2020_1课程设计—基于BC的证书格式转换工具的设计与实现—个人报告
个人贡献
1. 基础贡献
- 收集相关资料,学习证书格式的相关知识
- 收集相关资料,学习OpenSSL的使用方法
- 安装OpenSSL
- 使用OpenSSL命令行查看证书,并实现证书格式转换
- 收集相关资料,学习BouncyCastle的使用方法
2. 组织协调组内工作
3. 证书转换代码的编写
①主要思路
- 代码主要分为三个模块:
- 从读取各种证书文件到
X509Certificate对象 - 将
X509Certificate对象写入到各种证书文件中 - 写出主类,将前两部分拼接起来
- 从读取各种证书文件到
②UML图
- 整体
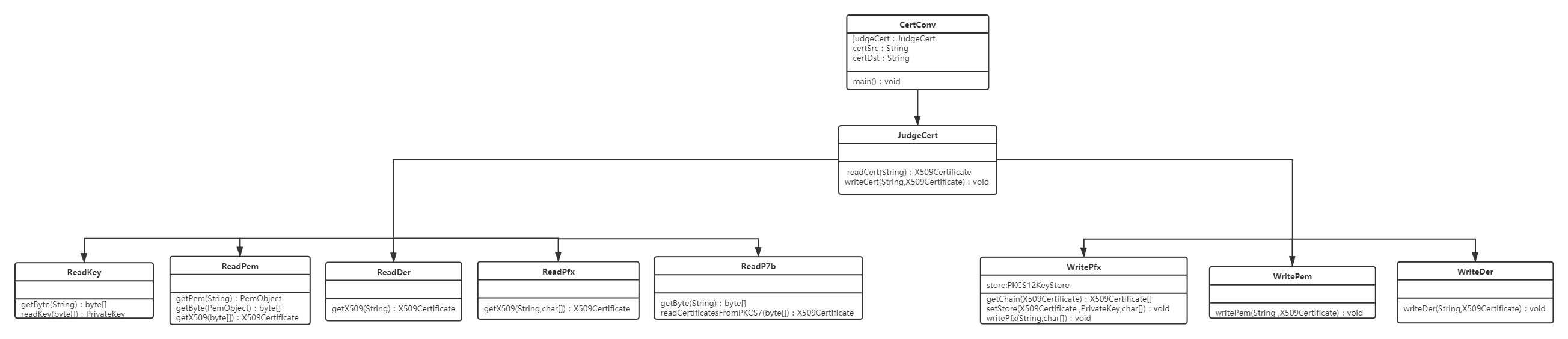
- 上半部分(前面好像看不清)

- 左半部分
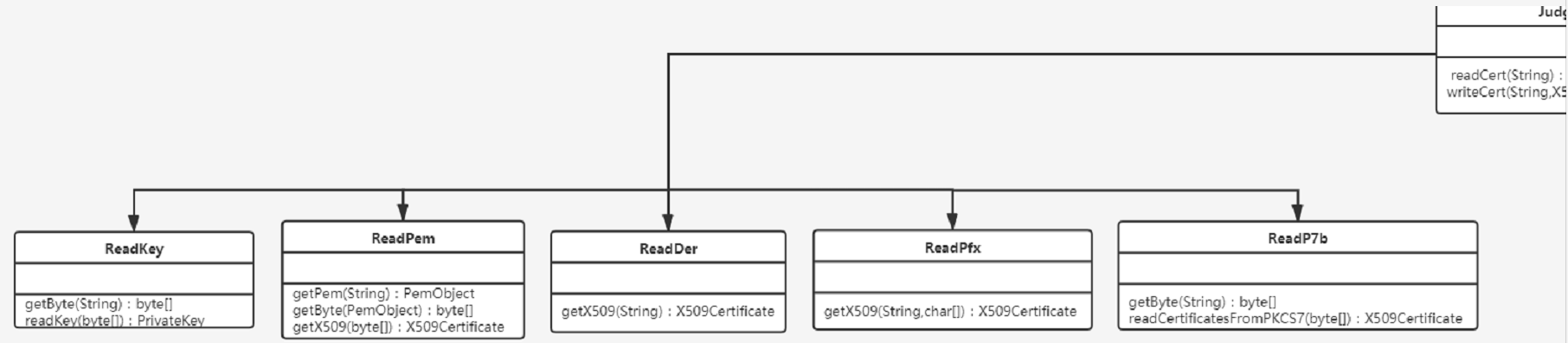
- 右半部分

③每个类的描述
CertConv
- 主类
- 输入证书类型
- 并通过
JudgeCert对象判断转换的类型,以进行下一步的操作
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CertConv {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
JudgeCert judgeCert = new JudgeCert();
System.out.println("请输入源证书格式:");
Scanner scanner1 = new Scanner(System.in);
String certSrc = scanner1.nextLine();
X509Certificate certificate = judgeCert.readCert(certSrc);
System.out.println("请输入目标证书格式:");
Scanner scanner2 = new Scanner(System.in);
String certDst = scanner2.nextLine();
judgeCert.writeCert(certDst,certificate);
}
}
JudgeCert
-
方法
readCert():判断源证书格式,并调用ReadXXX类,将其转换为X509Certificate对象 -
方法
writeCert():判断源证书格式,并调用WriteXXX类,将X509Certificate对象转换为目标格式证书
import org.bouncycastle.util.io.pem.PemObject;
import read.*;
import wirte.WriteDer;
import wirte.WritePem;
import wirte.WritePfx;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.security.KeyStoreException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import java.security.spec.InvalidKeySpecException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JudgeCert {
public X509Certificate readCert(String certSrc) throws Exception {
System.out.println("请输入源证书地址(形如:C:\\Users\\Administrator\\ca.cer):");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String pathSrc = scanner.nextLine();
String s = pathSrc.substring(pathSrc.length() - 3);
X509Certificate certificate = null;
if (certSrc.toLowerCase().equals("pem")) {
if (!((s.equals("pem"))||(s.equals("crt"))||(s.equals("cer")))){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
ReadPem readPem = new ReadPem();
PemObject pemObject = readPem.getPem(pathSrc);
byte[] b = readPem.getByte(pemObject);
certificate = readPem.getX509(b);
}
else if (certSrc.toLowerCase().equals("pfx")) {
if (!(s.equals("pfx")||s.equals("p12"))){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
Scanner scanner1 = new Scanner(System.in);
char[] passwd = scanner1.nextLine().toCharArray();
ReadPfx readPfx = new ReadPfx();
certificate = readPfx.getX509(pathSrc,passwd);
}
else if (certSrc.toLowerCase().equals("der")) {
if (!(s.equals("der"))){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
ReadDer reader = new ReadDer();
certificate = reader.getX509(pathSrc);
}
else if (certSrc.toLowerCase().equals("p7b")) {
if (!(s.equals("p7b")||s.equals("p7c"))){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
ReadP7b readP7b = new ReadP7b();
byte[] b = readP7b.getByte(pathSrc);
certificate = readP7b.readCertificatesFromPKCS7(b);
}
else {
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
return certificate;
}
public void writeCert(String certDst,X509Certificate certificate) throws IOException, CertificateException, InvalidKeySpecException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, KeyStoreException {
System.out.println("请输入目标证书地址(形如:C:\\Users\\Administrator\\ca.cer):");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String pathDst = scanner.nextLine();
String s = pathDst.substring(pathDst.length() - 3);
if (certDst.toLowerCase().equals("pem")) {
if (!((s.equals("pem"))||(s.equals("crt"))||(s.equals("cer")))){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
WritePem writePem = new WritePem();
writePem.writePem(pathDst,certificate);
}
else if (certDst.toLowerCase().equals("pfx")) {
if (!(s.equals("pfx")||s.equals("p12"))){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
Scanner scanner1 = new Scanner(System.in);
char[] passwd = scanner1.nextLine().toCharArray();
System.out.println("请输入您的私钥位置(形如:C:\\Users\\Administrator\\ca.cer):");
Scanner scanner2 = new Scanner(System.in);
String pathKey = scanner2.nextLine();
String s1 = pathKey.substring(pathKey.length() - 3);
if (!(s1.equals("pem"))){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
ReadKey readKey = new ReadKey();
byte[] b = readKey.getByte(pathKey);
PrivateKey privateKey = readKey.readKey(b);
WritePfx writePfx = new WritePfx();
writePfx.setStore(certificate,privateKey,passwd);
writePfx.writePfx(pathDst,passwd);
}
else if (certDst.toLowerCase().equals("der")) {
if (!(s.equals("der"))){
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
WriteDer writeDer = new WriteDer();
writeDer.writeDer(pathDst,certificate);
}
else {
System.out.println("输入错误!");
System.exit(-1);
}
}
}
ReadXXX——以ReadPem为例
- 使用BouncyCastle的
PemReader类,从PEM格式的证书中读取PemObject对象,并将其转化为X509Certificate证书对象
package read;
import org.bouncycastle.jce.provider.BouncyCastleProvider;
import org.bouncycastle.util.io.pem.PemObject;
import org.bouncycastle.util.io.pem.PemReader;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.security.Security;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.security.cert.CertificateFactory;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
public class ReadPem {
public PemObject getPem(String path) throws IOException {
Security.addProvider( new BouncyCastleProvider() );
PemReader reader = new PemReader( new FileReader( path ) );
Object pemObject = reader.readPemObject();
PemObject p = (PemObject)pemObject;
return p;
}
public byte[] getByte(PemObject p){
return p.getContent();
}
public X509Certificate getX509(byte[] b) throws CertificateException {
return (X509Certificate) CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509").generateCertificate(new ByteArrayInputStream(b));
}
}
WriteXXX——以WritePem为例
- 将
X509Certificate证书对象使用Base64进行编码,之后使用BouncyCastle的PemWriter类生成PEM证书
package wirte;
import org.bouncycastle.util.io.pem.PemObject;
import org.bouncycastle.util.io.pem.PemWriter;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.security.cert.CertificateEncodingException;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
public class WritePem {
public void writePem(String path,X509Certificate certificate) throws CertificateEncodingException, IOException {
PemObject pemObject = new PemObject("CERTIFICATE", certificate.getEncoded());
StringWriter str = new StringWriter();
PemWriter pemWriter = new PemWriter(str);
pemWriter.writeObject(pemObject);
pemWriter.close();
str.close();
FileOutputStream certOut = new FileOutputStream(path);
certOut.write(str.toString().getBytes());
System.out.println("转换成功!");
}
}
4. 前端代码优化
①添加输出证书的名字自定义
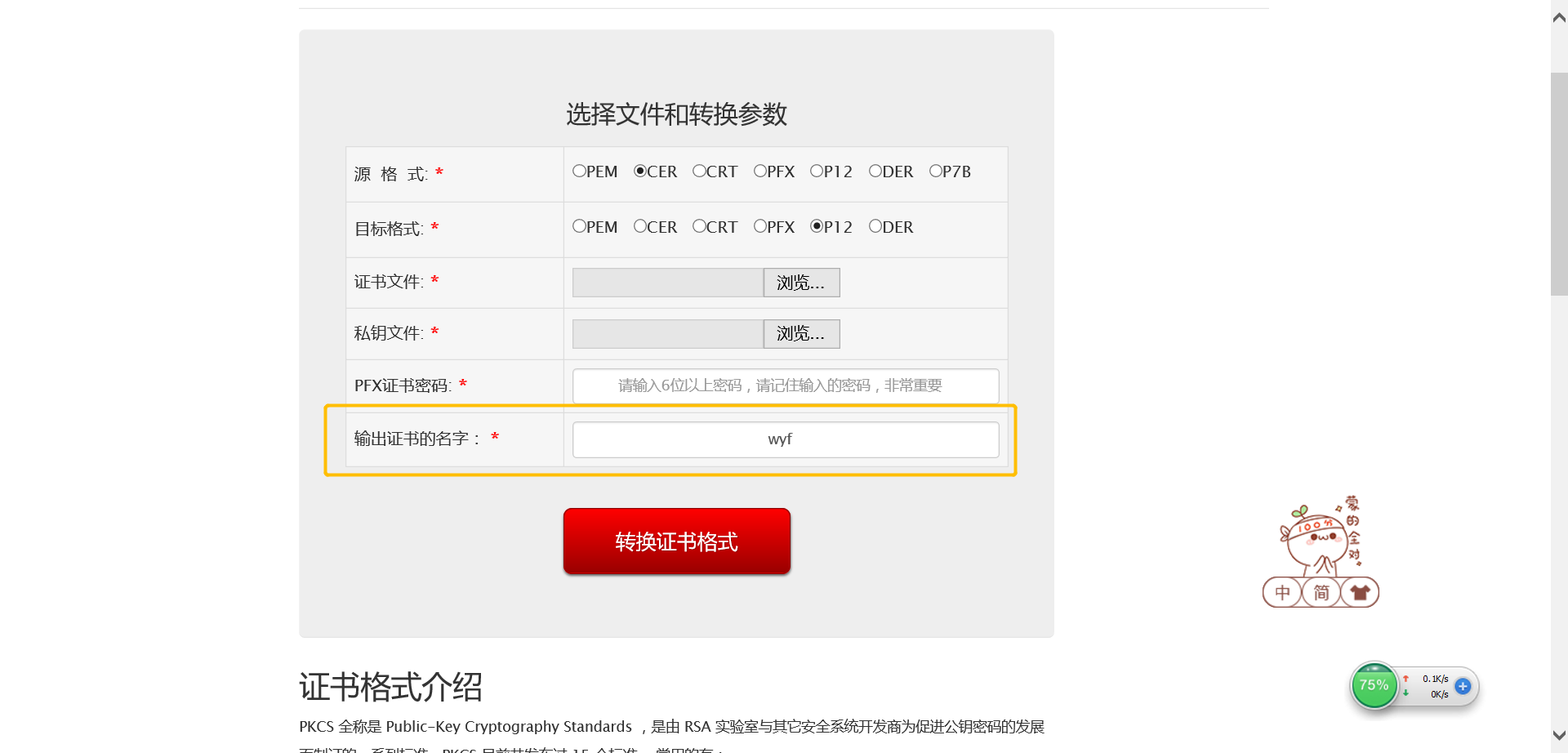
具体实现
- 前端添加输入文本框

- 后台serverlet将输入的名字与规定的路径、证书格式拼接成输出路径
②添加多种输入输出证书格式
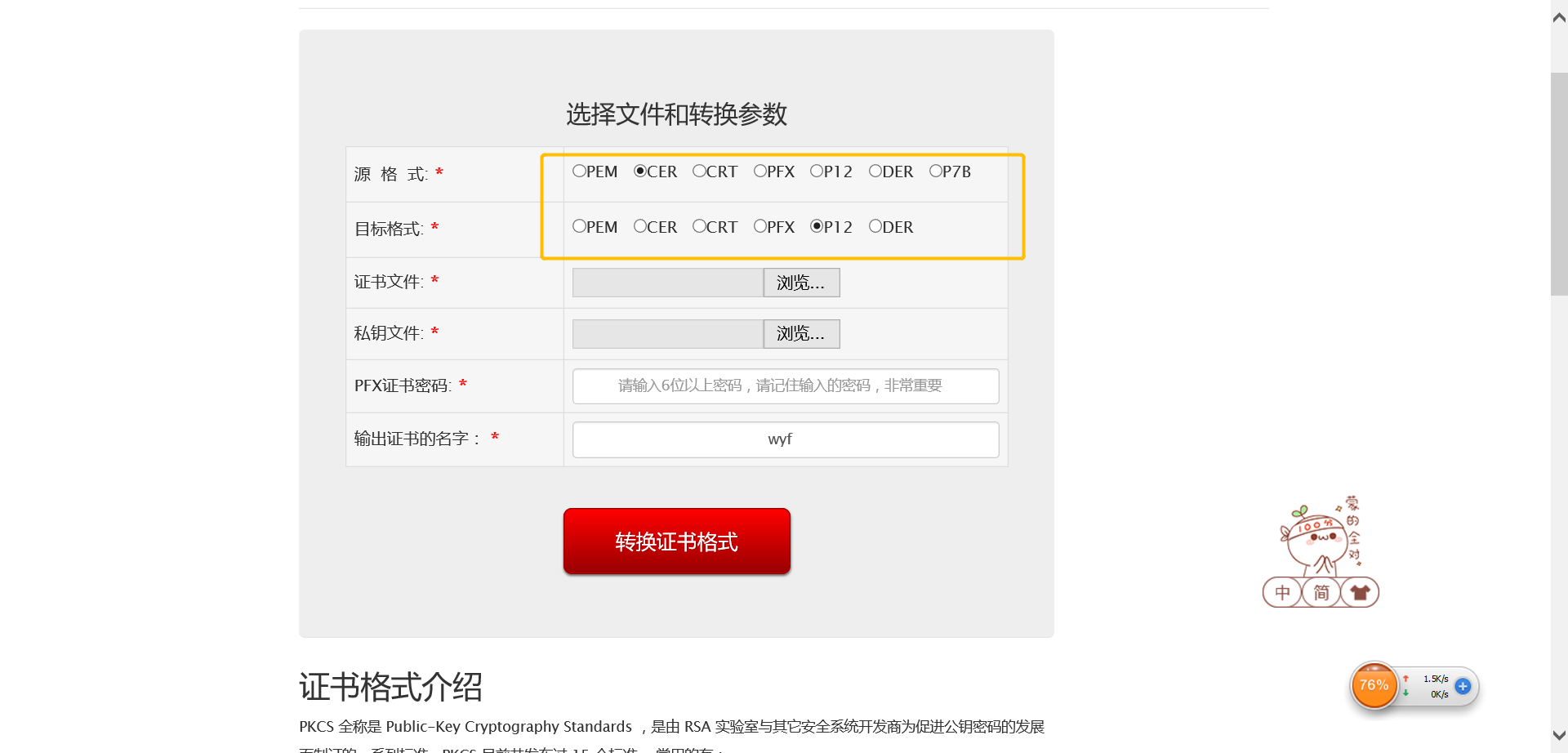
具体实现
- 前端增加证书单选框选项
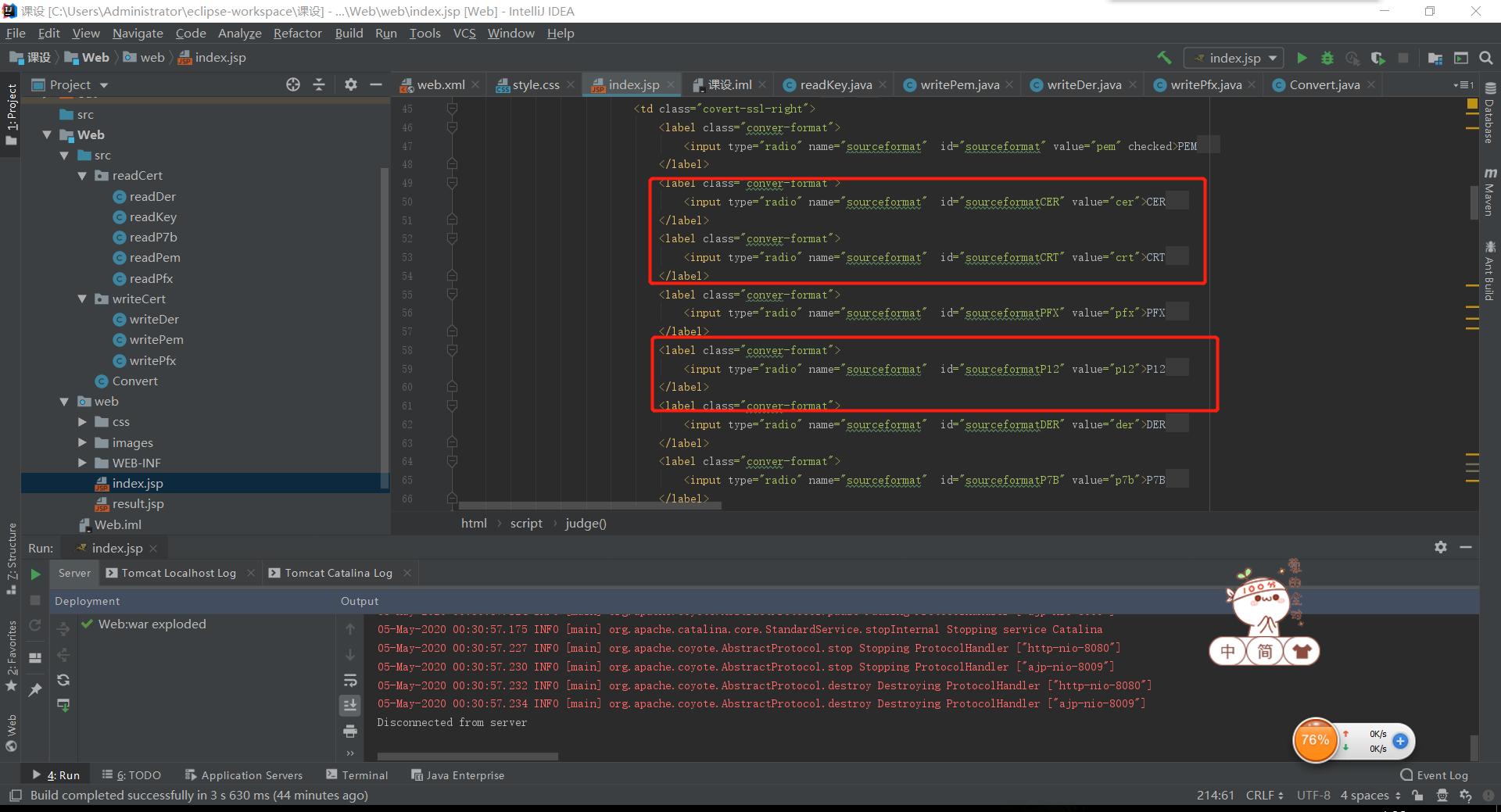
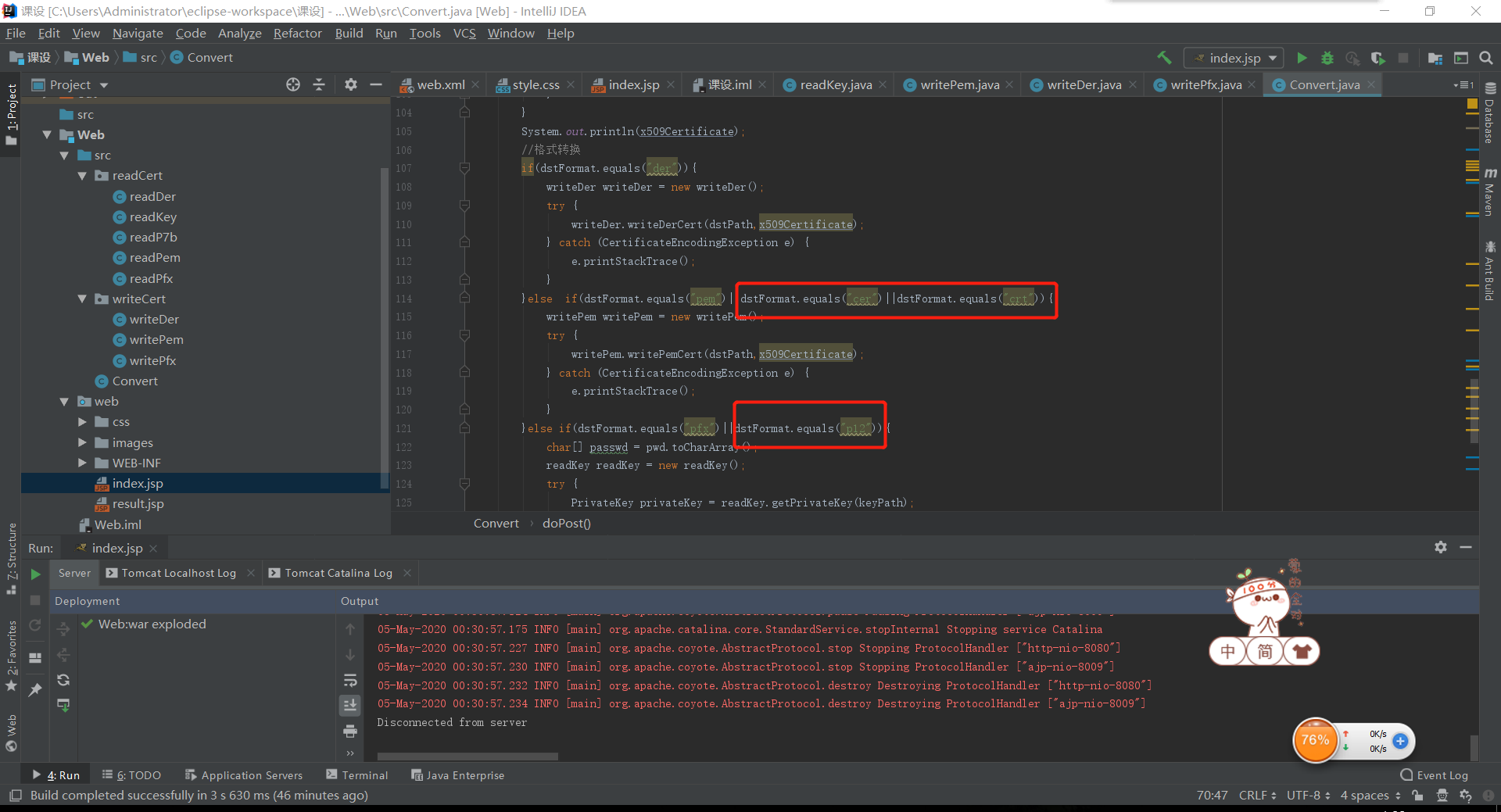
- 后台serverlet增加对这些证书格式的判断,将其使用对应的方法实现转换
5. 组内报告编写、汇总
设计中遇到的问题及解决方法
问题1:在开始使用BC对证书格式进行转化的时候没有头绪,网上有关BC实现证书转换的资料很少很少(就是没有)
解决1:在大量查阅有关BC编程、java证书转换的资料、示例之后,发现证书转换主要就是如何将证书从各种格式的证书文件中读出来,然后再怎么把证书写入各种格式的证书文件中。按照这种思路,我查询到了更多有用的资料和方法,最终初步实现了证书格式转换
问题2:在初步实现证书格式转换功能后,我发现我是按某种格式证书到另一种格式的证书一个主类这样写的程序,是“面向过程”而不符合java的“面向对象”。而且程序很乱,有很多重复的地方
解决2:我按之前的思路将程序对象分为两块,一块是read:从文件读取证书、另一块是write:将证书写入文件,再写出主类将两部分拼接起来
问题3:在小伙伴按我的思路写好前端代码后我发现了其中的一些问题:输出证书的名字是固定的,用户没办法手动输入、证书格式缺少,比如缺少和pem格式转换方式相同的cer格式
解决3:添加了用户手动输入输出的证书名、添加了多种证书格式
调试过程中遇到的主要问题,并说明解决方法
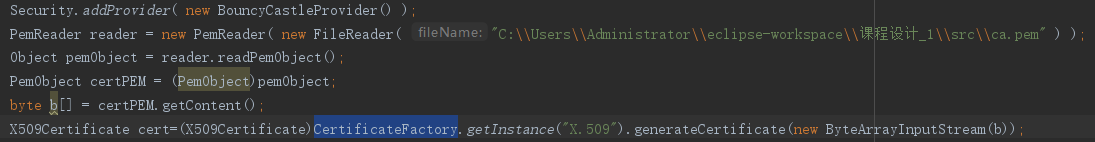
问题1:在提取PEM文件到X509Certificate对象的过程中,尝试直接强转,报错

解决1:先生成PemObject对象,提取字节数组,并使用CertificateFactory进行转换
问题2:加载PKCS12KeyStore对象时,发现缺少私钥
解决2:PEM文件中没有私钥,需要读入生成证书时保存的私钥文件中的私钥
问题3:在读取DER文件时,刚开始直接进行读取,在转为字节数组,出现转换错误的问题
解决3:使用ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream类读取字节数组
问题4:在添加证书格式时,先考虑的使用js代码进行格式判断,但达不到预期效果,出现警告框
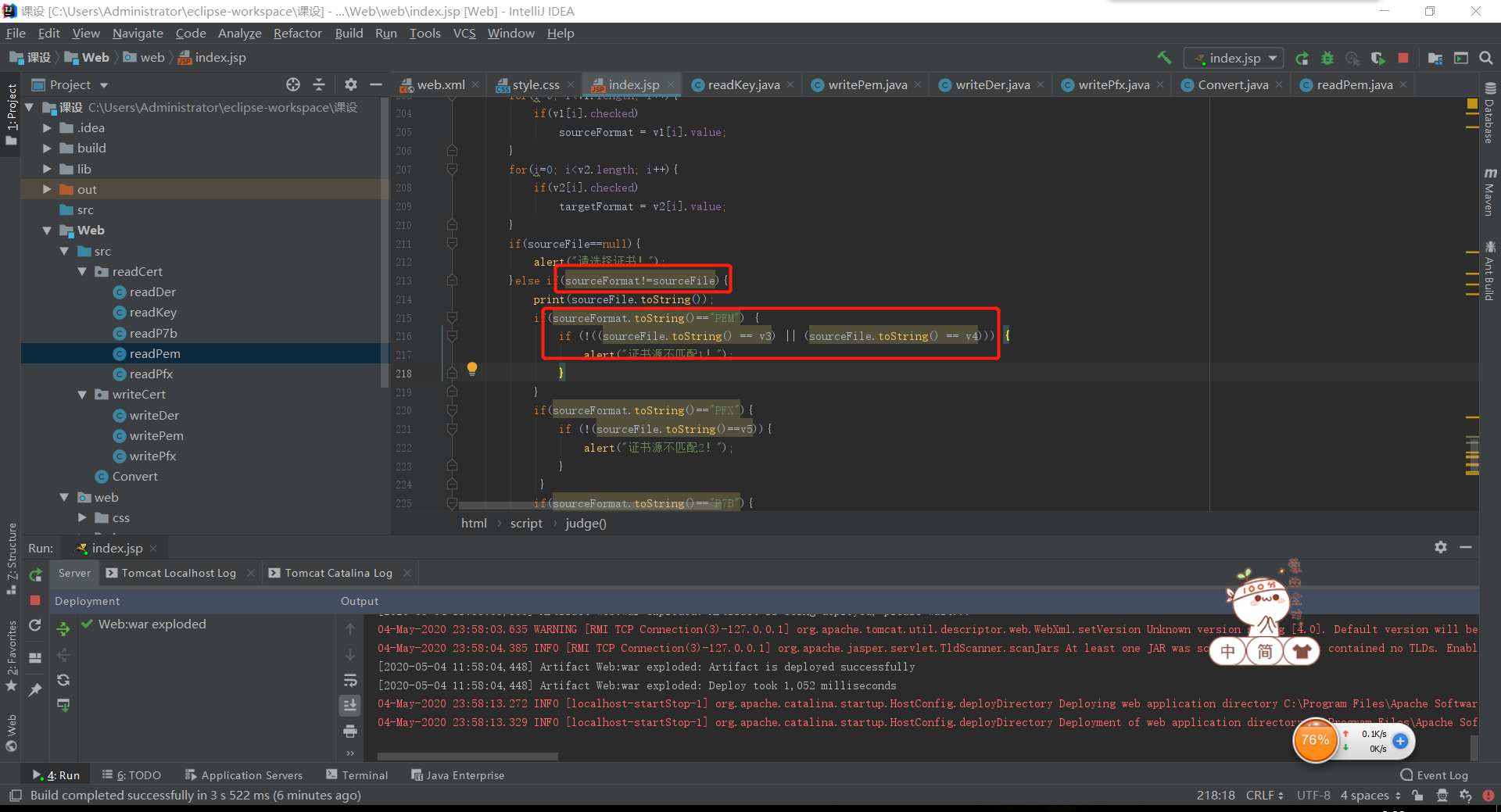
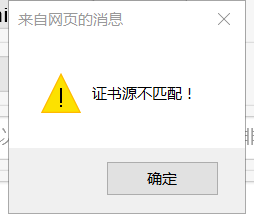
解决4:不再分大类判断了,直接将所有证书格式列为输入

问题5:单选框出现复选的情况
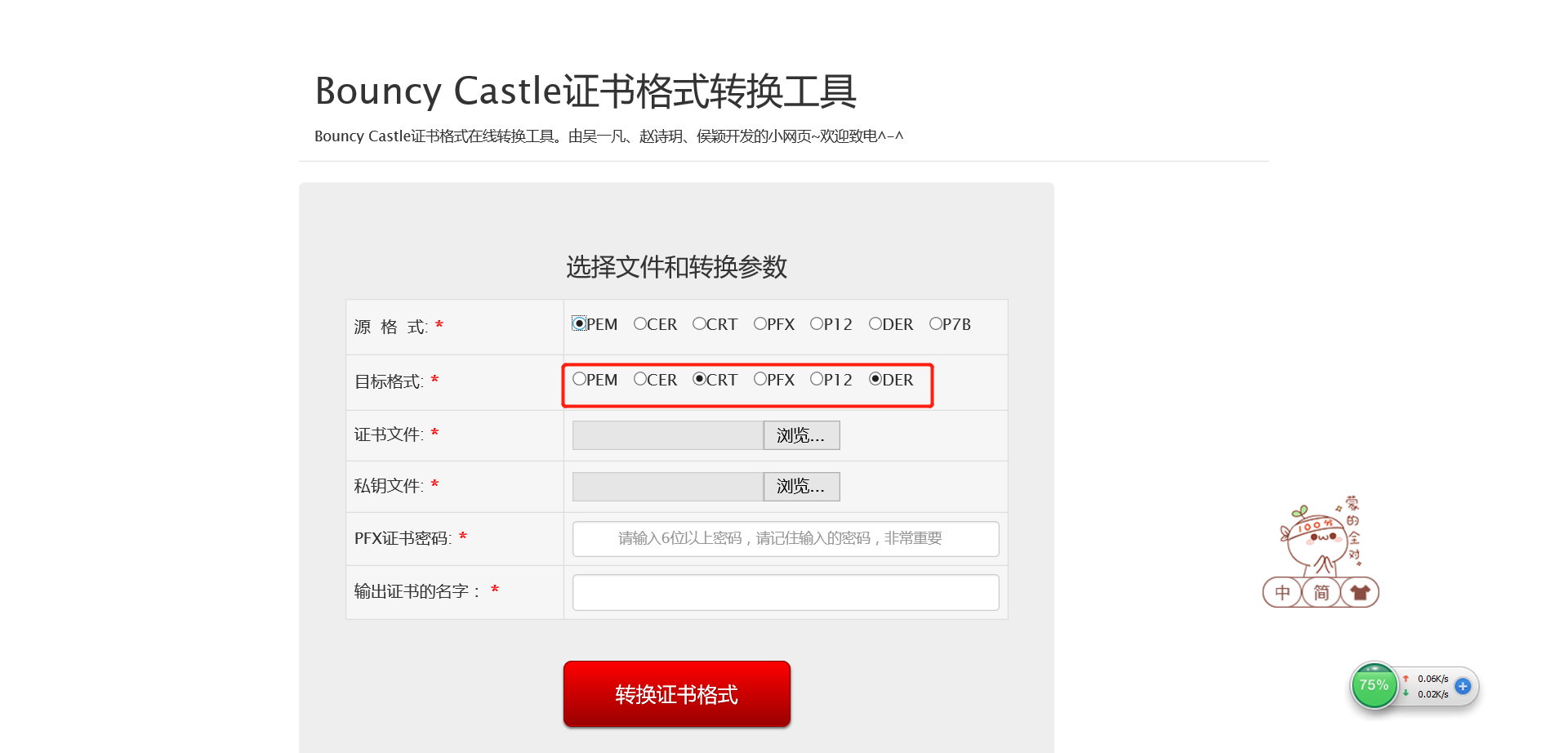
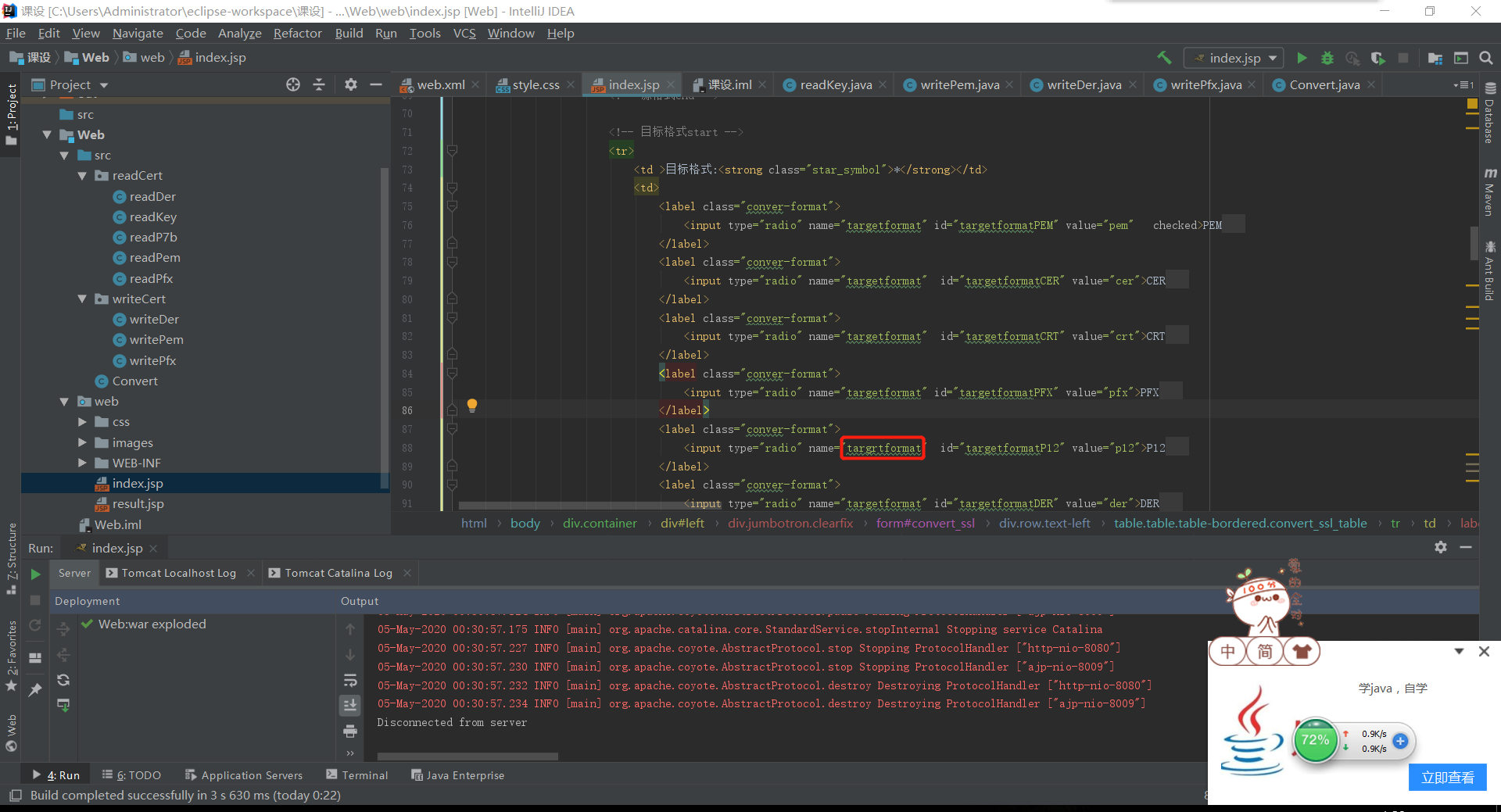
解决5:发现是有个name属性名字填错了
设计体会与收获
-
在开始的时候是真的没有思路,查了各种资料都跟题目没什么关系,但重要的还是没有放弃吧,经过大量的查阅后潜移默化的也会对题目有更深入的理解,突然有了新的思路、新的方向以后,就豁然开朗了很多,编程问题当然也就迎刃而解了
-
在编程的过程中也遇到了许许多多许许多多的问题,当然这次我学到了一点,就是其实有的时候有很多路,如果一条路走不通,可以尝试着换一种方法试试,有时候可能会有意想不到的收获
码云链接
参考资料
- 证书格式转换
- Bouncy Castle配置
- x509和pkcs12以及pkcs7的关系和区别
- 如何在Java中以编程方式读取p7b文件
- SSL证书格式转换工具
- base编码证书转化为der证书/源码/工具
- 如何验证Java中的PEM格式证书
- java利用bouncycastle生成国密x509证书并将证书以pem格式存入文件
- BouncyCastle产生一个PKCS#12规范的PFX/p12证书
- 如何使用来自Java PKCS#12密钥库的证书加密和解密文件
还有许许多多查阅到的对我有用的资料就不列举了
这里只列举我认为对我研究最有用的资料




