C#泛型基础知识点总结
1.0 什么是泛型
泛型是C#2.0和CLR(公共语言运行时)升级的一个新特性,泛型为.NET 框架引入了一个叫 type parameters(类型参数)的概念,type parameters 使得程序在设计的时候,不必设计其具体的参数,其具体的参数可以延迟到需要的时候声明或调用。使用泛型代码运行时避免了类型转换的装箱和拆箱操作。
2.0 泛型的延迟声明:把参数类型的声明推迟到调用,不是语法糖,而是由框架升级提供的功能
1 1 using System;
2 2 using System.Collections.Generic;
3 3 using System.Linq;
4 4 using System.Text;
5 5 using System.Threading.Tasks;
6 6
7 7 namespace _20171010Generic
8 8 {
9 9 /// <summary>
10 10 /// 泛型方法相关类
11 11 /// </summary>
12 12 public class GenericMethod
13 13 {
14 14 /// <summary>
15 15 /// 泛型方法:方法带<>和type parameters(类型参数 T)的
16 16 /// </summary>
17 17 /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
18 18 /// <param name="tParameters"></param>
19 19 public static void Show<T>(T tParameters)
20 20 {
21 21 Console.WriteLine("{0}方法,parameter={1}参数,type={2}类型", typeof(GenericMethod).Name, tParameters, tParameters.GetType().Name);
22 22 }
23 23 }
24 24 }
如代码所示,在声明泛型方法的时候没有指定具体的参数类型,等到需要调用的时候再指定,这就叫做延迟声明。泛型的设计思想(延迟思想,推迟一切可以推迟的)
1 1 using System;
2 2 using System.Collections.Generic;
3 3 using System.Linq;
4 4 using System.Text;
5 5 using System.Threading.Tasks;
6 6
7 7 namespace _20171010Generic
8 8 {
9 9 class Program
10 10 {
11 11 static void Main(string[] args)
12 12 {
13 13
14 14 int iValue = 123;
15 15 string sValue = "TestName";
16 16 DateTime dtValue = DateTime.Now;
17 17 object oValue = new object();
18 18
19 19 GenericMethod.Show(iValue);
20 20 GenericMethod.Show(sValue);
21 21 GenericMethod.Show(oValue);
22 22 GenericMethod.Show(dtValue);
23 23 Console.WriteLine("———————我是华丽的分割线————————");
24 24 GenericMethod.Show<int>(iValue);
25 25 GenericMethod.Show<string>(sValue);
26 26 GenericMethod.Show<object>(oValue);
27 27 GenericMethod.Show<DateTime>(dtValue);
28 28
29 29 Console.WriteLine("———————我是华丽的分割线————————");
30 30 Console.WriteLine(typeof(List<int>));
31 31 Console.WriteLine(typeof(Dictionary<,>));
32 32 Console.WriteLine("———————我是华丽的分割线————————");
33 33 }
34 34 }
35 35 }
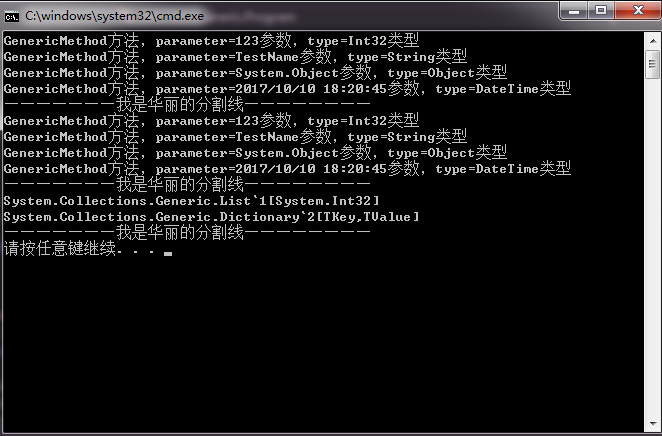
泛型方法的调用,第一种 GenericMethod.Show(iValue);调用方法不指定类型参数,在编译的时候编译器自动编译推算(语法糖),第二种 GenericMethod.Show<int>(iValue);调用方法指定类型参数,类型参数和参数类型须一致,否则编译不通过。VS2017鼠标移上去会提示可以简化方法名称。编译的时候,类型参数编译为占位符,程序运行的时候,JIT(即时编译(Just In-Time compile)即时编译为真实类型。所以使用泛型性能会比使用object作为参数的方法好,(ps:经过测试)。 Console.WriteLine(typeof(List<int>)); 和Console.WriteLine(typeof(Dictionary<,>));的运行结果中有个~1,和~2就表示类型参数的占位符。
3.0 泛型主要的四种:泛型类, 泛型方法,泛型接口,泛型委托
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _20171010Generic
{
/// <summary>
/// 动物类
/// </summary>
public class AnimalModel
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public String Name { get; set; }
public virtual void Cry()
{ }
}
public interface IEat
{
void Eat();
}
public interface ISleep
{
void Sleep();
}
/// <summary>
/// 狗类
/// </summary>
public class Dog:AnimalModel
{
public override void Cry()
{
Console.WriteLine("旺旺旺。。。。。");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 猫类
/// </summary>
public class Cat : AnimalModel
{
public override void Cry()
{
Console.WriteLine("喵喵瞄。。。。。。。");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 玫瑰花类
/// </summary>
public class Rose
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
首先先新建了一个AnimalModel类,里面定义了一个动物类,动物类里有个虚方法Cry,一个狗类,狗类继承了动物类,一个猫类,重写了虚方法Cry。一个IEat接口和ISleep接口,
1 using System;
2 using System.Collections.Generic;
3 using System.Linq;
4 using System.Text;
5 using System.Threading.Tasks;
6
7 namespace _20171010Generic
8 {
9 /// <summary>
10 /// 泛型类
11 /// </summary>
12 /// <typeparam name="T">类型参数</typeparam>
13 /// <typeparam name="S">类型参数</typeparam>
14 /// <typeparam name="K">类型参数</typeparam>
15 public class GenericClass<T, S, K>
16 {
17 /// <summary>
18 /// 无返回值的泛型方法
19 /// </summary>
20 /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
21 public void Show(T t)
22 {
23
24 }
25 /// <summary>
26 /// 有返回值的泛型方法
27 /// </summary>
28 /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
29 /// <returns></returns>
30 public T Get()
31 {
32 return default(T);
33 }
34 }
35
36 /// <summary>
37 /// 泛型接口
38 /// </summary>
39 /// <typeparam name="W"></typeparam>
40 public interface ISleep<W>
41 {
42 W Sleep(W t);
43 }
44
45 /// <summary>
46 /// 有返回值的泛型委托
47 /// </summary>
48 /// <typeparam name="Y"></typeparam>
49 /// <returns></returns>
50 public delegate Y DlgYFun<Y>();
51
52 public delegate int DlgIntFun();
53
54 /// <summary>
55 /// 泛型类
56 /// </summary>
57 /// <typeparam name="W"></typeparam>
58 /// <typeparam name="Y"></typeparam>
59 /// <typeparam name="M"></typeparam>
60 public class GenericChild<T, S, K>
61 //: GenericClass<T, S, K>直接继承泛型类
62 //: GenericClass<T, S, string>//类型参数可直接指定
63 //: ISleep<string>
64 : ISleep<T>//实现泛型接口
65 {
66 T ISleep<T>.Sleep(T t)
67 {
68 return default(T);
69 }
70 }
71
72 /// <summary>
73 /// 普通类
74 /// </summary>
75 public class Child
76 // :GenericClass<T,S,K>错误的继承,普通类不能直接继承泛型类
77 //: GenericClass<string, int, double>//必须指定全部确定的类型参数后可继承泛型
78 //:ISleep<W>错误的实现泛型接口,普通类不能直接实现泛型接口,
79 : ISleep<string>
80 {
81 public string Sleep(string t)
82 {
83 Console.WriteLine("实现了sleep泛型接口,返回参数是:{0}", t);
84 return t;
85 }
86 }
87 }
泛型类就在普通类名字后面加上<>和多个类型参数,需要注意的是 1.普通类不能直接继承泛型类和泛型接口,因为泛型的类型参数不确定,但是泛型类或泛型接口指定类型后可以继承泛型类或实现泛型接口,2.泛型类可以直接继承泛型类,也可以直接实现泛型接口,其子类的类型参数相当于声明了局部参数。
4.0泛型的约束(基类约束,接口约束,引用类型约束,值类型约束,无参构造函数约束)
回到上面写的那个GenericMethod类里的show方法,new 一个cat对象,Cat cat=new Cat(){ Id=1,Name="小黑猫"}; 然后调用genericMentod.show(cat)方法。但是如果想要在show方法里访问Id,或者Name却不行。T是个不明确类型参数,所以无法访问,如图
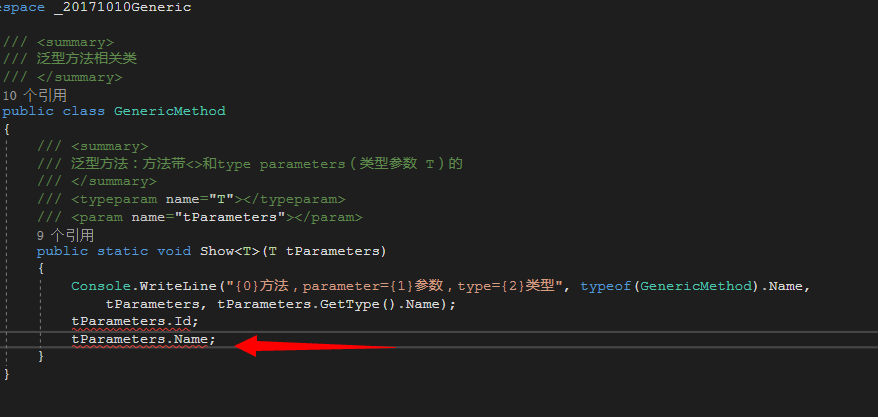
使用泛型约束解决方法:
1 using System;
2 using System.Collections.Generic;
3 using System.Linq;
4 using System.Text;
5 using System.Threading.Tasks;
6
7 namespace _20171010Generic
8 {
9 /// <summary>
10 /// 泛型约束
11 /// </summary>
12 public class Constraint
13 {
14
15 public static void Show<T>(T tParameter)
16 //where T: AnimalModel 基类约束,就可以访问该类的方法或属性
17 where T:Cat //或者该子类
18 {
19 Console.WriteLine("泛型约束show方法--------id={0},name={1}",tParameter.Id,tParameter.Name);
20 }
21
22 public static void Show(AnimalModel model)
23 {
24 Console.WriteLine("普通show方法--------id={0},name={1}", model.Id, model.Name);
25 }
26
27 public static void ShowInterface<T>(T tParameter)
28 //where T: AnimalModel 基类约束,就可以访问该类的方法或属性
29 where T : Cat,ISleep,IEat//或者该子类约束,多个接口约束
30
31 {
32 Console.WriteLine("泛型约束ShowInterface方法--------id={0},name={1}", tParameter.Id, tParameter.Name);
33 tParameter.Sleep();//接口的方法
34 tParameter.Eat();
35 }
36 }
37
Constraint类里的第一个show方法中在后面带个 where关键字 和 约束类型,泛型方法里就能访问Id和Name,第二个show方法是作为对比,虽然第二个方法也能实现同样的效果,但是相对泛型方法不灵活,泛型方法可以同时约束多个,比如第三个方法约束多个接口,和类,多个约束的关系是&&关系
泛型约束除了基类约束和接口约束几种,还有值类型约束,无参构造约束,引用类型约束等这几种。
基类约束:
1带来权利,可以使用基类里面的属性和方法。
2带来义务,类型参数必须是基类或者其子类。
1 public static T TestFun<T>()
2 // where T:class //引用类型约束
3 // where T:struct //值类型约束
4 where T : new() //无参构造函数约束
5 {
6 T t = new T();
7 return default(T);
8 }
5.0协变和逆变
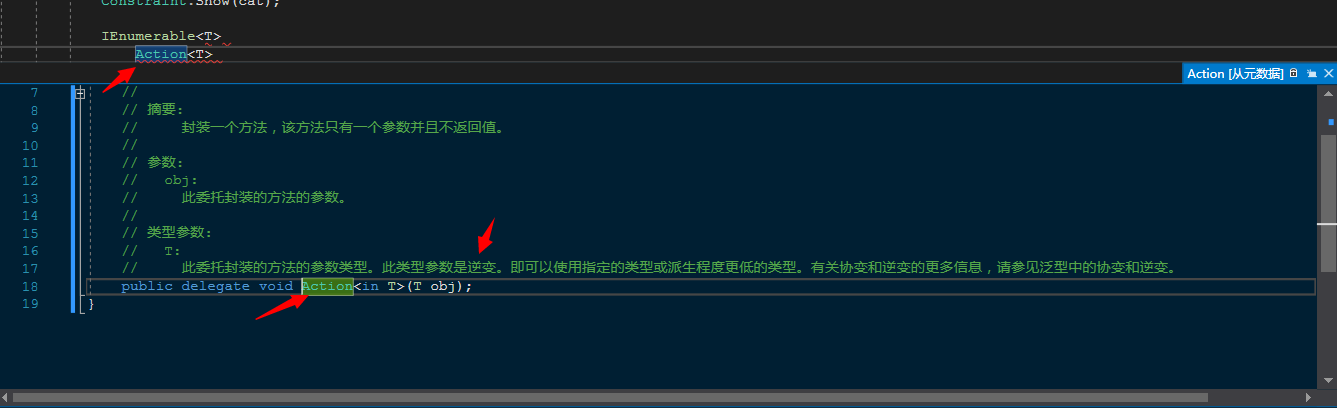
out 协变(covariant) 修饰返回值,in 逆变(contravariant) 修饰传入参数。out和in只能放在接口或者泛型委托的的参数前面,类没有协变和逆变。在.NET Framework里面,IEnumerable<T>转到定义去看,其实就是个带out参数的泛型接口,Action<T>转到定义去看就是个带in参数的泛型委托。还有一个逆变+协变的Func<T>。
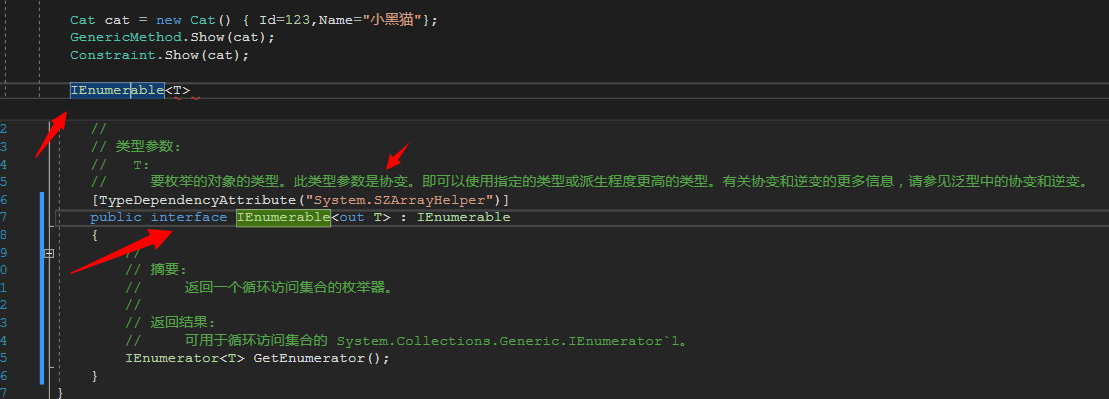
像平常一样写代码: AnimalModel animal = new AnimalModel();//实例化一个动物。
Dog dog = new Dog();//实例化一个条狗
AnimalModel dog2 = new Dog();//实例化一条狗(狗继承了动物父类,父类出现的地方都可以用子类代替,对的,狗一定是个动物),左边父类,右边子类。
// Dog dog3 = new AnimalModel();动物不一定是条狗,程序编译不通过
new一条狗没问题,new 一群狗试试看。
List<Dog> dogList = new List<Dog>();//实例化一群狗(编译通过)
List<AnimalModel> animalDog = new List<Dog>();//实例化一群狗(语法上不通过)
理论上来说第二种实例化一群狗的方式是没毛病的,一群狗也一定是一群动物,但是程序上是不通过是因为Listt<T>是个泛型 List<Dog>不是继承List<AnimalModel>,没有父子关系,程序只认关系。。。
要使上面那句代码编译通过,可以通过lambda表达式转化 List<AnimalModel> animalDog = new List<Dog>().Select(x => (AnimalModel)x).ToList();把每条狗都转换一遍
使用IEnumerable:IEnumerable<AnimalModel> animalDog= new List<Dog>(); //这就叫协变。IEnumerable<out T>在编译的时候就通过转化了,我个人理解为out 是表示转化后的T返回标识。平常在工作中,有用过out 关键字作为标识的返回参数,会用,但是不其所以然。原理明白后自己也可以定义一个协变的泛型接口。
1 public interface IMyTest<out T> 2 { 3 4 } 5 public class Test<T> : IMyTest<T> 6 { 7 8 } 9 10 11 IMyTest<Animal> test3 = new Test<Dog>();
逆变就和协变相反。逆变的in 的参数只能作为传入值,不能作为返回值。说白了,也是一种约束。协变和逆变的关键作用就是让编译器在运行时不报错。
1 1 public interface IMyTest<inT> 2 2 { 3 3 4 4 } 5 5 public class Test<T> : IMyTest<T> 6 6 { 7 7 8 8 } 9 9 10 10 11 11 IMyTest<Dog> test3 = new Test<Animal>();
为什么要用泛型:泛型就是为了满足不同类型,相同代码的重用
关于泛型的知识点还有很多,比如还有泛型的缓存,这个就有点难理解了。以上知识点是我平常通过各种途径学习总结的几点。如有不对欢迎指正。欢迎转载和分享,转载分享时请注明原创出处:如此拉风的女人



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号