kubernets集群的安全防护(上)
一 了解认证机制
1.1 API的服务器在接收来自客户端的请求的时候会对发起的用户进行几个步骤
-
- 认证插件进行认证,确认发起的用户是外部用户,还是集群中的某个命名空间里面的pod
- 确认用户属于哪个组,这个组被赋予对集群资源的哪些权限,是否有对这些资源的增删改查的权限
- 最后才确认能否成功的对资源进行修改
1.2 介绍serviceaccount
serviceaccount属于一种集群资源,可以在命名空间里面创建,并且每个命名空间里面都有一个默认的accountservice,在命名空间创建pod的时候,会将这个serviceaccount里面的token,ca.cart以及namespace渲染到容器里面的挂载路径 /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/
并且可以自己自定义serviceaccount,定义serviceaccount里面挂载的secrets列表,在默认情况下,集群里面的pod可以挂载任意多的secrets卷,但是当将ServiceAccount里面包含这个注解的时候kubernets.io/enforce-moutable-secrets="true"的时候,pod只要挂载了这个SA那么就只能挂载这个SA下面定义的secrets
二 介绍RBAC授权插件
2.1 RBAC这样的一个插件,授权在集群中的一个客户端是否允许在集群资源中执行的一系列动作
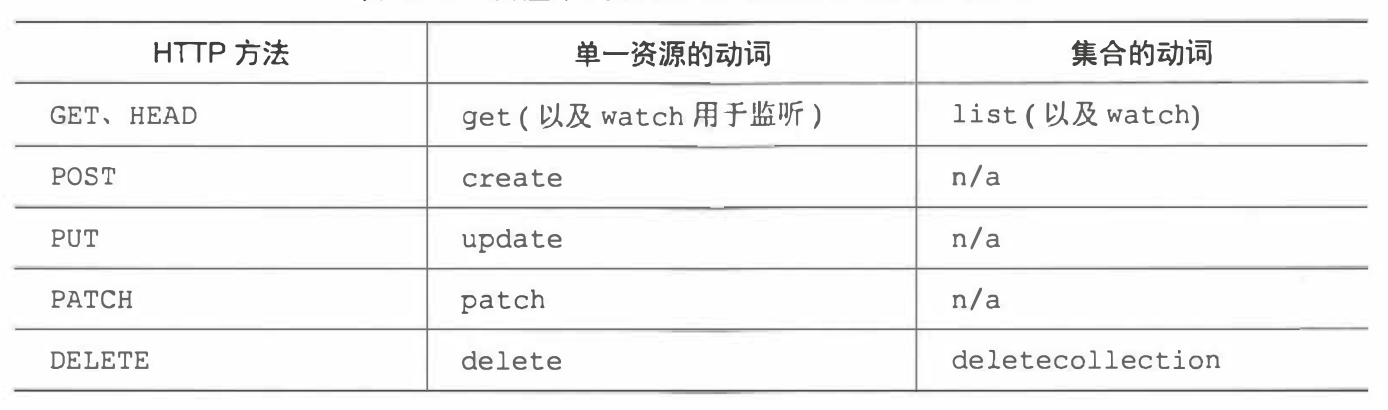
2.2 RBAC的核心思想是将用户与一系列的角色相关联,这个用户可以是serviceaccount或者是其他用户将可以关联很多角色,每个角色同时有对集群内部的一些资源的增删改查的权限,用户可以关联多个角色,并享有所有相关联的权限,没有与用户关联的角色的权限,用户自然也没有相关的任何权限
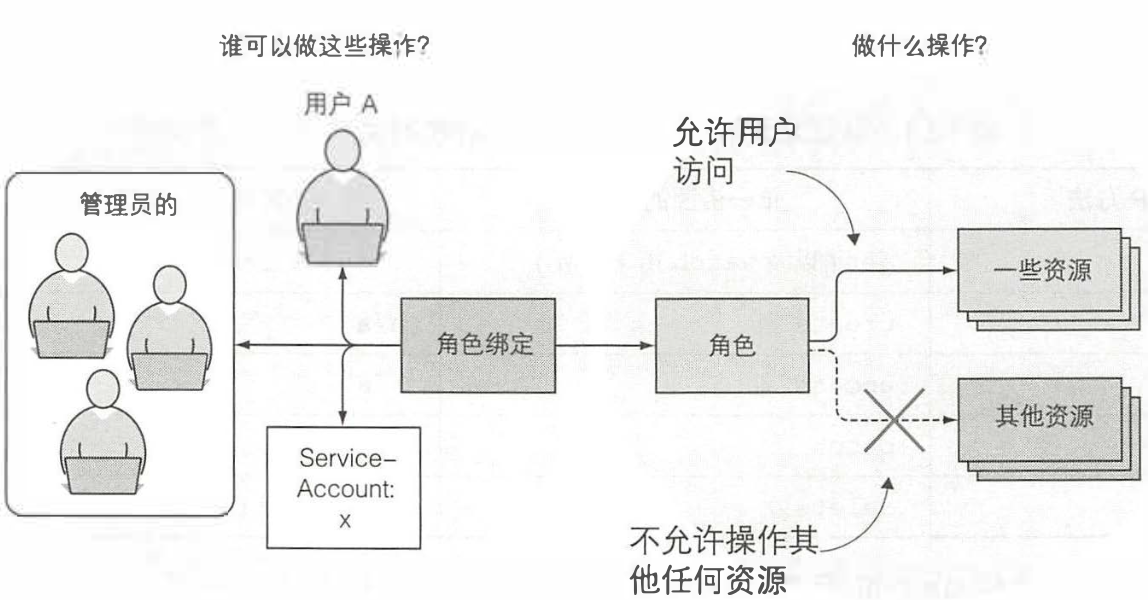
2.3 介绍RBAC资源
RBAC授权规则是通过四种资源进行配置的,他们分为2个组
- Role以及ClusterRole,他们决定了可以在资源上执行哪些动作
- RoleBinding以及ClusterRoleBinding,它们将上述角色绑定到特定的用户,组或者ServiceAccount上面
详细内容如图所示
2.4 值得一提的是,角色,与角色绑定属于命名空间级别的资源,集群角色与集群角色绑定属于集群级别的资源,他们之间的关系除了一一对应之外,还有其他的关系

-
- 可以看到在同一个命名空间里面可以有多个角色绑定,同样也可以有多个角色
- 单个命名空间里面的角色只能绑定其命名空间里面的角色
- 但是对于任意的命名空间的角色绑定是可以将集群的角色绑定到其命名空间的用户上面的,这点需要注意
三 练习RBAC资源如何限制集群中各个pod对集群资源的访问
3.1 在集群中开启RBAC鉴权
k delete clusterrolebinding permissive-binding
3.2 分别创建2个命名空间以及在2个命名空间里面创建pod
[root@node01 wxm]# k create ns wxm namespace/wxm created [root@node01 wxm]# k run test --image=luksa/kubectl-proxy -n wxm pod/test created [root@node01 wxm]# k create ns wdm namespace/wdm created [root@node01 wxm]# k run test --image=luksa/kubectl-proxy -n wdm pod/test created
3.3 之后进入一个命名空间里面的pod里面执行查询资源的命名
/ # curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/wdm/services { "kind": "Status", "apiVersion": "v1", "metadata": { }, "status": "Failure", "message": "services is forbidden: User \"system:serviceaccount:wxm:default\" cannot list resource \"services\" in API group \"\" in the namespace \"wdm\"", "reason": "Forbidden", "details": { "kind": "services" }, "code": 403 / # curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/default/services { "kind": "Status", "apiVersion": "v1", "metadata": { }, "status": "Failure", "message": "services is forbidden: User \"system:serviceaccount:wxm:default\" cannot list resource \"services\" in API group \"\" in the namespace \"default\"", "reason": "Forbidden", "details": { "kind": "services" }, "code": 403
- 可以看到在开启了RBAC的时候,由于默认的pod挂载的是集群中的默认的SA,但是没有给它赋予任何权限
- 所以无论访问API服务器的任何资源都会被拒绝
3.4 在wxm这个命名空间创建一个角色,这个角色的作用是支持查询wxm这个命名空间的所有资源,有两种形式来创建资源
3.4.1 yaml形式创建这个Role
[root@node01 Chapter12]# cat service-reader.yml apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: namespace: wxm name: wxm rules: - apiGroups: [""] verbs: ["get", "list"] resources: ["services"]
- role这个资源它属于rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1资源组
- 它区别于其他资源没有spec选项(笔者在创建的时候没发现)
- rules里面可以定义对哪些资源有着什么样子的操作权限以及资源属于什么API组的
3.4.2 以命令行的形式创建role
k create role service-reader --verb=get --verb=list --resource=services -n wdm
3.5 以命令行的形式创建角色绑定
k create rolebinding --name=test --role=service-reader --serviceaccount=wdm:default-n wdm
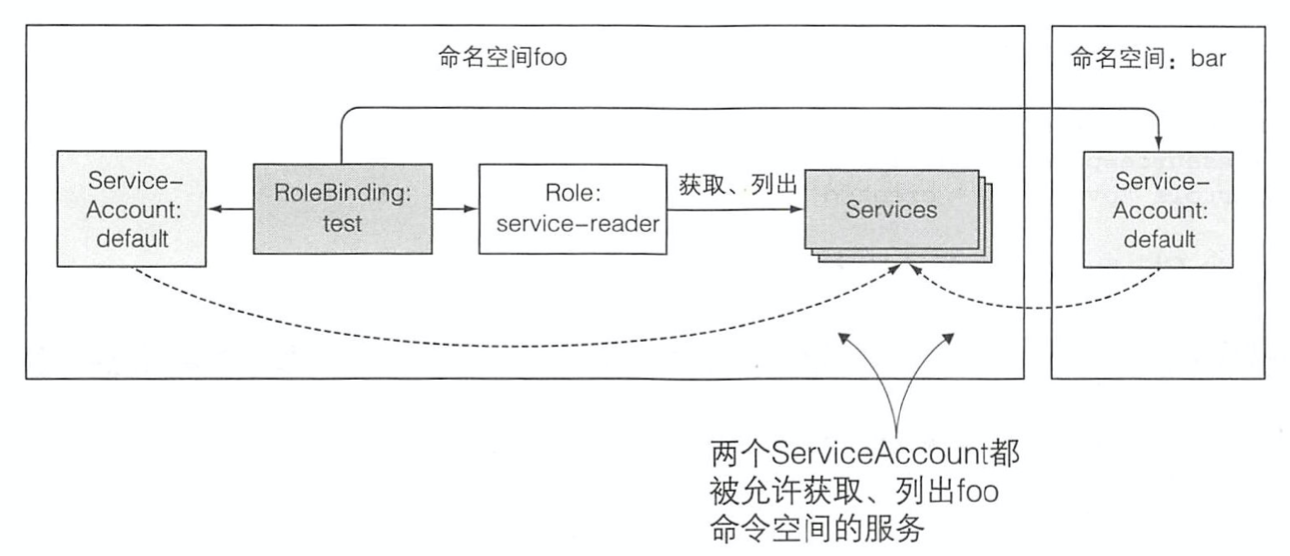
通过上面的命令将命名空间wdm的SA绑定了service-reader的role,至此我们就可以在wdm的pod里面去通过API服务器来访问wdm命名空间的services的清单了
[root@node01 Chapter12]# k exec -it test -n wdm sh kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead. / # curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/wdm/services { "kind": "ServiceList", "apiVersion": "v1", "metadata": { "selfLink": "/api/v1/namespaces/wdm/services", "resourceVersion": "3474903" }, "items": []
3.6 还有一点,当我们想在wxm这个命名空间里面的pod去访问wdm的service或者其他列表的时候仅仅需要在rolebinding里面添加wxm这个命名空间的SA,操作如下
[root@node01 Chapter12]# k get rolebinding test -o yaml -n wdm apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: creationTimestamp: "2021-01-14T08:44:08Z" name: test namespace: wdm resourceVersion: "3473068" selfLink: /apis/rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1/namespaces/wdm/rolebindings/test uid: aa8972d6-5644-11eb-ae9a-5254002a5691 roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: Role name: service-reader subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: default namespace: wdm - kind: ServiceAccount name: default namespace: wxm
- 红色字体为添加的部分
3.7 我们再试试在wxm这个命名空间的pod能否去访问wdm这个命名空间的service资源
/ # curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/wdm/services { "kind": "ServiceList", "apiVersion": "v1", "metadata": { "selfLink": "/api/v1/namespaces/wdm/services", "resourceVersion": "3473158" }, "items": [] / # curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/wxm/services { "kind": "Status", "apiVersion": "v1", "metadata": { }, "status": "Failure", "message": "services is forbidden: User \"system:serviceaccount:wxm:default\" cannot list resource \"services\" in API group \"\" in the namespace \"wxm\"", "reason": "Forbidden", "details": { "kind": "services" }, "code": 403 / # curl localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/wdm/services { "kind": "ServiceList", "apiVersion": "v1", "metadata": { "selfLink": "/api/v1/namespaces/wdm/services", "resourceVersion": "3475403" }, "items": [] }/ #
- 结果显而易见,wxm这个命名空间的pod无法访问自己的service
- 但是wxm这个命名空间pod却能访问wdm这个命名空间的service
- 这就是RBAC权限的神奇作用
3.8 下面来把演示的内容做成一幅图来更直观的看一下



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号