【数据结构与算法】单向链表
一.什么是链表结构?
1.1.简介
链表和数组一样, 可以用于存储一系列的元素, 但是链表和数组的实现机制完全不同,链表中的元素在内存不是连续的空间,链表的每个元素由一个存储元素本身(数据)的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(指针或者链接)组成。
通俗来说链表类似于火车: 有一个火车头, 火车头会连接一个节点, 节点上有乘客(数据), 并且这个节点会(通过指针)连接下一个节点, 以此类推...
-
链表的火车结构:

-
给火车加上数据结构后的结构:
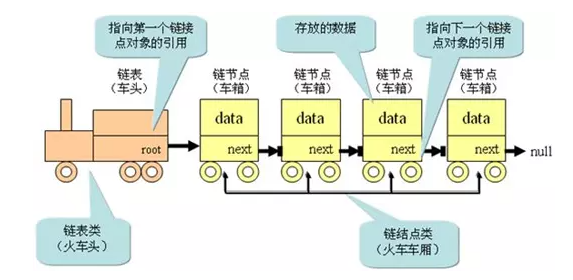
-
链表的数据结构:
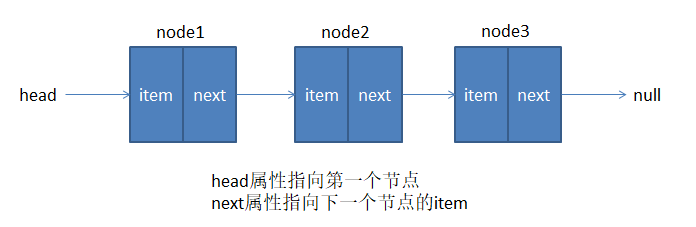
1.2.链表和数组的对比
数组存在的缺点:
- 数组的创建需要申请一段连续并且大小固定的内存空间,当数组不能满足容量的需求是,需要扩容(申请一个更大的数组,将原数组复制过去,反复创建数组会降低性能)
- 在数组开头或者中间位置插入数据的成本很高,需要进行大量元素的位移
链表的优点: - 链表中的元素在内存中不必是连续的空间,所有可以充分利用计算机的内存,实现灵活的内存动态管理
- 链表不不必在创建时确定大小,并且大小可以无限的延伸下去
- 链表在插入和删除数据时,因为不需要进行大量的位移,相对数据效率高很多
链表的缺点: - 因为其指针访问机制,当需要访问任何一个位置元素都需要从头开始访问,当链表数据量过大时性能低
- 无法像数组那样通过下标直接访问元素,访问机制都是从头开始查找
1.3.链表常见操作
- append(element):向列表尾部添加一个新的项
- insert(position, element):向列表的特定位置插入一个新的项。
- remove(element):从列表中移除一项。
- indexOf(element):返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1。
- removeAt(position):从列表的特定位置移除一项。
- isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表长度大于0则返回false。
- size():返回链表包含的元素个数。与数组的length属性类似。
- toString():由于列表项使用了Node类,就需要重写继承自JavaScript对象默认的toString方法,让其只输出元素的值。
二.封装单向链表类
2.1.创建单向链表类
// 封装单向链表类
function LinkedList() {
// 内部的类:节点类
function Node(data) {
this.data = data
this.next = null // 指向下一节点的引用默认为null
}
// 属性
this.head = null // 链表头部
this.length = 0 // 记录链表的长度
}
2.2.append(element)
代码实现
// 1.append 追加方法
LinkedList.prototype.append = function (data) {
// 1.创建新的节点
var newNode = new Node(data)
// 2.判断是否添加的是第一个节点
if (this.length === 0) {
// 2.1是第一个节点
this.head = newNode
} else {
// 2.2不是第一个节点
// 找到最后一个节点
// 判断current是否为空,为空即为链表最后一个节点,停止循环
var current = this.head // 此时this.head指向最后一个节点
while (current.next) {
current = current.next
}
// 让最后节点的next指向新添加的节点
current.next = newNode
}
// 3.length+1
this.length += 1
}
过程讲解
情况1:当添加的节点是第一个节点,直接在head后插入

情况2:当链表中已经有节点了,需要向最后的next中添加节点
-
添加一个变量current让其指向head,循环判断其next属性是否为空?
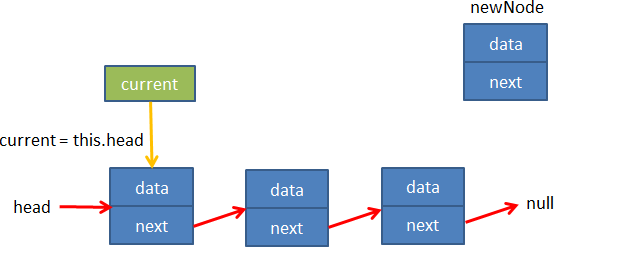
-
当current.next为空时current就是最后一个节点,此时让current.next指向添加的节点
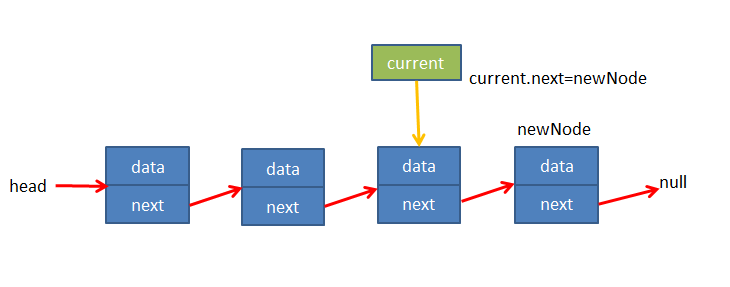
代码测试
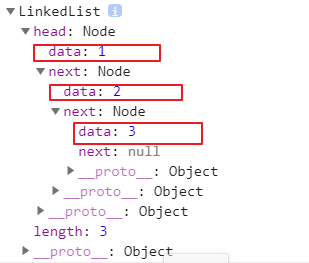
var list = new LinkedList()
list.append(1)
list.append(2)
list.append(3)
console.log(list)
2.3.toString()
代码实现
// 2.toString
LinkedList.prototype.toString = function () {
// 1.定义变量
var current = this.head
var listString = ''
// 2.循环获取一个个的节点
while (current) {
listString += current.data + ' '
current = current.next
}
return listString
}
代码测试
var list = new LinkedList()
list.append(1)
list.append(2)
list.append(3)
console.log(list.toString())

2.4.insert(positon,element)
代码实现
// 3.insert 插入 参数:传入位置和数据
LinkedList.prototype.insert = function (position, data) {
// 1.对 position 进行越界判断 不能为负数且不能超过链表长度
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return fasle
// 2.根据data创建newNode
var newNode = new Node(data)
// 3.判断插入的位置是否是第一个
if (position === 0) {
newNode.next = this.head // 先让newNode指向原第一个
this.head = newNode // 再让this.head指向插入的
} else {
var index = 0
var current = this.head
var previous = null
// 当index小于position就一直往后找
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
newNode.next = current
previous.next = newNode
}
// 4.链表长度增加1
this.length += 1
return true
}
过程解释
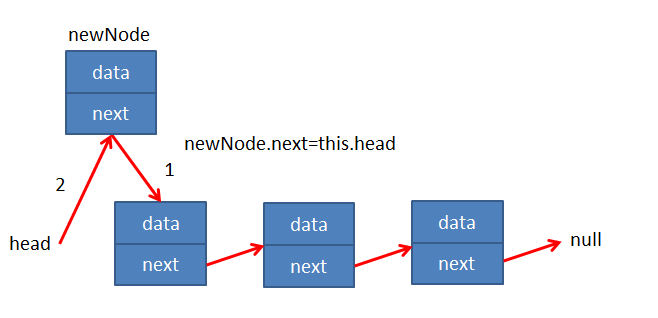
情况1:position=0
- 这个时候表示新添加的节点是头,需要将原来的头节点,作为新节点的next
- 另外这个时候的head应该指向新节点
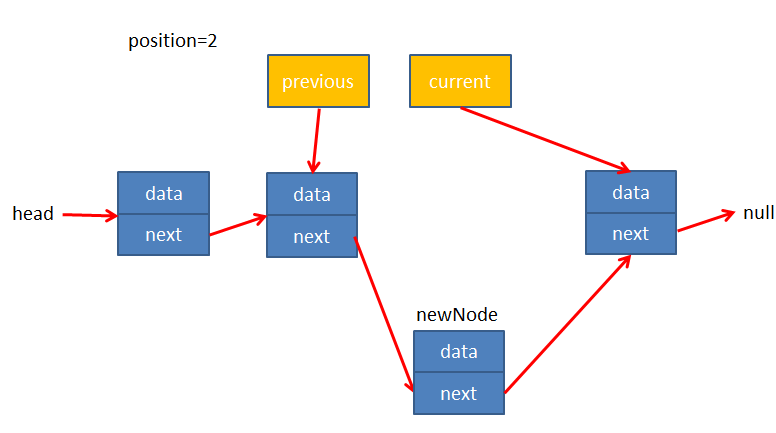
情况2:positon>0
我们需要定义两个变量previous和current分别指向需要插入位置的前一个节点和后一个节点
代码测试
var list = new LinkedList()
list.append('a')
list.append('b')
list.append('c')
list.insert(0, '我是头部插入的')
list.insert(2, '我是插入第二个的')
list.insert(5, '我是末尾插入的')

2.5.get(positon)
代码实现
// 4.get() 获取对应位置的元素
LinkedList.prototype.get = function (position) {
// 1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null
// 2.获取对应的数据
var current = this.head
var index = 0
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next
}
return current.data
}
过程解释
通过变量current指向当前数据,index保存索引,再循环判断index是否等于输入的位置
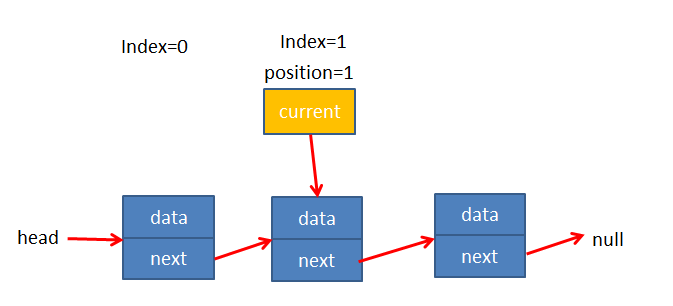
代码测试
var list = new LinkedList()
list.append('a')
list.append('b')
list.append('c')
console.log(list.get(1)) // b
2.6.indexOf(data)
代码实现
// 5.indexOf(element)返回元素在列表的索引,如果没有则返回-1
LinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function (data) {
// 1.定义变量
var current = this.head
var index = 0
// 2.开始查找
while (current) {
if (current.data === data) {
return index
}
current = current.next
index += 1
}
// 3.没有找到
return -1
}
过程解释
通过变量current指向当前数据,index保存索引,再循环判断current.data是否和输入的数据相等即可
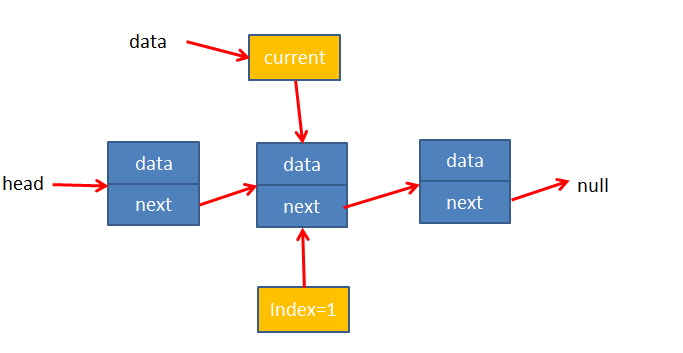
**代码测试**
// 测试代码
var list = new LinkedList()
list.append('a')
list.append('b')
list.append('c')
console.log(list.indexOf('b')) // 1
2.7.opdate(position,element)
代码实现
LinkedList.prototype.update = function (position, newData) {
// 1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null
// 2.查找正确的节点
var current = this.head
var index = 0
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next
}
// 3.将positon位置的node的data修改为新newDate
current.data = newData
return true
}
代码测试
var list = new LinkedList()
list.append('a')
list.append('b')
list.append('c')
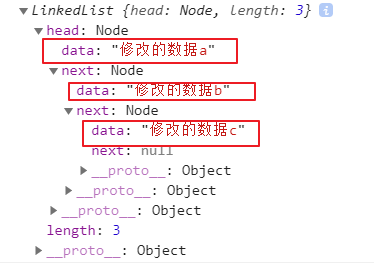
console.log(list.update(0, '修改的数据a'))
console.log(list.update(1, '修改的数据b'))
console.log(list.update(2, '修改的数据c'))
console.log(list)
2.8.removeAt(position)
代码实现
LinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function (position) {
// 1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null
var current = this.head
// 2.判断删除的是否是第一个节点
if (position === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next
} else {
var index = 0
var previous = this.head
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 让前一个节点的next指向current的next
previous.next = current.next
}
// 3.长度减小 -1
this.length -= 1
return current.data
}
}
过程解释
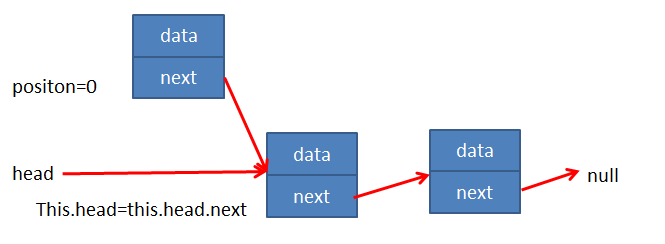
情况1:position=0
- 只需要修改 this.head 的指向即可
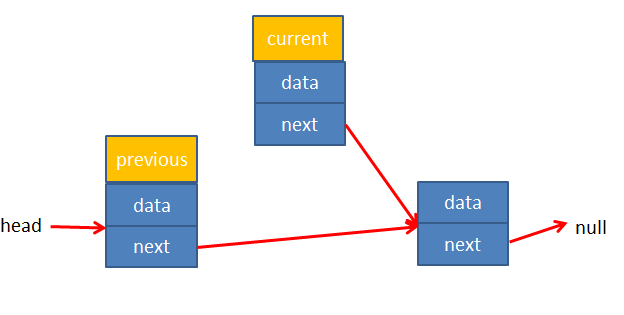
情况2:positon>0 - 这时候就需要通过变量previous和current分别指向删除元素的前一个数和需要删除的元素,再修改previous的next指向
代码测试
var list = new LinkedList()
list.append('a')
list.append('b')
list.append('c')
console.log(list.removeAt('1'))
console.log(list)
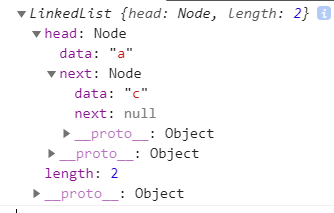
2.9.remove(element)
代码实现
LinkedList.prototype.remove = function (data) {
// 1.获取data在链表中的位置
var position = this.indexOf(data)
// 2.根据位置信息删除节点
return this.removeAt(position)
}
代码测试
var list = new LinkedList()
list.append('a')
list.append('b')
list.append('c')
console.log(list.remove('a'))
console.log(list)
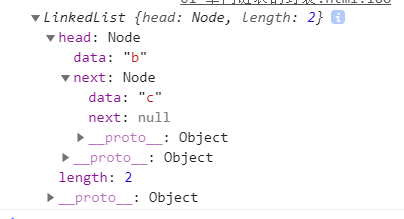
2.10.其他方法
代码实现
// 10.isEmpty()
LinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.length
}
// 11.size()
LinkedList.prototype.size = function () {
return this.length
}
代码测试
var list = new LinkedList()
list.append('a')
list.append('b')
list.append('c')
console.log(list.isEmpty()) // 3
console.log(list.size()) // 3
2.11.完整代码
// 封装单向链表类
function LinkedList() {
// 内部的类:节点类
function Node(data) {
this.data = data
this.next = null // 指向下一节点的引用默认为null
}
// 属性
this.head = null // 链表头部
this.length = 0 // 记录链表的长度
// 方法
// 1.append 追加方法
LinkedList.prototype.append = function (data) {
// 1.创建新的节点
var newNode = new Node(data)
// 2.判断是否添加的是第一个节点
if (this.length === 0) {
// 2.1是第一个节点
this.head = newNode
} else {
// 2.2不是第一个节点
// 找到最后一个节点
// 判断current是否为空,为空即为链表最后一个节点,停止循环
var current = this.head // 此时this.head指向最后一个节点
while (current.next) {
current = current.next
}
// 让最后节点的next指向新添加的节点
current.next = newNode
}
// 3.链表长度增加1
this.length += 1
}
// 2.toString
LinkedList.prototype.toString = function () {
// 1.定义变量
var current = this.head
var listString = ''
// 2.循环获取一个个的节点
while (current) {
listString += current.data + ' '
current = current.next
}
return listString
}
// 3.insert(position,data) 插入 参数:传入位置和数据
LinkedList.prototype.insert = function (position, data) {
// 1.对 position 进行越界判断 不能为负数且不能超过链表长度
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) return fasle
// 2.根据data创建newNode
var newNode = new Node(data)
// 3.判断插入的位置是否是第一个
if (position === 0) {
newNode.next = this.head // 先让newNode指向原第一个
this.head = newNode // 再让this.head指向插入的
} else {
var index = 0
var current = this.head
var previous = null
// 当index小于position就一直往后找
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
newNode.next = current
previous.next = newNode
}
// 4.链表长度增加1
this.length += 1
return true
}
// 4.get(position) 获取对应位置的元素
LinkedList.prototype.get = function (position) {
// 1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null
// 2.获取对应的数据
var current = this.head
var index = 0
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next
}
return current.data
}
// 5.indexOf(element)返回元素在列表的索引,如果没有则返回-1
LinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function (data) {
// 1.定义变量
var current = this.head
var index = 0
// 2.开始查找
while (current) {
if (current.data === data) {
return index
}
current = current.next
index += 1
}
// 3.没有找到
return -1
}
// 6.update(positon,element)
LinkedList.prototype.update = function (position, newData) {
// 1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null
// 2.查找正确的节点
var current = this.head
var index = 0
while (index++ < position) {
current = current.next
}
// 3.将positon位置的node的data修改为新newDate
current.data = newData
return true
}
// 7.removeAt(positon)
LinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function (position) {
// 1.越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null
var current = this.head
// 2.判断删除的是否是第一个节点
if (position === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next
} else {
var index = 0
var previous = this.head
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
// 让前一个节点的next指向current的next
previous.next = current.next
}
// 3.长度减小 -1
this.length -= 1
return current.data
}
// 9.remove(element)
LinkedList.prototype.remove = function (data) {
// 1.获取data在链表中的位置
var position = this.indexOf(data)
// 2.根据位置信息删除节点
return this.removeAt(position)
}
// 10.isEmpty()
LinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.length
}
// 11.size()
LinkedList.prototype.size = function () {
return this.length
}
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步