经典结构 窗口最大值更新结构
内容:
1、窗口内最大值更新结构
2、窗口移动
3、求达标的子数组个数
1、窗口内最大值更新结构
窗口:数组中的一系列数
- L与R之间的数就是窗口内的数
- L和R的初始位置为数组的左边,可表示为-1
- L和R都只能右移,不可后退;且L不可超过R
窗口内最大值更新结构实质上就是一个双端队列(双向链表实现),可以从头部放入数据、弹出数据,也可以从尾部放入数据、弹出数据(均是O(1))
双端队列中每个元素由value和index组成,value是值,index是时间戳(数组下标)
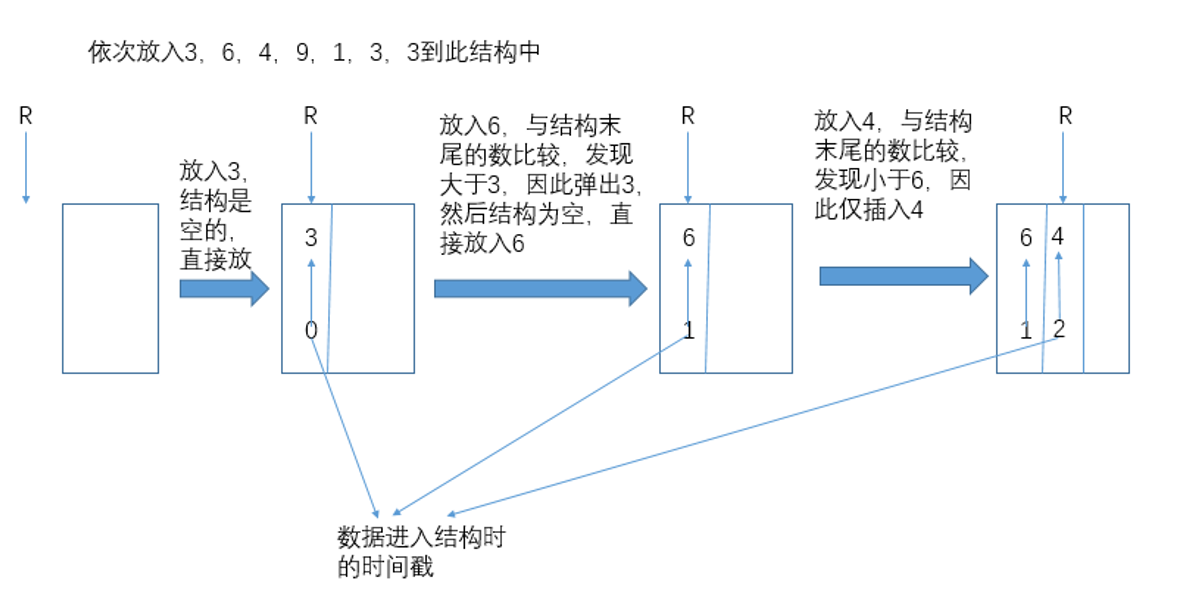
双向队列加数策略:R右移,则向双向队列中加数;如果尾部元素比要加入的数小,则弹出尾部的数,一直弹,
直到尾部的数大于新加入的数,或者队列为空。
解释:如果新加入的数据,比之前的数大,那么之前的数就不可能是窗口内最大值,可以舍弃掉。
双向队列减数策略: L右移,则需要处理,如果刚被移出窗口的数是队列头部的数则把队列头部的数弹出,这就是为什么要保存数组下标的原因
窗口内最小值类似:双向队列从头到尾依次递增,加数如果尾部数比要加的数大则弹出,减数也是过期就弹出;
代码:
1 // 最大值窗口更新结构 2 public class MaxValueWindow { 3 4 private LinkedList<Integer> queue; 5 public MaxValueWindow(){ 6 this.queue = new LinkedList<Integer>(); 7 } 8 9 // 更新窗口最大值 10 public void add(int i){ 11 while(!queue.isEmpty() && queue.getLast() <= i){ 12 queue.pollLast(); 13 } 14 queue.addLast(i); 15 } 16 17 // 获取窗口最大值 18 public int getMax(){ 19 if(!queue.isEmpty()){ 20 return queue.peekFirst(); 21 } 22 return Integer.MIN_VALUE; 23 } 24 25 // 使窗口最大值过期 26 public void expireMaxValue(){ 27 if(!queue.isEmpty()){ 28 queue.pollFirst(); 29 } 30 } 31 32 public static void main(String[] args) { 33 MaxValueWindow window = new MaxValueWindow(); 34 window.add(6); 35 window.add(4); 36 window.add(9); 37 window.add(8); 38 System.out.println(window.getMax()); // 9 39 window.expireMaxValue(); 40 System.out.println(window.getMax()); // 8 41 } 42 }
2、窗口移动
题目描述:
有一个整形数组arr和一个大小为w的窗口从数组的最左边滑到最右边,窗口每次向右滑动一个位置
例如:数组为[4,3,5,4,3,3,6,7],窗口大小为3时:
[4 3 5] 4 3 3 6 7 窗口中最大值为5
4 [3 5 4] 3 3 6 7 窗口中最大值为5
4 3 [5 4 3] 3 6 7 窗口中最大值为5
4 3 5 [4 3 3] 6 7 窗口中最大值为4
4 3 5 4 [3 3 6] 7 窗口中最大值为6
4 3 5 4 3 [3 6 7] 窗口中最大值为7
如果数组长度为n 窗口大小为w 则一共产生n-w+1个窗口的最大值
请实现一个函数:
输入:整形数组arr 窗口大小w
输出:一个长度为n-w+1的数组res res[i]表示每一种窗口状态下的最大值
以上面的数组为例,结果应该返回[5, 5, 5, 4, 6, 7]
思路:
前面介绍的窗口大值更新结构的特性是,先前放入的数如果还存在于结构中,那么该数一定比后放入的数都大。
此题窗口移动的过程就是从窗口中减一个数和增一个数的过程
代码:
1 public class SlidingWindowMaxArray { 2 public static int[] getMaxWindow(int[] arr, int w) { 3 if (arr == null || w < 1 || arr.length < w) { 4 return null; 5 } 6 LinkedList<Integer> qmax = new LinkedList<Integer>(); 7 int[] res = new int[arr.length - w + 1]; 8 int index = 0; 9 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 10 while (!qmax.isEmpty() && arr[qmax.peekLast()] <= arr[i]) { 11 qmax.pollLast(); 12 } 13 qmax.addLast(i); 14 if (qmax.peekFirst() == i - w) { 15 qmax.pollFirst(); 16 } 17 if (i >= w - 1) { 18 res[index++] = arr[qmax.peekFirst()]; 19 } 20 } 21 return res; 22 } 23 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 int[] arr = {4, 3, 5, 4, 3, 3, 6, 7}; 26 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(getMaxWindow(arr, 3))); 27 } 28 }
3、求达标的子数组个数
题目描述:求最大值减去最小值小于或等于num的子数组数量
给定数组arr和整数num,共返回有多少个子数组满足如下情况:
max(arr[i...j]) - min(arr[i..j]) <= num
max(arr[i...j])表示子数组arr[i...j]中的最大值,min(arr[i...j])表示子数组arr[i...j]中的最小值
要求:实现时间复杂度O(N)的算法
暴力思路:
遍历每个元素,再遍历以当前元素为首的所有子数组,再遍历子数组找到其中的大值和小值以判断其是否达标。
很显然这种方法的时间复杂度为 o(N^3) ,但如果使用窗口最大值更新结构,则能实现 O(N) 级别的解
代码:
1 // 暴力方法(O(N^3)) 2 public static int getNum1(int[] arr, int num) { 3 int res = 0; 4 // 遍历所有子数组 5 for (int start = 0; start < arr.length; start++) { 6 for(int end=start;end<arr.length;end++){ 7 if(isValid(arr, start, end, num)){ 8 res++; 9 } 10 } 11 } 12 return res; 13 } 14 15 public static boolean isValid(int[] arr, int start, int end, int num){ 16 // 判断子数组最大值和最小值是否小于num 17 int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; 18 int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 19 for(int i=start; i<=end;i++){ 20 max = Math.max(max, arr[i]); 21 min = Math.min(min, arr[i]); 22 } 23 return max - min <= num; 24 }
窗口最大值更新结构思路:
基本思想:
- 前提条件:用 L 和 R 两个指针指向数组的两个下标,且 L 在 R 的左边,下面两条是必然发生的
- 当 L~R 这一子数组达标时,可以推导出以 L 开头的长度不超过 R-L+1 的所有子数组都达标
- 当 L~R 这一子数组不达标时,无论 L 向左扩多少个位置或者 R 向 右扩多少个位置, L~R 还是不达标
O(N) 的解对应的算法是:
L 和 R 都从0开始, R 先向右移动, R 每右移一个位置就使用窗口最大值更新结构和窗口最小值更新结构
记录一下 L~R 之间的大值和小值的下标,当 R 移动到如果再右移一个位置 L~R 就不达标了时停 止,这时以当前 L开头
的长度不超过 R-L+1 的子数组都达标;然后 L 右移一个位置,同时更新一下结构( L-1 下标过期),
再右移 R 至 R 如果右移一个位置 L~R 就不达标了停止(每右移 R 一次也更新结构)……;直到
L 到达数组尾元素为止。将每次 R 停止时, R-L+1 的数量累加起来就是 O(N) 的解,因为 L 和 R 都只向右移动,
并且每次 R 停止时,以 L 开头的达标子串的数量直接通过 R-L+1 计算,所以 时间复杂度就是将数组遍历了一遍即 O(N)
代码:
1 // O(N)的解法 2 public static int getNum(int[] arr, int num) { 3 if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) { 4 return 0; 5 } 6 LinkedList<Integer> qmin = new LinkedList<Integer>(); 7 LinkedList<Integer> qmax = new LinkedList<Integer>(); 8 int L = 0; 9 int R = 0; 10 int res = 0; 11 while (L < arr.length) { 12 while (R < arr.length) { 13 // R往右扩 扩到不能扩停 14 while (!qmin.isEmpty() && arr[qmin.peekLast()] >= arr[R]) { 15 qmin.pollLast(); 16 } 17 qmin.addLast(R); 18 while (!qmax.isEmpty() && arr[qmax.peekLast()] <= arr[R]) { 19 qmax.pollLast(); 20 } 21 qmax.addLast(R); 22 if (arr[qmax.getFirst()] - arr[qmin.getFirst()] > num) { 23 // 不达标的情况 24 break; 25 } 26 R++; 27 } 28 // 更新最大最小值 29 if (qmin.peekFirst() == L) { 30 qmin.pollFirst(); 31 } 32 if (qmax.peekFirst() == L) { 33 qmax.pollFirst(); 34 } 35 // 加上已统计的结果 36 res += R - L + 1; 37 // L右扩 38 L++; 39 } 40 return res; 41 }



