源码分析之Dictionary笔记
接下来我们一步步来熟悉 Dictionary的底层结构实现,下面的MyDictionary等同于源码中的Dictionary看待。
首先我们定义一个类 MyDictionary,类中定义一个结构Entry,用来存储我们的key和value,除此之外,我们还要定义一个int变量用于存储key的hashCode,因为我们是根据hash值来查找的,然后我们再定义一个next变量 用于内部指向同一个桶下的下一个Entry(发生桶碰撞时,采用链式把冲突的链起来,即拉链法)
public class MyDictionary<TKey, TValue> { ....... private struct Entry { public int hashCode; // 31 位 hash code, -1 表示未用 public int next; // 下一个Entry的索引位置 -1 表示链最后一个 public TKey key; // Key of entry public TValue value; // Value of entry } ..... }
接下来接下来我们一个个加 其他字段,先简单说下这个hashCode到时候是怎么赋值的
我们源代码中是
int hashCode =comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
comparer是我们定义的一个类型为 IEqualityComparer<TKey> 的私有变量,而这个私有变量的赋值是在我们MyDictionary构造函数中赋值的。
这里另外说下 0x7FFFFFFF ,这个是16进制表示的 表示的和Int32.Max是一样的,即2147483647 。(hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) 将会得到一个正整数
这里取与操作是想要得到一个正整数,因为hash是与数组的index有关,这样可以避免出现下标为负数而出现异常。而且有趣的是 这个最大数也是个质数。
MyDictionary 构造函数有好多重载方法,主要参数有两个,一个是初始容量,另一个就是这个IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer
假设我们定义一个 var dic=Dictionary<int,string>();
public MyDictionary(): this(0, null) //走这里 { } public MyDictionary(int capacity): this(capacity, null) { } public MyDictionary(IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer): this(0, comparer) { } public MyDictionary(int capacity, IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer) //然后到这里 { if (capacity < 0) { throw new Exception("capacity异常"); } if (capacity > 0) Initialize(capacity); //初始化容器
this.comparer = comparer ?? EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default; //然后到这里 }
可以看到,我们没有指定它,这个comparer 用的是 EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default;
Dictionary内部的比较都是通过这个实例来进行的。我们继续看它源码级别的定义
public abstract class EqualityComparer<T> : IEqualityComparer, IEqualityComparer<T> { static readonly EqualityComparer<T> defaultComparer = CreateComparer(); public static EqualityComparer<T> Default { get { return defaultComparer; } } private static EqualityComparer<T> CreateComparer() //走到这里 { RuntimeType t = (RuntimeType)typeof(T); // Specialize type byte for performance reasons if (t == typeof(byte)) { return (EqualityComparer<T>)(object)(new ByteEqualityComparer()); } // If T implements IEquatable<T> return a GenericEqualityComparer<T> if (typeof(IEquatable<T>).IsAssignableFrom(t)) { return (EqualityComparer<T>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(GenericEqualityComparer<int>), t); } if (t.IsGenericType && t.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(Nullable<>)) { RuntimeType u = (RuntimeType)t.GetGenericArguments()[0]; if (typeof(IEquatable<>).MakeGenericType(u).IsAssignableFrom(u)) { return (EqualityComparer<T>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(NullableEqualityComparer<int>), u); } } // See the METHOD__JIT_HELPERS__UNSAFE_ENUM_CAST and METHOD__JIT_HELPERS__UNSAFE_ENUM_CAST_LONG cases in getILIntrinsicImplementation if (t.IsEnum) { TypeCode underlyingTypeCode = Type.GetTypeCode(Enum.GetUnderlyingType(t));
switch (underlyingTypeCode)
{
case TypeCode.Int16: // short
return (EqualityComparer<T>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(ShortEnumEqualityComparer<short>), t);
case TypeCode.SByte:
return (EqualityComparer<T>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(SByteEnumEqualityComparer<sbyte>), t);
case TypeCode.Int32:
case TypeCode.UInt32:
case TypeCode.Byte:
case TypeCode.UInt16: //ushort
return (EqualityComparer<T>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(EnumEqualityComparer<int>), t);
case TypeCode.Int64:
case TypeCode.UInt64:
return (EqualityComparer<T>)RuntimeTypeHandle.CreateInstanceForAnotherGenericParameter((RuntimeType)typeof(LongEnumEqualityComparer<long>), t);
}
} // Otherwise return an ObjectEqualityComparer<T> return new ObjectEqualityComparer<T>(); }
这个大致可以概括为:在CreateComparer我们可以看到如果我们的类型不是byte、没实现IEquatable<T>接口、不是Nullable<T>、不是enum的话,会默认给我们创建一个ObjectEqualityComparer<T>()。
ObjectEqualityComparer<T>(); 这个的源码定义为:
internal class ObjectEqualityComparer<T> : EqualityComparer<T> { public override bool Equals(T x, T y) { if (x != null) { if (y != null) return x.Equals(y); return false; } if (y != null) return false; return true; } public override int GetHashCode(T obj) { if (obj == null) return 0; return obj.GetHashCode(); } // Equals method for the comparer itself. public override bool Equals(Object obj) { ObjectEqualityComparer<T> comparer = obj as ObjectEqualityComparer<T>; return comparer != null; } public override int GetHashCode() { return this.GetType().Name.GetHashCode(); } }
要注意的是 这个 ObjectEqualityComparer 下的Equal方法 对于像值类型是有装箱操作的
我们使用Dictionary的时候一般的习惯应该就上面那样用,这种使用方法在我们使用内置的类型当key的时候没有问题,但是如果我们需要将一个自定义的值类型(struct)当作key的时候就需要注意了。这里有一个很容易忽略的问题,会导致使用Dictionary的时候带来大量不必要的性能开销。
我们先做一个实验来比较一下值类型和类作为key的性能有多大的差距。实验代码如下,这段代码中我插入1000个到10000个数据来得到所需要的时间。
ublic class/struct CustomKey { public int Field1; public int Field2; public override int GetHashCode() { return Field1.GetHashCode() ^ Field2.GetHashCode(); } public override bool Equals(object obj) { CustomKey key = (CustomKey)obj; return this.Field1 == key.Field1 && this.Field2 == key.Field2; } } Dictionary<CustomKey, int> dict = new Dictionary<CustomKey, int>(); int tryCount = 50; double totalTime = 0.0; for (int count = 1000; count < 10000; count += 1000) { for (int j = 0; j < tryCount; j++) { Stopwatch watcher = Stopwatch.StartNew(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { CustomKey key = new CustomKey() { Field1 = i * 2, Field2 = i * 2 + 1 }; dict.Add(key, i); } watcher.Stop(); dict.Clear(); totalTime += watcher.ElapsedMilliseconds; } Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", count, totalTime / tryCount); }
结果是这样子的:
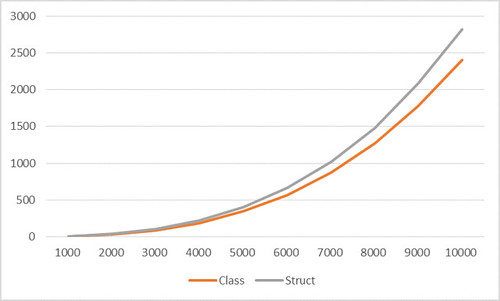
原因就在于:ObjectEqualityComparer的默认实现中会存在着很多的装箱操作,它是用来将值类型装箱成引用类型的。这个操作是很耗时的,因为它需要创建一个object并将值类型中的值拷贝到新创建的对象中。
说完hashCode,我们接下来引入几个私有字段
private int[] buckets; private Entry[] entries; private int count; private int version; private int freeList; private int freeCount;
前两个数组,一个是桶数组,存储对对应的Entry的的索引的,当然这个桶的索引也是有意义的,是根据哈希值与桶的总个数(即数组长度)取与,取选择我们的每个key/value应该存到哪个桶下关联的Entry下,另一个是存储每个Entry的数字。这两个数字的长度是一样的,扩容的时候都是一起扩的,她们是对应着的。
count表示当前MyDictionary有存了多少个有效的 key/value了,就是Entry[]下有多少个已经被用了,version表示MyDictionary的版本,每次对MyDictionary做新增或修改删除操作,版本都会加1,当然查询是不会的。这就是下面这个代码走第二个的时候会报错的根源
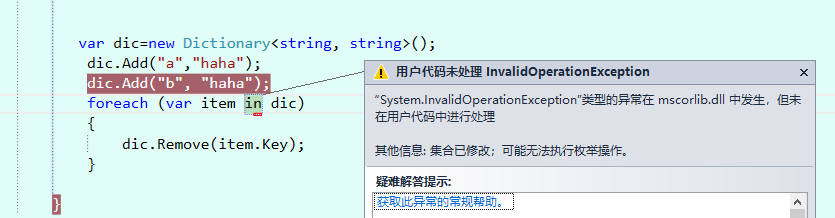
因为每次遍历时候都会去检查版本号,如果版本号发生改变了,那说明这个dictionary已经变了,就报错了。
freeList表示的是entries[] 中没有存东西的索引最小值,方便下次添加key/value时优先选择存储到那个位置,因为在MyDictionary后期可能会移除某个key/value,不能保证entries[]索引小的一定会有值 。freeCount表示没有使用过的个数。
接下来说下 MyDictionary的 Initialize(capacity); //初始化容器
private void Initialize(int capacity) { int size = HashHelpers.GetPrime(capacity); // 获取 capacity 下的最大 质数 size 应该第一个取的3吧,好像不是2 buckets = new int[size]; for (int i = 0; i < buckets.Length; i++)
{
buckets[i] = -1; //表示没有用
} entries = new Entry[size]; freeList = -1; }
HashHelpers.GetPrime(capacity); 当传0的时候,取的是内部定义的一个变量 primes 的第一个 应该是3
public static int GetPrime(int min)
{
if (min < 0)
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Arg_HTCapacityOverflow"));
Contract.EndContractBlock();
for (int i = 0; i < primes.Length; i++)
{
int prime = primes[i];
if (prime >= min) return prime;
}
//outside of our predefined table.
//compute the hard way.
for (int i = (min | 1); i < Int32.MaxValue;i+=2) // (min | 1) 能确保是奇数
{
if (IsPrime(i) && ((i - 1) % Hashtable.HashPrime != 0))
return i;
}
return min;
}
内部定义的一个一个静态变量 primes ,预存了七十来个,这样不用每次都动态算质数,如果实在是太大了,超过了我们预置的这么多,那只好去算传的数下最大质数了
public static readonly int[] primes = { 3, 7, 11, 17, 23, 29, 37, 47, 59, 71, 89, 107, 131, 163, 197, 239, 293, 353, 431, 521, 631, 761, 919, 1103, 1327, 1597, 1931, 2333, 2801, 3371, 4049, 4861, 5839, 7013, 8419, 10103, 12143, 14591, 17519, 21023, 25229, 30293, 36353, 43627, 52361, 62851, 75431, 90523, 108631, 130363, 156437, 187751, 225307, 270371, 324449, 389357, 467237, 560689, 672827, 807403, 968897, 1162687, 1395263, 1674319, 2009191, 2411033, 2893249, 3471899, 4166287, 4999559, 5999471, 7199369}
接下面我们看看Add操作,
public virtual void Add(Object key, Object value) { Insert(key, value, true); //调用的是私有方法 Insert }
私有方法 Insert
private void Insert(TKey key, TValue value, bool add) { if( key == null ) { ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key); } if (buckets == null) Initialize(0); int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF; int targetBucket = hashCode % buckets.Length; //对应要放到哪个桶的索引 #if FEATURE_RANDOMIZED_STRING_HASHING int collisionCount = 0; #endif //for循环开始 是对现有的检查碰撞的,当发现新加的key也放到的这个桶下,去检查这个桶下有没有相同的key值,如果有,并且是add(默认也是),就抛出异常
如果不是 记录累计碰撞次数,继续向下走
for (int i = buckets[targetBucket]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next) {
if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) {
if (add) {
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentException(ExceptionResource.Argument_AddingDuplicate);
}
entries[i].value = value;
version++;
return;
}
#if FEATURE_RANDOMIZED_STRING_HASHING
collisionCount++;
#endif
} //for循环结束
int index;
//指的是 要存在 Entry[]下哪个地方的索引
if (freeCount > 0) {
index = freeList;
freeList = entries[index].next;
freeCount--;
} else {
//如果哈希表存放哈希值已满,则重新从primers数组中取出值来作为哈希表新的大小 if (count == entries.Length) { Resize(); targetBucket = hashCode % buckets.Length; }
// 大小如果没满的逻辑 index = count; count++; } entries[index].hashCode = hashCode; entries[index].next = buckets[targetBucket]; entries[index].key = key; entries[index].value = value; buckets[targetBucket] = index; version++; #if FEATURE_RANDOMIZED_STRING_HASHING #endif }
综上可以看出 我们每次新add 一个,都是从 entries[] 的由索引小到大依次存的, 而每次存的Entry 下的next都是存的 上次对应的桶存的值,即上次关联到这个桶的entries的索引,同时,桶的存的值也改成最新Entries的索引,这样就通过 桶 形成了Entry的链关系,
这里链的关系如果理解的,我想我们查key的时候,你应该也会推出来 可以推测查找的时候,首先根据key值得到 targetBucket,然后去找 entries[targetBucket]下的key,如果和要查找的不一样,就判断他的next是不是>-1如果是 继续判断 entries [ entries[targetBucket].next ]的key,依次类推,直到找到key一样,就是这么一个链。
接下来我们开始一个图的概述(注意图中的 -1中 负不太清晰,容易看成 1):
初始化后:

添加元素时,集合内部Bucket和entries的变化
Test.Add(4,”4″)后:
根据Hash算法: 4.GetHashCode()%7= 4,因此碰撞到buckets中下标为4的槽上,此时由于Count为0,因此元素放在Entries中第0个元素上,添加后Count变为1

Test.Add(11,”11″)
根据Hash算法 11.GetHashCode()%7=4,因此再次碰撞到Buckets中下标为4的槽上,由于此槽上的值已经不为-1,此时Count=1,因此把这个新加的元素放到entries中下标为1的数组中,并且让Buckets槽指向下标为1的entries中,下标为1的entry之下下标为0的entries。

Test.Add(18,”18″)
我们添加18,让HashCode再次碰撞到Buckets中下标为4的槽上,这个时候新元素添加到count+1的位置,并且Bucket槽指向新元素,新元素的Next指向Entries中下标为1的元素。此时你会发现所有hashcode相同的元素都形成了一个链表,如果元素碰撞次数越多,链表越长。所花费的时间也相对较多。

Test.Add(19,”19″)
再次添加元素19,此时Hash碰撞到另外一个槽上,但是元素仍然添加到count+1的位置。

我们发现 插入的过程中还涉及到扩容,当entryies[]满了,或者碰撞次数大于阈值(默认设的100,HashHelpers.HashCollisionThreshold=100) 接下来我们看看扩容相关的 Resize()
private void Resize() { Resize(HashHelpers.ExpandPrime(count), false); }
我们看下 HashHelpers的 ExpandPrime的方法,他返回了一个我们要扩容的大小
public const int MaxPrimeArrayLength = 0x7FEFFFFD; //2146435069 一个界限 保证新的容量最大 2G元素
public static int ExpandPrime(int oldSize) { int newSize = 2 * oldSize; // Allow the hashtables to grow to maximum possible size (~2G elements) before encoutering capacity overflow. // Note that this check works even when _items.Length overflowed thanks to the (uint) cast if ((uint)newSize > MaxPrimeArrayLength && MaxPrimeArrayLength > oldSize) { Contract.Assert( MaxPrimeArrayLength == GetPrime(MaxPrimeArrayLength), "Invalid MaxPrimeArrayLength"); return MaxPrimeArrayLength; } return GetPrime(newSize); }
可以看出 每次扩容是 原来容量的两倍下的最大质数,并且最大2G个元素。然后去Resize()
private void Resize(int newSize, bool forceNewHashCodes) { Contract.Assert(newSize >= entries.Length); int[] newBuckets = new int[newSize]; for (int i = 0; i < newBuckets.Length; i++) newBuckets[i] = -1; Entry[] newEntries = new Entry[newSize];
//把原来存的复制到新开辟的newEntries中 Array.Copy(entries, 0, newEntries, 0, count);
//如果为是,去重算每个存的key值的hashCode if(forceNewHashCodes) { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if(newEntries[i].hashCode != -1) { newEntries[i].hashCode = (comparer.GetHashCode(newEntries[i].key) & 0x7FFFFFFF); } } }
//去重算每个key数据的 next,并更新桶的存的entries的新索引位置 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (newEntries[i].hashCode >= 0) { int bucket = newEntries[i].hashCode % newSize; newEntries[i].next = newBuckets[bucket]; newBuckets[bucket] = i; } } buckets = newBuckets; entries = newEntries; }
从扩容中可以看到,我们新做了个数组,把原来的存的数据复制到了新的下面,并重算hashCode和建立新的关系。当然我们内部有对 这个 forceNewHashCodes参数传true和false的时候,我们直接调 Resize();是默认为false的,不需要重算每个数据的hashCode,但是哈希碰撞到阈值后 会传true,这时候会去重算每个数据的hashCode。
#if FEATURE_CORECLR // In case we hit the collision threshold we'll need to switch to the comparer which is using randomized string hashing // in this case will be EqualityComparer<string>.Default. // Note, randomized string hashing is turned on by default on coreclr so EqualityComparer<string>.Default will // be using randomized string hashing if (collisionCount > HashHelpers.HashCollisionThreshold && comparer == NonRandomizedStringEqualityComparer.Default) { comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>) EqualityComparer<string>.Default; Resize(entries.Length, true); } #else if(collisionCount > HashHelpers.HashCollisionThreshold && HashHelpers.IsWellKnownEqualityComparer(comparer)) { comparer = (IEqualityComparer<TKey>) HashHelpers.GetRandomizedEqualityComparer(comparer); Resize(entries.Length, true); } #endif // FEATURE_CORECLR
如果我们达到了碰撞阈值,我们需要切换到使用随机字符串散列的比较器(切换比较器了)。注意,随机字符串散列在corecrl上默认打开,因此equalitycomparer<string>.Default 使用随机字符串哈希,即 单链接的节点数(冲突数)达到了一定的阈值,之后更新散列值,重新进行一次Hash操作,重排元素,以减少冲突概率,从而提高插入和查询时的效率
public static IEqualityComparer GetRandomizedEqualityComparer(object comparer) { Contract.Assert(comparer == null || comparer == System.Collections.Generic.EqualityComparer<string>.Default || comparer is IWellKnownStringEqualityComparer); if(comparer == null) { return new System.Collections.Generic.RandomizedObjectEqualityComparer(); } if(comparer == System.Collections.Generic.EqualityComparer<string>.Default) { return new System.Collections.Generic.RandomizedStringEqualityComparer(); } IWellKnownStringEqualityComparer cmp = comparer as IWellKnownStringEqualityComparer; if(cmp != null) { return cmp.GetRandomizedEqualityComparer(); } Contract.Assert(false, "Missing case in GetRandomizedEqualityComparer!"); return null; }
对应是key类型是 string 的比较器,获取哈希值,是调用底层的 String.InternalMarvin32HashString
public int GetHashCode(String obj) { if(obj == null) return 0; return String.InternalMarvin32HashString(obj, obj.Length, _entropy); }
接下来我们说说删除操作
删除元素时集合内部的变化
Test.Remove(4)
我们删除元素时,通过一次碰撞,并且沿着链表寻找3次,找到key为4的元素所在的位置,删除当前元素。并且把FreeList的位置指向当前删除元素的位置,FreeCount置为1

Test.Remove(18)
删除Key为18的元素,仍然通过一次碰撞,并且沿着链表寻找2次,找到当前元素,删除当前元素,并且让FreeList指向当前元素,当前元素的Next指向上一个FreeList元素。
此时你会发现FreeList指向了一个链表,链表里面不包含任何元素,FreeCount表示不包含元素的链表的长度。

Test.Add(20,”20″)
再添加一个元素,此时由于FreeList链表不为空,因此字典会优先添加到FreeList链表所指向的位置,添加后FreeCount减1,FreeList链表长度变为1

通过以上试验,我们可以发现Dictionary在添加,删除元素按照如下方法进行:
- 通过Hash算法来碰撞到指定的Bucket上,碰撞到同一个Bucket槽上所有数据形成一个单链表
- 默认情况Entries槽中的数据按照添加顺序排列
- 删除的数据会形成一个FreeList的链表,添加数据的时候,优先向FreeList链表中添加数据,FreeList为空则按照count依次排列
- 字典查询及其的效率取决于碰撞的次数,这也解释了为什么Dictionary的查找会很快
最后附上一大源码:

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace StructScript { /// <summary> /// 哈希表的查找算法主要分为两步: /// 第一步是用哈希函数将键转换为数组的一个索引,理想情况下不同的键都能转换为不同的索引值,但是实际上会有多个键哈希到到相同索引值上。 /// 因此,第二步就是处理碰撞冲突的过程。这里有两种处理碰撞冲突的方法:separate chaining(拉链法)和linear probing(线性探测法)。 /// </summary> public class DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> : IDictionary<TKey, TValue> { protected struct Entry { public int hashCode; //31位散列值,32最高位表示符号位,-1表示未使用 public int next; //下一项的索引值,-1表示结尾 public TKey key; //键 public TValue value; //值 } protected int[] buckets;//处理hash碰撞,储存由键转换成的数组索引 protected Entry[] entries;//元素数组,用于维护哈希表中的数据 protected int count;//元素数量 protected int freeList;//空闲的列表 protected int freeCount;//空闲列表元素数量 protected IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer;//哈希表中的比较函数 protected KeyCollection keys;//键集合 protected ValueCollection values;//值集合 protected const int MaxPrimeArrayLength = 0x7FEFFFFD; //预设素数数组 protected static readonly int[] primes = { 3, 7, 11, 17, 23, 29, 37, 47, 59, 71, 89, 107, 131, 163, 197, 239, 293, 353, 431, 521, 631, 761, 919, 1103, 1327, 1597, 1931, 2333, 2801, 3371, 4049, 4861, 5839, 7013, 8419, 10103, 12143, 14591, 17519, 21023, 25229, 30293, 36353, 43627, 52361, 62851, 75431, 90523, 108631, 130363, 156437, 187751, 225307, 270371, 324449, 389357, 467237, 560689, 672827, 807403, 968897, 1162687, 1395263, 1674319, 2009191, 2411033, 2893249, 3471899, 4166287, 4999559, 5999471, 7199369}; //调用本身的构造方法 public DictionaryScript() : this(0, null) { } public DictionaryScript(int capacity) : this(capacity, null) { } public DictionaryScript(int capacity, IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer) { if (capacity < 0) { throw new ArgumentNullException(); } if (capacity > 0) { Initialize(capacity); } this.comparer = comparer == null ? EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default : comparer; } /// <summary> /// 需要一个大小为M的数组来储存键值对,那么需要一个能够将任意键转为该数组范围内的索引(0到M-1)的哈希函数 /// 这个哈希函数应该易于计算并且能够均匀分布所有的键。即对于任意键,0到M-1之间的每个整数都有相等可能性与之对应 /// 除留余数法。这个方法选择大小为素数M的数组,对于任意正整数k,计算k除以M的余数 /// 如果M不是素数的话,将不能有效利用键中所包含的所有信息,导致算法不能均匀地分布所有键。 /// </summary> private void Initialize(int capacity) { //根据构造函数设定的初始容量,获取一个大于并接近的素数 int size = GetPrime(capacity); buckets = new int[size]; for (int i = 0; i < buckets.Length; i++) { buckets[i] = -1; } entries = new Entry[size]; freeList = -1; } /// <summary> /// 根据构造函数设定的初始容量,获取一个大于并接近的素数 /// </summary> public int GetPrime(int min) { if (min < 0) throw new ArgumentException(); for (int i = 0; i < primes.Length; i++) { int prime = primes[i]; if (prime >= min) return prime; } //如果超出预先的数组 for (int i = (min | 1); i < Int32.MaxValue; i += 2) { if (IsPrime(i) && ((i - 1) % 101 != 0)) return i; } return min; } /// <summary> /// 是否是素数 /// </summary> private bool IsPrime(int candidate) { if ((candidate & 1) != 0) { int limit = (int)Math.Sqrt(candidate); for (int divisor = 3; divisor <= limit; divisor += 2) { if ((candidate % divisor) == 0) return false; } return true; } return (candidate == 2); } /// <summary> /// 扩容 /// </summary> private int ExpandPrime(int oldSize) { int newSize = 2 * oldSize; if ((uint)newSize > MaxPrimeArrayLength && MaxPrimeArrayLength > oldSize) { return MaxPrimeArrayLength; } return GetPrime(newSize); } public TValue this[TKey key] { get { int i = FindEntry(key); if (i >= 0) { return entries[i].value; } else { throw new KeyNotFoundException(); } } set { Insert(key, value, false); } } public int Count { get { return count; } } public KeyCollection Keys { get { if (keys == null) keys = new KeyCollection(this); return keys; } } public ValueCollection Values { get { if (values == null) values = new ValueCollection(this); return values; } } ICollection<TKey> IDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Keys { get { if (keys == null) keys = new KeyCollection(this); return keys; } } ICollection<TValue> IDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Values { get { if (values == null) values = new ValueCollection(this); return values; } } public bool IsReadOnly { get { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } public void Add(KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue> item) { Add(item.Key, item.Value); } public void Add(TKey key, TValue value) { Insert(key, value, true); } private void Insert(TKey key, TValue value, bool add) { //key不能为空,value可以为空 if (key == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(); } if (buckets == null) { Initialize(0); } int collisionCount = 0; int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF; //将HashCode的返回值转化为数组索引 int bucketIndex = hashCode % buckets.Length; // 处理hash碰撞冲突 // 如果转换出的bucketIndex大于等于0,判断buckets数组中有没有相等的,如果相等,需要处理冲突 for (int i = buckets[bucketIndex]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next) { //如果转换的hash值与之前已经添加的hash值相等,同时插入的key与之前的相同,处理冲突,key是唯一的,不能重复 if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) { if (add) { throw new ArgumentException(); } entries[i].value = value; return; } collisionCount++; } //数组索引 int index; //如果空链表的长度大于0,FreeList链表不为空,因此字典会优先把新增元素添加到FreeList链表所指向的位置,添加后FreeCount减1 if (freeCount > 0) { index = freeList; freeList = entries[index].next; freeCount--; } else { //如果数组已满,需扩容 if (count == entries.Length) { Resize(); bucketIndex = hashCode % buckets.Length; } index = count; count++; } entries[index].hashCode = hashCode; //新增元素的next指向上一个元素的索引 entries[index].next = buckets[bucketIndex]; entries[index].key = key; entries[index].value = value; //记录新增元素的索引 buckets[bucketIndex] = index; // 冲突数达到了一定的阈值,之后更新Hash值 if (collisionCount > 100 && IsEqualityComparer(comparer)) { comparer = EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default; Resize(entries.Length, true); } } private bool IsEqualityComparer(object comparer) { return (comparer == null || comparer == EqualityComparer<string>.Default); } /// <summary> /// 扩容数组 /// </summary> private void Resize() { Resize(ExpandPrime(count), false); } private void Resize(int newSize, bool forceNewHashCodes) { int[] newBuckets = new int[newSize]; for (int i = 0; i < newBuckets.Length; i++) { newBuckets[i] = -1; } Entry[] newEntries = new Entry[newSize]; Array.Copy(entries, 0, newEntries, 0, count); if (forceNewHashCodes) { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (newEntries[i].hashCode != -1) { newEntries[i].hashCode = (comparer.GetHashCode(newEntries[i].key) & 0x7FFFFFFF); } } } for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (newEntries[i].hashCode >= 0) { int bucket = newEntries[i].hashCode % newSize; newEntries[i].next = newBuckets[bucket]; newBuckets[bucket] = i; } } buckets = newBuckets; entries = newEntries; } public void Clear() { if (count > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < buckets.Length; i++) buckets[i] = -1; Array.Clear(entries, 0, count); freeList = -1; count = 0; freeCount = 0; } } public bool Contains(KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue> item) { return ContainsKey(item.Key); } public bool ContainsKey(TKey key) { return FindEntry(key) >= 0; } public bool ContainsValue(TValue value) { if (value == null) { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (entries[i].hashCode >= 0 && entries[i].value == null) return true; } } else { EqualityComparer<TValue> c = EqualityComparer<TValue>.Default; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (entries[i].hashCode >= 0 && c.Equals(entries[i].value, value)) return true; } } return false; } public void CopyTo(KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>[] array, int arrayIndex) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public bool Remove(KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue> item) { return Remove(item.Key); } public bool Remove(TKey key) { if (key == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(); } if (buckets != null) { int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF; int bucket = hashCode % buckets.Length; int last = -1; for (int i = buckets[bucket]; i >= 0; last = i, i = entries[i].next) { if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) { //如果key在索引0,直接找到或者遍历到数组索引0找到key if (last < 0) { // 把当前索引的bucket数组中的值重置,设置为-1 buckets[bucket] = entries[i].next; } else { //遍历数组时,找到key,把当前删除元素的下一个元素的索引赋值给当前删除元素的上一个元素的next entries[last].next = entries[i].next; } entries[i].hashCode = -1; entries[i].next = freeList; entries[i].key = default(TKey); entries[i].value = default(TValue); freeList = i; freeCount++; return true; } } } return false; } public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TValue value) { int i = FindEntry(key); if (i >= 0) { value = entries[i].value; return true; } value = default(TValue); return false; } private int FindEntry(TKey key) { if (key == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(); } if (buckets != null) { int hashCode = comparer.GetHashCode(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF; for (int i = buckets[hashCode % buckets.Length]; i >= 0; i = entries[i].next) { if (entries[i].hashCode == hashCode && comparer.Equals(entries[i].key, key)) return i; } } return -1; } public Enumerator GetEnumerator() { return new Enumerator(this, Enumerator.KeyValuePair); } IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>> IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>>.GetEnumerator() { return new Enumerator(this, Enumerator.KeyValuePair); } IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() { return new Enumerator(this, Enumerator.DictEntry); } public struct Enumerator : IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>> { private DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary; private int index; private KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue> current; private int getEnumeratorRetType; internal const int DictEntry = 1; internal const int KeyValuePair = 2; internal Enumerator(DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary, int getEnumeratorRetType) { this.dictionary = dictionary; index = 0; this.getEnumeratorRetType = getEnumeratorRetType; current = new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(); } public bool MoveNext() { while ((uint)index < (uint)dictionary.count) { if (dictionary.entries[index].hashCode >= 0) { current = new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(dictionary.entries[index].key, dictionary.entries[index].value); index++; return true; } index++; } index = dictionary.count + 1; current = new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(); return false; } public KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue> Current { get { return current; } } public void Dispose() { } object IEnumerator.Current { get { if (getEnumeratorRetType == DictEntry) { return new DictionaryEntry(current.Key, current.Value); } else { return new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(current.Key, current.Value); } } } void IEnumerator.Reset() { index = 0; current = new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(); } } public sealed class KeyCollection : ICollection<TKey> { private DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary; public KeyCollection(DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary) { if (dictionary == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(); } this.dictionary = dictionary; } public KeyEnumerator GetEnumerator() { return new KeyEnumerator(dictionary); } IEnumerator<TKey> IEnumerable<TKey>.GetEnumerator() { return new KeyEnumerator(dictionary); } IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() { return new KeyEnumerator(dictionary); } public int Count { get { return dictionary.Count; } } public bool IsReadOnly { get { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } public void Add(TKey item) { throw new NotSupportedException(); } public void Clear() { throw new NotSupportedException(); } public bool Contains(TKey item) { return dictionary.ContainsKey(item); } public void CopyTo(TKey[] array, int arrayIndex) { throw new NotSupportedException(); } public bool Remove(TKey item) { throw new NotSupportedException(); } } public struct KeyEnumerator : IEnumerator<TKey>, IEnumerator { private DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary; private int index; private TKey currentKey; internal KeyEnumerator(DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary) { this.dictionary = dictionary; index = 0; currentKey = default(TKey); } public void Dispose() { } public bool MoveNext() { while ((uint)index < (uint)dictionary.count) { if (dictionary.entries[index].hashCode >= 0) { currentKey = dictionary.entries[index].key; index++; return true; } index++; } index = dictionary.count + 1; currentKey = default(TKey); return false; } public TKey Current { get { return currentKey; } } Object IEnumerator.Current { get { if (index <= 0 || (index > dictionary.count)) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); } return currentKey; } } void IEnumerator.Reset() { index = 0; currentKey = default(TKey); } } public sealed class ValueCollection : ICollection<TValue> { private DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary; public ValueCollection(DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary) { if (dictionary == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(); } this.dictionary = dictionary; } public ValueEnumerator GetEnumerator() { return new ValueEnumerator(dictionary); } IEnumerator<TValue> IEnumerable<TValue>.GetEnumerator() { return new ValueEnumerator(dictionary); } IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator() { return new ValueEnumerator(dictionary); } public int Count { get { return dictionary.Count; } } public bool IsReadOnly { get { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } public void CopyTo(TValue[] array, int arrayIndex) { throw new NotSupportedException(); } public void Add(TValue item) { throw new NotSupportedException(); } public void Clear() { throw new NotSupportedException(); } public bool Contains(TValue item) { return dictionary.ContainsValue(item); } public bool Remove(TValue item) { throw new NotSupportedException(); } } public struct ValueEnumerator : IEnumerator<TValue>, IEnumerator { private DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary; private int index; private TValue currentValue; internal ValueEnumerator(DictionaryScript<TKey, TValue> dictionary) { this.dictionary = dictionary; index = 0; currentValue = default(TValue); } public void Dispose() { } public bool MoveNext() { while ((uint)index < (uint)dictionary.count) { if (dictionary.entries[index].hashCode >= 0) { currentValue = dictionary.entries[index].value; index++; return true; } index++; } index = dictionary.count + 1; currentValue = default(TValue); return false; } public TValue Current { get { return currentValue; } } Object IEnumerator.Current { get { if (index <= 0 || (index > dictionary.count)) { throw new IndexOutOfRangeException(); } return currentValue; } } void IEnumerator.Reset() { index = 0; currentValue = default(TValue); } } } public class TestDictionary { static void Main(string[] args) { DictionaryScript<int, string> testDic = new DictionaryScript<int, string>(6); testDic.Add(4, "4"); //在容量为6的情况下,传入4和11的key,得到的hashcode都是一样的,这里就要处理hash碰撞的问题 testDic.Add(11, "11"); DictionaryScript<int, string> test1Dic = new DictionaryScript<int, string>(6); test1Dic.Add(4, "4"); test1Dic.Add(10, "11"); test1Dic.Add(9, "11"); test1Dic.Add(8, "11"); test1Dic.Add(7, "11"); test1Dic.Add(6, "11"); test1Dic.Add(5, "11"); //根据构造函数设定的初始容量,获取一个大于并接近的素数7 //C#内部有一个素数数组,在DictionaryScript的初始化函数Initialize中有具体实现 //超出数组容量,需要扩容,这里有数组扩容操作 test1Dic.Add(3, "11"); string value1; test1Dic.TryGetValue(2, out value1); test1Dic.Remove(3); //下面是官方调用实例 DictionaryScript<string, string> openWith = new DictionaryScript<string, string>(); openWith.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); openWith.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); // The Add method throws an exception if the new key is // already in the dictionary. try { openWith.Add("txt", "winword.exe"); } catch (ArgumentException) { Console.WriteLine("An element with Key = \"txt\" already exists."); } // The Item property is another name for the indexer, so you // can omit its name when accessing elements. Console.WriteLine("For key = \"rtf\", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // The indexer can be used to change the value associated // with a key. openWith["rtf"] = "winword.exe"; Console.WriteLine("For key = \"rtf\", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // If a key does not exist, setting the indexer for that key // adds a new key/value pair. openWith["doc"] = "winword.exe"; // The indexer throws an exception if the requested key is // not in the dictionary. try { Console.WriteLine("For key = \"tif\", value = {0}.", openWith["tif"]); } catch (KeyNotFoundException) { Console.WriteLine("Key = \"tif\" is not found."); } // When a program often has to try keys that turn out not to // be in the dictionary, TryGetValue can be a more efficient // way to retrieve values. string value = ""; if (openWith.TryGetValue("tif", out value)) { Console.WriteLine("For key = \"tif\", value = {0}.", value); } else { Console.WriteLine("Key = \"tif\" is not found."); } // ContainsKey can be used to test keys before inserting // them. if (!openWith.ContainsKey("ht")) { openWith.Add("ht", "hypertrm.exe"); Console.WriteLine("Value added for key = \"ht\": {0}", openWith["ht"]); } // When you use foreach to enumerate dictionary elements, // the elements are retrieved as KeyValuePair objects. Console.WriteLine(); foreach (KeyValuePair<string, string> kvp in openWith) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", kvp.Key, kvp.Value); } // To get the values alone, use the Values property. DictionaryScript<string, string>.ValueCollection valueColl = openWith.Values; // The elements of the ValueCollection are strongly typed // with the type that was specified for dictionary values. Console.WriteLine(); foreach (string s in valueColl) { Console.WriteLine("Value = {0}", s); } // To get the keys alone, use the Keys property. DictionaryScript<string, string>.KeyCollection keyColl = openWith.Keys; // The elements of the KeyCollection are strongly typed // with the type that was specified for dictionary keys. Console.WriteLine(); foreach (string s in keyColl) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}", s); } // Use the Remove method to remove a key/value pair. Console.WriteLine("\nRemove(\"doc\")"); openWith.Remove("doc"); if (!openWith.ContainsKey("doc")) { Console.WriteLine("Key \"doc\" is not found."); } Console.ReadLine(); } } }
再简单说下hashset,
hashset和字典在下层是雷同的,这里主要说下在大数据量上的风险,以hashset为例
当字典的元素个数为 2893249 的时候触发扩容变成了 2893249 * 2 => 5786498 最接近的一个质数为:5999471,
也就是 289w 暴增到了 599w,一下子就是 599w -289w = 310w 的空间虚占,
这可是增加了两倍多哦,吓人不? 下面写个代码验证下。
static void Main(string[] args) { var hashSet = new HashSet<int>(Enumerable.Range(0, 2893249)); hashSet.Add(int.MaxValue); Console.Read(); } 0:000> !clrstack -l 000000B8F4DBE500 00007ffaf00132ae ConsoleApplication3.Program.Main(System.String[]) [C:\4\ConsoleApp1\ConsoleApp1\Program.cs @ 16] LOCALS: 0x000000B8F4DBE538 = 0x0000020e0b8fcc08 0:000> !DumpObj /d 0000020e0b8fcc08 Name: System.Collections.Generic.HashSet`1[[System.Int32, System.Private.CoreLib]] Size: 64(0x40) bytes File: C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App\5.0.0-preview.5.20278.1\System.Collections.dll Fields: MT Field Offset Type VT Attr Value Name 00007ffaf0096d10 4000017 8 System.Int32[] 0 instance 0000020e2025e9f8 _buckets 00007ffaf00f7ad0 4000018 10 ...ivate.CoreLib]][] 0 instance 0000020e2bea1020 _slots 00007ffaeffdf828 4000019 28 System.Int32 1 instance 2893250 _count 0:000> !DumpObj /d 0000020e2025e9f8 Name: System.Int32[] Size: 23997908(0x16e2dd4) bytes Array: Rank 1, Number of elements 5999471, Type Int32 (Print Array) Fields: None
而且最重要的是,这里是一次性扩容的,而非像redis中实现的那样渐进式扩容,时间开销也是大家值得注意的。
空间上的风险
可以看一下:289w 和 599w 两个HashSet的占用空间大小
static void Main(string[] args) { var hashSet1 = new HashSet<int>(Enumerable.Range(0, 2893249)); var hashSet2 = new HashSet<int>(Enumerable.Range(0, 2893249)); hashSet2.Add(int.MaxValue); Console.Read(); } 0:000> !clrstack -l OS Thread Id: 0x4a44 (0) 000000B1B4FEE460 00007ffaf00032ea ConsoleApplication3.Program.Main(System.String[]) [C:\4\ConsoleApp1\ConsoleApp1\Program.cs @ 18] LOCALS: 0x000000B1B4FEE4B8 = 0x000001d13363cc08 0x000000B1B4FEE4B0 = 0x000001d13363d648 0:000> !objsize 0x000001d13363cc08 sizeof(000001D13363CC08) = 46292104 (0x2c25c88) bytes (System.Collections.Generic.HashSet`1[[System.Int32, System.Private.CoreLib]]) 0:000> !objsize 0x000001d13363d648 sizeof(000001D13363D648) = 95991656 (0x5b8b768) bytes (System.Collections.Generic.HashSet`1[[System.Int32, System.Private.CoreLib]])
可以看到, hashSet1的占用: 46292104 / 1024 / 1024 = 44.1M, hashSet2 的占用 : 95991656 / 1024 / 1024 = 91.5M,一下子就浪费了: 91.5 - 44.1 = 47.4M。
你真以为仅仅浪费了 47.4M 的话,那你就大错特错了,不要忘了底层在扩容的时候,使用新的 size 覆盖了老的 size,而这个 老的 size 集合在GC还没有回收的时候会一直占用堆上空间的
可以用 windbg 去托管堆上抓一下 Slot[] m_slots 和 int[] m_buckets 两个数组,我把代码修改如下
static void Main(string[] args) { var hashSet2 = new HashSet<int>(Enumerable.Range(0, 2893249)); hashSet2.Add(int.MaxValue); Console.Read(); } 0:011> !dumpheap -stat 00007ffaf84f7ad0 3 123455868 System.Collections.Generic.HashSet`1+Slot[[System.Int32, System.Private.CoreLib]][]
这里就拿 Slot[] 说事,从上面代码可以看到,托管堆上有三个 Slot[] 数组,这就有意思了,怎么有三个哈,是不是有点懵逼,没关系,我们将三个 Slot[] 的地址找出来,一个一个看。
0:011> !DumpHeap /d -mt 00007ffaf84f7ad0 Address MT Size 0000016c91308048 00007ffaf84f7ad0 16743180 0000016c928524b0 00007ffaf84f7ad0 34719012 0000016ce9e61020 00007ffaf84f7ad0 71993676 0:011> !gcroot 0000016c91308048 Found 0 unique roots (run '!gcroot -all' to see all roots). 0:011> !gcroot 0000016c928524b0 Found 0 unique roots (run '!gcroot -all' to see all roots). 0:011> !gcroot 0000016ce9e61020 Thread 2b0c: 0000006AFAB7E5F0 00007FFAF84132AE ConsoleApplication3.Program.Main(System.String[]) [C:\4\ConsoleApp1\ConsoleApp1\Program.cs @ 15] rbp-18: 0000006afab7e618 -> 0000016C8000CC08 System.Collections.Generic.HashSet`1[[System.Int32, System.Private.CoreLib]] -> 0000016CE9E61020 System.Collections.Generic.HashSet`1+Slot[[System.Int32, System.Private.CoreLib]][]
从上面可以看到,我通过 gcroot 去找这三个地址的引用根,有两个是没有的,最后一个有的自然就是新的 599w 的size,对不对,接下来用 !do 打出这三个地址的值。
0:011> !do 0000016c91308048 Name: System.Collections.Generic.HashSet`1+Slot[[System.Int32, System.Private.CoreLib]][] Size: 16743180(0xff7b0c) bytes Array: Rank 1, Number of elements 1395263, Type VALUETYPE (Print Array) Fields: None 0:011> !do 0000016c928524b0 Name: System.Collections.Generic.HashSet`1+Slot[[System.Int32, System.Private.CoreLib]][] Size: 34719012(0x211c524) bytes Array: Rank 1, Number of elements 2893249, Type VALUETYPE (Print Array) Fields: None 0:011> !do 0000016ce9e61020 Name: System.Collections.Generic.HashSet`1+Slot[[System.Int32, System.Private.CoreLib]][] Size: 71993676(0x44a894c) bytes Array: Rank 1, Number of elements 5999471, Type VALUETYPE (Print Array) Fields: None
从上面的 Rank 1, Number of elements 信息中可以看到,原来托管堆不仅有扩容前的Size :2893249,还有更前一次的扩容Size: 1395263,所以按这种情况算: 托管堆上的总大小近似为: 23.7M + 47.4M + 91.5M = 162.6M,我去,不简单把。。。 也就是说:托管堆上有 162.6 - 91.5 =71.1M 的未回收垃圾 ➕ 刚才的 47.4M 的空间虚占用,总浪费为:118.5M,但愿我没有算错。。。
有解决方案吗?
在List中大家可以通过 Capacity 去控制List的Size,但是很遗憾,在 HashSet 中并没有类似的解决方案,只有一个很笨拙的裁剪方法: TrimExcess,用于将当前Size扩展到最接近的 质数 值, 如下代码所示:
public void TrimExcess() { int prime = HashHelpers.GetPrime(m_count); Slot[] array = new Slot[prime]; int[] array2 = new int[prime]; int num = 0; for (int i = 0; i < m_lastIndex; i++) { if (m_slots[i].hashCode >= 0) { array[num] = m_slots[i]; int num2 = array[num].hashCode % prime; array[num].next = array2[num2] - 1; array2[num2] = num + 1; num++; } } }
HashSet的时间和空间上虚占远比你想象的大很多,而且实占也不小,因为底层用到了双数组 m_slots 和 m_buckets,每个Slot还有三个元素: struct Slot { int hashCode;internal int next;internal T value; },所以了解完原理之后谨慎着用吧


