python—sift特征提取
2020-03-08 15:16 工班 阅读(4240) 评论(2) 编辑 收藏 举报一、SIFT提出的目的和意义
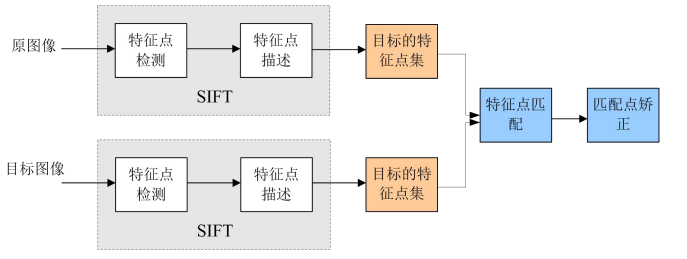
二、SIFT的特征简介
三、SIFT算法实现步骤简述
四、图像集
五、匹配地理标记图像
六、SIFT算法代码实现
- 代码
- 结果截图
- 小结
七、SIFT实验总结
八、实验遇到的问题
一、SIFT提出的目的和意义
1999年David G.Lowe教授总结了基于特征不变技术的检测方法,在图像尺度空间基础上,提出了对图像缩放、旋转保持不变性的图像局部特征描述算子-SIFT(尺度不变特征变换),该算法在2004年被加以完善。
- 目标的旋转、缩放、平移(RST)
- 图像仿射/投影变换(视点viewpoint)
- 弱光照影响(illumination)
- 部分目标遮挡(occlusion)
- 杂物场景(clutter)
- 噪声
操作步骤:
1.把vlfeat文件夹下win64中的sift.exe和vl.dll这两个文件复制到项目的文件夹中
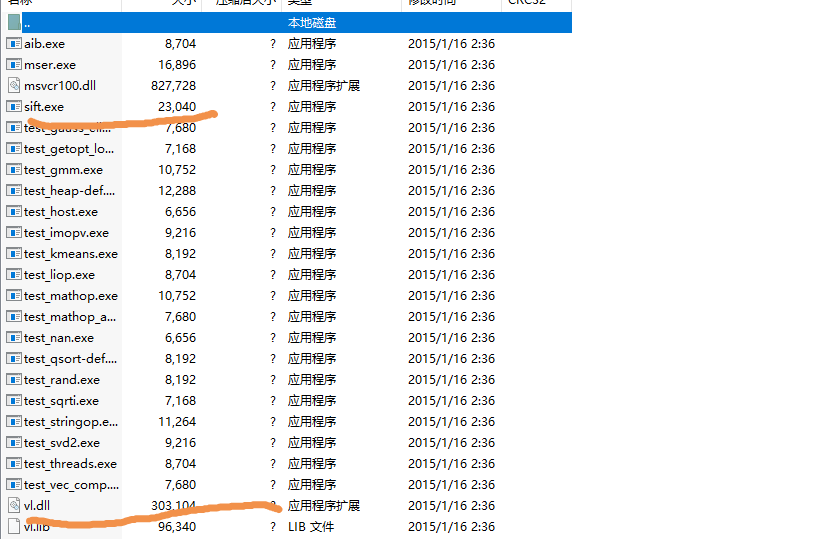
2.修改PCV文件夹内的(我的PCV位置为D:\Anaconda2\Lib\site-packages\PCV))文件夹里面的localdescriptors文件夹中的sift.py文件,用记事本打开,修改其中的cmmd内的路径cmmd=str(r"D:\new\sift.exe“+imagename+” --output="+resultname+" "+params) (路径是你项目文件夹中的sift.exe的路径)一定要在括号里加上r。

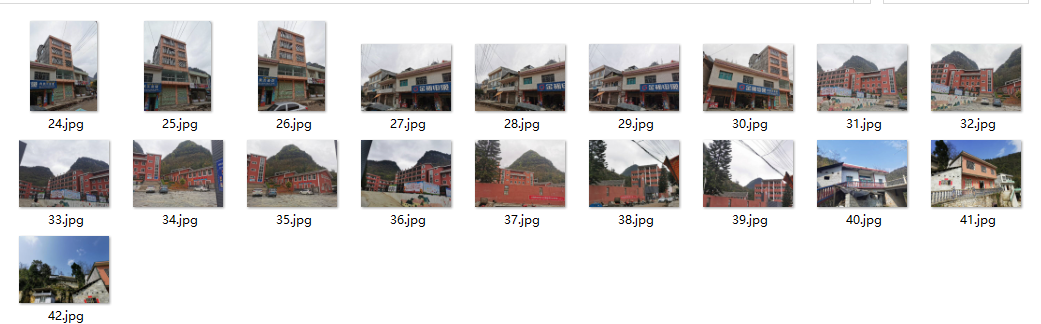
图2
五、匹配地理标记图像
1、做此实验我们需用pydot工具包中的GraphViz,可以点击https://graphviz.gitlab.io/_pages/Download/Download_windows.html下载安装包,安装步骤如下:
配置环境: 保存graphviz安装时,一定要记住保存路径,方便找到你的安装包安装中的gvedit.exe的位置,我的是C:\Program Files (x86)\Graphviz2.38\bin
把gvedit.exe发送到桌面快捷方式,然后去系统里点击高级系统设置->点击环境变量->点击系统变量的path选择编辑->输入C:\Program Files (x86)\Graphviz2.38\bin,之后就确定保存。
接下来是验证环境配置是否成功,输入dot -version命令,成功如下:
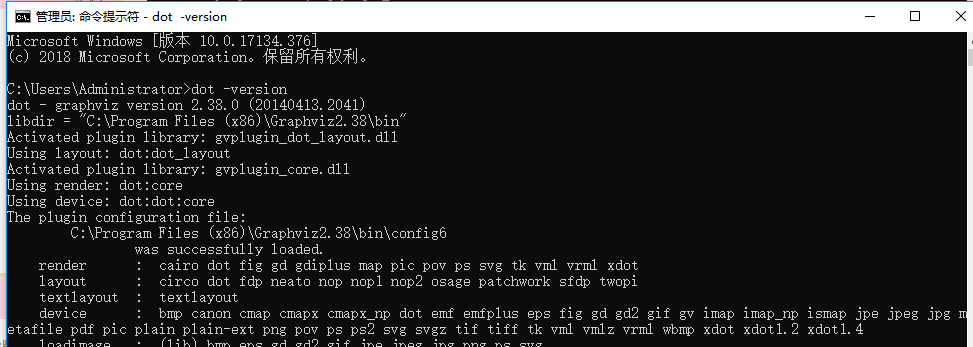
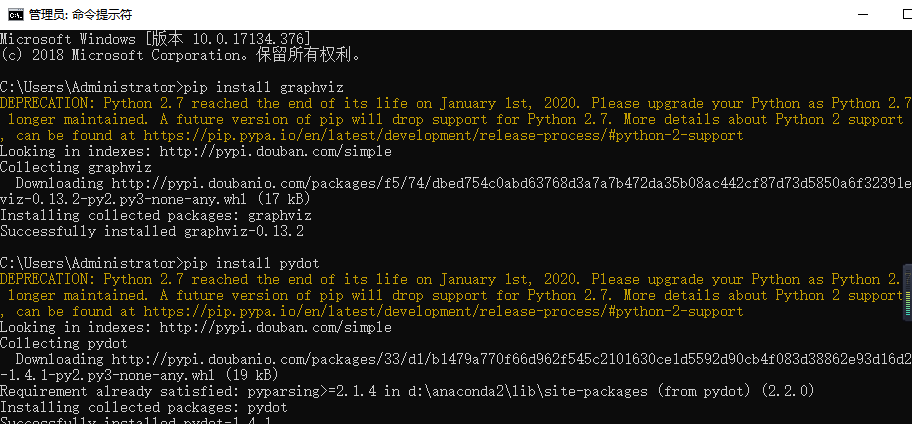
然后依次执行以下命令:
pip install graphviz
pip install pydot
成功如下:
 d
d
2、实验代码:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 from pylab import * 3 from PIL import Image 4 from PCV.localdescriptors import sift 5 from PCV.tools import imtools 6 import pydot 7 8 """ This is the example graph illustration of matching images from Figure 2-10. 9 To download the images, see ch2_download_panoramio.py.""" 10 11 #download_path = "panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images 12 #path = "/FULLPATH/panoimages/" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path) 13 14 #download_path = "F:\\dropbox\\Dropbox\\translation\\pcv-notebook\\data\\panoimages" # set this to the path where you downloaded the panoramio images 15 #path = "F:\\dropbox\\Dropbox\\translation\\pcv-notebook\\data\\panoimages\\" # path to save thumbnails (pydot needs the full system path) 16 download_path = "D:/new" 17 path = "D:/new" 18 # list of downloaded filenames 19 imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path) 20 nbr_images = len(imlist) 21 22 # extract features 23 featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist] 24 for i, imname in enumerate(imlist): 25 sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i]) 26 27 matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images)) 28 29 for i in range(nbr_images): 30 for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle 31 print 'comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j] 32 l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i]) 33 l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j]) 34 matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2) 35 nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0) 36 print 'number of matches = ', nbr_matches 37 matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches 38 print "The match scores is: %d", matchscores 39 40 #np.savetxt(("../data/panoimages/panoramio_matches.txt",matchscores) 41 42 # copy values 43 for i in range(nbr_images): 44 for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal 45 matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j] 46 47 threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link 48 49 g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph 50 51 for i in range(nbr_images): 52 for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): 53 if matchscores[i, j] > threshold: 54 # first image in pair 55 im = Image.open(imlist[i]) 56 im.thumbnail((100, 100)) 57 filename = path + str(i) + '.png' 58 im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size 59 g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename)) 60 61 # second image in pair 62 im = Image.open(imlist[j]) 63 im.thumbnail((100, 100)) 64 filename = path + str(j) + '.png' 65 im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size 66 g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename)) 67 68 g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j))) 69 g.write_png('protect2.png')
3、结果截图:
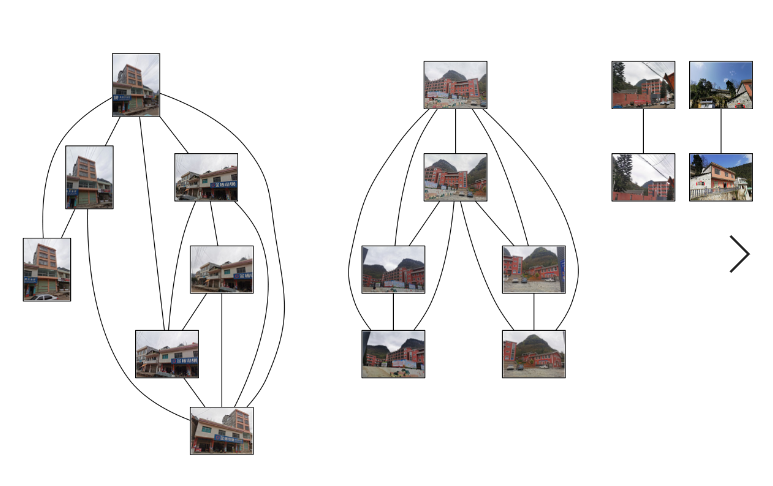
实验小结:图像集一共有十九张图片,运行出来只有十七张图片,我拍摄的照片范围过小,只选择了六个地点拍摄,没有显示出来的两张图片是跟以上图片没有太多相似的特征点的。显示出来的第一个连线的部分,是在同一个位置拍摄,只是从不同的角度,但是提取出来的特征点匹配度很高,说明了sift算法角度不变性,还有色彩影响不是很大,并且只要有一点特征点匹配度的图片就会相连起来,第二部分和第三部分依然如此。
代码:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 from PIL import Image 3 from pylab import * 4 from PCV.localdescriptors import sift 5 from PCV.localdescriptors import harris 6 7 # 添加中文字体支持 8 from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties 9 font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\SimSun.ttc", size=14) 10 11 imname = 'siftt/24.jpg' 12 im = array(Image.open(imname).convert('L')) 13 sift.process_image(imname, '24.sift') 14 l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('24.sift') 15 16 figure() 17 gray() 18 subplot(131) 19 sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=False) 20 title(u'SIFT特征',fontproperties=font) 21 subplot(132) 22 sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=True) 23 title(u'用圆圈表示SIFT特征尺度',fontproperties=font) 24 25 # 检测harris角点 26 harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im) 27 28 subplot(133) 29 filtered_coords = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, 6, 0.1) 30 imshow(im) 31 plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*') 32 axis('off') 33 title(u'Harris角点',fontproperties=font) 34 35 show()
原图

运行结果:
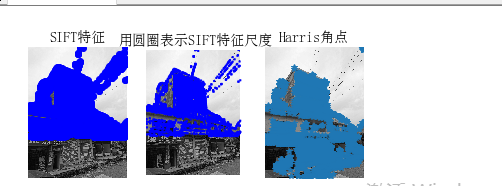
小结:由图看出,sift算法检测出来的特征点比harris角点算法检测出的角点多。sift算法测出来的特征点大多数都是重合的。
2、图像集里的所有图像的sift特征提取
代码:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 from PIL import Image 3 from pylab import * 4 from PCV.localdescriptors import sift 5 from PCV.localdescriptors import harris 6 from PCV.tools.imtools import get_imlist # 导入原书的PCV模块 7 8 # 添加中文字体支持 9 from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties 10 font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\SimSun.ttc", size=14) 11 12 # 获取project2_data文件夹下的图片文件名(包括后缀名) 13 filelist = get_imlist('siftt/') 14 15 for infile in filelist: # 对文件夹下的每张图片进行如下操作 16 print(infile) # 输出文件名 17 18 im = array(Image.open(infile).convert('L')) 19 sift.process_image(infile, 'infile.sift') 20 l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('infile.sift') 21 i=1 22 23 figure(i) 24 i=i+1 25 gray() 26 27 subplot(131) 28 sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=False) 29 title(u'SIFT特征',fontproperties=font) 30 31 subplot(132) 32 sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=True) 33 title(u'用圆圈表示SIFT特征尺度',fontproperties=font) 34 35 # 检测harris角点 36 harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im) 37 38 subplot(133) 39 filtered_coords = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, 6, 0.1) 40 imshow(im) 41 plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*') 42 axis('off') 43 title(u'Harris角点',fontproperties=font) 44 45 show()
结果截图:

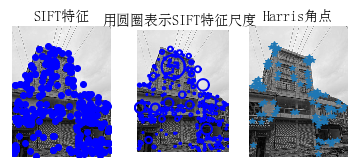









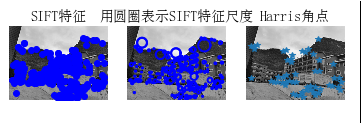


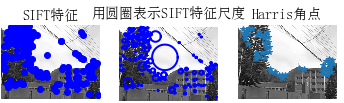



3、两张图片,计算sift特征匹配结果
代码:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 from PIL import Image 3 from pylab import * 4 from numpy import * 5 import os 6 7 def process_image(imagename, resultname, params="--edge-thresh 10 --peak-thresh 5"): 8 """ 处理一幅图像,然后将结果保存在文件中""" 9 if imagename[-3:] != 'pgm': 10 #创建一个pgm文件 11 im = Image.open(imagename).convert('L') 12 im.save('tmp.pgm') 13 imagename ='tmp.pgm' 14 cmmd = str("sift "+imagename+" --output="+resultname+" "+params) 15 os.system(cmmd) 16 print 'processed', imagename, 'to', resultname 17 18 def read_features_from_file(filename): 19 """读取特征属性值,然后将其以矩阵的形式返回""" 20 f = loadtxt(filename) 21 return f[:,:4], f[:,4:] #特征位置,描述子 22 23 def write_featrues_to_file(filename, locs, desc): 24 """将特征位置和描述子保存到文件中""" 25 savetxt(filename, hstack((locs,desc))) 26 27 def plot_features(im, locs, circle=False): 28 """显示带有特征的图像 29 输入:im(数组图像),locs(每个特征的行、列、尺度和朝向)""" 30 31 def draw_circle(c,r): 32 t = arange(0,1.01,.01)*2*pi 33 x = r*cos(t) + c[0] 34 y = r*sin(t) + c[1] 35 plot(x, y, 'b', linewidth=2) 36 37 imshow(im) 38 if circle: 39 for p in locs: 40 draw_circle(p[:2], p[2]) 41 else: 42 plot(locs[:,0], locs[:,1], 'ob') 43 axis('off') 44 45 def match(desc1, desc2): 46 """对于第一幅图像中的每个描述子,选取其在第二幅图像中的匹配 47 输入:desc1(第一幅图像中的描述子),desc2(第二幅图像中的描述子)""" 48 desc1 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc1]) 49 desc2 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc2]) 50 dist_ratio = 0.6 51 desc1_size = desc1.shape 52 matchscores = zeros((desc1_size[0],1),'int') 53 desc2t = desc2.T #预先计算矩阵转置 54 for i in range(desc1_size[0]): 55 dotprods = dot(desc1[i,:],desc2t) #向量点乘 56 dotprods = 0.9999*dotprods 57 # 反余弦和反排序,返回第二幅图像中特征的索引 58 indx = argsort(arccos(dotprods)) 59 #检查最近邻的角度是否小于dist_ratio乘以第二近邻的角度 60 if arccos(dotprods)[indx[0]] < dist_ratio * arccos(dotprods)[indx[1]]: 61 matchscores[i] = int(indx[0]) 62 return matchscores 63 64 def match_twosided(desc1, desc2): 65 """双向对称版本的match()""" 66 matches_12 = match(desc1, desc2) 67 matches_21 = match(desc2, desc1) 68 ndx_12 = matches_12.nonzero()[0] 69 # 去除不对称的匹配 70 for n in ndx_12: 71 if matches_21[int(matches_12[n])] != n: 72 matches_12[n] = 0 73 return matches_12 74 75 def appendimages(im1, im2): 76 """返回将两幅图像并排拼接成的一幅新图像""" 77 #选取具有最少行数的图像,然后填充足够的空行 78 rows1 = im1.shape[0] 79 rows2 = im2.shape[0] 80 if rows1 < rows2: 81 im1 = concatenate((im1, zeros((rows2-rows1,im1.shape[1]))),axis=0) 82 elif rows1 >rows2: 83 im2 = concatenate((im2, zeros((rows1-rows2,im2.shape[1]))),axis=0) 84 return concatenate((im1,im2), axis=1) 85 86 def plot_matches(im1,im2,locs1,locs2,matchscores,show_below=True): 87 """ 显示一幅带有连接匹配之间连线的图片 88 输入:im1, im2(数组图像), locs1,locs2(特征位置),matchscores(match()的输出), 89 show_below(如果图像应该显示在匹配的下方) 90 """ 91 im3=appendimages(im1, im2) 92 if show_below: 93 im3=vstack((im3, im3)) 94 imshow(im3) 95 cols1 = im1.shape[1] 96 for i in range(len(matchscores)): 97 if matchscores[i]>0: 98 plot([locs1[i,0],locs2[matchscores[i,0],0]+cols1], [locs1[i,1],locs2[matchscores[i,0],1]],'c') 99 axis('off') 100 101 im1f = 'siftt/25.jpg' 102 im2f = 'siftt/26.jpg' 103 104 im1 = array(Image.open(im1f)) 105 im2 = array(Image.open(im2f)) 106 107 process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt') 108 l1,d1 = read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt') 109 figure() 110 gray() 111 subplot(121) 112 plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False) 113 114 process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt') 115 l2,d2 = read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt') 116 subplot(122) 117 plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False) 118 119 matches = match_twosided(d1, d2) 120 print '{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0])) 121 122 figure() 123 gray() 124 plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True) 125 show()
结果截图:


小结:用siftt算法提取两张图的特征点,然后双向匹配两张图片的描述子,用线将两幅图相匹配的描述子相连,连的线越多,说明这两幅图的匹配度越高,两幅图越相似。
4、给定一张图片,输出匹配度最高的三张图片
代码:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 from PIL import Image 3 from pylab import * 4 from numpy import * 5 import os 6 from PCV.tools.imtools import get_imlist # 导入原书的PCV模块 7 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # plt 用于显示图片 8 import matplotlib.image as mpimg # mpimg 用于读取图片 9 10 def process_image(imagename, resultname, params="--edge-thresh 10 --peak-thresh 5"): 11 """ 处理一幅图像,然后将结果保存在文件中""" 12 if imagename[-3:] != 'pgm': 13 #创建一个pgm文件 14 im = Image.open(imagename).convert('L') 15 im.save('tmp.pgm') 16 imagename ='tmp.pgm' 17 cmmd = str("sift "+imagename+" --output="+resultname+" "+params) 18 os.system(cmmd) 19 print 'processed', imagename, 'to', resultname 20 21 def read_features_from_file(filename): 22 """读取特征属性值,然后将其以矩阵的形式返回""" 23 f = loadtxt(filename) 24 return f[:,:4], f[:,4:] #特征位置,描述子 25 26 def write_featrues_to_file(filename, locs, desc): 27 """将特征位置和描述子保存到文件中""" 28 savetxt(filename, hstack((locs,desc))) 29 30 def plot_features(im, locs, circle=False): 31 """显示带有特征的图像 32 输入:im(数组图像),locs(每个特征的行、列、尺度和朝向)""" 33 34 def draw_circle(c,r): 35 t = arange(0,1.01,.01)*2*pi 36 x = r*cos(t) + c[0] 37 y = r*sin(t) + c[1] 38 plot(x, y, 'b', linewidth=2) 39 40 imshow(im) 41 if circle: 42 for p in locs: 43 draw_circle(p[:2], p[2]) 44 else: 45 plot(locs[:,0], locs[:,1], 'ob') 46 axis('off') 47 48 def match(desc1, desc2): 49 """对于第一幅图像中的每个描述子,选取其在第二幅图像中的匹配 50 输入:desc1(第一幅图像中的描述子),desc2(第二幅图像中的描述子)""" 51 desc1 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc1]) 52 desc2 = array([d/linalg.norm(d) for d in desc2]) 53 dist_ratio = 0.6 54 desc1_size = desc1.shape 55 matchscores = zeros((desc1_size[0],1),'int') 56 desc2t = desc2.T #预先计算矩阵转置 57 for i in range(desc1_size[0]): 58 dotprods = dot(desc1[i,:],desc2t) #向量点乘 59 dotprods = 0.9999*dotprods 60 # 反余弦和反排序,返回第二幅图像中特征的索引 61 indx = argsort(arccos(dotprods)) 62 #检查最近邻的角度是否小于dist_ratio乘以第二近邻的角度 63 if arccos(dotprods)[indx[0]] < dist_ratio * arccos(dotprods)[indx[1]]: 64 matchscores[i] = int(indx[0]) 65 return matchscores 66 67 def match_twosided(desc1, desc2): 68 """双向对称版本的match()""" 69 matches_12 = match(desc1, desc2) 70 matches_21 = match(desc2, desc1) 71 ndx_12 = matches_12.nonzero()[0] 72 # 去除不对称的匹配 73 for n in ndx_12: 74 if matches_21[int(matches_12[n])] != n: 75 matches_12[n] = 0 76 return matches_12 77 78 def appendimages(im1, im2): 79 """返回将两幅图像并排拼接成的一幅新图像""" 80 #选取具有最少行数的图像,然后填充足够的空行 81 rows1 = im1.shape[0] 82 rows2 = im2.shape[0] 83 if rows1 < rows2: 84 im1 = concatenate((im1, zeros((rows2-rows1,im1.shape[1]))),axis=0) 85 elif rows1 >rows2: 86 im2 = concatenate((im2, zeros((rows1-rows2,im2.shape[1]))),axis=0) 87 return concatenate((im1,im2), axis=1) 88 89 def plot_matches(im1,im2,locs1,locs2,matchscores,show_below=True): 90 """ 显示一幅带有连接匹配之间连线的图片 91 输入:im1, im2(数组图像), locs1,locs2(特征位置),matchscores(match()的输出), 92 show_below(如果图像应该显示在匹配的下方) 93 """ 94 im3=appendimages(im1, im2) 95 if show_below: 96 im3=vstack((im3, im3)) 97 imshow(im3) 98 cols1 = im1.shape[1] 99 for i in range(len(matchscores)): 100 if matchscores[i]>0: 101 plot([locs1[i,0],locs2[matchscores[i,0],0]+cols1], [locs1[i,1],locs2[matchscores[i,0],1]],'c') 102 axis('off') 103 104 # 获取project2_data文件夹下的图片文件名(包括后缀名) 105 filelist = get_imlist('project2_data/') 106 107 # 输入的图片 108 im1f = '23.jpg' 109 im1 = array(Image.open(im1f)) 110 process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt') 111 l1, d1 = read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt') 112 113 i=0 114 num = [0]*30 #存放匹配值 115 for infile in filelist: # 对文件夹下的每张图片进行如下操作 116 im2 = array(Image.open(infile)) 117 process_image(infile, 'out_sift_2.txt') 118 l2, d2 = read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt') 119 matches = match_twosided(d1, d2) 120 num[i] = len(matches.nonzero()[0]) 121 i=i+1 122 print '{} matches'.format(num[i-1]) #输出匹配值 123 124 i=1 125 figure() 126 while i<4: #循环三次,输出匹配最多的三张图片 127 index=num.index(max(num)) 128 print index, filelist[index] 129 lena = mpimg.imread(filelist[index]) # 读取当前匹配最大值的图片 130 # 此时 lena 就已经是一个 np.array 了,可以对它进行任意处理 131 # lena.shape # (512, 512, 3) 132 subplot(1,3,i) 133 plt.imshow(lena) # 显示图片 134 plt.axis('off') # 不显示坐标轴 135 num[index] = 0 #将当前最大值清零 136 i=i+1 137 show()
结果截图:
给定的图片

输出的图片

小结:通过用给定的图匹配图像集中的每张图片的描述子,然后用线与图像集中的图片的描述子相连,匹配度最高的图片就会被输出。
七、SIFT实验总结
1、sift算法提取特征点稳定,不会因为光照、旋转、尺度等因素而改变图像的特征点。
2、图像的尺度越大,图像就会越模糊。
3、sift算法可以对多张图像进行快速的、准确的关键点匹配,产生大量的特征点,可以适用于生活中的很多运用。
4、sift算法提取的特征点会有重叠。
5、在用sift算法提取特征时,应该降低图片的像素,像素过高会导致运行时间过长或失败。
八、实验遇到的问题
出现的问题:1、运行代码时出现这样的错误:
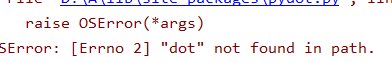
在D:\Anaconda2\Lib\site-packages目录中找到pydot.py ,用记事本打开,把self.prog = 'dot‘改成self.prog = r'C:\Program Files (x86)\Graphviz2.38\bin\dot.exe',保存,关掉运行软件再打开就可以了。
2、运行代码出现这样的结果

我用的项目的路径,出现以上报错,把路径改成了图片的路径,图片的后缀改成.jpg就可以了。
3、因为图片像素过高,运行时间会过长,结果一直出不来,还以为是代码出来了错误,但是不报错,想着可能是照片是自己拍的,像素过高了,就去降低了图片的像素,运行速率变快,结果就出来了。