SpringBoot整合Swagger 自动生成在线API文档 偷懒必备,同时也是我们的基本操作啦!!!
现在大都数项目都已是前后端分离的啦,那么接口文档就成了项目中非常重要的一部分啦,SpringBoot整合Swagger可以自动生成RESTFUL风格的API文档,也可以在其中进行测试,比起以前手写的文档,不仅方便很多,而且也易于修改和测试。
很喜欢一句话:
”八小时内谋生活,八小时外谋发展“
我们:"待别日相见时,都已有所成”😁
一、前言
1)引入
现在小伙伴学习SpringBoot大都数是前后端开发的,这个API接口文档真的不可缺少的一部分。
我们开发好项目-->启动-->测试-->前端查看API文档-->数据渲染。用Swagger可以不用写自己写了,可以直接在代码中声明,非常方便,也易于更改。
我这个东东可以直接CV哈,没啥特殊的,直接可以跑起来滴。😁😁😁
2)介绍
Swagger 是一个用于生成、描述和调用 RESTful 接口的 Web 服务。通俗的来讲,Swagger 就是将项目中所有(想要暴露的)接口展现在页面上,并且可以进行接口调用和测试的服务。
3)作用
- 将项目中所有的接口展现在页面上,这样后端程序员就不需要专门为前端使用者编写专门的接口文档;
- 当接口更新之后,只需要修改代码中的 Swagger 描述就可以实时生成新的接口文档了,从而规避了接口文档老旧不能使用的问题;
- 通过 Swagger 页面,我们可以直接进行接口调用,降低了项目开发阶段的调试成本。
二、快速开始
案例:
写一个RESTFUL风格的增删改查哈,然后展示接口哈。
2.1、步骤:
- 新建一个SpringBoot项目
- 导入依赖
- 书写配置
- 编码
- 启动测试 -->完事👨💻(继续摸鱼)
2.2、导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
2.3、yml配置文件
server:
port: 8088
spring:
application:
name: springboot-swagger
swagger:
enable: true
2.4、SwaggerConfig配置类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @author: crush
* @date: 2020-12-01 10:48
* @EnableSwagger2 启动使用Swagger2
*/
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
// 通过配置文件中这个变量的值来开启或关闭
@Value("${swagger.enable}")
private Boolean enable;
@Bean
public Docket docket(Environment environment) {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.enable(enable)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.crush.swagger"))
.build();
}
public ApiInfo apiInfo() {
// 这里是作者信息及文档的基本信息 和页面展示信息一一对照即可
Contact contact = new Contact("springboot-swagger ", "https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45821811?spm=1011.2124.3001.5343", "951930136@qq.com");
return new ApiInfo(
"springboot-swagger Demo API接口文档",
"此处填写描述信息",
"1.0",
"urn:tos",
contact,
"Apache 2.0",
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
new ArrayList()
);
}
}
2.4、实体类
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
@ApiModel(description = "账户相关信息类")
public class Account {
@ApiModelProperty("账号")
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
private String password;
}
2.5、Service层
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 注册
* @param account
* @return
*/
boolean register(Account account);
/**
* 查询全部
*/
List<Account> select();
}
impl:我此处只是用了静态变量模拟了一下(太懒啦捂脸)
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private static List<Account> accountList = new ArrayList<Account>();
@Override
public boolean register(Account account) {
accountList.add(account);
return true;
}
@Override
public List<Account> select() {
return accountList;
}
}
2.6、Controller
@Api(tags = "账户相关接口")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/account")
public class AccountController {
private final AccountService accountService;
public AccountController(AccountService accountService) {
this.accountService = accountService;
}
@ApiOperation("注册接口")
@PostMapping("/register")
public String register(@RequestBody @ApiParam(required = true, value = "注册账户需要的信息") Account account) {
accountService.register(account);
return "OK";
}
@ApiOperation("查询全部")
@GetMapping
public List<Account> select() {
return accountService.select();
}
}
启动类就是普普通通的没啥特殊的,让我们直接开始吧。
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootSwagger {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootSwagger.class);
log.info("API接口访问链接:http://localhost:8088/swagger-ui.html");
}
}
三、测试
初始信息:
启动之后输入:就能看到页面
http://localhost:8088/swagger-ui.html
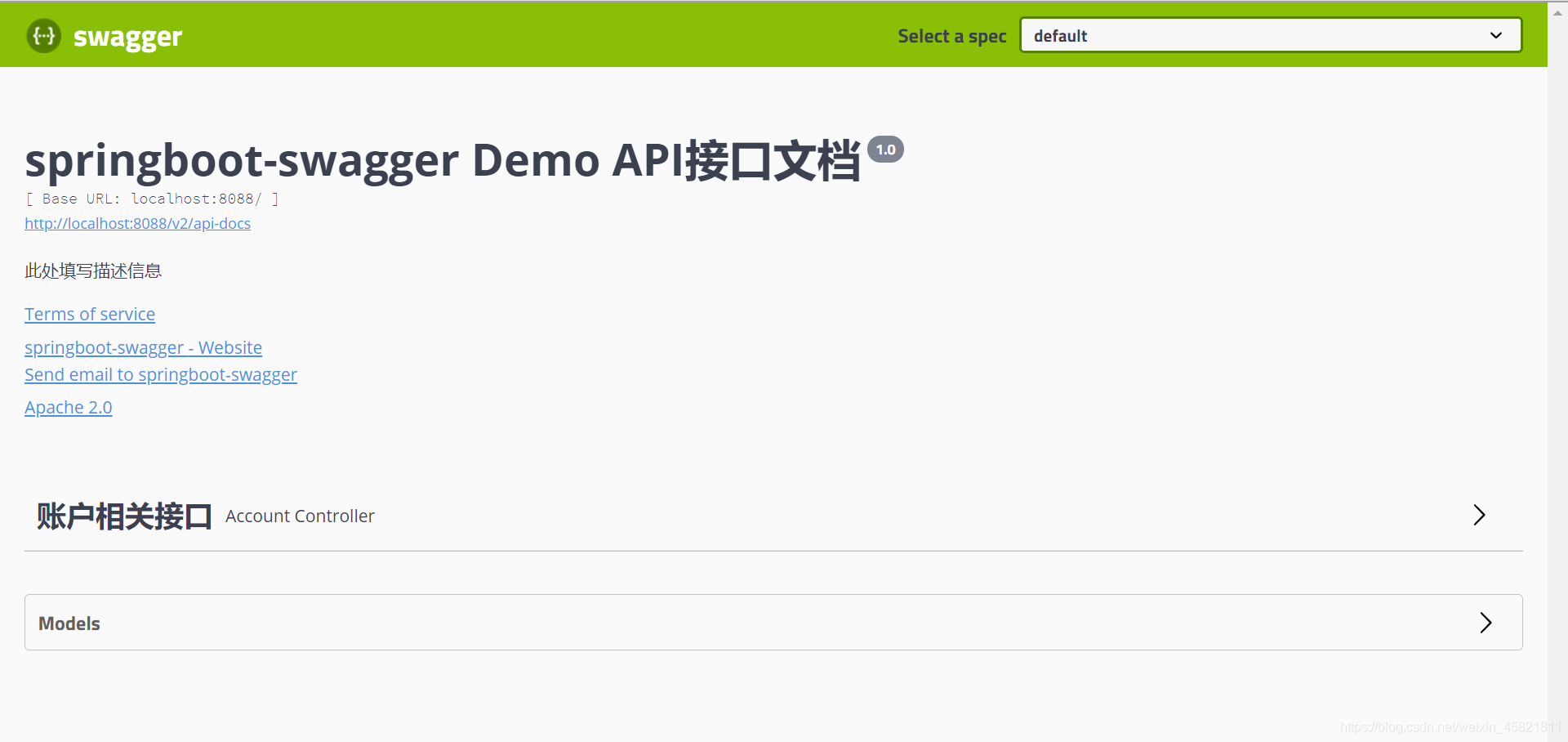
之前配置的相关信息就也会全部展示在上面。
接口:
我们点开接口看一下
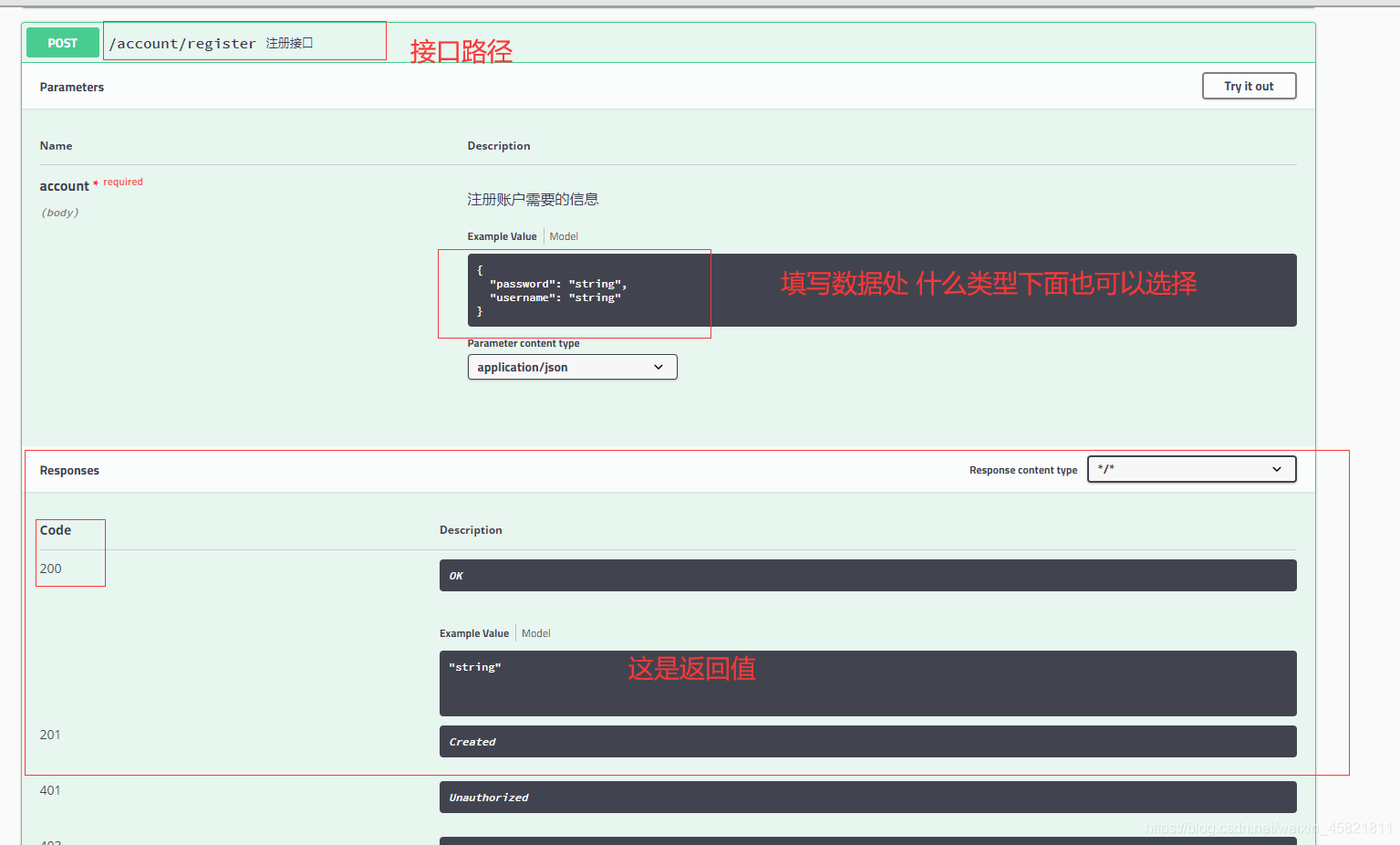
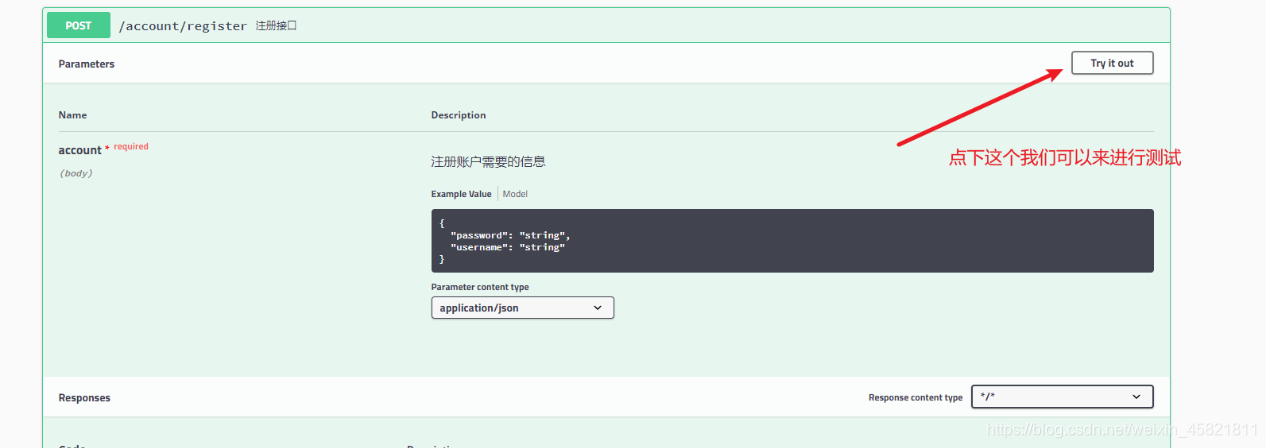
测试:
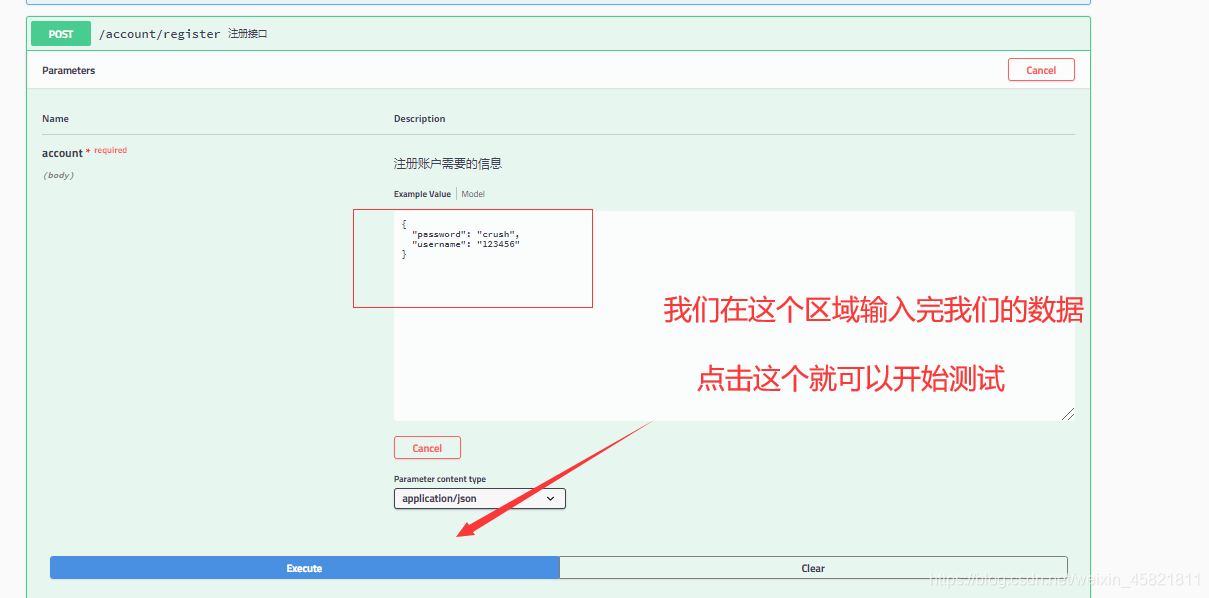
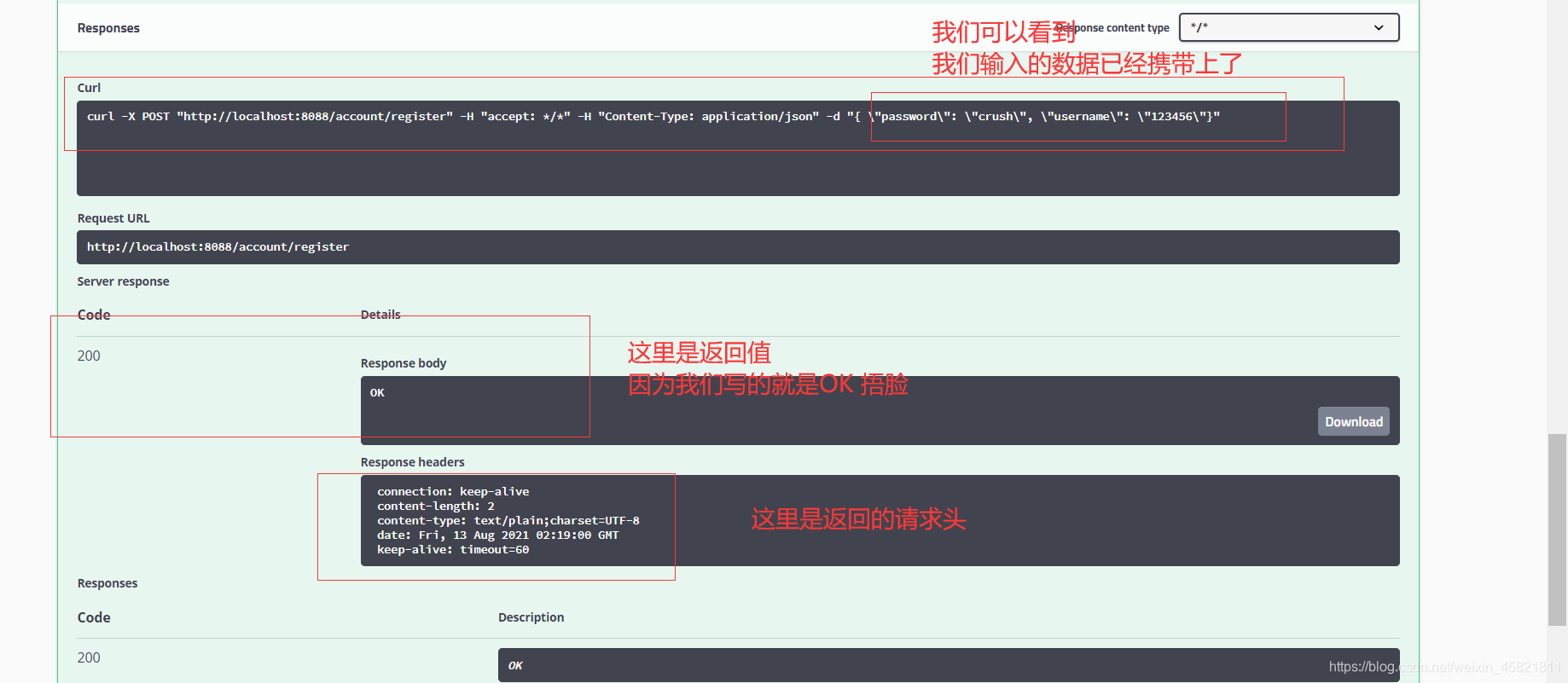
然后我们通过我们的查询接口也能够查询到了
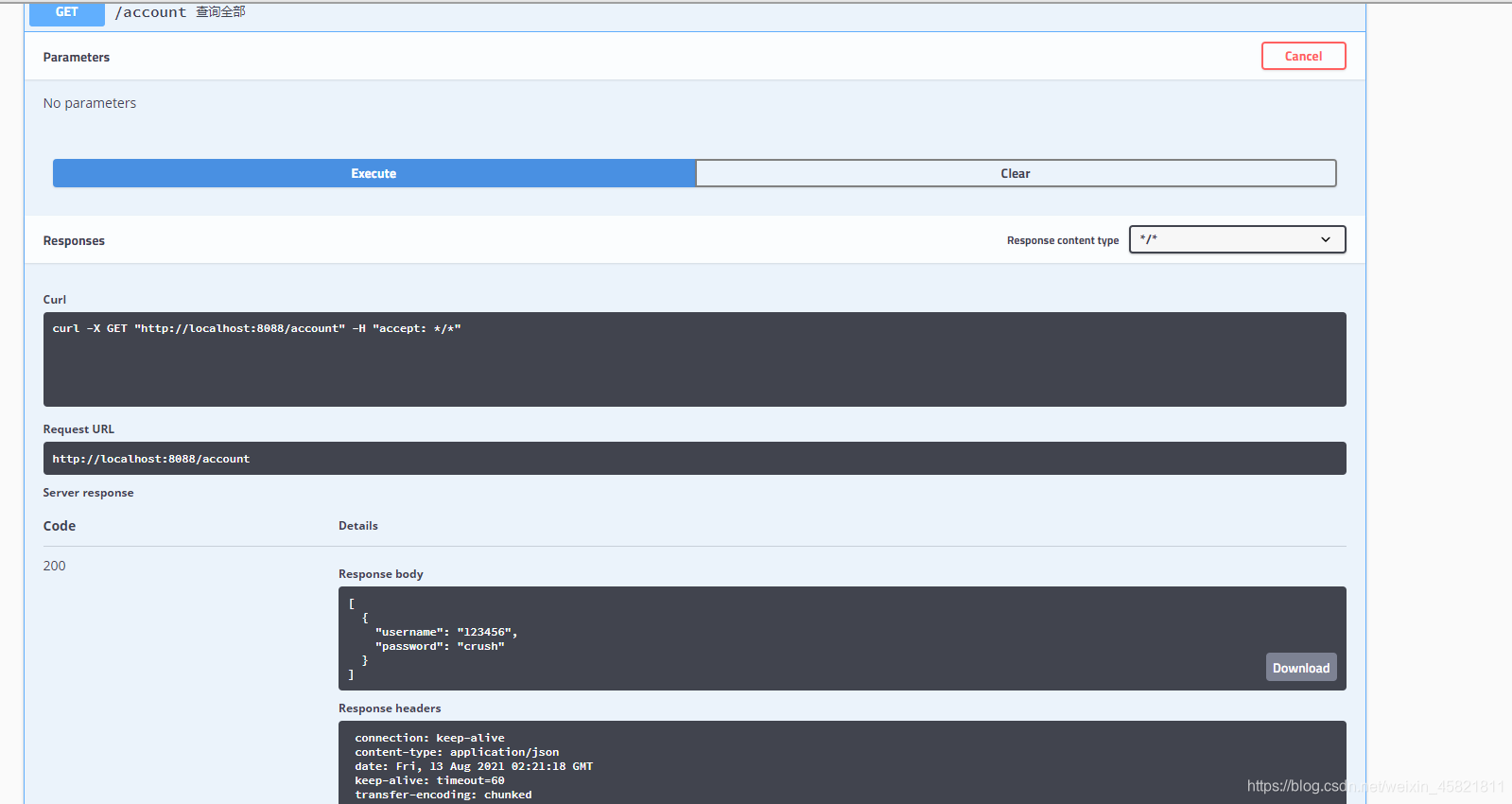
完事啦,摸鱼啦摸鱼啦👨💻
四、Swagger VS PostMan
Swagger的优点:
- 便于更改,易读简单明了,非常方便。
缺点:
- 缺点:也很明,就是不能够自动化,每次都需要自己输入数据,这点很不好。
- 但是Swagger是可以把API导入到Postman中的。下篇文章讲(狗头保命🙆♂️)
Postaman的优点:
- 可以自动化测试。
- 可以设计数据集,不用自己输入,可以保存环境变量。
缺点我我没杂感觉到。
结论:对于我们来讲,无论是Swagger和PostMan都是需要掌握的,这是最基本最基本的要求。
五、自言自语
你好,我是博主宁在春😁
如果你看到这篇文章,并且觉得对你有益的话,就给个赞吧,让我感受一下分享的喜悦吧,蟹蟹。🤗
如若有写的有误的地方,也请大家不啬赐教!!
同样如若有存在疑惑的地方,请留言或私信,定会在第一时间回复你。
持续更新中



