关于PTA第二次大作业的总结
一.前言
这一次的作业,总体来说是有一定难度的,主要考察了类与对象的关系,java封装的技术特性,字符串的使用和正则表达式的使用等,还有java类的设计原则,题量比之前的作业减少了,但是难度在慢慢上升。特别是习题六,代码的数量上来了,关于类的设计就要谨慎。
二.设计与分析
设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 两个信息。
订单分:桌号标识、点菜记录和删除信息、代点菜信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行或多行。
桌号标识独占一行,包含两个信息:桌号、时间。
桌号以下的所有记录都是本桌的记录,直至下一个桌号标识。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
如果序号不对,输出"delete error"
代点菜信息包含:桌号 序号 菜品名称 份额 分数
代点菜是当前桌为另外一桌点菜,信息中的桌号是另一桌的桌号,带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌。
程序最后按输入的先后顺序依次输出每一桌的总价(注意:由于有代点菜的功能,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和)。
每桌的总价等于那一桌所有菜的价格之和乘以折扣。如存在小数,按四舍五入规则计算,保留整数。
折扣的计算方法(注:以下时间段均按闭区间计算):
周一至周五营业时间与折扣:晚上(17:00-20:30)8折,周一至周五中午(10:30--14:30)6折,其余时间不营业。
周末全价,营业时间:9:30-21:30
如果下单时间不在营业范围内,输出"table " + t.tableNum + " out of opening hours"
参考以下类的模板进行设计:菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish\[\] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号\\
Dish d;//菜品\\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)\\
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格\\
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record\[\] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
### 输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
### 输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+”:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:桌号、菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等,在本系列的后续作业中会做要求。
输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:桌号、菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等,在本系列的后续作业中会做要求。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2023/3/22 12/2/3
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
table 1: 38
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2023/3/22 17/0/0
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
1 delete
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
table 1: 22
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2023/3/22 16/59/59
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
1 delete
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
table 1 out of opening hours
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2022/12/5 15/03/02
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
5 delete
7 delete
table 2 2022/12/3 15/03/02
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
7 delete
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
delete error;
delete error;
table 2:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
delete error;
table 1 out of opening hours
table 2: 63
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2022/12/3 19/5/12
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
table 2 2022/12/3 15/03/02
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
1 4 麻婆豆腐 1 1
7 delete
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 麻辣鸡丝 does not exist table 2: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 麻辣鸡丝 does not exist 4 table 2 pay for table 1 12 delete error; table 1: 63 table 2: 75
刚开始看这道题目的时候,我是没什么头绪的,我是最后才来做这道题的。源码如下:
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main (String[] args){ 5 // Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 // int i = 0; 7 // Dish dish[] = new Dish(); 8 // do{ 9 // dish[i].name = input.next(); 10 // dish[i].unit_price = input.nextInt(); 11 // } 12 13 } 14 } 15 class Dish{ 16 String name;//菜品名称 17 int unit_price;//单价 18 19 Dish(){ 20 21 } 22 Dish(String name,int unit_price){ 23 this.name = name; 24 this.unit_price = unit_price; 25 } 26 27 public int getPrice(int portion){//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) 28 if(portion == 1) 29 return unit_price*1; 30 if(portion == 2) 31 return unit_price*1.5; 32 if(portion == 3) 33 return unit_price*2; 34 } 35 } 36 class Menu{ 37 Dish[] dishs;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息 38 39 public Dish searchDish(String dishName){//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。 40 for(int i = 0;i < dishs.length;i++){ 41 if(dishs[i].equals(dishName)){ 42 return dishs[i]; 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 public Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price){//添加一道菜品信息 47 // dishs[dishs.length] = new Dish(dishName,unit_price); 48 } 49 50 } 51 class Record{ 52 int orderNum;//序号 53 Dish d;//菜品 54 int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份) 55 56 Record(){ 57 58 } 59 //Record(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int portion 60 // this.orderNUm = orderNum; 61 // d.dishName = dishName; 62 // // d.portion 63 //} 64 65 66 public int getPrice(){//计价,计算本条记录的价格\\ 67 int result ; 68 if(portion == 1){ 69 result = d.unit_price*1; 70 } 71 if(portion == 2) 72 result =(int) ( d.unit_price*1.5); 73 if(portion == 3) 74 result = d.unit_price*2; 75 } 76 } 77 // class Order{ 78 // Record[] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录 79 80 // int getTotalPrice(){//计算订单的总价 81 // int sum = 0; 82 // for(i = 0; i < records.length;i++){ 83 // sum += records[i].getPrice(); 84 // } 85 // } 86 // Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num){//添加一条菜品信息 87 // this.orderNum = orderNum; 88 // d.dishName = dishName; 89 // d.portion = portion; 90 // this.num = num; 91 // } 92 // delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum){//根据序号删除一条记录 93 // Record[num] = 94 // } 95 // findRecordByNUm(int orderNum){////根据序号查找一条记录 96 97 // } 98 // }
可以看到笔者的代码还不完整,还有一些功能没有完善,仅仅只有一些框架,按照题目意思:menu类里有dish对象,order里有record对象。这些类之间为依赖关系,测试如下:
可以看到只得了一分。
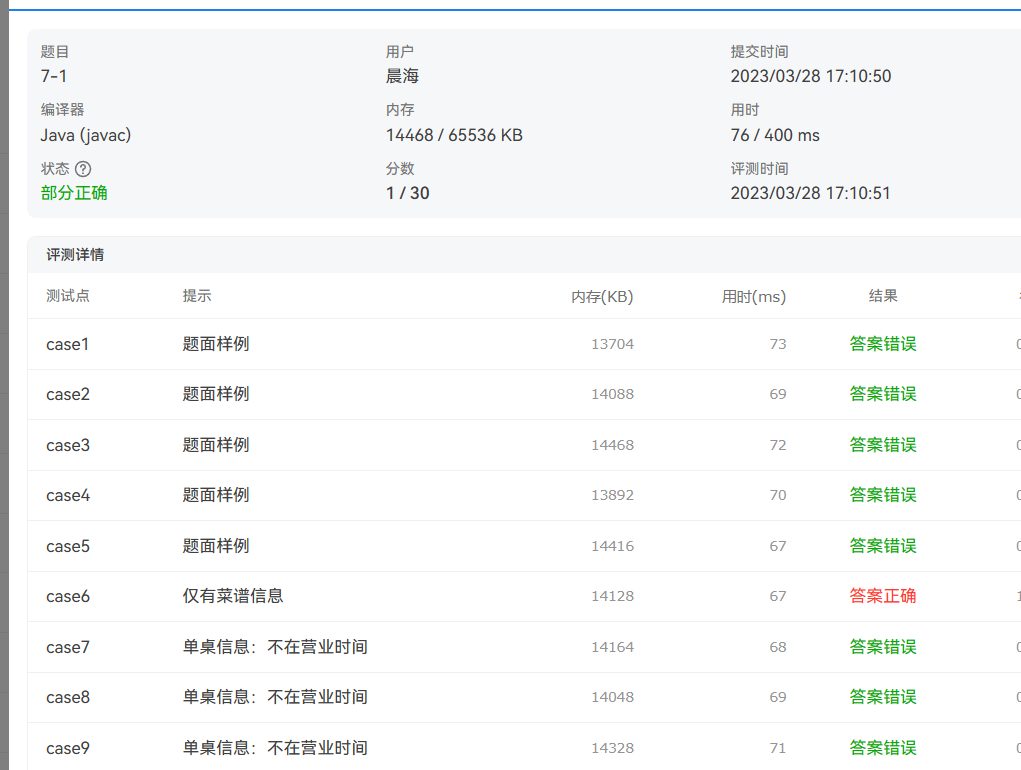
后面就不知道怎么做了,总在纠结要不要用二维数组来存储输入的信息,然后后面的具体方法的实现就没怎么写,最够也没写出这道题。
生成的类图如下:
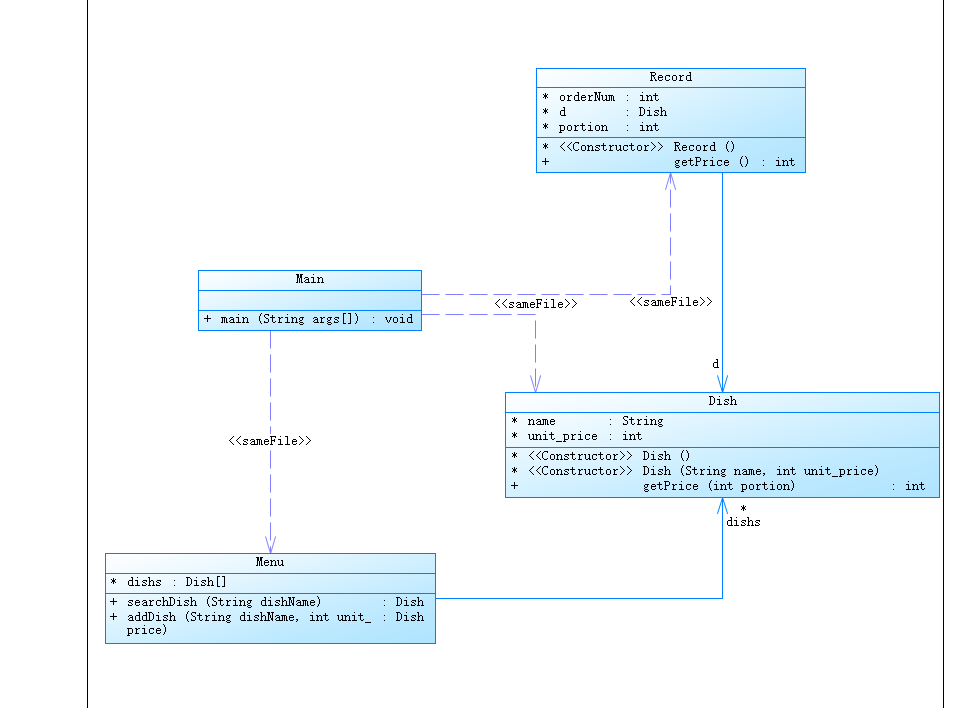
参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format - 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day - 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day - 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
天数值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2312
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1935 2 17 125340
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1591-12-17
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2017-2-24
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
源码如下:

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 String str = input.nextLine(); 7 String[] str1 = str.split(" "); 8 switch(str1[0]){ 9 case "1":{ 10 int y = Integer.valueOf(str1[1]); 11 int m = Integer.valueOf(str1[2]); 12 int d = Integer.valueOf(str1[3]); 13 int n = Integer.valueOf(str1[4]); 14 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(d,m,y); 15 if(date.checkInputValidity()) 16 System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(n).showDate()); 17 else 18 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 19 }break; 20 case "2":{ 21 int y = Integer.valueOf(str1[1]); 22 int m = Integer.valueOf(str1[2]); 23 int d = Integer.valueOf(str1[3]); 24 int n = Integer.valueOf(str1[4]); 25 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(d,m,y); 26 if(date.checkInputValidity()) 27 System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 28 else 29 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 30 }break; 31 case "3":{ 32 int y1 = Integer.valueOf(str1[1]); 33 int m1 = Integer.valueOf(str1[2]); 34 int d1 = Integer.valueOf(str1[3]); 35 int y2 = Integer.valueOf(str1[4]); 36 int m2 = Integer.valueOf(str1[5]); 37 int d2 = Integer.valueOf(str1[6]); 38 DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(d1,m1,y1); 39 DateUtil date2 = new DateUtil(d2,m2,y2); 40 int n = date1.getDaysofDates(date2); 41 System.out.println(n); 42 43 }break; 44 default:{ 45 46 } 47 }//switch 48 } 49 } 50 class DateUtil{ 51 private Day day = new Day(); 52 53 54 DateUtil(){ 55 56 } 57 DateUtil(int d, int m, int y){ 58 day.setValue(d); 59 day.getMonth().setValue(m); 60 day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(y); 61 } 62 63 64 public Day getDay(){ 65 return day; 66 } 67 public void setDay(Day d){ 68 this.day = d; 69 } 70 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ 71 72 if(day.getMonth().getYear().validate()){ 73 if(day.getMonth().validate()){ 74 if(day.validate()) 75 return true; 76 else 77 return false; 78 79 } 80 else 81 return false; 82 } 83 else 84 return false; 85 86 } 87 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){ 88 if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) { 89 return true; 90 } 91 else if(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() < date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) { 92 return false; 93 } 94 else { 95 if(day.getMonth().getValue() > date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) { 96 return true; 97 } 98 else if(day.getMonth().getValue() < date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) { 99 return false; 100 } 101 else { 102 if(day.getValue() > date.getDay().getValue()) 103 return true; 104 else 105 return false; 106 107 } 108 } 109 } 110 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ 111 if(day.getValue() == date.getDay().getValue() && day.getMonth().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getValue() && day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() == date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) 112 return true; 113 else 114 return false; 115 } 116 public String showDate(){ 117 String str = "" + day.getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + day.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + day.getValue(); 118 return str; 119 } 120 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ 121 for( ; n > 0 ; n--){ 122 if(day.getMonth().getValue() != 12){ 123 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 2){ 124 if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){ 125 if(day.getValue() != 29) 126 day.dayIncrement(); 127 else{ 128 day.resetMin(); 129 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 130 131 } 132 } 133 else{//不是闰年 134 if(day.getValue() != 28) 135 day.dayIncrement(); 136 else{ 137 day.resetMin(); 138 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 139 } 140 } 141 }//2月 142 else{//不是二月 143 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 1 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 3 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 5 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 7 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 8 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 10){ 144 if(day.getValue() != 31) 145 day.dayIncrement(); 146 else{ 147 day.resetMin(); 148 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 149 } 150 151 } 152 else { 153 if(day.getValue() != 30) 154 day.dayIncrement(); 155 else{ 156 day.resetMin(); 157 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 158 159 } 160 } 161 162 } 163 } 164 else{ //是12月 165 if(day.getValue() != 31) 166 day.dayIncrement(); 167 else{ 168 day.resetMin(); 169 day.getMonth().resetMin(); 170 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 171 } 172 } 173 174 }//n 175 DateUtil newDate = new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()); 176 return newDate; 177 } 178 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ 179 for( ; n > 0 ; n--){ 180 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 1){ 181 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 182 day.resetMax(); 183 day.getMonth().resetMax(); 184 day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 185 } 186 else{ 187 day.dayReduction(); 188 } 189 } 190 else { 191 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 192 day.getMonth().monthReduction(); 193 day.resetMax(); 194 } 195 else 196 day.dayReduction(); 197 } 198 } 199 200 DateUtil newDate = new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()); 201 return newDate; 202 203 } 204 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ 205 int n = 0;int flag = 0; 206 if(compareDates(date) ){ 207 flag = 1; 208 } 209 else 210 flag = 0; 211 if(flag == 0){ 212 for( ; this.equalTwoDates(date) == false ; n++){ 213 if(day.getMonth().getValue() != 12){ 214 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 2){ 215 if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){ 216 if(day.getValue() != 29) 217 day.dayIncrement(); 218 else{ 219 day.resetMin(); 220 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 221 } 222 } 223 else{//不是闰年 224 if(day.getValue() != 28) 225 day.dayIncrement(); 226 else{ 227 day.resetMin(); 228 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 229 } 230 } 231 }//2月 232 else{//不是二月 233 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 1 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 3 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 5 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 7 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 8 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 10){ 234 if(day.getValue() != 31) 235 day.dayIncrement(); 236 else{ 237 day.resetMin(); 238 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 239 } 240 241 } 242 else { 243 if(day.getValue() != 30) 244 day.dayIncrement(); 245 else{ 246 day.resetMin(); 247 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 248 } 249 } 250 251 } 252 } 253 else{ //是12月 254 if(day.getValue() != 31) 255 day.dayIncrement(); 256 else{ 257 day.resetMin(); 258 day.getMonth().resetMin(); 259 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 260 } 261 } 262 } 263 } 264 else { 265 for( ; this.equalTwoDates(date) == false ; n++ ){ 266 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 1){ 267 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 268 day.resetMax(); 269 day.getMonth().resetMax(); 270 day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 271 } 272 else{ 273 day.dayReduction(); 274 } 275 } 276 else { 277 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 278 day.getMonth().monthReduction(); 279 day.resetMax(); 280 } 281 else 282 day.dayReduction(); 283 } 284 } 285 } 286 287 return n; 288 } 289 } 290 291 class Day{ 292 private int value; 293 private Month month = new Month(); 294 private int[] mon_maxnum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 295 296 Day(){ 297 298 } 299 Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue){ 300 value = dayValue; 301 month.setValue(monthValue); 302 month.getYear().setValue(dayValue); 303 } 304 305 public int getValue(){ 306 return value; 307 } 308 public void setValue(int value){ 309 this.value = value; 310 } 311 public Month getMonth(){ 312 return month; 313 } 314 public void setMonth(Month value){ 315 this.month = value; 316 } 317 public void resetMin(){ 318 value = 1; 319 } 320 public void resetMax(){ 321 if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()){ 322 if(month.getValue() == 2) 323 value = 29; 324 else 325 value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]; 326 } 327 else{ 328 if(month.getValue() == 2) 329 value = 28; 330 else 331 value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]; 332 } 333 334 } 335 public boolean validate(){ 336 if(month.getValue() == 2){ 337 if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()){ 338 if(value >= 1 && value <= 29) 339 return true; 340 else 341 return false; 342 } 343 else{ 344 if(value >= 1 && value <= 28) 345 return true; 346 else 347 return false; 348 } 349 350 } 351 else{ 352 if(value >= 1 && value <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]) 353 return true; 354 else 355 return false; 356 } 357 358 } 359 public void dayIncrement(){ 360 value++; 361 } 362 public void dayReduction(){ 363 value--; 364 } 365 } 366 367 class Month{ 368 private int value; 369 private Year year = new Year(); 370 371 Month(){ 372 373 } 374 Month(int yearValue, int monthValue){ 375 value = monthValue; 376 year.setValue(yearValue); 377 } 378 379 public int getValue(){ 380 return value; 381 } 382 public void setValue(int value){ 383 this.value = value; 384 } 385 public Year getYear(){ 386 return year; 387 } 388 public void setYear(Year year){ 389 this.year = year; 390 } 391 public void resetMin(){ 392 value = 1; 393 } 394 public void resetMax(){ 395 value = 12; 396 } 397 public boolean validate(){ 398 if(value >= 1 && value <= 12) 399 return true; 400 else 401 return false; 402 } 403 public void monthIncrement(){ 404 value++; 405 } 406 public void monthReduction(){ 407 value--; 408 } 409 } 410 411 class Year{ 412 private int value; 413 414 Year(){ 415 416 } 417 Year(int value){ 418 this.value = value; 419 } 420 421 public int getValue(){ 422 return value; 423 } 424 public void setValue(int value){ 425 this.value = value; 426 } 427 public boolean isLeapYear(){ 428 if((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0) || value % 400 == 0) 429 return true; 430 else 431 return false; 432 } 433 public boolean validate(){ 434 if(value >= 1900 && value <= 2050) 435 return true; 436 else 437 return false; 438 } 439 public void yearIncrement(){ 440 value++; 441 } 442 public void yearReduction(){ 443 value--; 444 } 445 } 446 447
运行结果如下:
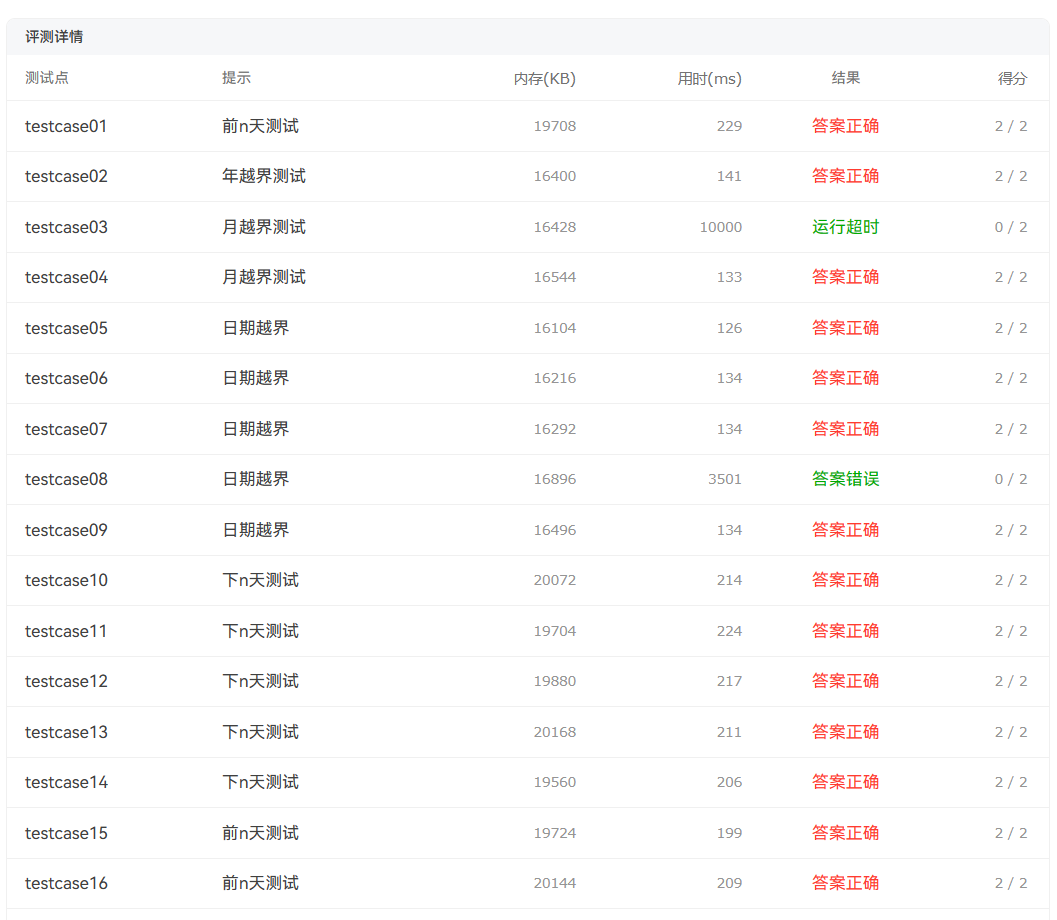
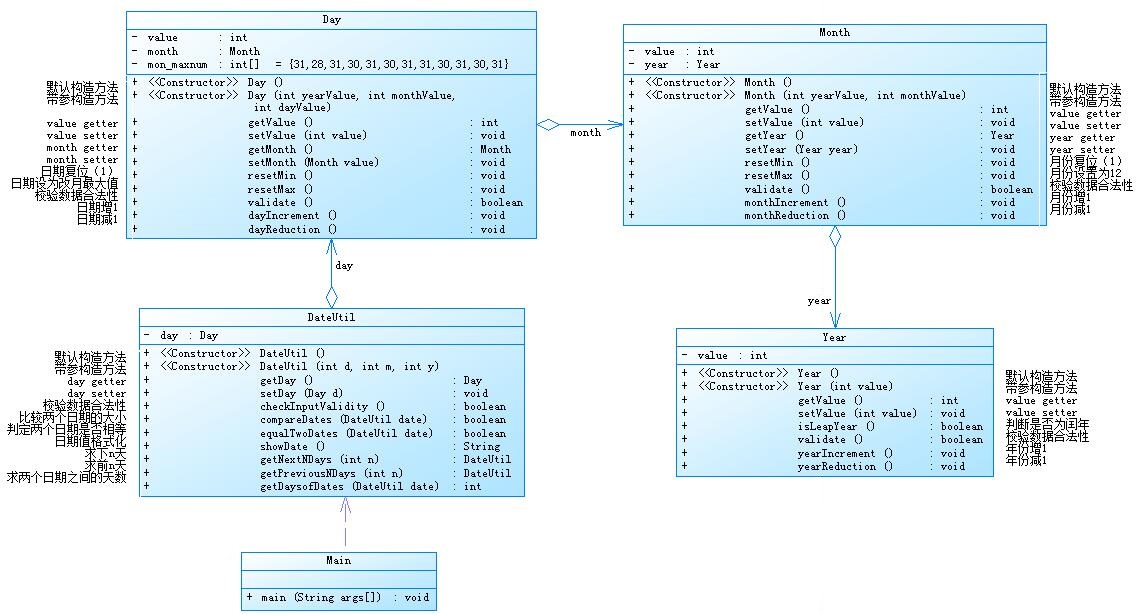
这题的话,在DateUtil类中有Day类对象,Day类中有Month对象,在Month类中有Year对象,这些类之间的关系都是聚合关系;这个题目更好解释了类与类之间的关系,如下图:
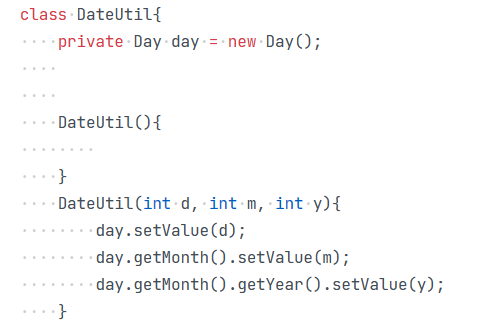
day对象调用month对象,month对象再调用year对象,year对象调用setValue方法,从而实现改变年份。我写的时候对年份的判定老是出现错误,其实参照习题四的题目就行了。在下写求两个日期的之间的天数,我用的是循环的方法,若前面的日期更小,则调用下N天的函数,循环N次;若前面的日期较大,则调用求上N天的方法,循环N次,这样就得到了两个日期之间的天数。相应的代码如下:
1 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ 2 int n = 0;int flag = 0; 3 if(compareDates(date) ){ 4 flag = 1; 5 } 6 else 7 flag = 0; 8 if(flag == 0){ 9 for( ; this.equalTwoDates(date) == false ; n++){ 10 if(day.getMonth().getValue() != 12){ 11 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 2){ 12 if(day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()){ 13 if(day.getValue() != 29) 14 day.dayIncrement(); 15 else{ 16 day.resetMin(); 17 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 18 } 19 } 20 else{//不是闰年 21 if(day.getValue() != 28) 22 day.dayIncrement(); 23 else{ 24 day.resetMin(); 25 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 26 } 27 } 28 }//2月 29 else{//不是二月 30 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 1 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 3 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 5 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 7 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 8 || day.getMonth().getValue() == 10){ 31 if(day.getValue() != 31) 32 day.dayIncrement(); 33 else{ 34 day.resetMin(); 35 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 36 } 37 38 } 39 else { 40 if(day.getValue() != 30) 41 day.dayIncrement(); 42 else{ 43 day.resetMin(); 44 day.getMonth().monthIncrement(); 45 } 46 } 47 48 } 49 } 50 else{ //是12月 51 if(day.getValue() != 31) 52 day.dayIncrement(); 53 else{ 54 day.resetMin(); 55 day.getMonth().resetMin(); 56 day.getMonth().getYear().yearIncrement(); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 } 61 else { 62 for( ; this.equalTwoDates(date) == false ; n++ ){ 63 if(day.getMonth().getValue() == 1){ 64 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 65 day.resetMax(); 66 day.getMonth().resetMax(); 67 day.getMonth().getYear().yearReduction(); 68 } 69 else{ 70 day.dayReduction(); 71 } 72 } 73 else { 74 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 75 day.getMonth().monthReduction(); 76 day.resetMax(); 77 } 78 else 79 day.dayReduction(); 80 } 81 } 82 } 83 84 return n; 85 }
这个题目将一个功能交给一个方法实现,体现了java中的单一职责原则,代码实现过程也更好写。
生成的类图如下:
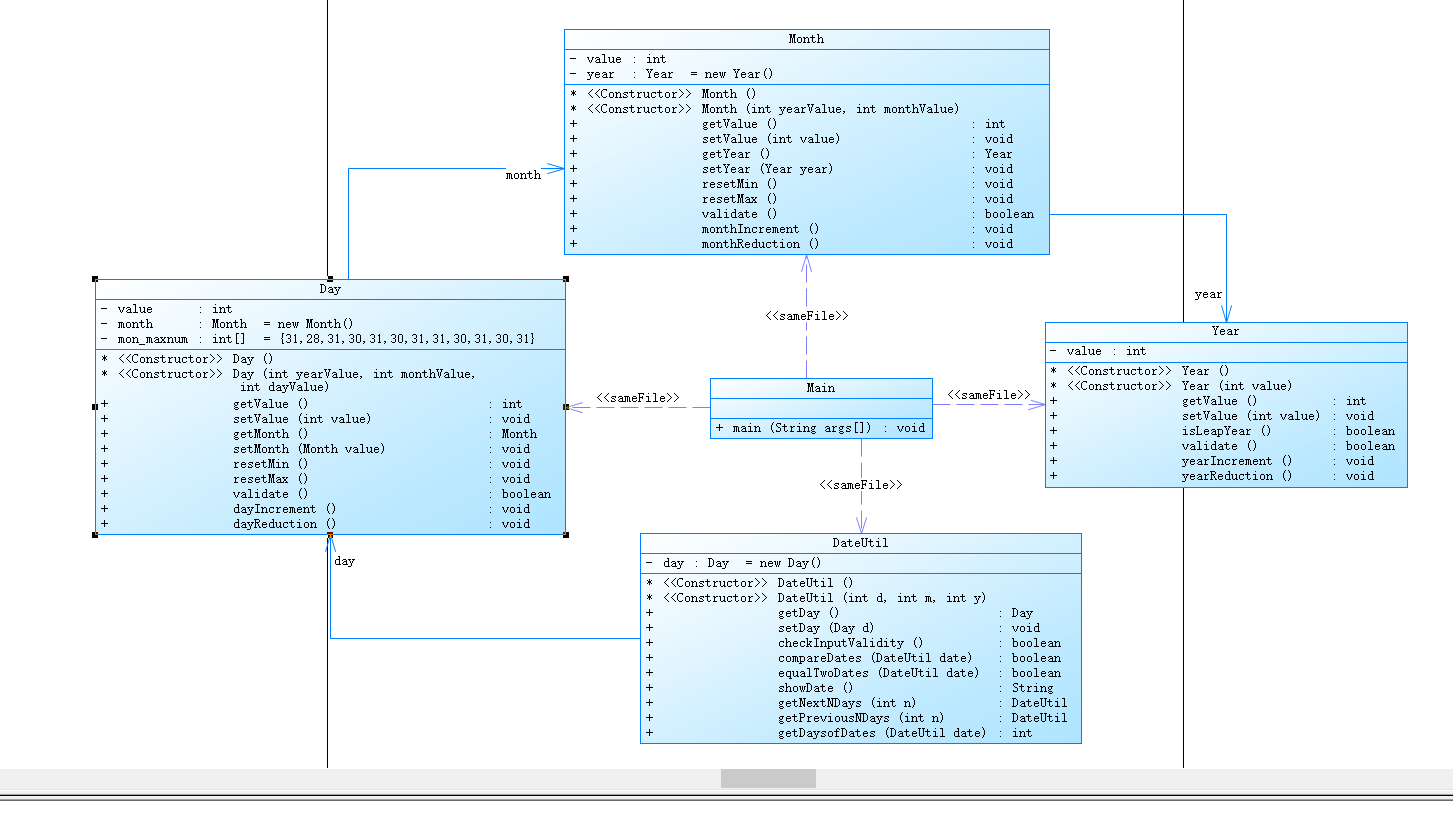
生成的类图,由于都在一个java文件中,main与其他类都有依赖关系,不完全符合题目的要求。
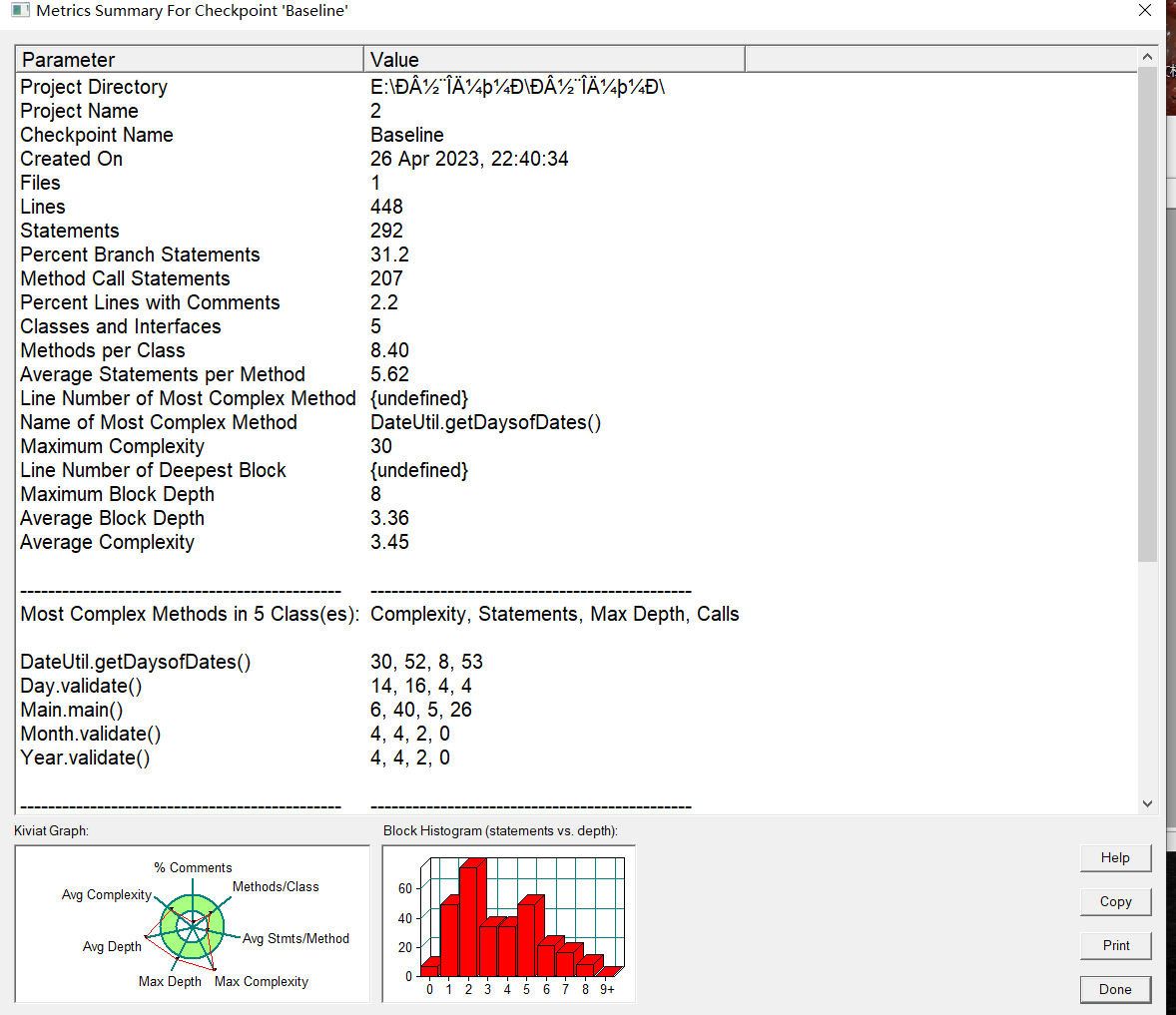
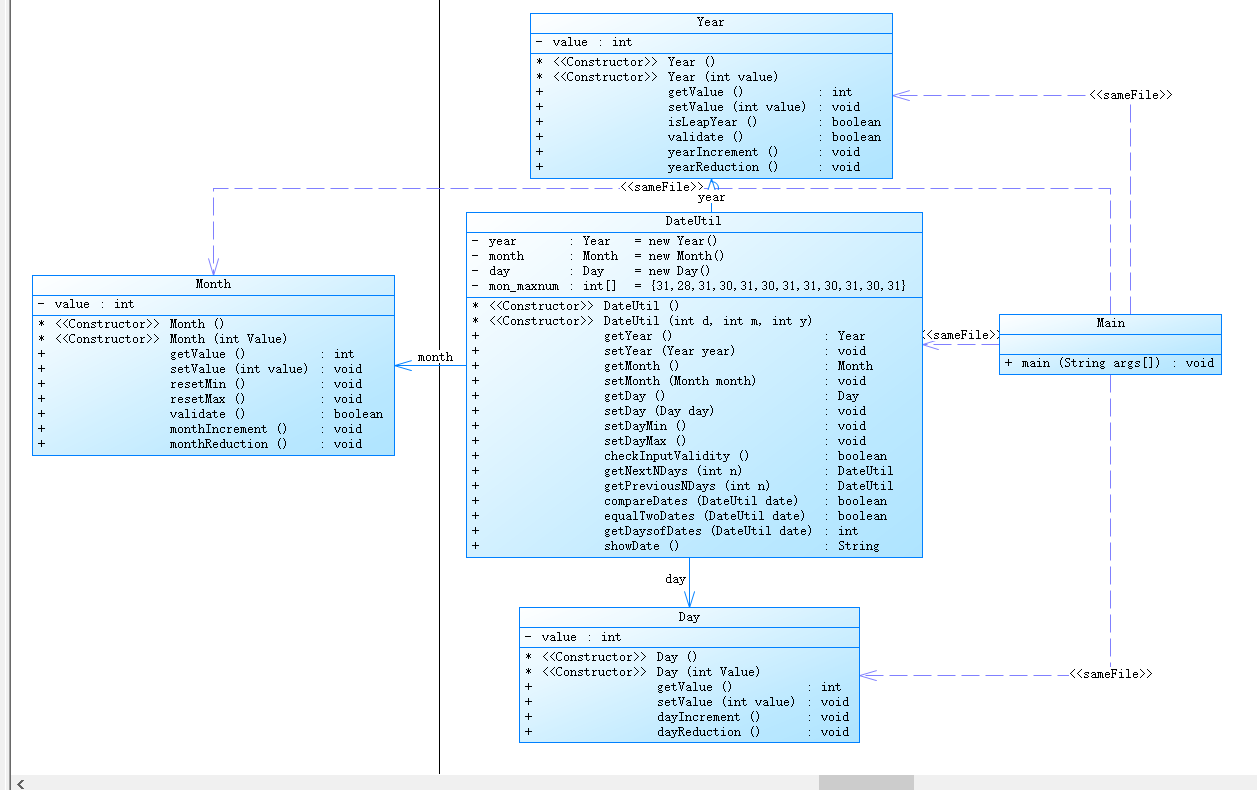
参考题目7-3的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
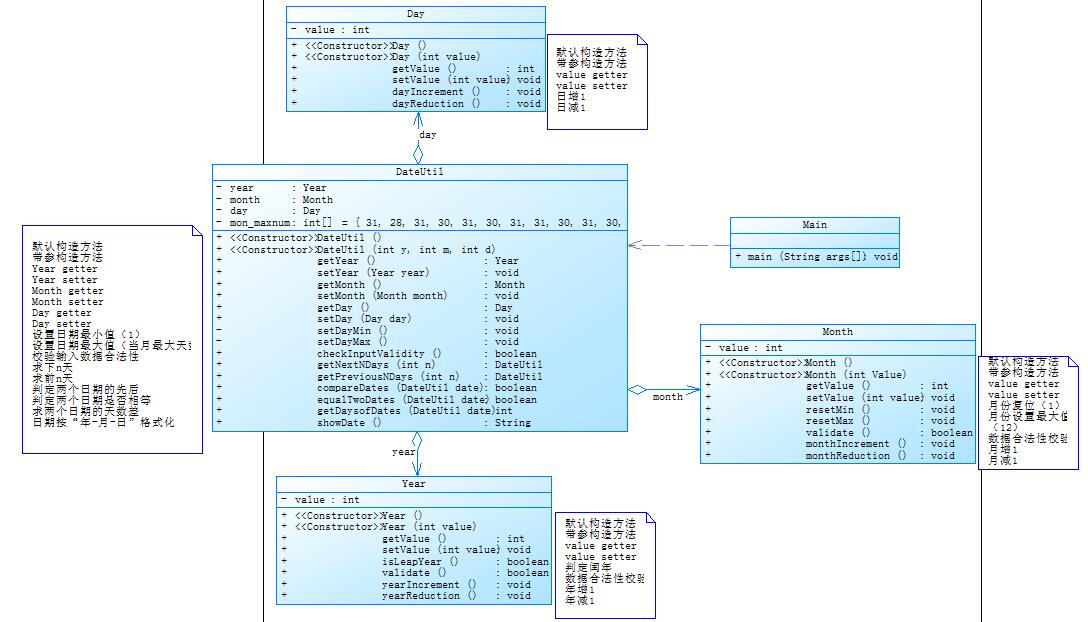
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format - 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 next n days is:year2-month2-day2 - 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 previous n days is:year2-month2-day2 - 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
The days between year1-month1-day1 and year2-month2-day2 are:值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The days between 2014-2-14 and 2020-6-14 are:2312
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1834 2 17 7821
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1834-2-17 previous 7821 days is:1812-9-19
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1999-3-28 next 6543 days is:2017-2-24
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format

1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 String str = input.nextLine(); 7 String[] str1 = str.split(" "); 8 switch(str1[0]){ 9 case "1":{ 10 int y = Integer.valueOf(str1[1]); 11 int m = Integer.valueOf(str1[2]); 12 int d = Integer.valueOf(str1[3]); 13 int n = Integer.valueOf(str1[4]); 14 15 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(d,m,y); 16 if(date.checkInputValidity()) 17 System.out.println(date.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " next " + n + " days is:" + date.getNextNDays(n).showDate()); 18 else 19 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 20 }break; 21 case "2":{ 22 int y = Integer.valueOf(str1[1]); 23 int m = Integer.valueOf(str1[2]); 24 int d = Integer.valueOf(str1[3]); 25 int n = Integer.valueOf(str1[4]); 26 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(d,m,y); 27 if(date.checkInputValidity()) 28 System.out.println(date.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " previous " + n + " days is:" + date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 29 else 30 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 31 }break; 32 case "3":{ 33 int y1 = Integer.valueOf(str1[1]); 34 int m1 = Integer.valueOf(str1[2]); 35 int d1 = Integer.valueOf(str1[3]); 36 int y2 = Integer.valueOf(str1[4]); 37 int m2 = Integer.valueOf(str1[5]); 38 int d2 = Integer.valueOf(str1[6]); 39 DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(d1,m1,y1); 40 DateUtil date2 = new DateUtil(d2,m2,y2); 41 System.out.print("The days between " + date1.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date1.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date1.getDay().getValue() + " and " + date2.getYear().getValue() + "-" + date2.getMonth().getValue() + "-" + date2.getDay().getValue() + " are:"); 42 int n = date1.getDaysofDates(date2); 43 System.out.print(n); 44 }break; 45 default:{ 46 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 47 } 48 }//switch 49 } 50 } 51 class DateUtil{ 52 private Year year = new Year(); 53 private Month month = new Month(); 54 private Day day = new Day(); 55 private int[] mon_maxnum = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 56 57 58 59 DateUtil(){ 60 61 } 62 DateUtil(int d, int m, int y){ 63 year.setValue(y); 64 month.setValue(m); 65 day.setValue(d); 66 } 67 public Year getYear(){ 68 return year; 69 } 70 public void setYear(Year year){ 71 this.year = year; 72 } 73 public Month getMonth(){ 74 return month; 75 } 76 public void setMonth(Month month){ 77 this.month = month; 78 } 79 public Day getDay(){ 80 return day; 81 } 82 public void setDay(Day day){ 83 this.day = day; 84 } 85 public void setDayMin(){ 86 day.setValue(1); 87 } 88 public void setDayMax(){ 89 if(year.isLeapYear()){ 90 if(month.getValue() == 2) 91 day.setValue(29); 92 else 93 day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]); 94 } 95 else{ 96 if(month.getValue() == 2) 97 day.setValue(28); 98 else 99 day.setValue(mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]) ; 100 } 101 102 } 103 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ 104 if(year.validate()){ 105 if(month.validate()){ 106 if(month.getValue() == 2){ 107 if(year.isLeapYear()){ 108 if(day.getValue() >= 1 && day.getValue() <= 29) 109 return true; 110 else 111 return false; 112 } 113 else{ 114 if(day.getValue() >= 1 && day.getValue() <= 28) 115 return true; 116 else 117 return false; 118 } 119 120 } 121 else{ 122 if(day.getValue() >= 1 && day.getValue() <= mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]) 123 return true; 124 else 125 return false; 126 } 127 } 128 else 129 return false; 130 } 131 else 132 return false; 133 134 } 135 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ 136 for( ; n > 0 ; n--){ 137 if(month.getValue() != 12) {//不是12月 138 if(month.getValue() == 2){//二月 139 if(year.isLeapYear()){ 140 if(day.getValue() != 29) 141 day.dayIncrement(); 142 else{ 143 setDayMin(); 144 month.monthIncrement(); 145 146 } 147 } 148 else{//不是闰年 149 if(day.getValue() != 28) 150 day.dayIncrement(); 151 else{ 152 setDayMin(); 153 month.monthIncrement(); 154 } 155 } 156 }//2月 157 else{//不是二月 158 if(month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10){ 159 if(day.getValue() != 31) 160 day.dayIncrement(); 161 else{ 162 this.setDayMin(); 163 month.monthIncrement(); 164 } 165 166 } 167 else { 168 if(day.getValue() != 30) 169 day.dayIncrement(); 170 else{ 171 this.setDayMin(); 172 month.monthIncrement(); 173 174 } 175 } 176 177 } 178 } 179 else{ //是12月 180 if(day.getValue() != 31) 181 day.dayIncrement(); 182 else{ 183 this.setDayMin(); 184 month.resetMin(); 185 year.yearIncrement(); 186 } 187 } 188 189 }//n 190 DateUtil newDate = new DateUtil(day.getValue(),month.getValue(),year.getValue()); 191 return newDate; 192 } 193 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ 194 for( ; n > 0 ; n--){ 195 if(month.getValue() == 1){ 196 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 197 this.setDayMax(); 198 month.resetMax(); 199 year.yearReduction(); 200 } 201 else{ 202 day.dayReduction(); 203 } 204 } 205 else { 206 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 207 month.monthReduction(); 208 this.setDayMax(); 209 } 210 else 211 day.dayReduction(); 212 } 213 } 214 DateUtil newDate = new DateUtil(day.getValue(),month.getValue(),year.getValue()); 215 return newDate; 216 } 217 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){ 218 if(this.year.getValue() > date.year.getValue()) 219 return true; 220 else if(this.year.getValue() < date.year.getValue()) 221 return false; 222 else{ 223 if(this.month.getValue() > date.month.getValue()) 224 return true; 225 else if(this.month.getValue() < date.month.getValue()) 226 return false; 227 else{ 228 if(this.day.getValue() > date.day.getValue()) 229 return true; 230 else 231 return false; 232 } 233 } 234 } 235 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){ 236 if(this.year.getValue() == date.year.getValue() && this.month.getValue() == date.month.getValue() && this.day.getValue() == date.day.getValue()) 237 return true; 238 else 239 return false; 240 } 241 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){ 242 int n = 0;int flag = 0; 243 if(this.compareDates(date)) 244 flag = 1; 245 else 246 flag = 0; 247 248 249 if(flag == 0) { 250 251 252 for( ; this.equalTwoDates(date) == false ; n++){ 253 if(month.getValue() != 12){ 254 if(month.getValue() == 2){ 255 if(year.isLeapYear()){ 256 if(day.getValue() != 29) 257 day.dayIncrement(); 258 else{ 259 setDayMin(); 260 month.monthIncrement(); 261 } 262 } 263 else{//不是闰年 264 if(day.getValue() != 28) 265 day.dayIncrement(); 266 else{ 267 setDayMin(); 268 month.monthIncrement(); 269 } 270 } 271 }//2月 272 else{//不是二月 273 if(month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10){ 274 if(day.getValue() != 31) 275 day.dayIncrement(); 276 else{ 277 setDayMin(); 278 month.monthIncrement(); 279 } 280 281 } 282 else { 283 if(day.getValue() != 30) 284 day.dayIncrement(); 285 else{ 286 setDayMin(); 287 month.monthIncrement(); 288 } 289 } 290 291 } 292 } 293 else{ //是12月 294 if(day.getValue() != 31) 295 day.dayIncrement(); 296 else{ 297 setDayMin(); 298 month.resetMin(); 299 year.yearIncrement(); 300 } 301 } 302 } 303 return n; 304 } 305 //if 306 else{ 307 for( ; this.equalTwoDates(date) == false ; n++){ 308 if(month.getValue() == 1){ 309 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 310 this.setDayMax(); 311 month.resetMax(); 312 year.yearReduction(); 313 } 314 else{ 315 day.dayReduction(); 316 } 317 } 318 else { 319 if(day.getValue() == 1){ 320 month.monthReduction(); 321 this.setDayMax(); 322 } 323 else 324 day.dayReduction(); 325 } 326 } 327 return n; 328 } 329 330 } 331 public String showDate(){ 332 String str = "" + year.getValue() + "-" + month.getValue() + "-" + day.getValue(); 333 return str; 334 } 335 } 336 337 class Day{ 338 private int value; 339 340 Day(){ 341 342 } 343 Day(int Value){ 344 value = Value; 345 } 346 347 public int getValue(){ 348 return value; 349 } 350 public void setValue(int value){ 351 this.value = value; 352 } 353 public void dayIncrement(){ 354 value++; 355 } 356 public void dayReduction(){ 357 value--; 358 } 359 } 360 361 class Month{ 362 private int value; 363 364 Month(){ 365 366 } 367 Month(int Value){ 368 this.value = Value; 369 } 370 371 public int getValue(){ 372 return value; 373 } 374 public void setValue(int value){ 375 this.value = value; 376 } 377 public void resetMin(){ 378 value = 1; 379 } 380 public void resetMax(){ 381 value = 12; 382 } 383 public boolean validate(){ 384 if(value >= 1 && value <= 12) 385 return true; 386 else 387 return false; 388 } 389 public void monthIncrement(){ 390 value++; 391 } 392 public void monthReduction(){ 393 value--; 394 } 395 } 396 397 class Year{ 398 private int value; 399 400 Year(){ 401 402 } 403 Year(int value){ 404 this.value = value; 405 } 406 407 public int getValue(){ 408 return value; 409 } 410 public void setValue(int value){ 411 this.value = value; 412 } 413 public boolean isLeapYear(){ 414 if((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0) || value % 400 == 0) 415 return true; 416 else 417 return false; 418 } 419 public boolean validate(){ 420 if(value >= 1820 && value <= 2020) 421 return true; 422 else 423 return false; 424 } 425 public void yearIncrement(){ 426 value++; 427 } 428 public void yearReduction(){ 429 value--; 430 } 431 } 432 433
这道题和之前那到题虽然题目类似,但是类与类之间的关系不一样。DateUtil类中有Day,Mnoth和Year对象,它们之间的关系为DateUtil类与Day类,Month类,Year类都聚合,而Day,Month,Year之间没有关系,符合迪米特法则,类的耦合性更低。

现在在DateUtil类中,就可以用this.属性.方法直接调用想用的方法了。
笔者在DateUtil类中添加有关月份的数组,便于DateUtil的对象直接使用。通过这个题目,我学到了迪米特法则的使用,降低类与类之间的耦合性,使得程序易于维护。
生成的类图如下:
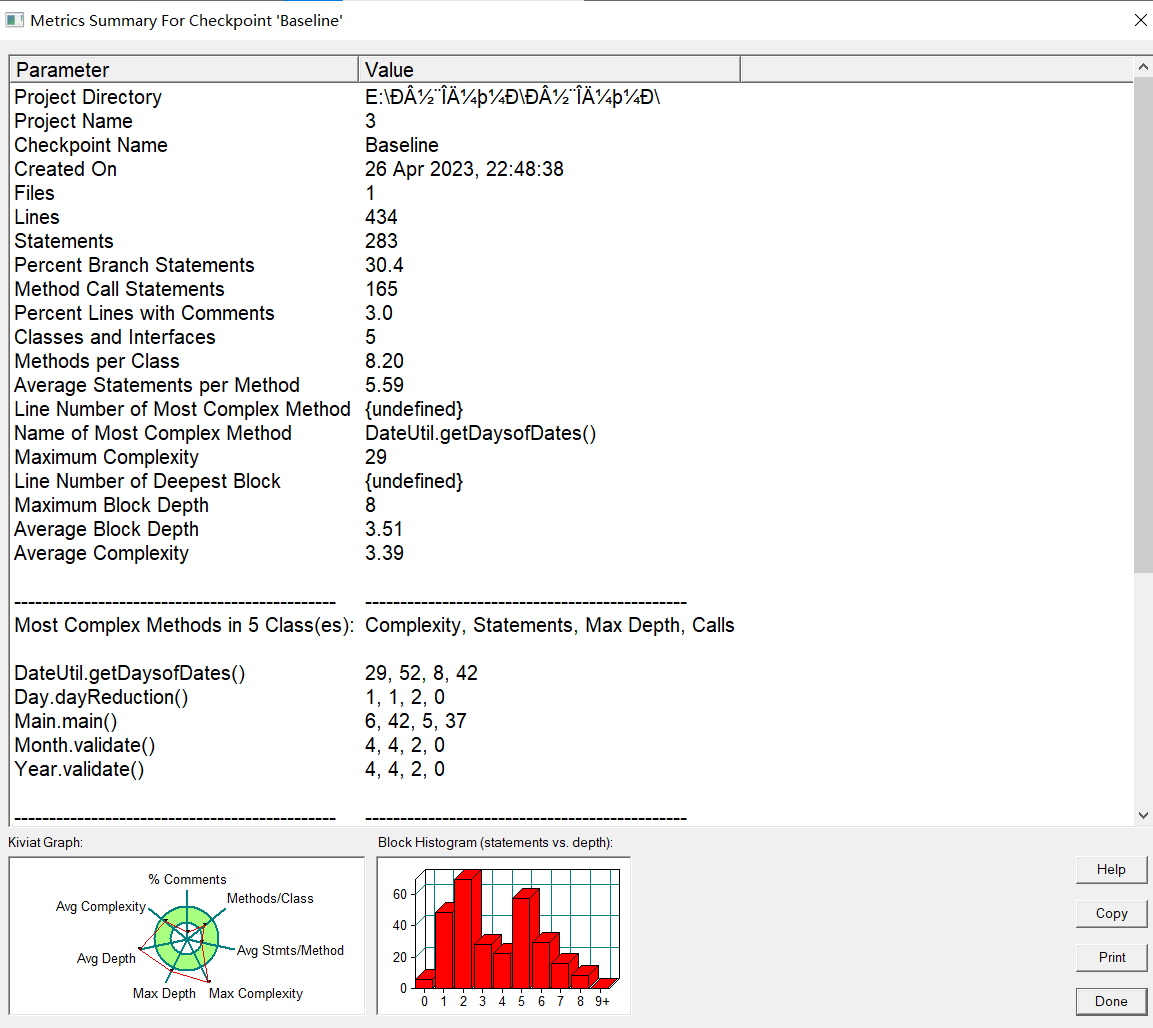
题目集六.
本体大部分内容与菜单计价程序-3相同,增加的部分用加粗文字进行了标注。
设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 两个信息。
订单分:桌号标识、点菜记录和删除信息、代点菜信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行或多行。
桌号标识独占一行,包含两个信息:桌号、时间。
桌号以下的所有记录都是本桌的记录,直至下一个桌号标识。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
如果序号不对,输出"delete error"
代点菜信息包含:桌号 序号 菜品名称 份额 分数
代点菜是当前桌为另外一桌点菜,信息中的桌号是另一桌的桌号,带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌。
程序最后按输入的桌号从小到大的顺序依次输出每一桌的总价(注意:由于有代点菜的功能,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和)。
每桌的总价等于那一桌所有菜的价格之和乘以折扣。如存在小数,按四舍五入规则计算,保留整数。
折扣的计算方法(注:以下时间段均按闭区间计算):
周一至周五营业时间与折扣:晚上(17:00-20:30)8折,周一至周五中午(10:30--14:30)6折,其余时间不营业。
周末全价,营业时间:9:30-21:30
如果下单时间不在营业范围内,输出"table " + t.tableNum + " out of opening hours"
参考以下类的模板进行设计(本内容与计价程序之前相同,其他类根据需要自行定义):
菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish[] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号
Dish d;//菜品\\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record[] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
本次课题比菜单计价系列-3增加的异常情况:
1、菜谱信息与订单信息混合,应忽略夹在订单信息中的菜谱信息。输出:"invalid dish"
2、桌号所带时间格式合法(格式见输入格式部分说明,其中年必须是4位数字,月、日、时、分、秒可以是1位或2位数),数据非法,比如:2023/15/16 ,输出桌号+" date error"
3、同一桌菜名、份额相同的点菜记录要合并成一条进行计算,否则可能会出现四舍五入的误差。
4、重复删除,重复的删除记录输出"deduplication :"+序号。
5、代点菜时,桌号不存在,输出"Table number :"+被点菜桌号+" does not exist";本次作业不考虑两桌记录时间不匹配的情况。
6、菜谱信息中出现重复的菜品名,以最后一条记录为准。
7、如果有重复的桌号信息,如果两条信息的时间不在同一时间段,(时段的认定:周一到周五的中午或晚上是同一时段,或者周末时间间隔1小时(不含一小时整,精确到秒)以内算统一时段),此时输出结果按不同的记录分别计价。
8、重复的桌号信息如果两条信息的时间在同一时间段,此时输出结果时合并点菜记录统一计价。前提:两个的桌号信息的时间都在有效时间段以内。计算每一桌总价要先合并符合本条件的饭桌的点菜记录,统一计价输出。
9、份额超出范围(1、2、3)输出:序号+" portion out of range "+份额,份额不能超过1位,否则为非法格式,参照第13条输出。
10、份数超出范围,每桌不超过15份,超出范围输出:序号+" num out of range "+份数。份数必须为数值,最高位不能为0,否则按非法格式参照第16条输出。
11、桌号超出范围[1,55]。输出:桌号 +" table num out of range",桌号必须为1位或多位数值,最高位不能为0,否则按非法格式参照第16条输出。
12、菜谱信息中菜价超出范围(区间(0,300)),输出:菜品名+" price out of range "+价格,菜价必须为数值,最高位不能为0,否则按非法格式参照第16条输出。
13、时间输入有效但超出范围[2022.1.1-2023.12.31],输出:"not a valid time period"
14、一条点菜记录中若格式正确,但数据出现问题,如:菜名不存在、份额超出范围、份数超出范围,按记录中从左到右的次序优先级由高到低,输出时只提示优先级最高的那个错误。
15、每桌的点菜记录的序号必须按从小到大的顺序排列(可以不连续,也可以不从1开始),未按序排列序号的输出:"record serial number sequence error"。当前记录忽略。(代点菜信息的序号除外)
16、所有记录其它非法格式输入,统一输出"wrong format"
17、如果记录以“table”开头,对应记录的格式或者数据不符合桌号的要求,那一桌下面定义的所有信息无论正确或错误均忽略,不做处理。如果记录不是以“table”开头,比如“tab le 55 2023/3/2 12/00/00”,该条记录认为是错误记录,后面所有的信息并入上一桌一起计算。
本次作业比菜单计价系列-3增加的功能:
菜单输入时增加特色菜,特色菜的输入格式:菜品名+英文空格+基础价格+"T"
例如:麻婆豆腐 9 T
菜价的计算方法:
周一至周五 7折, 周末全价。
注意:不同的四舍五入顺序可能会造成误差,请按以下步骤累计一桌菜的菜价:
计算每条记录的菜价:将每份菜的单价按份额进行四舍五入运算后,乘以份数计算多份的价格,然后乘以折扣,再进行四舍五入,得到本条记录的最终支付价格。
最后将所有记录的菜价累加得到整桌菜的价格。
输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+”:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“** does not exist”,**是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的原始总价+英文空格+当前桌的计算折扣后总价
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table 31 2023/2/1 14/20/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 16
2 油淋生菜 1 2
2 delete
2 delete
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 31:
1 num out of range 16
2 油淋生菜 18
deduplication 2
table 31: 0 0
输入样例1:
份数超出范围+份额超出范围。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table 31 2023/2/1 14/20/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 16
2 油淋生菜 4 2
end
输出样例1:
份数超出范围+份额超出范围。例如:
table 31:
1 num out of range 16
2 portion out of range 4
table 31: 0 0
输入样例2:
桌号信息错误。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table a 2023/3/15 12/00/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
输入样例3:
混合错误:桌号信息格式错误+混合的菜谱信息(菜谱信息忽略)。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table 55 2023/3/31 12/000/00
麻辣香锅 15
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
输入样例4:
错误的菜谱记录。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12.0
油淋生菜 9 T
table 55 2023/3/31 12/00/00
麻辣香锅 15
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
table 55:
invalid dish
麻婆豆腐 does not exist
2 油淋生菜 14
table 55: 14 10
输入样例5:
桌号格式错误(以“table”开头)+订单格式错误(忽略)。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table a 2023/3/15 12/00/00
1 麻婆 豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例5:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
输入样例6:
桌号格式错误,不以“table”开头。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table 1 2023/3/15 12/00/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
tab le 2 2023/3/15 12/00/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例6:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 12
2 油淋生菜 14
wrong format
record serial number sequence error
record serial number sequence error
table 1: 26 17这个题目比之前的题目添加了更多的异常情况,测试点也变得更多,笔者没有写出来。我的代码如下:

import java.util.*; public class Main{ public static void main (String[] args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int dishFlag = 0; int tableNum = 0; String[] str= new String[100];//输入的字符串数组 Menu menu = new Menu(); Tables tables = new Tables();//桌子数组 int tableFlag = -1;//桌子号 int i = -1; do { i++; str[i] = input.nextLine(); //System.out.println(str[i-1]); }while(!str[i].matches("end"));//输入信息 //菜单处理 int dishNum = 0; for(i = 0 ; i < str.length ; i++) { if(!(str[i].charAt(0) == 't')){ String[] dishString = str[i].split(" "); if(!dishString[1].matches("[0-9]|[1-9][0-9]|[1-9][0-9][0-9]")) { System.out.println("wrong format"); } else { if(Integer.parseInt(dishString[1]) > 0 && Integer.parseInt(dishString[1] ) < 300) { menu.addDish(dishString[0], Integer.parseInt(dishString[1])); if(dishString.length == 3) menu.getDishs().get(dishNum).setSpecial(dishString[2]); else menu.getDishs().get(dishNum).setSpecial("F"); dishNum++; } else {//菜价超出范围 System.out.println(dishString[0] + " price out of range " + dishString[1]); } } } if(str[i].charAt(0) == 't') {//到了桌号标识 dishFlag = i-1;//菜单的下标 break; } } //处理桌号 for( i = dishFlag + 1; i < str.length ; i++) { String[] tableString = str[i].split(" "); if(str[i].charAt(0) == 't') {//桌号标识 if(tableString[0].matches("table")) { if(!tableString[1].matches("[1-9]|[1-9][0-9]|[1-9][0-9][0-9]") ) { System.out.println("wrong format"); } else {//桌号是数字 if(!(Integer.parseInt(tableString[1]) >= 1) && !( Integer.parseInt(tableString[1]) <= 55) ){ System.out.println(tableString[1] + " table num out of range"); } else { tables.addATable(); tables.getTables().get(tableNum).setTableNum(Integer.parseInt(tableString[1])); tables.getTables().get(tableNum).setTime1(tableString[2]); tables.getTables().get(tableNum).setTime2(tableString[3]); System.out.println(tableString[0] +" "+ tableString[1] +":"); } } //else if(tableString[2].matches("[1-2][1-9][1-9][1-9]/[]")) } else {//桌号标识错误 } } if(!(str[i].charAt(0) == 't') && !str[i].contains("delete") && tableString.length == 4) {//点菜记录处理 boolean recordIsTrue = true; if(tableString.length == 2) {//混杂的菜谱信息, System.out.println("invalid dish"); continue;//忽略这条菜谱 } if(tableString.length == 4) {//点菜记录 if(!tableString[2].matches("[1-9]")) {//份额格式错误 recordIsTrue = false; System.out.println("wrong format"); // } if(tableString[2].matches("[1-9]")) {//份额为数值 if(menu.searchDish(tableString[1]) != null) {//找到了菜名 if(menu.searchDish(tableString[1]).getSpecial() == "T") { //特价菜 if((tableString[2] != "1" || tableString[2] != "3")) { System.out.println(tableString[0] + "portion out of range" + tableString[2]); recordIsTrue = false; } else {//普通菜 if((tableString[2] != "1" || tableString[2] != "2" || tableString[2] != "3")) { System.out.println(tableString[0] + "portion out of range" + tableString[2]); recordIsTrue = false ; } } } } else { } } if(!tableString[3].matches("[1-9]|[1-9][0-9]")) {//份数非法 recordIsTrue = false; System.out.println("wrong format"); } if(tableString[3].matches("[1-9]|[1-9][0-9]")) {//份数越界 if(!(Integer.parseInt(tableString[3]) >= 1 && Integer.parseInt(tableString[3]) <= 15)) { System.out.println(tableString[0] + " num out of range " + tableString[3]); recordIsTrue = false; } } if(tableString.length == 4 && recordIsTrue == true) {//添加点菜记录 tables.getTables().get(tableNum).getOrder().addARecord(Integer.parseInt(tableString[0]), tableString[1], Integer.parseInt(tableString[2]), Integer.parseInt(tableString[3])); } }//点菜结束 if(str[i].contains("delete") && tableString.length == 2) {//删除记录 tables.getTables().get(tableNum).getOrder().delARecordByOrderNum(Integer.parseInt(tableString[0])); } if(str[i].matches("end")) { break; } }//点菜记录的处理 } } } class Dish { String name;//菜品名称 int unit_price;//单价 String special ;//特价菜标识 Dish(){ } Dish(String name,int unit_price){ this.name = name; this.unit_price = unit_price; } public String getName() { return this.name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getUnit_Price() { return this.unit_price; } public void setUnit_Price(int unit_price) { this.unit_price = unit_price; } public String getSpecial() { return special; } public void setSpecial(String special) { this.special = special; } public int getPrice(int portion){//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) int result = 0; if(portion == 1) result = unit_price*1; if(portion == 2) result = (int)(unit_price*1.5); if(portion == 3) result = unit_price*2; return result; } } class Menu{ private ArrayList<Dish> dishs = new ArrayList<>() ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息 private int dishNum = 0; Menu(){ super(); } public ArrayList<Dish> getDishs() { return dishs; } public void setDishs(ArrayList<Dish> dishs) { this.dishs = dishs; } public Dish searchDish(String dishName){//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。 for(int i = 0; i < dishs.size() ; i++){ if(dishs.get(i).getName() == dishName){ return dishs.get(i); } } return null; } public void addDish(String dishName,int unit_price){//添加一道菜品信息 Dish dish = new Dish(); dish.setName(dishName); dish.setUnit_Price(unit_price); dishs.add(dish); } } class Table{ int tableNum;//桌号 String time1;//日期 String time2;//时间 Order order = new Order();//点菜记录 String[] delRecord = new String[3];//删除记录 String[] addRecord = new String[3];//代点菜记录 Table(){ } public Table(int tableNum, String time1, String time2, Order order, String[] delRecord, String[] addRecord) { super(); this.tableNum = tableNum; this.time1 = time1; this.time2 = time2; this.order = order; this.delRecord = delRecord; this.addRecord = addRecord; } public int getTableNum() { return tableNum; } public void setTableNum(int tableNum) { this.tableNum = tableNum; } public String getTime1() { return time1; } public void setTime1(String time1) { this.time1 = time1; } public String getTime2() { return time2; } public void setTime2(String time2) { this.time2 = time2; } public Order getOrder() { return order; } public void setOrder(Order order) { this.order = order; } public String[] getDelRecord() { return delRecord; } public void setDelRecord(String[] delRecord) { this.delRecord = delRecord; } public String[] getAddRecord() { return addRecord; } public void setAddRecord(String[] addRecord) { this.addRecord = addRecord; } } class Time{ public static boolean CheckTime1Validity(String time1) { String[] str = time1.split("/"); if(str[0].matches("[1-9][0-9][0-9][0-9]") && str[1].matches("[1-9]|[1-9][0-9]") && str[2].matches("[1-9]|[1-9][0-9]")) { return true; } else { return false; } } public static boolean CheckTime1Range(String time1) { String[] str = time1.split("/"); int year = Integer.parseInt(str[0]); int month = Integer.parseInt(str[1]); int day = Integer.parseInt(str[2]); int[] mon_Max = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; if(year >= 2022 && year <= 2023 && month >= 1 && month <= 12 && day >=1 && day <= mon_Max[month]){ return true; } else return false; } public static boolean CheckTime2Validity(String time2) { String[] str = time2.split("/"); if(str[0].matches("[1-9]|[1-9][0-9]") && str[1].matches("[1-9]|[1-9][0-9]") && str[2].matches("[1-9]|[1-9][0-9]")) { return true; } else return false; } public static boolean CheckTime2Range(String time2){ String[] str = time2.split("/"); int hour = Integer.parseInt(str[0]); int minute = Integer.parseInt(str[1]); int second = Integer.parseInt(str[2]); if(hour > 0 && hour < 23 && minute > 0 && minute < 60 && second > 0 && second < 60) return true; else return false; } } class Tables{ ArrayList<Table> tables = new ArrayList<>(); public Tables() { super(); // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 } public Tables(ArrayList<Table> tables) { super(); this.tables = tables; } public ArrayList<Table> getTables() { return tables; } public void setTables(ArrayList<Table> tables) { this.tables = tables; } public void addATable() { Table table = new Table(); tables.add(table); } } class Record{//点菜记录 int orderNum;//序号 Dish d;//菜品 int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份) int num;//份数 Record(){ } public Record(int orderNum, Dish d, int portion, int num) { super(); this.orderNum = orderNum; this.d = d; this.portion = portion; this.num = num; } public int getOrderNum() { return orderNum; } public void setOrderNum(int orderNum) { this.orderNum = orderNum; } public Dish getD() { return d; } public void setD(Dish d) { this.d = d; } public int getPortion() { return portion; } public void setPortion(int portion) { this.portion = portion; } public int getNum() { return num; } public void setNum(int num) { this.num = num; } public int getPrice(){//计价,计算本条记录的价格 int result; result = d.getPrice(portion)*num; return result; } } class Order{//保存用户点的所有菜的信息。//点菜记录 ArrayList<Record> records = new ArrayList<>();//保存订单上每一道的记录 private int RecordNum = 0; public Record getRecord(int i) { return records.get(i); } public int getTotalPrice(){//计算订单的总价 int sum = 0;int i = 0 ; for(i = 0; i < records.size();i++){ sum += records.get(i).getPrice(); } return sum; } public void addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num){//添加一条菜品信息 records.get(RecordNum).setOrderNum(orderNum); records.get(RecordNum).getD().setName(dishName); records.get(RecordNum).setPortion(portion); records.get(RecordNum).setNum(num); RecordNum++; } public void delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum){//根据序号删除一条记录 for(int i = 0; i < records.size(); i++) { if(records.get(i).getOrderNum() == orderNum) { records.remove(i); } } } public Record findRecordByNUm(int orderNum){////根据序号查找一条记录 for(int i = 0 ; i < records.size() ; i++) { if(records.get(i).getOrderNum() == orderNum) { return records.get(i); } } return null; } }
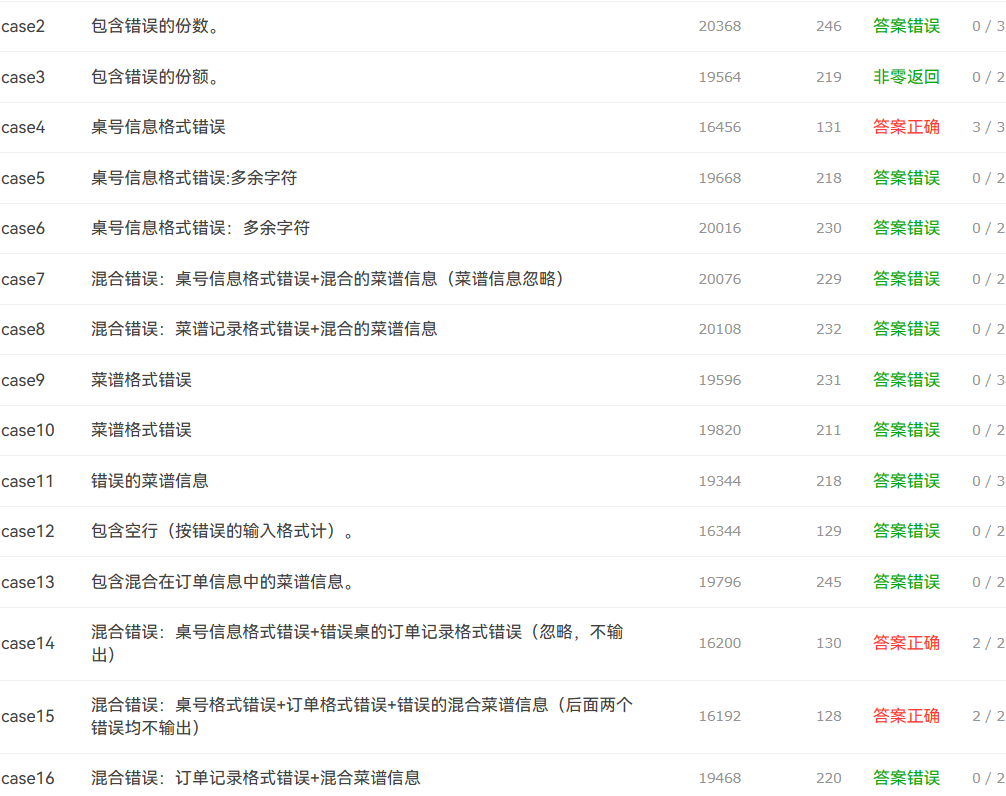
运行结果如上图:
只有一两个测试点对了,导致这个题目几乎没有分。
一开始写的时候,我是想着先写完后面具体的类的具体方法,最后再来写main类中的具体的逻辑。我的思路是先一行行得输入,遇到这个字符串为“end”时,就结束输入的循环,然后进行判断的操作:
若第一个字符不是t,则该行为菜单,菜单包含很多条菜;如果按空格切开来为2个,则为普通菜;如果切开来为3个,则为特殊菜。然后继续循环判断下一条字符串。如果字符串第一个字符为t,则跳出之前的循环,进入一个新的循环,之前的字符串都判定为菜单字符串;在新循环里,若该行第一个字符是t,则该行是桌号标识字符串,存在做好标识数组中;若该行不含delete且切开来是四个,则该行是点菜信息;若该行含有delete,且切开来是两行,则该行是删除记录,删除相应的菜谱信息;若该行含有“table”且切开来为6行,则该字符串为代点菜信息。如此循环,直到该字符串为end.
这个题目只有两个异常情况对了,正常的情况一个都没对;这还是因为我对类与类之间的关系还不够熟悉,再加上题目有一定难度,并且其他同学不想写的呼声很大,包括我自己也偷懒,写到一半就半途而废,所以这道题的分数就很低。
相应的类图如下:

三.踩坑心得
1.在写去除重复的数据这个题目的时候,我的源码如下:
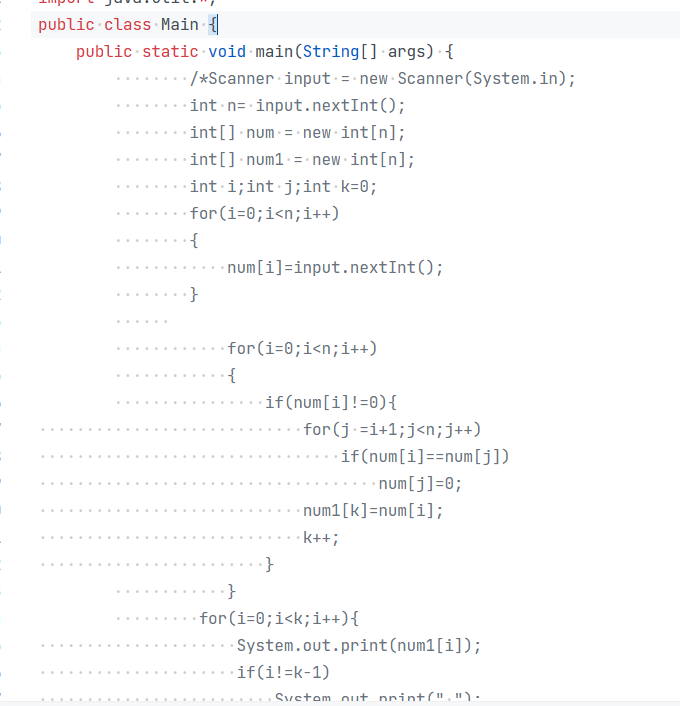
用的是后接法,把有重复的数据变成0,然后再输出不含0的项就行了,但是这个方法再N很大的时候就不行了,会运行超时。
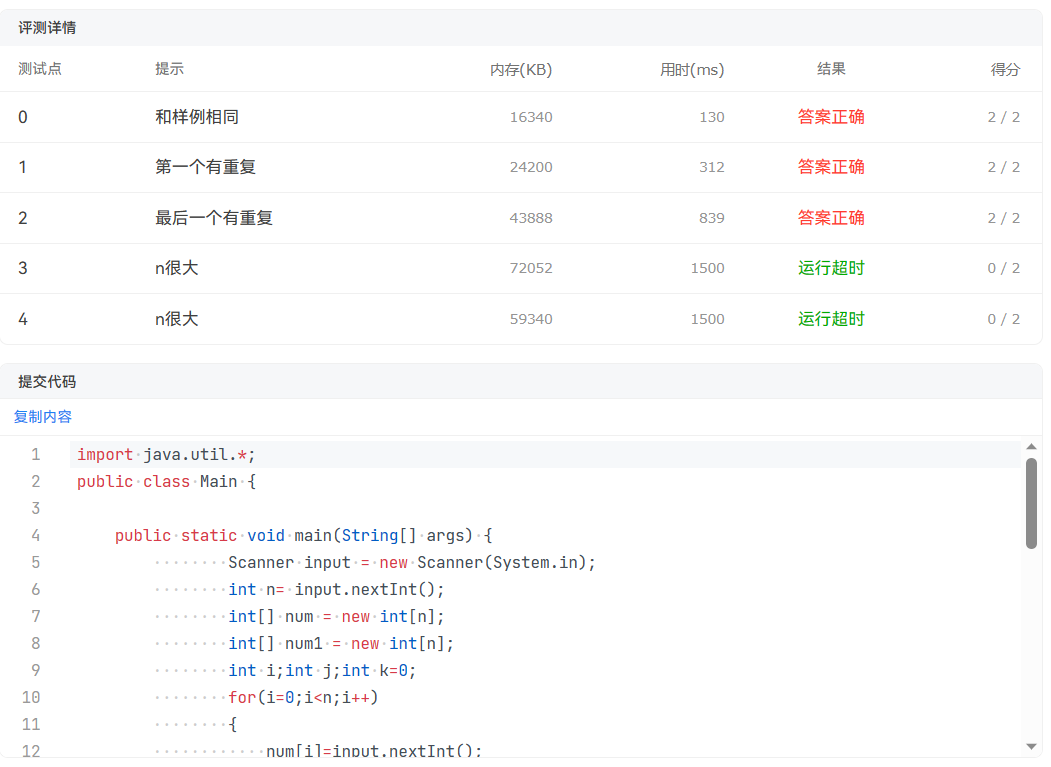
于是我就用了hashset和linkedhashset来避免有重复的数据,这样就不会出现N很大会运行超时的情况。
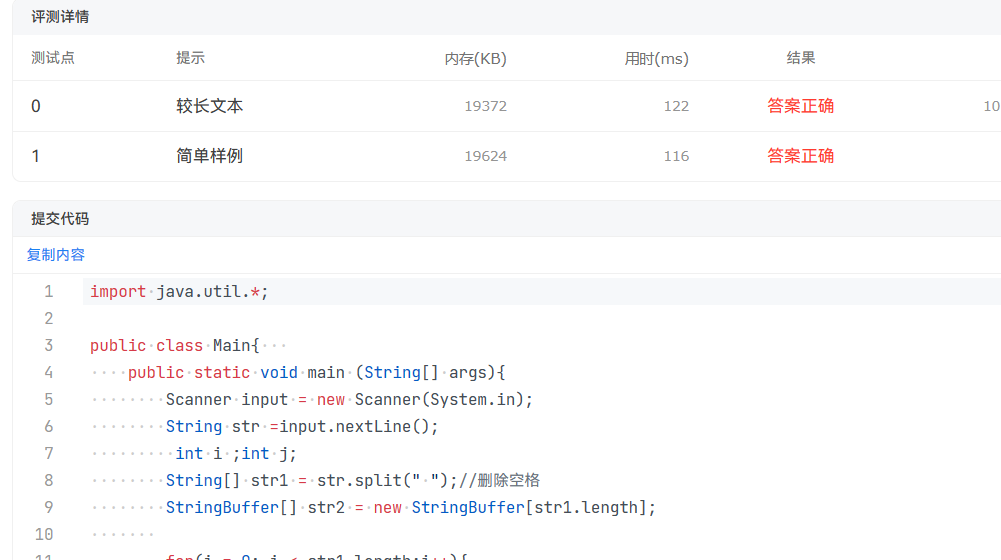
2.在写单词统计与排序这道题的时候,我一开始想着直接按照空格,逗号,句号来切割字符串:
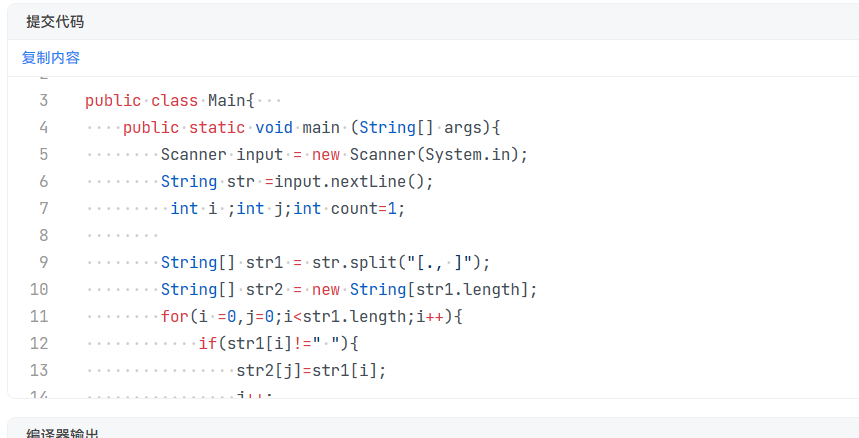
结果发现它并不会直接按照这些切割成一个个单词,而是返回空指针;后面我就转变了思路,先切割空格,再看切割出的单词是否含有句号或者逗号,然后删掉逗号和句号,最后按照单词的长度和大小来进行排序(可能是我正则表达式用的有问题),最后才得到正确答案。
3.在写日期问题面向对象设计的题目时,在DateUtil调用Month,Day和Year对象的时候,我一开始写的是date.day.month.year.getValue();导致运行的时候都是错误,后面问了同学才知道。每个类里的get方法可以返回该类含有的对象,于是将代码改为date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();这样就可以一直调用了。
四.改进建议
1.在写题目集四的判断两个日期之间的天数的时候,我的输出的函数如下:

一个是前面的日期更大的情况,另一个是前面的天数更小的情况。两个输出都有相同的部分,可以改成先根据日期的大小,判断两日期之间的天数是正数还是负数,对两个日期的天数进行处理 ,然后在进行输出,这样就不会有重复的代码。
2.题目集5的7-5判断日期是否合理的方法:
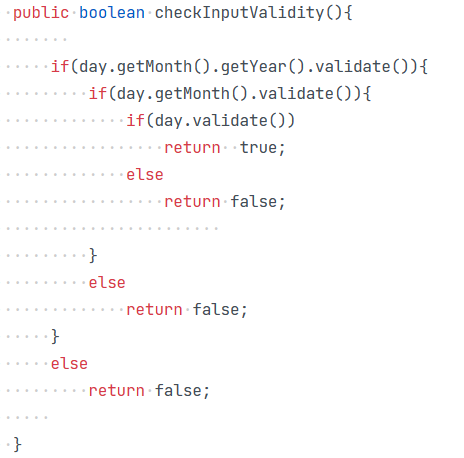
我是先判断年是否合理,再判断月份是否合理,最后再判断天数是否合理,后续可以改成if(day.getMonth().getYear()).validate() && day.getMonth().validate() && day.validate())直接判断三个值是否合法,否则返回false;这样比之前的更简洁,也不容易搞混括号的范围。
在求下N天的方法时

1 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ 2 for( ; n > 0 ; n--){ 3 if(month.getValue() != 12) {//不是12月 4 if(month.getValue() == 2){//二月 5 if(year.isLeapYear()){ 6 if(day.getValue() != 29) 7 day.dayIncrement(); 8 else{ 9 setDayMin(); 10 month.monthIncrement(); 11 12 } 13 } 14 else{//不是闰年 15 if(day.getValue() != 28) 16 day.dayIncrement(); 17 else{ 18 setDayMin(); 19 month.monthIncrement(); 20 } 21 } 22 }//2月 23 else{//不是二月 24 if(month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10){ 25 if(day.getValue() != 31) 26 day.dayIncrement(); 27 else{ 28 this.setDayMin(); 29 month.monthIncrement(); 30 } 31 32 } 33 else { 34 if(day.getValue() != 30) 35 day.dayIncrement(); 36 else{ 37 this.setDayMin(); 38 month.monthIncrement(); 39 40 } 41 } 42 43 } 44 } 45 else{ //是12月 46 if(day.getValue() != 31) 47 day.dayIncrement(); 48 else{ 49 this.setDayMin(); 50 month.resetMin(); 51 year.yearIncrement(); 52 } 53 } 54 55 }//n 56 DateUtil newDate = new DateUtil(day.getValue(),month.getValue(),year.getValue()); 57 return newDate; 58 }
我没次都是判断最后的日期不是临界值的时候,就让day++;后续可以改成一开始就让day++,再判断是否为临界值,如果是临界值的话,就让day等于1,然后月份和年也做相应的变换,这样可以节省很多行的 day.dayIncrement();节省空间。
五.总结
1.首先,通过这几次作业,我已经对类与对象的关系有了基本了解,类与类之间的关系有关联,依赖,聚合等,类可以实例化一个或多个对象,一个类中可以含有另一个类的对象,这样就形成了聚合关系。
2.题目集4的7-3去除重复数据,我知道了有LinkedHashSet这个工具,可以让存储的数据不重复,并且保持输入顺序的不变性,这在很多情况下就可以不用进行删除的步骤。
3.题目集4的最后一题,我知道了有关时间的很多方法,LocalDate类中比较两个日期之间的天数,返回的是相差的天数,有正也有负。
4.题目集5主要考察了正则表达式的使用,正则表达式是符合某种规则的字符串,只要满足这种规则的字符串就会返回true,利用这个可以检验QQ号,账号名,学号,验证码等有一定规律的字符串。
5.题目集5的日期类问题,我了解了类与类之间的关系,以及如何正确地设计类与类之间的关系。一个类可以包含另一个类中的对象,比如DateUtil类中含有Day类,Day类中含有Month类,Month类中含有Year类,它们之间的关系为聚集。




