201871010126 王亚涛 《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第十四周学习总结
|
|
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11953993.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
|
随笔博文正文内容包括:
第一部分:总结第十二章本周理论知识(25分)
第十二章 Swing用户界面组件
12.1 布局管理概述
Java的GUI界面定义是由AWT类包和Swing类包来完成的,对于布局的管理交给专门的布局管理器类(LayoutManager)来完成。
Java中的布局管理器类有:FlowLayout、BorderLayout、GridLayout、GridBagLayout等
一、布局管理器所属类包
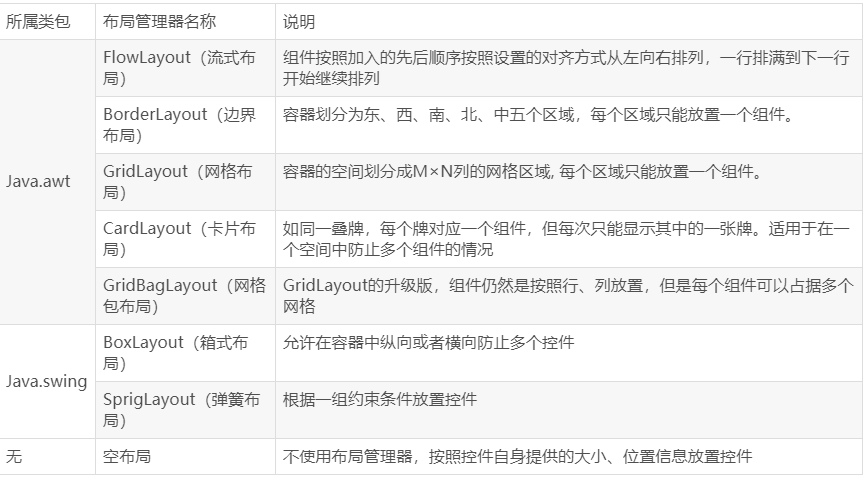
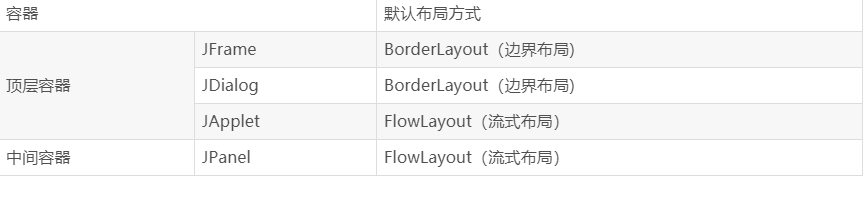
二、容器的默认布局管理器
三、FlowLayout(流式布局)
使用FlowLayout布局方式的容器中组件按照加入的先后顺序按照设置的对齐方式(居中、左对齐、右对齐)从左向右排列,一行排满(即组件超过容器宽度后)到下一行开始继续排列。
1、流式布局特征如下:
l 组件按照设置的对齐方式进行排列
l 不管对齐方式如何,组件均按照从左到右的方式进行排列,一行排满,转到下一行。(比如按照右对齐排列,第一个组件在第一行最右边,添加第二个组件时,第一个组件向左平移,第二个组件
变成该行最右边的组件,这就是从左向右方式进行排列)
2、流式布局FlowLayout类的常用构造函数和方法
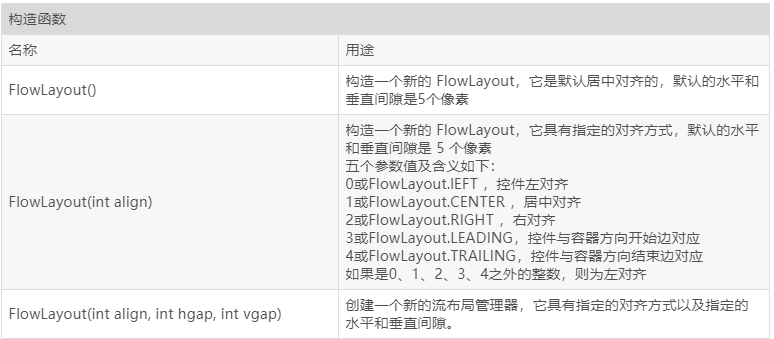
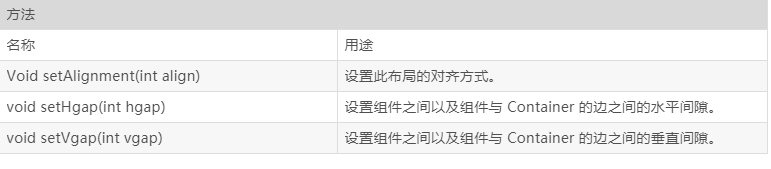
3、FlowLayout 布局应用代码段举例
1)设置FlowLayout 布局
JFrame fr=new JFrame( );
FlowLayout flow=new FlowLayout( );
fr.setLayout(flow);
上面的语句可以简化成:
fr.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
2)设置框架fr为组件左对齐的FlowLayout布局
fr.setLayout(newFlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
3)设置框架fr为组件左对齐的FlowLayout布局,并且组件的水平间距为20像素,垂直间距为40像素。
fr.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT,20,40));
12.2 文本输入
12.2.1 文本域
JTextField的(文本框)使用:
JTextField 是一个轻量级组件,它允许编辑单行文本。
1.JTextField的常用构造方法:
JTextField() 构造一个新的 TextField。
JTextField(int columns) 构造一个具有指定列数的新的空 TextField。
JTextField(String text) 构造一个用指定文本初始化的新TextField。
JTextField(String text, int columns) 构造一个用指定文本和列初始化的新TextField。
2.JTextField的常用方法:
SetText(string) 设置文本域中的文本值
GetText()返回文本域中的输入文本值
getColumns()返回文本域的列数
setEditable(Boolean) 设置文本域是否为只读状态
12.2.2 文本区
JTextArea(文本区)的使用:
1.JTextArea的常用构造方法:
JTextArea() 构造新的 TextArea。
JTextArea(String text) 构造显示指定文本的新的 TextArea。
JTextArea(int rows, int columns) 构造具有指定行数和列数的新的空 TextArea。
JTextArea(String text, int rows, int columns) 构造具有指定文本、行数和列数的新的 TextArea。
文本区与文本域的异同相同之处:
文本域和文本区组件都可用于获取文本输入。
不同之处:
文本域只能接受单行文本的输入; 文本区能够接受多行文本的输入。
12.2.3Java组件
主要因素:内容、外观、行为;
这三个主要元素与模型—视图—控制器模式的 三部件的对应关系为:
内容——控制器(作用:处理用户输入)
外观——视图(作用:显示内容)
行为——模型(作用:存储内容)
12.3 组件
12.3.1 标签组件
标签是容纳文本的组件。它们没有任何修饰(如没有边界 ),也不响应用户输入。
标签的常用用途之一就是标识组件,例如标识文本域。其使用步骤如下:
12.3.2 选择组件
复选框 单选按钮 边框 组合框 滑动条
(1)复选框构造器 1.bold = new JCheckBox("Bold"); 复选框自动地带有表示标签。
JCheckBox(String label,Icon icon); 构造带有标签与图标的复选框,默认初始未被选择。
JCheckBox(String label,boolean state); 用指定的标签和初始化选择状态构造一个复选框单选按钮的构造器。
1.JRadioButton(String label,Icon icon); 创建一个带标签和图标的单选按钮RadioButton(String label,boolean state);
用指定的标签和初始化状态构造单选按钮按钮组:为单选按钮组构造一个ButtonGroup的对象。 然后,再将JRadioButton类型的对象添加到按钮 组中。
按钮组负责在新按钮被按下的时,取消前一 个按钮的选择状态。如果在一个窗口中 有多组复选框或单选按 钮,就需要可视化的形 式指明哪些按钮属于同 一组。
Swing提供了一 组很有用的边框)如果有多个选择项,使用单选按钮占据的屏幕空 间太大时,就可以选择组合框。
组合框的事件监听:为了判断组合框的哪个选项被选择,可通过 事件参数调用getSource方法来得到发送事件的组 合框引用,接着调用getSelectdeItem方法获取当 前选择的选项。
滑动条:滑动条可以让用户从一组离散值中进行选择 ,并且它还允许进行连续值得选择。
12.4 菜单
菜单创建 菜单项中的图标 复选框和单选按钮菜单项 弹出菜单 快捷键和加速器 启用和禁用菜单项 工具栏 工具提示
网格组布局 (GridBagLayout):GridBagLayout与GridLayout有点相似,它也是 将组件排在格子里,但是GridBagLayout在网格 的基础上提供更复杂的布局。
GridBagLayout允许单个组件在一个单元中不填 满整个单元,而只是占用最佳大小,也允许单个 组件扩展成不止一个单元,并且可以用任意顺序 加入组件。
定制布局管理器: 程序员可通过自己设计LayoutManager类来实现 特殊的布局方式。定制布局管理器需要实现LayoutManager接口, 并覆盖以下方法。
12.5 对话框
选项对话框 创建对话框 数据选择 文件对话框 颜色选择器
(1)对话框是一种大小不能变化、不能有菜单的容器窗口; 对话框不能作为一个应用程序的主框架,而必须包含在其 他的容器中。
(2)选项对话框:JOptionPane提供的对话框是模式对话框。当模 式对话框显示时,它不允许用户输入到程序的 其他的窗口。使用JOptionPane,可以创建和自 定义问题、信息、警告和错误等几种类型的对 话框。
(3)数据交换:输入对话框含有供用户输入文本的文本框、一个确认和取 消按钮,是有模式对话框。当输入对话框可见时,要求用户 输入一个字符串。
(4)文件对话框:专门用于对文件(或目录)进行浏览和选择的对 话框,常用的构造方法: – JFileChooser():根据用户的缺省目录创建文件对话框 – JFileChooser(File currentDirectory):根据File型参数 currentDirectory指定的目录创建文件对话框
(5)颜色对话框: javax.swing包中的JColorChooser类的静态方 法: public static Color showDialog(Component component, String title, Color initialColor)创建一个颜色对话框
(6)参数component指定对话框所依赖的组件,title 指定对话框的标题;initialColor 指定对话框返回 的初始颜色,即对话框消失后,返回的默认值。 颜色对话框可根据用户在颜色对话框中选择的颜 色返回一个颜色对象.
第二部分:实验部分
实验1: 导入第12章示例程序,测试程序并进行组内讨论。
测试程序1
l 在elipse IDE中运行教材479页程序12-1,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握布局管理器的用法;
l 理解GUI界面中事件处理技术的用途。
l 在布局管理应用代码处添加注释;
例题12.1程序代码及注释如下:
package calculator; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.35 2018-04-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Calculator { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { var frame = new CalculatorFrame(); frame.setTitle("Calculator");//设置框架名称 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//窗口关闭按钮设置为可用 frame.setVisible(true);//将框架设置为可见 }); } }
package calculator; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a calculator panel. */ public class CalculatorFrame extends JFrame { public CalculatorFrame() { add(new CalculatorPanel()); pack(); } }
package calculator; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A panel with calculator buttons and a result display.一个带有计算机的按钮和结果显示的面板 */ public class CalculatorPanel extends JPanel { //私有属性 private JButton display; private JPanel panel; private double result; private String lastCommand; private boolean start; //构造器 public CalculatorPanel() { setLayout(new BorderLayout());//设定新的边框布局管理器 result = 0; lastCommand = "="; start = true; // add the display添加显示 display = new JButton("0");//用来显示完成算式计算结果 display.setEnabled(false);//setEnabled设置只显示不能点击的按钮 add(display, BorderLayout.NORTH);//将display添加到上方区域 //生成器监听对象 var insert = new InsertAction(); var command = new CommandAction(); // add the buttons in a 4 x 4 grid //在4 x 4网格中添加按钮 panel = new JPanel();//新建窗格组件 panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 4));//设定4行4列的网格布局管理器 //添加组件 addButton("7", insert); addButton("8", insert); addButton("9", insert); addButton("/", command); addButton("4", insert); addButton("5", insert); addButton("6", insert); addButton("*", command); addButton("1", insert); addButton("2", insert); addButton("3", insert); addButton("-", command); addButton("0", insert); addButton(".", insert); addButton("=", command); addButton("+", command); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);//将panel添加到中部区域 } /** * Adds a button to the center panel.Adds 向中间面板添加按钮 * @param label the button label * @param listener the button lis tener */ private void addButton(String label, ActionListener listener) { var button = new JButton(label);//生成按钮对象 button.addActionListener(listener);//注册监听器对象 panel.add(button);//将其添加到窗格中 } /** * This action inserts the button action string to the end of the display text. //标记按钮标签此操作将按钮操作字符串插入到显示框中 */ //内部类 private class InsertAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { String input = event.getActionCommand(); if (start) { display.setText(""); start = false; } display.setText(display.getText() + input); } } /** * This action executes the command that the button action string denotes. */ //内部类 private class CommandAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { String command = event.getActionCommand(); if (start) { if (command.equals("-")) { display.setText(command); start = false; } else lastCommand = command; } else { calculate(Double.parseDouble(display.getText()));//将数字字符串转化为数字 lastCommand = command; start = true; } } } /** * Carries out the pending calculation.//执行计算 * @param x the value to be accumulated with the prior result. */ //计算方法 public void calculate(double x) { if (lastCommand.equals("+")) result += x; else if (lastCommand.equals("-")) result -= x; else if (lastCommand.equals("*")) result *= x; else if (lastCommand.equals("/")) result /= x; else if (lastCommand.equals("=")) result = x; display.setText("" + result);//将数字转化为数字字符串输出 } }
运行截图如下: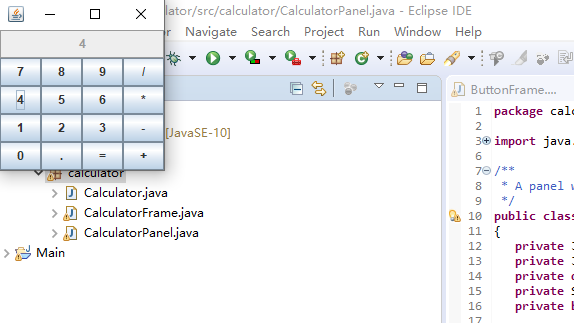
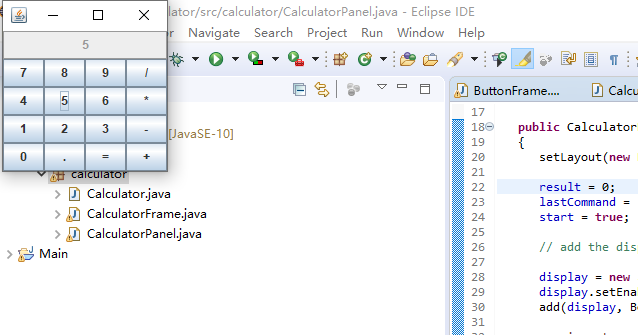
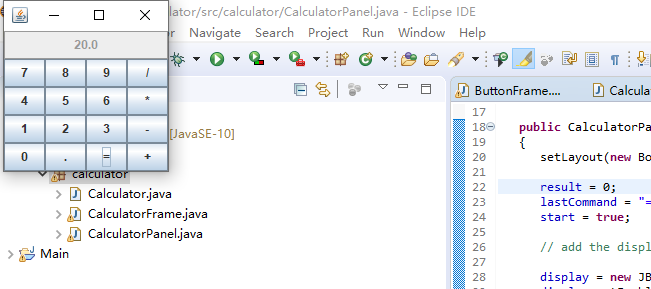
测试程序2
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材486页程序12-2,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握文本组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
例题12.2程序代码如下:
package text; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.42 2018-04-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class TextComponentTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { var frame = new TextComponentFrame(); frame.setTitle("TextComponentTest");//设置框架名称 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//窗口关闭按钮设置为可用 frame.setVisible(true);//将框架设置为可见 }); } }
package text; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JPasswordField; import javax.swing.JScrollPane; import javax.swing.JTextArea; import javax.swing.JTextField; import javax.swing.SwingConstants; /** * A frame with sample text components.包含示例文本组件的框架 */ public class TextComponentFrame extends JFrame { public static final int TEXTAREA_ROWS = 8; public static final int TEXTAREA_COLUMNS = 20;//定义网格的行数为8,列数为20 public TextComponentFrame() { var textField = new JTextField(); var passwordField = new JPasswordField();//定义一个新的文本框和密码框 var northPanel = new JPanel(); northPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2)); //SwingConstants通常用于在屏幕上定位或定向组件的常量的集合 northPanel.add(new JLabel("User name: ", SwingConstants.RIGHT)); northPanel.add(textField); northPanel.add(new JLabel("Password: ", SwingConstants.RIGHT)); northPanel.add(passwordField); add(northPanel, BorderLayout.NORTH);//在面板上添加一个布局方式在上方的边框 var textArea = new JTextArea(TEXTAREA_ROWS, TEXTAREA_COLUMNS); var scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textArea);//创建一个新的文本框和滚动窗口 add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);//添加滚动窗口 // add button to append text into the text area var southPanel = new JPanel(); var insertButton = new JButton("Insert"); southPanel.add(insertButton); //将给定文本追加到文档结尾 insertButton.addActionListener(event -> textArea.append("User name: " + textField.getText() + " Password: " + new String(passwordField.getPassword()) + "\n")); add(southPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }
运行截图如下:
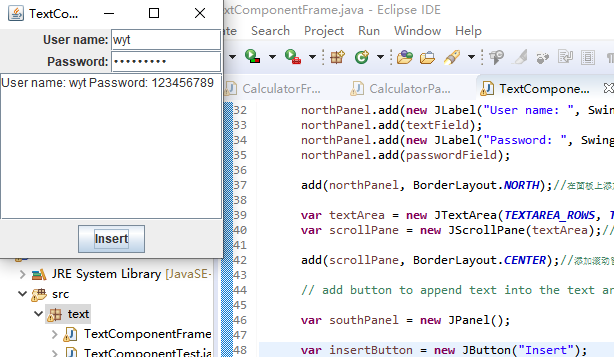
测试程序3
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材489页程序12-3,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握复选框组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
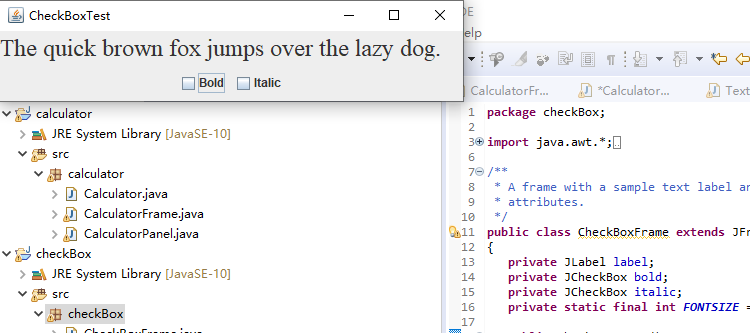
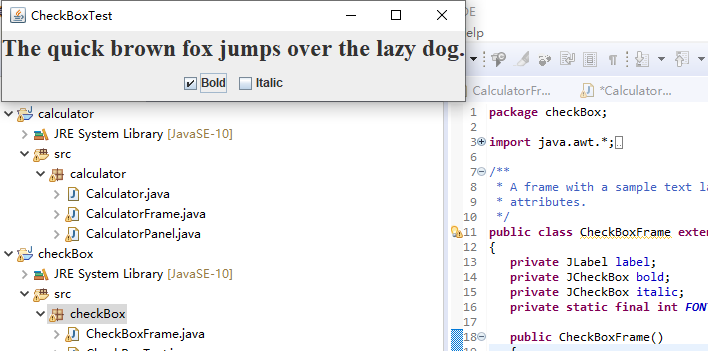
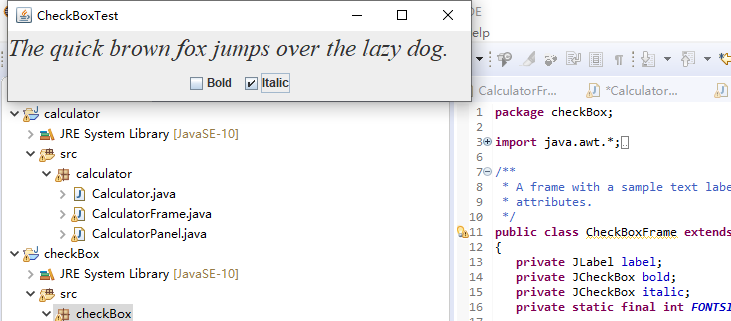
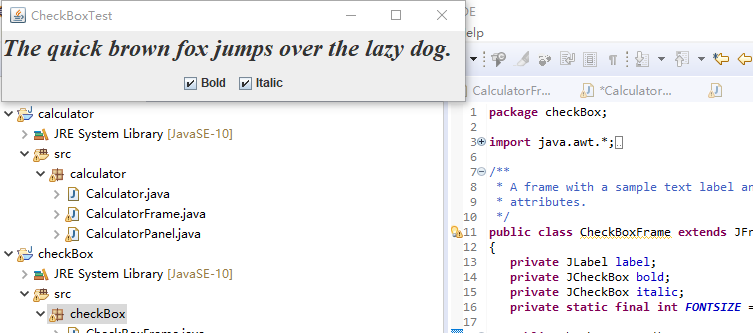
例题12.3程序代码及截图如下:
package checkBox; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.35 2018-04-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class CheckBoxTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { var frame = new CheckBoxFrame(); frame.setTitle("CheckBoxTest");//设置框架名称 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//窗口关闭按钮设置为可用 frame.setVisible(true);//将框架设置为可见//窗口关闭按钮设置为可用 }); } }
package checkBox; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a sample text label and check boxes for selecting font * attributes. */ public class CheckBoxFrame extends JFrame { private JLabel label; private JCheckBox bold; private JCheckBox italic; private static final int FONTSIZE = 24; public CheckBoxFrame() { // add the sample text label // 添加示例文本标签 label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."); label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, FONTSIZE)); add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // this listener sets the font attribute of // the label to the check box state // 字体属性 // 复选框状态的标签 ActionListener listener = event -> { int mode = 0; if (bold.isSelected()) mode += Font.BOLD; if (italic.isSelected()) mode += Font.ITALIC; label.setFont(new Font("Serif", mode, FONTSIZE)); }; // add the check boxes // 添加复选框 var buttonPanel = new JPanel(); bold = new JCheckBox("Bold"); bold.addActionListener(listener); bold.setSelected(true); buttonPanel.add(bold); italic = new JCheckBox("Italic"); italic.addActionListener(listener); buttonPanel.add(italic); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }
运行截图如下:
测试程序4
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材491页程序12-4,运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握单选按钮组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
例题12.4程序代码及注释如下:
package radioButton; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.35 2018-04-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class RadioButtonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { var frame = new RadioButtonFrame(); frame.setTitle("RadioButtonTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
package radioButton; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a sample text label and radio buttons for selecting font sizes. */ //带有示例文本标签和用于选择字体大小的单选按钮的框架 public class RadioButtonFrame extends JFrame { private JPanel buttonPanel; private ButtonGroup group; private JLabel label; private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 36; public RadioButtonFrame() { // add the sample text label label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."); label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE)); add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // add the radio buttons buttonPanel = new JPanel(); group = new ButtonGroup(); addRadioButton("Small", 8); addRadioButton("Medium", 12); addRadioButton("Large", 18); addRadioButton("Extra large", 36); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } /** * Adds a radio button that sets the font size of the sample text. * @param name the string to appear on the button * @param size the font size that this button sets */ // 添加一个单选按钮,用于设置示例文本的字体大小。 // 大小的规格要出现在按钮上的字符串 //按钮设置的字体大小 public void addRadioButton(String name, int size) { boolean selected = size == DEFAULT_SIZE; var button = new JRadioButton(name, selected); group.add(button); buttonPanel.add(button); // this listener sets the label font size // 此监听器设置标签字体大小 ActionListener listener = event -> label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, size)); button.addActionListener(listener); } }
运行截图如下:
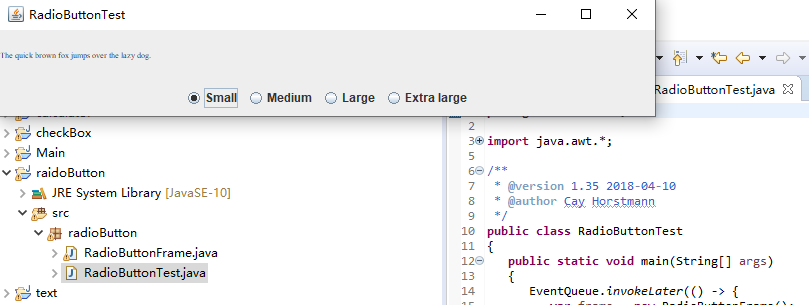
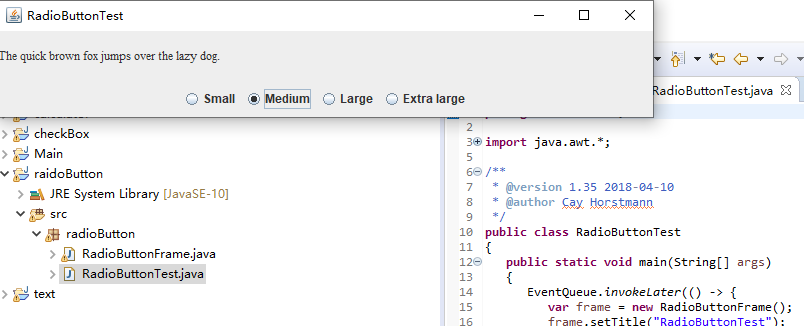
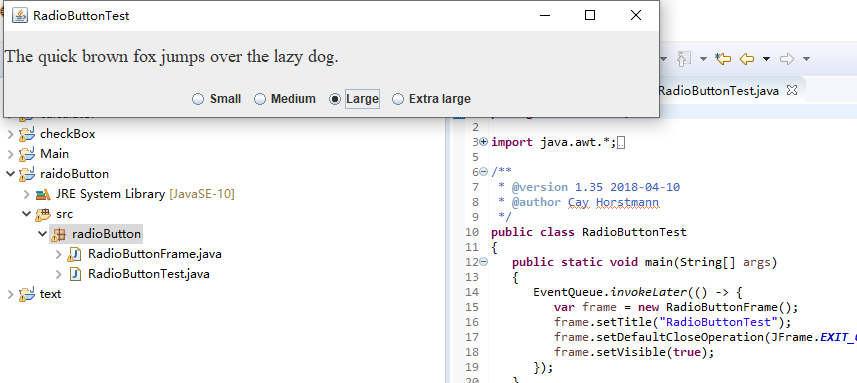
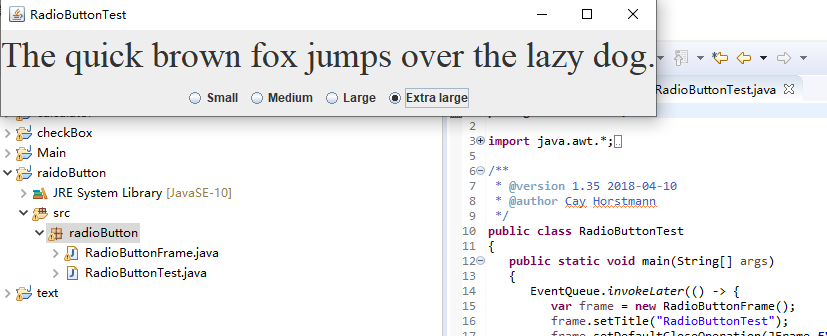
测试程序5
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材494页程序12-5,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握边框的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
例题12.5程序代码及注释如下:
package border; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.35 2018-04-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class BorderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { var frame = new BorderFrame(); frame.setTitle("BorderTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
package border; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.border.*; /** * A frame with radio buttons to pick a border style. // 带有单选按钮以选择边框样式的框架。 */ public class BorderFrame extends JFrame { private JPanel demoPanel; private JPanel buttonPanel; private ButtonGroup group; public BorderFrame() { demoPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel = new JPanel(); group = new ButtonGroup(); //设置不同的边框类型按钮,共六种(提供标准 Border 对象的工厂类) addRadioButton("Lowered bevel", BorderFactory.createLoweredBevelBorder()); addRadioButton("Raised bevel", BorderFactory.createRaisedBevelBorder()); addRadioButton("Etched", BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder()); addRadioButton("Line", BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color.BLUE)); addRadioButton("Matte", BorderFactory.createMatteBorder(10, 10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE)); addRadioButton("Empty", BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder()); Border etched = BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder(); Border titled = BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(etched, "Border types"); buttonPanel.setBorder(titled); setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1)); add(buttonPanel); add(demoPanel); pack(); } public void addRadioButton(String buttonName, Border b) { var button = new JRadioButton(buttonName); button.addActionListener(event -> demoPanel.setBorder(b)); group.add(button); buttonPanel.add(button); } }
运行截图如下:
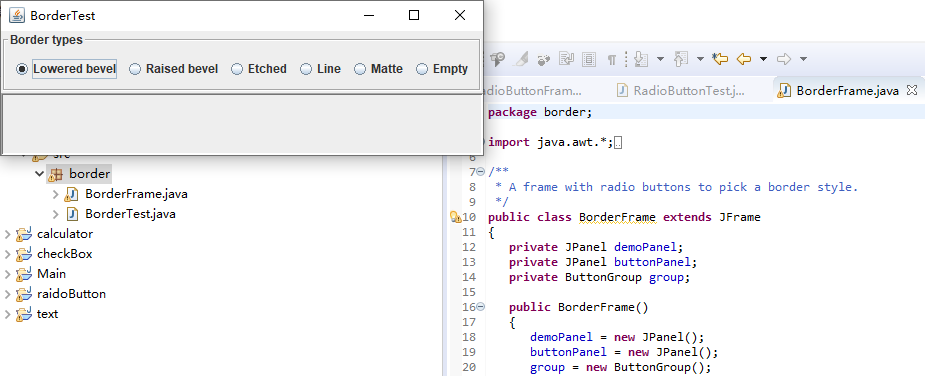
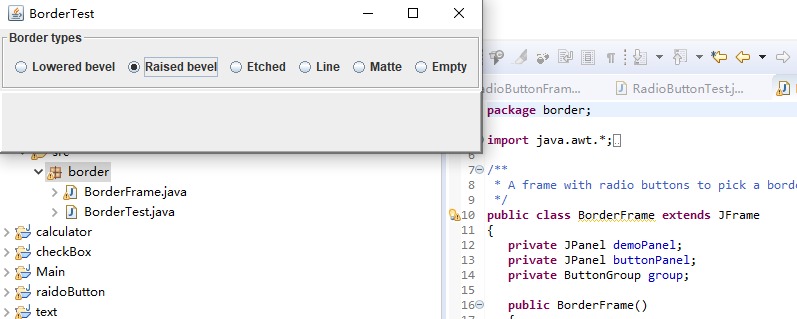
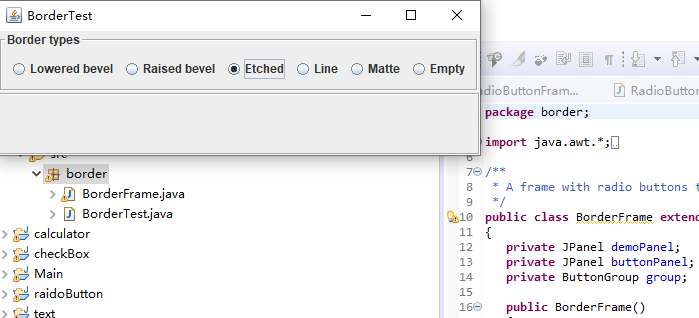

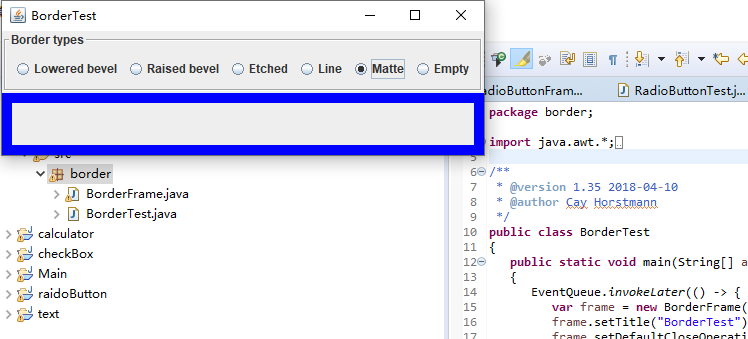
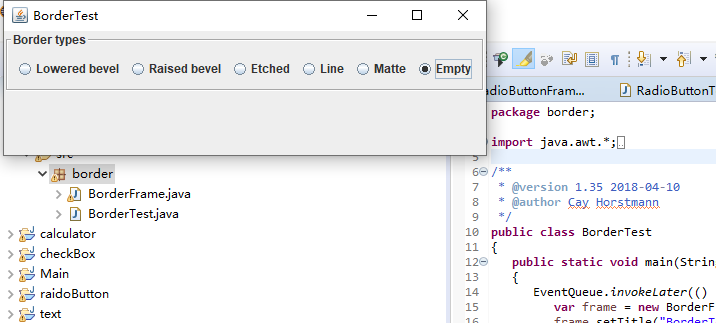
测试程序6
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材498页程序12-6,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握组合框组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
例题12.6程序代码及注释如下:
package comboBox; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.36 2018-04-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ComboBoxTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //lambda表达式 EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { var frame = new ComboBoxFrame(); frame.setTitle("ComboBoxTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
package comboBox; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Font; import javax.swing.JComboBox; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; /** * A frame with a sample text label and a combo box for selecting font faces. */ //带有示例文本标签和用于选择字体的组合框的框架。 public class ComboBoxFrame extends JFrame { private JComboBox<String> faceCombo; private JLabel label; private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 24; public ComboBoxFrame() { // add the sample text label // 添加示例文本标签 label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."); label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE)); //添加到边框布局管理器的中间 add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // make a combo box and add face names // 创建一个组合框对象并添加项目名称 faceCombo = new JComboBox<>(); faceCombo.addItem("Serif"); faceCombo.addItem("SansSerif"); faceCombo.addItem("Monospaced"); faceCombo.addItem("Dialog"); faceCombo.addItem("DialogInput"); // the combo box listener changes the label font to the selected face name // 组合框监听器将标签字体更改为所选的名称(添加监听器,使用lambda表达式) faceCombo.addActionListener(event -> label.setFont( //getItemAt用于返回指定索引处的列表项;getSelectedIndex用于返回当前选择的选项 new Font(faceCombo.getItemAt(faceCombo.getSelectedIndex()), Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE))); // add combo box to a panel at the frame's southern border //将组合框添加到框架南边的面板 var comboPanel = new JPanel(); comboPanel.add(faceCombo); add(comboPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }
运行截图如下:
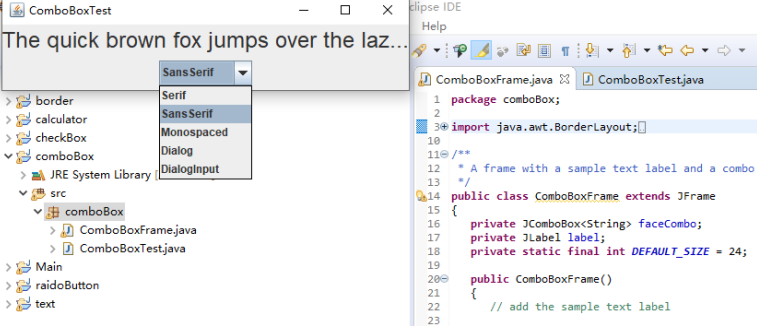
实验2:结对编程练习
利用所掌握的GUI技术,设计一个用户信息采集程序,要求如下:
(1) 用户信息输入界面如下图所示:

(2) 用户点击提交按钮时,用户输入信息显示在录入信息显示区,格式如下:
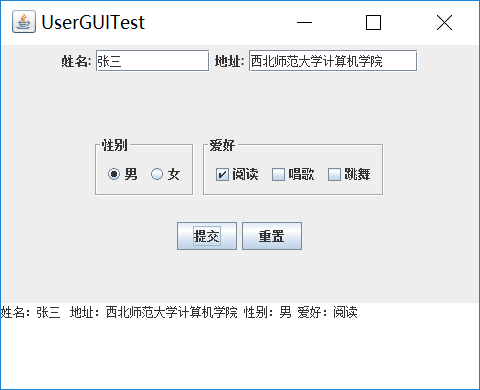
(3) 用户点击重置按钮后,清空用户已输入信息;
(4) 点击窗口关闭,程序退出。
结对编程代码如下:
import java.awt.EventQueue; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new GUIFrame(); frame.setTitle("UserGUITest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.FlowLayout; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.BorderFactory; import javax.swing.ButtonGroup; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JCheckBox; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JRadioButton; import javax.swing.JScrollPane; import javax.swing.JTextArea; import javax.swing.JTextField; import javax.swing.border.Border; public class GUIFrame extends JFrame{ public GUIFrame() { setSize(500,380); JPanel northPanel = new JPanel(); add(northPanel,BorderLayout.NORTH); //northPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1,4)); JLabel nameLabel = new JLabel("姓名:",JLabel.RIGHT); JTextField nameText = new JTextField(8); JLabel adressLabel = new JLabel("地址:",JLabel.RIGHT); JTextField adressText = new JTextField(15); northPanel.add(nameLabel); northPanel.add(nameText); northPanel.add(adressLabel); northPanel.add(adressText); JPanel centerPanel = new JPanel(); centerPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,1)); add(centerPanel,BorderLayout.CENTER); JPanel blankPanel = new JPanel(); centerPanel.add(blankPanel); JPanel choosePanel = new JPanel(); choosePanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); centerPanel.add(choosePanel); choosePanel.setSize(100,100); JPanel sexPanel = new JPanel(); choosePanel.add(sexPanel); Border etched = BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder(); Border titled1 = BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(etched,"性别"); sexPanel.setBorder(titled1); ButtonGroup sexGroup = new ButtonGroup(); JRadioButton manButton = new JRadioButton("男",true); sexGroup.add(manButton); JRadioButton womenButton = new JRadioButton("女",false); sexGroup.add(womenButton); sexPanel.add(manButton); sexPanel.add(womenButton); JPanel hobbyPanel = new JPanel(); choosePanel.add(hobbyPanel); Border titled2 = BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(etched,"爱好"); hobbyPanel.setBorder(titled2); JCheckBox read = new JCheckBox("阅读"); JCheckBox sing = new JCheckBox("唱歌"); JCheckBox dance = new JCheckBox("跳舞"); hobbyPanel.add(read); hobbyPanel.add(sing); hobbyPanel.add(dance); JPanel ButtonPanel = new JPanel(); centerPanel.add(ButtonPanel); JButton submit = new JButton("提交"); JButton reset = new JButton("重置"); ButtonPanel.add(submit); ButtonPanel.add(reset); JTextArea southText = new JTextArea("录入信息显示区!",6,10); JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(southText); //滚动 southText.setLineWrap(true); add(scrollPane,BorderLayout.SOUTH); submit.addActionListener(event->{ String hobby=""; if(read.isSelected()) hobby=hobby+"阅读 "; if(sing.isSelected()) hobby=hobby+"唱歌 "; if(dance.isSelected()) hobby=hobby+"跳舞 "; String sex=""; if(manButton.isSelected()) sex="男"; else sex="女"; if(southText.getText().equals("录入信息显示区!")) southText.setText(""); southText.append("姓名:"+nameText.getText()+" 地址:"+adressText.getText()+" 性别:"+sex+" 爱好:"+hobby+"\n"); }); reset.addActionListener(event->{ southText.setText(""); nameText.setText(""); adressText.setText(""); }); } }
运行截图如下:
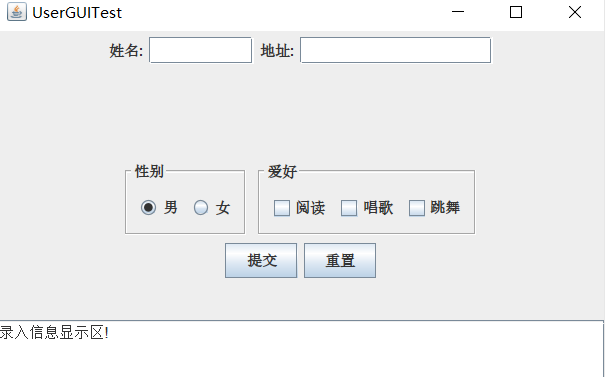
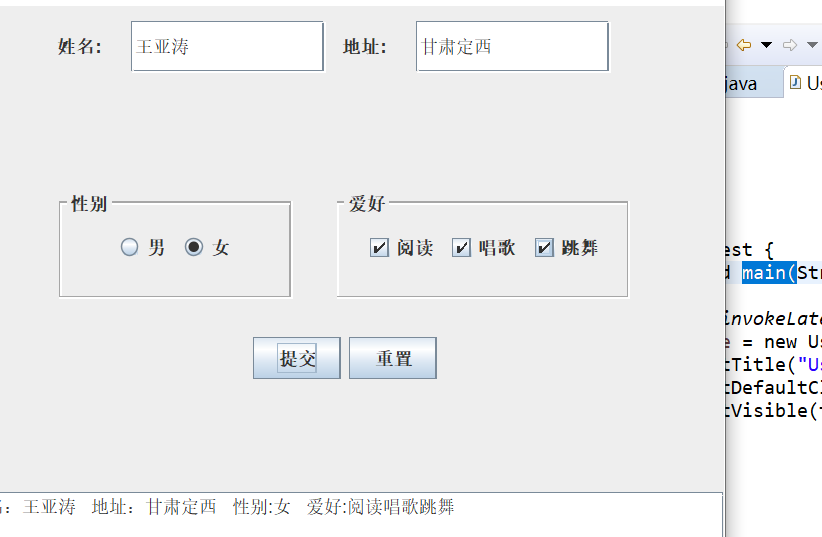
图片如下:

实验总结:(20分)
1):通过本次课程的学习让我们对Java中第十二章相关内容有了初步的了解;在上课老师的讲解过程中学习了Java中的布局管理及几种布局和各种组件等相关知识。掌握GUI布局管理器用法;掌握Java Swing文本输入组件的用途及常用API和Java Swing选择输入组件的用途及常用API等。
2):通过老师上课详细的讲解和实验过程中助教的讲解我们对第十二章的知识点有了进一步的强化认识,在做作业的过程中遇到了一些问题,但都通过问同学一一解决了,在讨论的过程中了解了自己的不足,掌握了许多不知道不熟悉的知识,对布局管理器,文本输入,选择组件的相关知识进一步的理解与掌握。
3).通过这次的实验使我学到了不少实用的知识,并且锻炼了自己的动手能力;虽然在学习的过程中遇到了许多不懂得地方,但是通过问同学及查找相关资料都一一解决了;在这次实验中意识到自己的动手能力很差,应在课下多学习多交流,相信在以后的学习中,通过不断努力,我可以学到更多的关于Java编程的相关知识。




