LCS算法
一.问题描述
如果字符串一的所有字符按其在字符串中的顺序出现在另外一个字符串二中,则字符串一称之为字符串二的子串。
注意,并不要求子串(字符串一)的字符必须连续出现在字符串二中。
二.最长公共子序列的结构
最长公共子序列的结构有如下表示:
设序列X=<x1, x2, …, xm>和Y=<y1, y2, …, yn>的一个最长公共子序列Z=<z1, z2, …, zk>,则:
- 若xm=yn,则zk=xm=yn且Zk-1是Xm-1和Yn-1的最长公共子序列;
- 若xm≠yn且zk≠xm ,则Z是Xm-1和Y的最长公共子序列;
- 若xm≠yn且zk≠yn ,则Z是X和Yn-1的最长公共子序列
 View Code
View Codeimport java.io.FileInputStream; public class LCS { public static void LCS_LENGHT(String str1, String str2) { char[] arr1 = str1.toCharArray(); char[] arr2 = str2.toCharArray(); int[][] matri = new int[arr1.length + 1][arr2.length + 1]; for (int i = 1; i <=arr1.length; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <=arr2.length; j++) { if (arr1[i - 1] == arr2[j - 1]) { matri[i][j] = matri[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; } else if (matri[i - 1][j] >=matri[i][j - 1]) { matri[i][j]=matri[i-1][j]; } else { matri[i][j]=matri[i][j-1]; } } } PRINT_LCS(matri, arr1, arr2, arr1.length,arr2.length); } public static void PRINT_LCS(int[][] matri,char[] x,char[] y,int xlength,int ylength){ if(xlength==0||ylength==0){ return; } if(x[xlength-1]==y[ylength-1]){ PRINT_LCS(matri, x, y, xlength-1, ylength-1); System.out.println(x[xlength-1]); }else if(matri[xlength - 1][ylength] >=matri[xlength][ylength - 1]){ PRINT_LCS(matri, x, y, xlength-1, ylength); }else { PRINT_LCS(matri, x, y, xlength, ylength-1); } } public static void main(String[] args) { String str1="ABCBDAB"; String str2="BDCABA"; LCS_LENGHT(str1, str2); } }
其中Xm-1=<x1, x2, …, xm-1>,Yn-1=<y1, y2, …, yn-1>,Zk-1=<z1, z2, …, zk-1>。
三.子问题的递归结构
由最长公共子序列问题的最优子结构性质可知,要找出X=<x1, x2, …, xm>和Y=<y1, y2, …, yn>的最长公共子序列,可按以下方式递归地进行:当xm=yn时,找出Xm-1和Yn-1的最长公共子序列,然后在其尾部加上xm(=yn)即可得X和Y的一个最长公共子序列。当xm≠yn时,必须解两个子问题,即找出Xm-1和Y的一个最长公共子序列及X和Yn-1的一个最长公共子序列。这两个公共子序列中较长者即为X和Y的一个最长公共子序列。
由此递归结构容易看到最长公共子序列问题具有子问题重叠性质。例如,在计算X和Y的最长公共子序列时,可能要计算出X和Yn-1及Xm-1和Y的最长公共子序列。而这两个子问题都包含一个公共子问题,即计算Xm-1和Yn-1的最长公共子序列。
与矩阵连乘积最优计算次序问题类似,我们来建立子问题的最优值的递归关系。用c[i,j]记录序列Xi和Yj的最长公共子序列的长度。其中Xi=<x1, x2, …, xi>,Yj=<y1, y2, …, yj>。当i=0或j=0时,空序列是Xi和Yj的最长公共子序列,故c[i,j]=0。其他情况下,由定理可建立递归关系如下: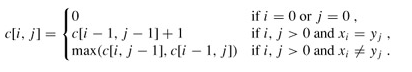 LCS源代码
LCS源代码

public class LCS { private static Set<String> set = new TreeSet<String>(); public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "ABCBDAB"; String str2 = "BDCABA"; LCS_LENGHT(str1, str2); for (String string : set) { System.out.println(string); } } public static void LCS_LENGHT(String str1, String str2) { int[][] mat = new int[str1.length() + 1][str2.length() + 1]; for (int i = 0; i <= str1.length(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= str2.length(); j++) { if(i==0||j==0) mat[i][j]=0; else if (str1.charAt(i-1) == str2.charAt(j-1)) { mat[i][j] = mat[i -1][j - 1] + 1; } else { mat[i][j]=Math.max(mat[i - 1][j] , mat[i][j - 1] ); } } } PRINT_LCS_ALL(mat, str1, str2, str1.length(), str2.length(),new String()); } //因为两个字符串的最长公共子序列不唯一,此方法返回全部的公共子序列 private static void PRINT_LCS_ALL(int[][] mat, String str1, String str2, int m, int n, String str) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) { if (str.length()!= 0) set.add(new StringBuilder(str).reverse().toString()); return; } if (str1.charAt(m-1)== str2.charAt(n-1)) { PRINT_LCS_ALL(mat, str1, str2, m - 1, n - 1, str+str1.charAt(m-1)); } else if (mat[m][n - 1] > mat[m - 1][n]) { PRINT_LCS_ALL(mat, str1, str2, m, n - 1, str); } else if (mat[m][n - 1] < mat[m - 1][n]) { PRINT_LCS_ALL(mat, str1, str2, m - 1, n, str); } else { PRINT_LCS_ALL(mat, str1, str2, m, n - 1, str); PRINT_LCS_ALL(mat, str1, str2, m - 1, n, str); } } }


