django框架:可视化界面之数据增删改查、django请求生命周期流程图、django路由层、反向解析
一、可视化界面之数据增删改查
小知识点:
- 针对数据对象主键字段的获取可以使用更加方便的 obj.pk获取
- 在模型类中定义双下str方法可以在数据对象被执行打印操作的时候方便的查看
- form表单中能够触发调剂动作的按钮只有两个
<input type='submit'/> <button></button>
数据增删改查功能
1.数据展示功能
开设接口、获取数据、传递页面、展示数据
view.py
def user_list_func(request): user_data = models.UserInfor.objects.filter() return render(request,'userListPage.html',{'user_data':user_data})
html文件
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>List</title> {% load static %} <script src="{% static 'jquery-3.6.1.js' %}"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css' %}"> <script src="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/js/bootstrap.min.js' %}"></script> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <h1 class="text-center">数据展示页</h1> <div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2"> <a href="/user_add/" class="btn btn-success">数据添加</a> <table class="table table-hover table-striped"> <thead> <tr> <th>Id</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Pwd</th> <th class="text-center">Operation</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for user_obj in user_data %} <tr> <td>{{ user_obj.pk }}</td> <td>{{ user_obj.name }}</td> <td>{{ user_obj.pwd }}</td> <td class="text-center"> <a href="/user_edit/?edit_id={{ user_obj.pk }}" class="btn btn-primary btn-xs">编辑</a> <a href="/user_delete/?delete_id={{ user_obj.pk }}" class="btn btn-danger btn-xs delBtn">删除</a> </td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> </table> </div> </div> </div> <script> $('.delBtn').click(function (){ let res = confirm('确定删除吗') if (res){ }else { return false } }) </script> </body> </html>
2.数据添加功能
开设接口、获取数据、发送数据、校验数据、录入数据、重定向
view.py
def user_add_func(request): if request.method == 'POST': name_infor = request.POST.get('name') pwd_infor = request.POST.get('pwd') if len(name_infor) == 0 or len(pwd_infor) == 0: return HttpResponse('用户名或年龄不能为空') user_infor = models.UserInfor.objects.filter(name=name_infor) if user_infor: return HttpResponse('用户名已存在') models.UserInfor.objects.create(name=name_infor, pwd=pwd_infor) return redirect('/user_list/') return render(request, 'userAddPage.html')
html文件
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>add</title> {% load static %} <script src="{% static 'jquery-3.6.1.js' %}"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/css/bootstrap.css' %}"> <script src="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/js/bootstrap.js' %}"></script> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <h1 class="text-center">数据添加页</h1> <div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3"> <form action="" method="post"> <p>name: <input type="text" name="name" class="form-control"> </p> <p>pwd: <input type="text" name="pwd" class="form-control"> </p> <input type="submit" value="添加用户" class="btn btn-warning btn-block"> </form> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
3.数据编辑功能
开设接口、后端如何区分所要编辑的数据(问号携带参数)、后端获取用户数据、前端展示默认数据、获取用户并完成更新
view.py
def user_edit_func(request): target_edit_id = request.GET.get('edit_id') if request.method == 'POST': name_infor = request.POST.get('name') pwd_infor = request.POST.get('pwd') if len(name_infor) == 0 or len(pwd_infor) == 0: return HttpResponse('用户名或年龄不能为空') models.UserInfor.objects.filter(pk=target_edit_id).update(name=name_infor, pwd=pwd_infor) return redirect('/user_list/') target_edit_obj = models.UserInfor.objects.filter(pk=target_edit_id)[0] print(target_edit_obj) return render(request, 'userEditPage.html', {'target_edit_obj': target_edit_obj})
html文件
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>edit</title> {% load static %} <script src="{% static 'jquery-3.6.1.js' %}"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/css/bootstrap.css' %}"> <script src="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/js/bootstrap.js' %}"></script> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <h1 class="text-center">数据编辑页</h1> <div> <form action="" method="post"> <p>name: <input type="text" name="name" class="form-control" value="{{ target_edit_obj.name }}"> </p> <p>pwd: <input type="text" name="pwd" class="form-control" value="{{ target_edit_obj.pwd }}"> </p> <input type="submit" value="编辑用户" class="btn btn-primary btn-block"> </form> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
4.数据删除功能
开设接口、问号携带参数、删除二次确认
view.py
def user_delete_func(request): target_delete_id = request.GET.get('delete_id') models.UserInfor.objects.filter(pk=target_delete_id).delete() return redirect('/user_list/')
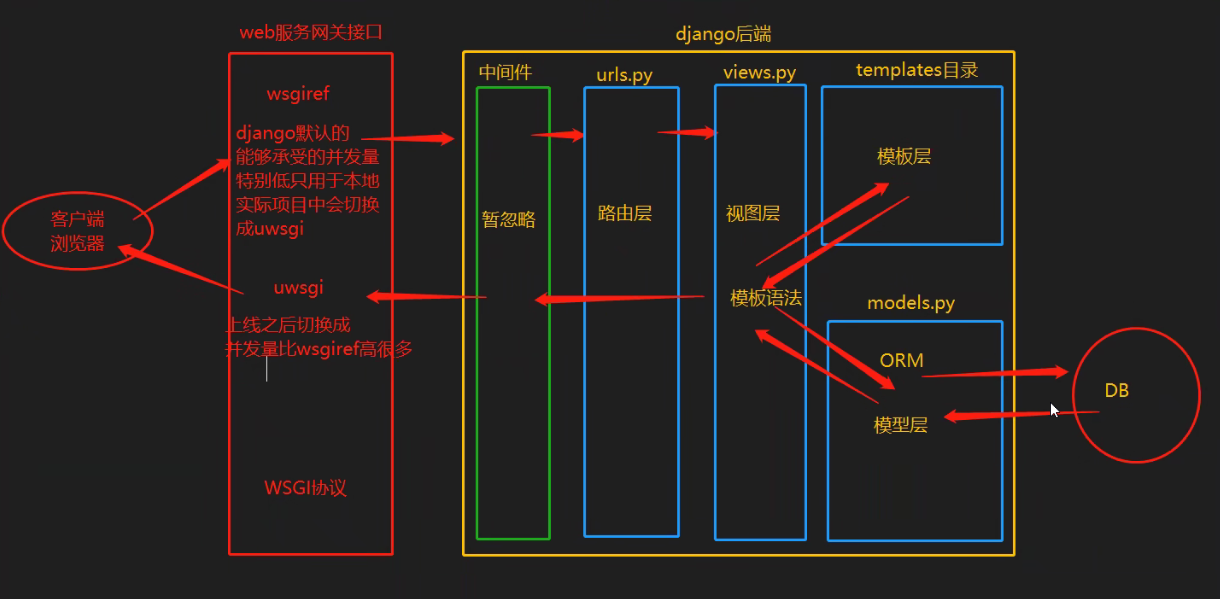
二、django请求生命周期流程图
1、Django请求的生命周期的含义
Django请求的生命周期是指:当用户在浏览器上输入url到用户看到网页的这个时间段内,Django后台所发生的事情。**
2、Django请求的生命周期图解及流程
这个图很重要 无论是学习阶段还是复习阶段
学习流程
通过这个生命周期图我们可以了解到接下去的学习流程为:路由层、视图层、模板层、模型层、组件、BBS项目
- Django自带的web服务网管接口是wsgiref,因为他能承受的并发量特别低,因此我们在项目中会换成uwsgi,它的并发量比wsgiref高很多。
- WSGI与wsgiref和uwsgi之间的关系是:WSGI是协议,wsgiref和uwsgi是实现协议功能的模块。
- 中间件可以看成保安,数据的进出都会经过他的检查。
- 路由层就是存放网址后缀与视图之间的关系。
- 视图层存放功能函数,通过函数调用模版层中的html网页,同时在函数内通过models.py建立与数据库的交互。
三、django路由层
1.路由匹配
django2.X及以上 path第一个参数写什么就匹配什么
django1.X第一个参数是正则表达式
无论什么版本django都自带加斜杠后缀的功能,也可以取消
ps:当我们在用网址访问网页的时候,有些网址需要在末尾加上‘/’符号,有些则不用,但是这些不用‘/’结尾的网址在跳转后,末尾自动补了一个‘/’。我们在配置文件中修改APPEND_SLASH 配置就可以设置这个功能,当他的值为True,就会自动添加斜杠进行匹配,如果改成False就不会自动匹配。
APPEND_SLASH = False
2.转换器
什么时候用转换器?
- 当网址后缀不固定的时候 可以使用转换器来匹配
如何写path转换器?
path('login/<int:year>/<str:desc>/', views.login)
具体情况分析
- 正常情况下很多网站都会有很多相似的网址 如果我们每一个都单独开设路由不合理,因此使用转换器动态匹配
django2.X及以上版本路由动态匹配有转换器(五种)
- str:匹配除路径分隔符外的任何非空字符串。
- int:匹配0或者任意正整数。
- slug:匹配任意一个由字母或数字组成的字符串。
- uuid:匹配格式化后的UUID。
- path:能够匹配完整的URL路径
ps:还支持自定义转换器(自己写正则表达式匹配更加细化的内容)
转换器:
将对应位置匹配到的数据转换成固定的数据类型(如果数据类型不匹配会报错)。
path('index/<str:info>/', views.index_func) # index_func(实参request对象,info='转换器匹配到的类型转换之后的内容') path('index/<str:info>/<int:id>/', views.index_func) # index_func(实参request对象,info='转换器匹配到的类型转换之后的内容',id='转换器匹配到的类型转换之后的内容')
3.正则匹配
不同版本的区别
django1.x版本用的是url的形式直接使用正则进行匹配网址后缀,代码如下:
from django.conf.urls import url urlpatterns = [ url(正则表达式, views视图函数,参数,别名), ]
django2.X及以上版本则替换成了path,django1.X路由匹配使用的是url() 功能与django2.X及以上的re_path()一致,第一个参数是正则。
from django.urls import path urlpatterns = [ path('articles/2003/', views.special_case_2003), path('articles/<int:year>/', views.year_archive), path('articles/<int:year>/<int:month>/', views.month_archive), path('articles/<int:year>/<int:month>/<slug:slug>/', views.article_detail), re_path('^test/$', views.test) ]
正则匹配斜杠导致的区别
正则匹配的时候要区分斜杠的作用,如果后面不写斜杠,匹配的结果就是网址中间有符合匹配条件的内容就会跳转,如果加了斜杠结尾,就是连着斜杠一起匹配(相当于匹配网址的结尾符合条件的网址)。
ps:正则匹配的本质是只要第一个正则表达式能够从用户输入的路由中匹配到数据就算匹配成功会立刻停止路由层其他的匹配直接执行对应的视图函数
4、正则匹配的无名有名分组
分组匹配
分组匹配就是使用小括号,产生分组优先,然后括号内匹配到的数据会当成参数传递给对应的函数。
无名分组
re_path('^test/(\d{4})/', views.test) re_path('^test/(\d{4})/(.*?)/', views.test) # test(实参request对象,括号内正则匹配到的内容)
会将括号内正则匹配到的内容当做位置参数传递给视图函数,在函数的参数中写位置参数接收即可。
有名分组
re_path('^test/(?P<year>\d{4})/', views.test) re_path('^test/(?P<year>\d{4})/(?P<others>.*?)/', views.test) # test(实参request对象,year='\d{4}匹配到的内容',others='.*?匹配到的内容') re_path('^test/(\d{4})/(?P<others>.*?)/', views.test) # test(实参request对象,year='\d{4}匹配到的内容',others='.*?匹配到的内容')
会将括号内正则匹配到的内容当做关键字参数传递给视图函数,也需要使用位置参数接收。
ps:注意上述的有名分组和无名分组不能混合使用!!!
四、反向解析
1.引入反向解析
页面上的一些超链接、重定向等路由都是写死的,一旦路由发生变化则会导致所有页面相关链接失效,而反向解析就是用来防止出现该问题的。
2.反向解析使用
方式一:路由对应关系起别名
在路由中给对应关系再取一个别名这样网页中使用时直接调用这个别名,就相当于调用了对应的后缀
路由层: path('后缀',views.视图函数,name='关系名')
方式二:使用反向解析语法
html页面与后端都可以进行调用
html调用: {% url '关系名' %} 后端跳转调用(需要先导入模块): from django.shortcuts import reverse reverse('关系名')
ps:反向解析的操作三个方法都一样:path()、re_path()、url()
3.有名无名反向解析(动态路由反向解析)
如果路由里面有不确定的因素那么在使用反向解析的时候必须人为传递数据,且有几个不确定因素就得传几个值
eg: 路由层: path('func1/<str:others>/', views.func1_func, name='func1_view') 视图层: reverse('func1_view', args=('嘿嘿嘿',)) html页: {% url 'func1_view' 'jason' %}
ps:html页面上模板语法(因为定义动态路由的时候有一部分是动态匹配,所以需要指定一个参数)
五、作业
利用路由匹配与反向解析改写作业讲解
urls.py
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path,re_path from app001 import views urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('index/', views.index_func), path('login/', views.login_func), path('jump/',views.jump_func), path('haohaohao/',views.haohaohao_func), path('signin/',views.signin_func), # 访问用户数据的接口 path('user_list/', views.user_list_func, name='list_view'), # user_list_func(实参request对象) # 添加用户数据的接口 path('user_add/', views.user_add_func, name='add_view'), # 编辑用户数据的接口 path('user_edit/<str:edit_id>/', views.user_edit_func, name='edit_view'), # 删除用户数据的接口 re_path('^user_delete/(?P<delete_id>.*?)/', views.user_delete_func, name='delete_view'), ]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect from app001 import models def user_list_func(request): user_data = models.UserInfor.objects.filter() return render(request, 'userListPage.html', {'user_data': user_data}) def user_add_func(request): if request.method == 'POST': name_infor = request.POST.get('name') pwd_infor = request.POST.get('pwd') if len(name_infor) == 0 or len(pwd_infor) == 0: return HttpResponse('用户名或年龄不能为空') user_infor = models.UserInfor.objects.filter(name=name_infor) if user_infor: return HttpResponse('用户名已存在') models.UserInfor.objects.create(name=name_infor, pwd=pwd_infor) return redirect('/user_list/') return render(request, 'userAddPage.html') def user_edit_func(request, edit_id): target_edit_id = edit_id if request.method == 'POST': name_infor = request.POST.get('name') pwd_infor = request.POST.get('pwd') if len(name_infor) == 0 or len(pwd_infor) == 0: return HttpResponse('用户名或年龄不能为空') models.UserInfor.objects.filter(pk=target_edit_id).update(name=name_infor, pwd=pwd_infor) return redirect('/user_list/') target_edit_obj = models.UserInfor.objects.filter(pk=target_edit_id)[0] print(target_edit_obj) return render(request, 'userEditPage.html', {'target_edit_obj': target_edit_obj}) def user_delete_func(request, delete_id): target_delete_id = delete_id models.UserInfor.objects.filter(pk=target_delete_id).delete() return redirect('/user_list/')
userListPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>List</title> {% load static %} <script src="{% static 'jquery-3.6.1.js' %}"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css' %}"> <script src="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/js/bootstrap.min.js' %}"></script> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <h1 class="text-center">数据展示页</h1> <div class="col-md-8 col-md-offset-2"> <a href="{% url 'add_view' %}" class="btn btn-success">数据添加</a> <table class="table table-hover table-striped"> <thead> <tr> <th>Id</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Pwd</th> <th class="text-center">Operation</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for user_obj in user_data %} <tr> <td>{{ user_obj.pk }}</td> <td>{{ user_obj.name }}</td> <td>{{ user_obj.pwd }}</td> <td class="text-center"> <a href="{% url 'edit_view' edit_id=user_obj.pk %}" class="btn btn-primary btn-xs">编辑</a> <a href="{% url 'delete_view' delete_id=user_obj.pk %}" class="btn btn-danger btn-xs delBtn">删除</a> </td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> </table> </div> </div> </div> <script> $('.delBtn').click(function (){ let res = confirm('确定删除吗') if (res){ }else { return false } }) </script> </body> </html>
userAddPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>add</title> {% load static %} <script src="{% static 'jquery-3.6.1.js' %}"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/css/bootstrap.css' %}"> <script src="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/js/bootstrap.js' %}"></script> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <h1 class="text-center">数据添加页</h1> <div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3"> <form action="" method="post"> <p>name: <input type="text" name="name" class="form-control"> </p> <p>pwd: <input type="text" name="pwd" class="form-control"> </p> <input type="submit" value="添加用户" class="btn btn-warning btn-block"> </form> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>
userEditPage.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>edit</title> {% load static %} <script src="{% static 'jquery-3.6.1.js' %}"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/css/bootstrap.css' %}"> <script src="{% static 'bootstrap-3.4.1-dist/js/bootstrap.js' %}"></script> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="row"> <h1 class="text-center">数据编辑页</h1> <div> <form action="" method="post"> <p>name: <input type="text" name="name" class="form-control" value="{{ target_edit_obj.name }}"> </p> <p>pwd: <input type="text" name="pwd" class="form-control" value="{{ target_edit_obj.pwd }}"> </p> <input type="submit" value="编辑用户" class="btn btn-primary btn-block"> </form> </div> </div> </div> </body> </html>



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY