timer,runloop,thread,task小总结(转)
对这几个也算不上有很深的理解,只是平时用到些许timer,thread。
想起有次去baidu笔试遇到runloop和timer等的区别,当时就不会。
两三月过去了,如今终于稍微整理了下。
有不对的地方盼指正。
(版权所有哦)
· NSThread:常见的线程
每个进程里都有多个线程,我们一般如下实用thread:
[NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(myThreadMainMethod:) toTarget:self withObject:nil];
如果函数需要输入参数,那么可以从object传进去。你也可以这样实现
NSThread* myThread = [[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(myThreadMainMethod:) object:nil];
[myThread start]; // Actually create the thread
(from apple: threading PG)
你的对象也可以直接使用线程:
[myObj performSelectorInBackground:@selector(doSomething) withObject:nil];
· NSTimer:定时器
等待一定时间后,触发某个事件发生,可循环触发。默认是添加到当前runloop。你也可以添加到自己新建的runloop里去,注意如果添加的话runloop会retain timer,你应当release timer而将timer交给runloop,就像将operation加入operationQueue中一样。
可以很简单的调用:
[NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:2 target:self selector:@selector(addLabel) userInfo:nil repeats:YES];
- (void)addLabel
{
label.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d",num++];
}
每隔2秒,就触发定时器,向self发送addLabel消息。
· NSRunLoop
当有输入信号(input source,比如键盘鼠标的操作、),NSPort和NSConnection对象时,runloop提供了一个程序接口,即等待输入。但是我们从来都不需要去创建或者去管理一个runloop。在每个进程中都相应的有runloop,不管时当前的主进程还是你新建的进程。如果需要访问当前进程的runloop可以调用类方法:+ (NSRunLoop *)currentRunLoop。
[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] performSelector:@selector(addLabel2)
target:self
argument:nil
order:0
modes:[NSArray arrayWithObjects:@"NSDefaultRunLoopMode",nil]]
//举个例子而已,一般不会这样用
一般需要使用runloop也就是对于netservice,stream等对象以某种模式schedule在当前的runloop,如:
[[_session inputStream] scheduleInRunLoop:[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] forMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode];。
Runloop的作用在于当有事情要做时它使当前的thread工作,没有事情做时又使thread 休眠sleep。注意Runloop并不是由系统自动控制的,尤其是对那些你新建的次线程你需要对其进行显示的控制。
Runloop顾名思义就是一个不停的循环,不断的去check输入,如下图。
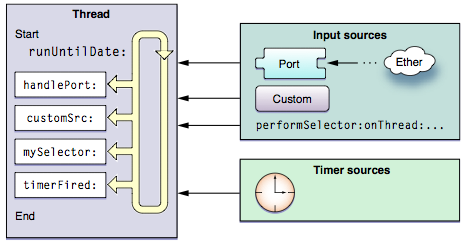
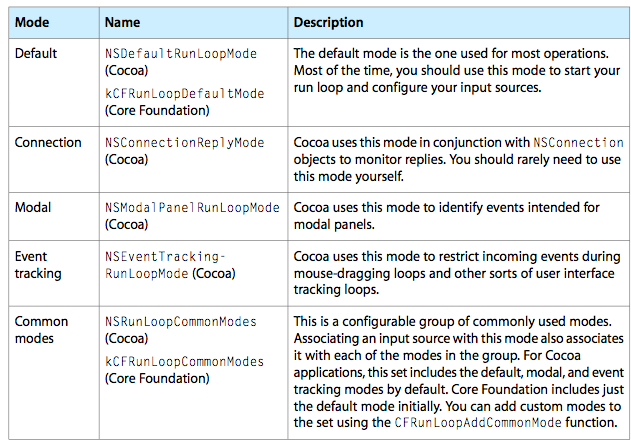
我们需要了解runloop modes这对判断事件来源以及添加到runloop时很有必要。
正如之前我们所说,只有创建了次线程才需要我们管理runloop,但是也并不是创建了次线程就一定需要管理runloop,仅当:
o Use ports or custom input sources to communicate with other threads.
o Use timers on the thread.
o Use any of the performSelector... methods in a Cocoa application.
o Keep the thread around to perform periodic tasks.
你还可以注册runloop,这样可以使用kvo。
· NSTask:
使用task你可以运行其它程序作为当前程序的子进程,并监控它的运行。它和线程的不同之处在于它并不何创建它的进程(父进程)共享内存。可以说是“完全”独立的一个东西。




