LeetCode——994. 腐烂的橘子
994. 腐烂的橘子
在给定的网格中,每个单元格可以有以下三个值之一:
- 值
0代表空单元格; - 值
1代表新鲜橘子; - 值
2代表腐烂的橘子。
每分钟,任何与腐烂的橘子(在 4 个正方向上)相邻的新鲜橘子都会腐烂。
返回直到单元格中没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数。如果不可能,返回 -1。
示例 1:
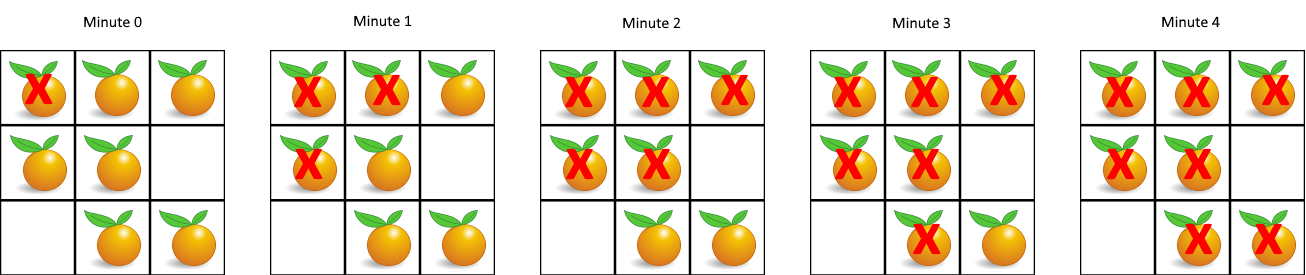
输入:[[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
输出:4
示例 2:
输入:[[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]]
输出:-1
解释:左下角的橘子(第 2 行, 第 0 列)永远不会腐烂,因为腐烂只会发生在 4 个正向上。
示例 3:
输入:[[0,2]]
输出:0
解释:因为 0 分钟时已经没有新鲜橘子了,所以答案就是 0 。
提示:
1 <= grid.length <= 101 <= grid[0].length <= 10grid[i][j]仅为0、1或2
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotting-oranges/
广度优先搜索(BFS)
C++
class Solution {
public:
int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int res = 0;
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
vector<pair<int,int>> dirs;
dirs.push_back(make_pair(-1,0));
dirs.push_back(make_pair(1,0));
dirs.push_back(make_pair(0,-1));
dirs.push_back(make_pair(0,1));
queue<pair<int,int>> rot;
multiset<pair<int,int>> good;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 2) rot.push(make_pair(i,j));
if(grid[i][j] == 1) good.insert(make_pair(i,j));
}
}
while(!rot.empty()){
int size = rot.size();
int flag = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
auto [x,y] = rot.front(); rot.pop();
for(auto couple : dirs){
auto tmp = make_pair(x + couple.first,y + couple.second);
if(good.find(tmp) != good.end()){ //找到有与腐烂橘子相邻的好橘子
good.erase(tmp); //好橘子被传染,从好橘子集合移除
rot.push(tmp); //加入坏橘子队列
flag = 1;
}
}
}
if(flag) res+=1;
}
if(good.size() > 0) return -1;
return res;
}
};
java
class Solution {
int[] dr = new int[]{-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dc = new int[]{0, -1, 0, 1};
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
int R = grid.length, C = grid[0].length;
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque();
Map<Integer, Integer> depth = new HashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < R; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < C; ++j)
if (grid[r][c] == 2) {
int code = i * C + j;
queue.add(code);
depth.put(code, 0);
}
int ans = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int code = queue.remove();
int i = code / C, j = code % C;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int nr = i + dr[k];
int nc = j + dc[k];
if (0 <= nr && nr < R && 0 <= nc && nc < C && grid[nr][nc] == 1) {
grid[nr][nc] = 2;
int ncode = nr * C + nc;
queue.add(ncode);
depth.put(ncode, depth.get(code) + 1);
ans = depth.get(ncode);
}
}
}
for (int[] row: grid)
for (int v: row)
if (v == 1)
return -1;
return ans;
}
}
python
class Solution:
def orangesRotting(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# 网格的长,宽
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
# 网格每一个坐标的访问状态
visit = [[False] * n for y in range(m)]
# 找出最开始时,网格中所有坏橘子的坐标
stack = [[y,x] for y in range(m) for x in range(n) if grid[y][x]==2]
# 坏橘子传染好橘子的四个方向,上下左右
direction = [[-1,0], [1,0], [0,-1], [0,1]]
# 初始时间
minute = 0
# 开始坏橘子传染好橘子的循环,直到没有好橘子可以被传染
while True:
# 初始化一个stack_next,把这一轮变坏的橘子装进里面
stack_next = []
# 开始对坏橘子进行审查,主要是看上下左右有没有好橘子
while stack:
# 拿出坏橘子的坐标点
y, x = stack.pop()
# 再看坏橘子上下左右的坐标对应的坐标
for d in direction:
y_new, x_new = y + d[0], x + d[1]
# 如果坐标在网格范围内,而且坐标没有被访问过,且这个坐标确实有个好橘子
if -1 < y_new < m and -1 < x_new < n and not \
visit[y_new][x_new] and grid[y_new][x_new] == 1:
# 观察慰问一下这个好橘子,表示已经访问过了
visit[y_new][x_new] = True
# 告诉这个好橘子,你已被隔壁的坏橘子感染,现在你也是坏橘子了
grid[y_new][x_new] = 2
# 放进stack_next里面,集中管理,精准隔离,方便排查下一轮会变坏的橘子
stack_next.append([y_new, x_new])
# 如果橘子们都检查完了发现再无其他坏橘子,终止循环,宣布疫情结束
if not stack_next: break
# 把这一轮感染的坏橘子放进stack里,因为我们每一轮都是从stack开始搜索的
stack = stack_next
# 看来橘子们还没凉透,来,给橘子们续一秒,哦不,续一分钟
minute += 1
# 经过传染,审查,隔离的循环后,如果还有好橘子幸存,返回-1宣布胜利,否则返回橘子们的存活时间
return -1 if ['survive' for y in range(m) for x in range(n) if grid[y][x]==1] else minute



