javase基础
Lambda表示式
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectFactory; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; public class InterfaceMain { private static final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); User addDate(){ System.out.println("ceshi"); return new User(); } void test(){ map.put("1",()->addDate()); } public static void main(String[] args) { new InterfaceMain().test(); System.out.println(map.get("1").getObject()); } }
throw和throws的区别
throw是在方法内部主动去使用,然后抛出。throws是可能会发生,然后去抛出,抛出的上一级需要去捕获,处理这个异常。
public static void testMethod1() throws ArithmeticException{ int a = 1/0; System.out.println("111"); } public static void main(String[] args) { try { Test4.testMethod1(); }catch (ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println("222"); } } }
222
Process finished with exit code 0
3.sleep()、wait()、join()、yield()的区别?
1.锁池:所有需要竞争同步锁的线程都会放入锁池,比如当前对象的锁已经被其中一个线程得到,则其他线程需要在这个锁池进行等待,当前面的线程释放同步锁后锁池中的线程去竞争同步锁,当某个线程得到后会进入就绪队列进行等待cpu资源分配。
2.等待池:当我们调用wait()方法后,线程会放到等待池当中,等待池的线程是不会去竞争同步锁。只有调用了notify()或notifyAll()后等待池的线程才会开始去竞争锁,notify是随机从等待池选出一个线程放到锁池,而notifyAll是将等待池的所有线程放到锁池当中。
》》》》
1.sleep是Thread的静态本地方法,wait则是Object类的本地方法。
2.sleep方法不会释放lock,但是wait会释放,加入到等待池中。
sleep就是把cpu的执行资格和执行权释放出去,不再运行此线程,当定时时间结束再取回cpu资源。参与cpu调度,获取到cpu资源后就可以继续执行了。而如果sleep时该线程有锁,那么sleep不会释放这个锁,而是把锁带着进入了冻结状态,也就是说其他线程根本不可能获得这个锁。如果在睡眠期间其他线程调用了这个线程的interrupt方法,那么这个线程也会抛出interruptexception异常返回,这点和wait是一样的。
3.sleep方法不依赖同步器synchronized,但是wait需要依赖synchronized关键字。
4.sleep不需要被唤醒,但是wait需要
5.sleep一般用于当前线程休眠,或者轮训暂停操作,wait则用于多线程之间的通信(这也导致了依赖synchronized,多线程之前通信为了功能完成一件事,所以需要共同的东西,所以需要锁)
yield执行后线程直接进入就绪状态,马上释放了cpu的执行权,但是依然保留了cpu的执行资格,所有有可能cpu下次进行线程调度还会让这个线程获取到执行权继续进行。(好比上厕所,只有一个坑位,有个人特别急,你就让他先拉了,他拉完了就是你上了)。
join执行后线程进入阻塞状态,例如在线程B中调用线程A的join(),那线程B会进入到阻塞队列,直到线程A结束或中断线程。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("2000"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); t1.start(); t1.join(); System.out.println("1111111"); }
2000
1111111
main线程进入了休眠,所以等待了3秒后,输出了2000,t1线程执行结束,main线程唤醒,输出1111111。
4.
强引用:指针指向堆中。
软引用:指针指向堆中的一个对象,堆中这个对象又指向一个对象,这个引用叫做软引用。垃圾回收看到软引用,不会进行回收。但是当内存不足时,垃圾回收机制会回收软引用。
弱引用:垃圾回收看到,就会直接清理。
虚引用:也叫幽灵引用,他形同虚设。虚引用并不会影响对象的生命周期。虚引用一般与ReferenceQueue搭配使用。他的作用可以是这个对象被清理时,做进一步的动作。(当ReferenceQueue中取出值,说明即将要被清理,可以再对象被清理之前,做一些动作)
5.CountDownLatch的使用
public class Test { /** * 让主线程等待 */ private static CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("22222"); countDownLatch.countDown(); countDownLatch.await(); System.out.println("33333"); } }
countDown减1,await阻塞。
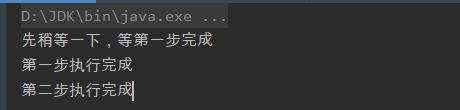
public class Test1 { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1); private void testMethod(){ executorService.execute(new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("先稍等一下,等第一步完成"); try { countDownLatch.await(); System.out.println("第二步执行完成"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } })); executorService.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("第一步执行完成"); countDownLatch.countDown(); } }); } public static void main(String[] args) { new Test1().testMethod(); } }
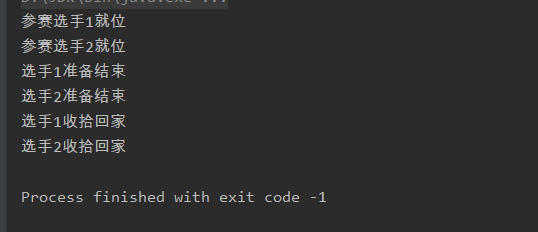
public class Test1 { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(2); private void testMethod(){ executorService.execute(new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("参赛选手1就位"); try { cyclicBarrier.await(); System.out.println("选手1准备结束"); cyclicBarrier.await(); System.out.println("选手1收拾回家"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } })); executorService.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("参赛选手2就位"); try { cyclicBarrier.await(); System.out.println("选手2准备结束"); cyclicBarrier.await(); System.out.println("选手2收拾回家"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } public static void main(String[] args) { new Test1().testMethod(); } }
5.事务以及interm的使用
@Service public class TransactionTest { @Autowired private DaoService daoService; @Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class) public void testMethod1(){ daoService.findData();//有效的事务提交 } @Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class) public void testMethod2(){ this.findData();//无效的事务提交,事务本身是借助于AOP,要通过spring管理的对象去进行调用 } //锁要包含事务,只有事务提交后,再能将锁放开 public void findData(){ String msg = "test"; synchronized (msg.intern()){//intern能保证是同一个对象,这样能够锁住 //代码块 } } }
6.反射中get的作用
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException { People people = new People("tom",10); People people1 = new People("kitten",16); Field field = People.class.getDeclaredField("name"); field.setAccessible(true); System.out.println(field.get(people)); }
field能存储所有对象的name属性。
7.spring初始化的前后顺序
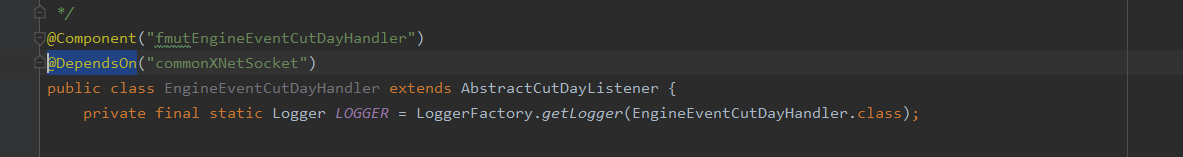
“fmutEngineEventCutDayHandler对象肯定会在commonXNetSocket对象生成后才会生成
8.枚举类的遍历
public static <T extends MonitorLinkStateEnums.ChannelCode > String getMemoByCode(String param, Class<T> clazz) { for (T t: clazz.getEnumConstants()) { if (t.getCode().equals(param)) { return t.getMemo(); } } return ""; }
clazz.getEnumConstants获取class枚举对象的所有元素。
》》可以使用value方法,遍历所有对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | public enum PlanTypeEnums { MANUAL(0, "手工"), STRATEGY(1, "策略"), MARKET(2, "市场行情接入"), TRADER(3, "模拟交易所接入"); private int code; private String cName; PlanTypeEnums(int code, String cName) { this.code = code; this.cName = cName; } public int getCode() { return code; } public String getcName() { return cName; } public static PlanTypeEnums getByCode(int code) { for (PlanTypeEnums value : values()) { if (value.getCode() == code) { return value; } } return STRATEGY; }} |
9.ordinal的作用
private static final Function<PlanDataMessage, List<MockData>>[] FUNCTIONS = new Function[PlanTypeEnums.values().length]; { FUNCTIONS[PlanTypeEnums.MANUAL.ordinal()] = this::getManualMockDataList; FUNCTIONS[PlanTypeEnums.STRATEGY.ordinal()] = this::getStrategyMockDataList; FUNCTIONS[PlanTypeEnums.TRADER.ordinal()] = this::getTradeMockDataList; }
ordinal从0开始 顺序一次递增。好处是通过数组以这种ordinal存入生成的坐标,下次取的时候可以采用同样的方式取。
public List<MockData> doAdapter(PlanDataMessage planDataMessage) { return FUNCTIONS[PlanTypeEnums.getByCode(planDataMessage.getPlanType()).ordinal()].apply(planDataMessage); }
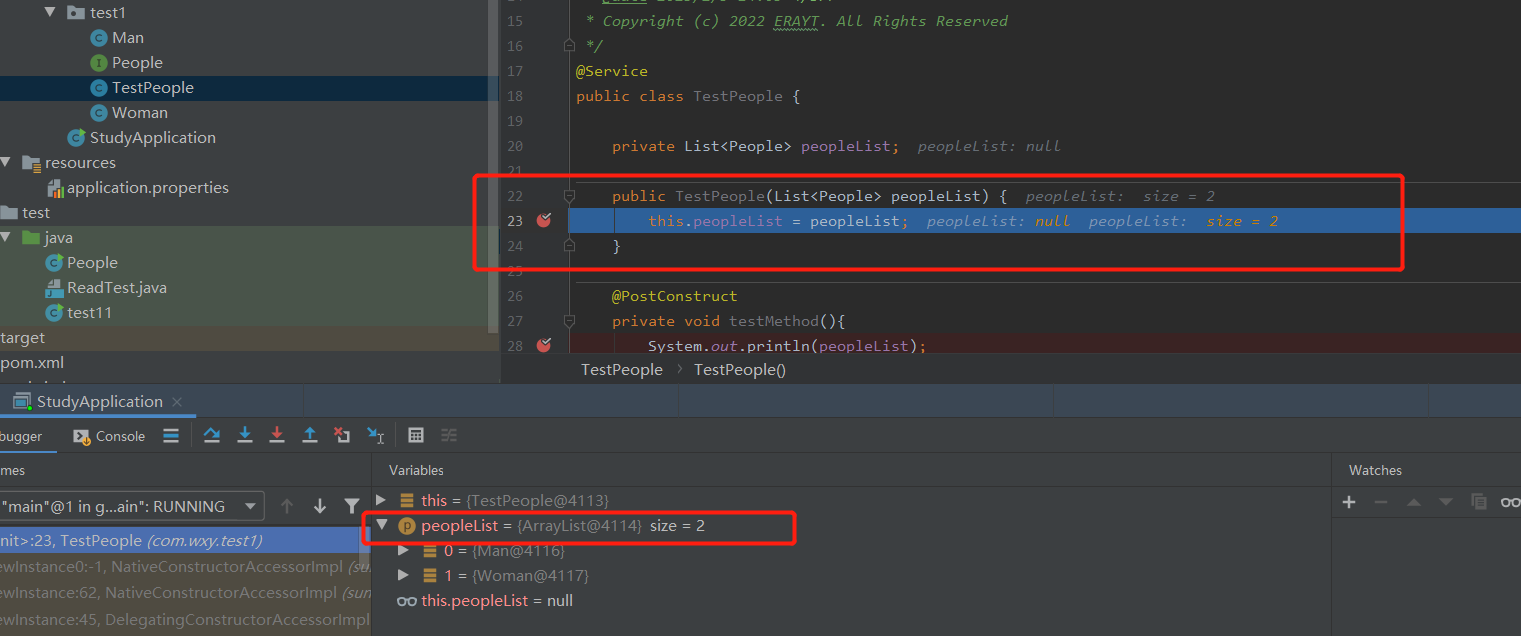
10 Map的注入
@Resource
private Map<String, MarketDataAdapter> marketDataAdapterMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(8);
会将MarketDataAdapter的实现类全部注入,可以为spring的name。
》》List注入-方式1
》》List注入-方式2
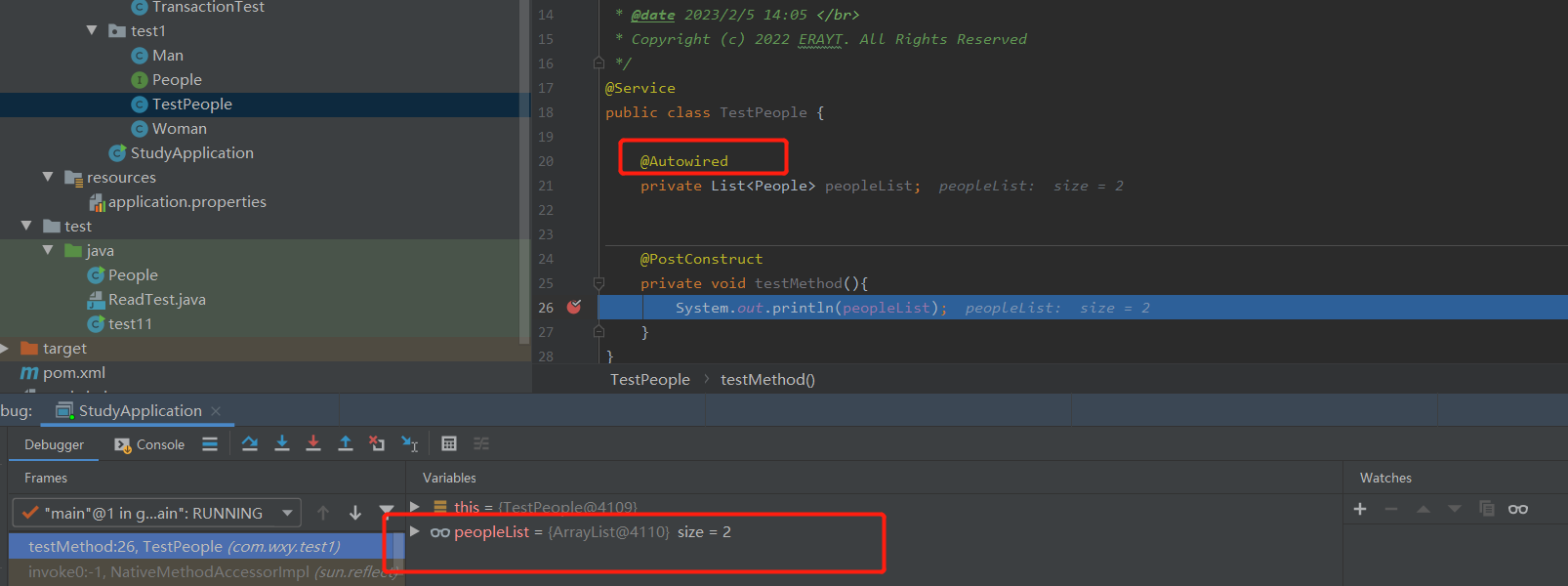
11.接口的优化
一个接口如果有很多实现类,但是某些方法是这些实现类全部都有使用。可以在接口中使用
default void genPrice(List<MockData> mockDataList, MockParam mockParam, BiConsumer<List<MockPrice>, PlanDataMessage> biConsumer, Function<PlanDataMessage, MockPrice> createMockPrice) {
}
12.接口和抽象类啥时候使用
如果子类有些方法是公用的,可以用抽象类,把公共方法写在抽象类中。如果子类的每个方法都是不同的,可以用接口是实现。
13.想要在项目ioc容器完全启动后,做一些业务操作。
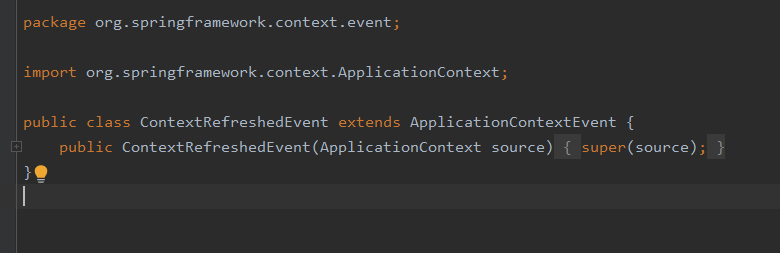
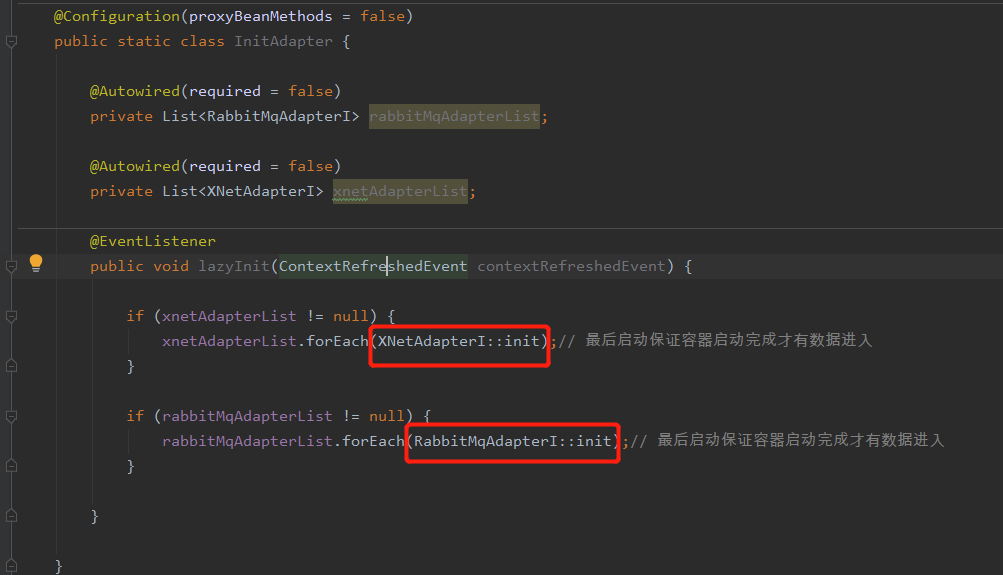
14.如何实现配置类的多态化。
》定义一个父类,将所有的字段进行定义。用map字段。
》子类可以进行赋值注入。
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "routingkey")
public class MqRoutingKeyConfiguration extends MqBasicConfiguration {
}
15.一个数据表中的数据插入到另一个数据表中:
<insert id="insterXswapOrderList" >
INSERT INTO FMUT2_ORDER_XSWAP_HIS
(
<include refid="XswapOrderHisPojoField"/>
)
SELECT
<include refid="XswapOrderHisPojoField"/>
FROM FMUT2_ORDER_XSWAP
<!--VALUES (
<include refid="XswapOrderHisPojoValue"/>
)-->
</insert>
16.一个抽象类有多个实现,在代码中如何设置指定的实现
public abstract class AbstractBondTrackService<T extends Pojo> {}
=====
@Resource
private AbstractBondTrackService<CashBondAskRespPojo> bondTrackRespService;
17.需要做每个不同的行为的时候,且行为不复杂,可以在枚举类做这种处理。(行为复杂的,可以参考模拟器的做法)
public enum CheckRule { /** * entity_instrument_pair 索引 */ PRIMARY_KEY((pojo) -> { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(pojo.getEntity()).append(BaseConstant.UNDERLINE_CHAR).append(pojo.getInstrument()) .append(BaseConstant.UNDERLINE_CHAR).append(pojo.getPair()); return sb.toString(); }); private static final List<SysParamIndex<CheckRulePojo>> SYS_PARAM_INDEX_LIST; static { SYS_PARAM_INDEX_LIST = new ArrayList<>(); for (CheckRule index : CheckRule.values()) { SYS_PARAM_INDEX_LIST.add(index.getIndex()); } } private SysParamIndex<CheckRulePojo> index; private CheckRule(SysParamIndex<CheckRulePojo> index) { this.index = index; } public SysParamIndex<CheckRulePojo> getIndex() { return index; } public static List<SysParamIndex<CheckRulePojo>> getIndexs() { return SYS_PARAM_INDEX_LIST; } public String buildKey(CheckRulePojo pojo) { return getIndex().buildIndex(pojo); } }
@FunctionalInterface public interface SysParamIndex<T> { String buildIndex(T pojo); }
List<CheckRulePojo> res = super.findSome(SysParamCacheKey.CheckRule.PRIMARY_KEY.getIndex(), queryPojo);
18.elps表达式
@Value("#{'${market.cnyBondFut.bondCode:TL8#140256,T2003#190015,TS2006#190013}'.split(',')}")
private List<String> relationList;
19.内部类构架eic
OptQuoteParamServiceImpl
20.科学计数法转换为非科学计数法
1 2 3 4 5 | double a = 10000000000000000000000000000000d;System.out.println(a);DecimalFormat decimalFormat = new DecimalFormat("#");String normalNumber = decimalFormat.format(a);System.out.println(normalNumber); |





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix