints = 20; font.Boldweight = 700; headStyle.SetFont(font); headerRow.GetCell(0).CellStyle = headStyle; } #endregion #region 列头及样式 { IRow headerRow = sheet.CreateRow(1); ICellStyle headStyle = workbook.CreateCellStyle(); headStyle.Alignment = HorizontalAlignment.Center; IFont font = workbook.CreateFont(); font.FontHeightInPoints = 10; font.Boldweight = 700; headStyle.SetFont(font); foreach (DataColumn column in dtSource.Columns) { headerRow.CreateCell(column.Ordinal).SetCellValue(dir[column.ColumnName]); headerRow.GetCell(column.Ordinal).CellStyle = headStyle; //设置列宽 sheet.SetColumnWidth(column.Ordinal, (arrColWidth[column.Ordinal] + 1) * 256 * 2); } } #endregion rowIndex = 2; } #endregion #region 填充内容 IRow dataRow = sheet.CreateRow(rowIndex); foreach (DataColumn column in dtSource.Columns) { ICell newCell = dataRow.CreateCell(column.Ordinal); string drValue = row[column].ToString(); switch (column.DataType.ToString()) { case "System.String": //字符串类型 double result; if (isNumeric(drValue, out result)) { double.TryParse(drValue, out result); newCell.SetCellValue(result); break; } else { newCell.SetCellValue(drValue); break; } case "System.DateTime": //日期类型 DateTime dateV; DateTime.TryParse(drValue, out dateV); newCell.SetCellValue(dateV); newCell.CellStyle = dateStyle; //格式化显示 break; case "System.Boolean": //布尔型 bool boolV = false; bool.TryParse(drValue, out boolV); newCell.SetCellValue(boolV); break; case "System.Int16": //整型 case "System.Int32": case "System.Int64": case "System.Byte": int intV = 0; int.TryParse(drValue, out intV); newCell.SetCellValue(intV); break; case "System.Decimal": //浮点型 case "System.Double": double doubV = 0; double.TryParse(drValue, out doubV); newCell.SetCellValue(doubV); break; case "System.DBNull": //空值处理 newCell.SetCellValue(""); break; default: newCell.SetCellValue(drValue.ToString()); break; } } #endregion rowIndex++; } workbook.Write(fs); fs.Close(); } #endregion #region 导出excel表格 /// <summary> /// DataTable导出到Excel文件,xls文件 /// </summary> /// <param name="dtSource">数据源</param> /// <param name="strHeaderText">表名</param> /// <param name="strFileName">excel文件名</param> /// <param name="dir">datatable和excel列名对应字典</param> /// <param name="sheetRow">每个sheet存放的行数</param> public static void ExportDTtoExcel(DataTable dtSource, string strHeaderText, string strFileName, Dictionary<string, string> dir, bool isNew, int sheetRow = 50000) { int currentSheetCount = GetSheetNumber(strFileName);//现有的页数sheetnum if (sheetRow <= 0) { sheetRow = dtSource.Rows.Count; } string[] temp = strFileName.Split('.'); string fileExtens = temp[temp.Length - 1]; int sheetCount = (int)Math.Ceiling((double)dtSource.Rows.Count / sheetRow);//sheet数目 if (temp[temp.Length - 1] == "xls" && dtSource.Columns.Count < 256 && sheetRow < 65536) { if (isNew) { currentSheetCount = 0; } for (int i = currentSheetCount; i < currentSheetCount + sheetCount; i++) { DataTable pageDataTable = dtSource.Clone(); int hasRowCount = dtSource.Rows.Count - sheetRow * (i - currentSheetCount) < sheetRow ? dtSource.Rows.Count - sheetRow * (i - currentSheetCount) : sheetRow; for (int j = 0; j < hasRowCount; j++) { pageDataTable.ImportRow(dtSource.Rows[(i - currentSheetCount) * sheetRow + j]); } using (MemoryStream ms = ExportDT(strFileName, pageDataTable, strHeaderText, dir, i)) { using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(strFileName, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write)) { byte[] data = ms.ToArray(); fs.Write(data, 0, data.Length); fs.Flush(); } } } } else { if (temp[temp.Length - 1] == "xls") strFileName = strFileName + "x"; if (isNew) { currentSheetCount = 0; } for (int i = currentSheetCount; i < currentSheetCount + sheetCount; i++) { DataTable pageDataTable = dtSource.Clone(); int hasRowCount = dtSource.Rows.Count - sheetRow * (i - currentSheetCount) < sheetRow ? dtSource.Rows.Count - sheetRow * (i - currentSheetCount) : sheetRow; for (int j = 0; j < hasRowCount; j++) { pageDataTable.ImportRow(dtSource.Rows[(i - currentSheetCount) * sheetRow + j]); } FileStream readfs = new FileStream(strFileName, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Read); MemoryStream readfsm = new MemoryStream(); readfs.CopyTo(readfsm); readfs.Close(); using (FileStream writefs = new FileStream(strFileName, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write)) { ExportDTI(pageDataTable, strHeaderText, writefs, readfsm, dir, i); } readfsm.Close(); } } } #endregion #endregion #region 从excel文件中将数据导出到datatable/datatable /// <summary> /// 将制定sheet中的数据导出到datatable中 /// </summary> /// <param name="sheet">需要导出的sheet</param> /// <param name="HeaderRowIndex">列头所在行号,-1表示没有列头</param> /// <param name="dir">excel列名和DataTable列名的对应字典</param> /// <returns></returns> static DataTable ImportDt(ISheet sheet, int HeaderRowIndex, Dictionary<string, string> dir) { DataTable table = new DataTable(); IRow headerRow; int cellCount; try { //没有标头或者不需要表头用excel列的序号(1,2,3..)作为DataTable的列名 if (HeaderRowIndex < 0) { headerRow = sheet.GetRow(0); cellCount = headerRow.LastCellNum; for (int i = headerRow.FirstCellNum; i <= cellCount; i++) { DataColumn column = new DataColumn(Convert.ToString(i)); table.Columns.Add(column); } } //有表头,使用表头做为DataTable的列名 else { headerRow = sheet.GetRow(HeaderRowIndex); cellCount = headerRow.LastCellNum; for (int i = headerRow.FirstCellNum; i <= cellCount; i++) { //如果excel某一列列名不存在:以该列的序号作为Datatable的列名,如果DataTable中包含了这个序列为名的列,那么列名为重复列名+序号 if (headerRow.GetCell(i) == null) { if (table.Columns.IndexOf(Convert.ToString(i)) > 0) { DataColumn column = new DataColumn(Convert.ToString("重复列名" + i)); table.Columns.Add(column); } else { DataColumn column = new DataColumn(Convert.ToString(i)); table.Columns.Add(column); } } //excel中的某一列列名不为空,但是重复了:对应的Datatable列名为“重复列名+序号” else if (table.Columns.IndexOf(headerRow.GetCell(i).ToString()) > 0) { DataColumn column = new DataColumn(Convert.ToString("重复列名" + i)); table.Columns.Add(column); } else //正常情况,列名存在且不重复:用excel中的列名作为datatable中对应的列名 { string colName = dir.Where(s => s.Value == headerRow.GetCell(i).ToString()).First().Key; DataColumn column = new DataColumn(colName); table.Columns.Add(column); } } } int rowCount = sheet.LastRowNum; for (int i = (HeaderRowIndex + 1); i <= sheet.LastRowNum; i++)//excel行遍历 { try { IRow row; if (sheet.GetRow(i) == null)//如果excel有空行,则添加缺失的行 { row = sheet.CreateRow(i); } else { row = sheet.GetRow(i); } DataRow dataRow = table.NewRow(); for (int j = row.FirstCellNum; j <= cellCount; j++)//excel列遍历 { try { if (row.GetCell(j) != null) { switch (row.GetCell(j).CellType) { case CellType.String://字符串 string str = row.GetCell(j).StringCellValue; if (str != null && str.Length > 0) { dataRow[j] = str.ToString(); } else { dataRow[j] = default(string); } break; case CellType.Numeric://数字 if (DateUtil.IsCellDateFormatted(row.GetCell(j)))//时间戳数字 { dataRow[j] = DateTime.FromOADate(row.GetCell(j).NumericCellValue); } else { dataRow[j] = Convert.ToDouble(row.GetCell(j).NumericCellValue); } break; case CellType.Boolean: dataRow[j] = Convert.ToString(row.GetCell(j).BooleanCellValue); break; case CellType.Error: dataRow[j] = ErrorEval.GetText(row.GetCell(j).ErrorCellValue); break; case CellType.Formula://公式 switch (row.GetCell(j).CachedFormulaResultType) { case CellType.String: string strFORMULA = row.GetCell(j).StringCellValue; if (strFORMULA != null && strFORMULA.Length > 0) { dataRow[j] = strFORMULA.ToString(); } else { dataRow[j] = null; } break; case CellType.Numeric: dataRow[j] = Convert.ToString(row.GetCell(j).NumericCellValue); break; case CellType.Boolean: dataRow[j] = Convert.ToString(row.GetCell(j).BooleanCellValue); break; case CellType.Error: dataRow[j] = ErrorEval.GetText(row.GetCell(j).ErrorCellValue); break; default: dataRow[j] = ""; break; } break; default: dataRow[j] = ""; break; } } } catch (Exception exception) { loger.Error(exception.ToString()); } } table.Rows.Add(dataRow); } catch (Exception exception) { loger.Error(exception.ToString()); } } } catch (Exception exception) { loger.Error(exception.ToString()); } return table; } /// <summary> /// 读取Excel文件特定名字sheet的内容到DataTable /// </summary> /// <param name="strFileName">excel文件路径</param> /// <param name="sheet">需要导出的sheet</param> /// <param name="HeaderRowIndex">列头所在行号,-1表示没有列头</param> /// <param name="dir">excel列名和DataTable列名的对应字典</param> /// <returns></returns> public static DataTable ImportExceltoDt(string strFileName, Dictionary<string, string> dir, string SheetName, int HeaderRowIndex = 1) { DataTable table = new DataTable(); using (FileStream file = new FileStream(strFileName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)) { if (file.Length > 0) { IWorkbook wb = WorkbookFactory.Create(file); ISheet isheet = wb.GetSheet(SheetName); table = ImportDt(isheet, HeaderRowIndex, dir); isheet = null; } } return table; } /// <summary> /// 读取Excel文件某一索引sheet的内容到DataTable /// </summary> /// <param name="strFileName">excel文件路径</param> /// <param name="sheet">需要导出的sheet序号</param> /// <param name="HeaderRowIndex">列头所在行号,-1表示没有列头</param> /// <param name="dir">excel列名和DataTable列名的对应字典</param> /// <returns></returns> public static DataTable ImportExceltoDt(string strFileName, Dictionary<string, string> dir, int HeaderRowIndex = 1, int SheetIndex = 0) { DataTable table = new DataTable(); using (FileStream file = new FileStream(strFileName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)) { if (file.Length > 0) { IWorkbook wb = WorkbookFactory.Create(file); ISheet isheet = wb.GetSheetAt(SheetIndex); table = ImportDt(isheet, HeaderRowIndex, dir); isheet = null; } } return table; } #endregion /// <summary> /// 获取excel文件的sheet数目 /// </summary> /// <param name="outputFile"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static int GetSheetNumber(string outputFile) { int number = 0; using (FileStream readfile = new FileStream(outputFile, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Read)) { if (readfile.Length > 0) { IWorkbook wb = WorkbookFactory.Create(readfile); number = wb.NumberOfSheets; } } return number; } /// <summary> /// 判断内容是否是数字 /// </summary> /// <param name="message"></param> /// <param name="result"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static bool isNumeric(String message, out double result) { Regex rex = new Regex(@"^[-]?\d+[.]?\d*$"); result = -1; if (rex.IsMatch(message)) { result = double.Parse(message); return true; } else return false; } /// <summary> /// 验证导入的Excel是否有数据 /// </summary> /// <param name="excelFileStream"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static bool HasData(Stream excelFileStream) { using (excelFileStream) { IWorkbook workBook = new HSSFWorkbook(excelFileStream); if (workBook.NumberOfSheets > 0) { ISheet sheet = workBook.GetSheetAt(0); return sheet.PhysicalNumberOfRows > 0; } } return false; } }


