@SpringBootApplication:
包含 @Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan
通常用在主类上。
@ComponentScan:
作用是组件扫描和自动装配。相当于 <context:component-scan>,如果扫描到有 @Component @Controller @Service 等等这些注解的类,则把这些类注册为bean。
扫描的范围默认是它所在的包以及子包中所有带有注解的对象(程序启动类所在的目录及其子目录)。
@Configuration:
@Configuration用在类上面,表明这个是个配置类。指出该类是 Bean 配置的信息源,相当于XML中的 <beans></beans>,如下配置文件。
@Configuration 注解类表示这个类可以使用 Spring IoC 容器作为 bean 定义的来源。@Bean 注解告诉 Spring,一个带有 @Bean 的注解方法将返回一个对象,该对象应该被注册为在 Spring 应用程序上下文中的 bean。

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 5 <!--实例化一个Person对象--> 6 <bean id="userBean" class="com.springboot.com.study.userBean"/> 7 </beans>
@Bean:
相当于XML中的<bean></bean>,放在方法的上面,而不是类,意思是产生一个bean,并交给spring管理。

1 public class UserBean { 2 3 public UserBean() { 4 System.out.println("UserBean初始化成功!"); 5 } 6 7 private int id; 8 9 private String userName; 10 11 private String userAccount; 12 13 private String userPwd; 14 15 public int getId() { 16 return id; 17 } 18 19 public void setId(int id) { 20 this.id = id; 21 } 22 23 public String getUserName() { 24 return userName; 25 } 26 27 public void setUserName(String userName) { 28 this.userName = userName; 29 } 30 31 public String getUserAccount() { 32 return userAccount; 33 } 34 35 public void setUserAccount(String userAccount) { 36 this.userAccount = userAccount; 37 } 38 39 public String getUserPwd() { 40 return userPwd; 41 } 42 43 public void setUserPwd(String userPwd) { 44 this.userPwd = userPwd; 45 } 46 47 @Override 48 public String toString() { 49 return "UserBean{" + 50 "id=" + id + 51 ", userName='" + userName + '\'' + 52 ", userAccount='" + userAccount + '\'' + 53 ", userPwd='" + userPwd + '\'' + 54 '}'; 55 } 56 }

1 @Configuration 2 public class BeanConfiguration { 3 4 public BeanConfiguration(){ 5 System.out.println("AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 初始化成功!"); 6 } 7 8 @Bean 9 public UserBean getUserBean(){ 10 UserBean userBean=new UserBean(); 11 userBean.setId(1); 12 userBean.setUserAccount("admin"); 13 userBean.setUserName("管理员"); 14 userBean.setUserPwd("123"); 15 return userBean; 16 } 17 18 }

@SpringBootTest public class AnnotationTest { @Autowired private UserBean userBean; @Test public void beanConfiguration(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(UserBean.class); UserBean userBean = (UserBean) applicationContext.getBean("userBean"); System.out.println(userBean.toString()); } }
@EnableAutoConfiguration:
让 Spring Boot 根据应用所声明的依赖来对 Spring 框架进行自动配置,一般加在主类上(也可以不加主类上,能够初始化就行)。
跟踪 @EnableAutoConfiguration ,查看 @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) 注解:
@Import:
在应用中,有时没有把某个类注入到IOC容器中,但在运用的时候需要获取该类对应的bean,此时就需要用到@Import注解。可以理解为,只要加了这个注解,这个类就会被 Spring进行管理。
这个注解类似于:
<import resource="classpath*:/spring/***" />
注入Bean实例:

public class DogBean { public DogBean() { System.out.println("汪汪汪"); } private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } public class CatBean { public CatBean() { System.out.println("喵喵喵"); } private int id; private String name; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }

@Configuration @Import(value = {DogBean.class,CatBean.class}) public class BeanConfiguration2 { } @SpringBootTest public class AnnotationTest { @Autowired private DogBean dogBean; @Autowired private CatBean catBean; }

@PropertySource 和 @ConfigurationProperties @Value
@ConfigurationProperties 注解默认读取主配置文件,springboot 中主配置文件是 application.properties 和 application.yml
@PropertySource 注解指定此配置文件路径。是SpringBoot标注了IOC容器里面的对象。
当IOC容器里的对象初始化完成后,再去扫描@ConfigurationProperties ,根据配置文件内的前缀,把配置信息注入到这个对象内的set 方法。
Bean必须有 Set()方法,否则可以用 @Data() 注解替代 Set()方法
@Value 将外部的值动态注入到Bean中,使用的情况。
配置文件代码:application.properties方式:

configbeans.id=123 configbeans.name=zhangsan configbeans.arrays=1,2,3 configbeans.lists=jinan,qingdao,weifang configbeans.maps.name1=zhangsan configbeans.maps.name2=lisi configbeans.maps.name3=wangerma configbeans.sets=shandong,shanxi,bejing,shanghai configbeans.birthday=2020/03/19 22:22:10

/* 注入的Bean对象 */ @Component @PropertySource("classpath:application.properties") @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "configbeans") public class ConfigInjectBean { private Integer id; private String name; private String[] arrays; private List<String> lists; private Map<String, String> maps; private Set<String> sets; private Date birthday; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String[] getArrays() { return arrays; } public void setArrays(String[] arrays) { this.arrays = arrays; } public List<String> getLists() { return lists; } public void setLists(List<String> lists) { this.lists = lists; } public Map<String, String> getMaps() { return maps; } public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) { this.maps = maps; } public Set<String> getSets() { return sets; } public void setSets(Set<String> sets) { this.sets = sets; } public Date getBirthday() { return birthday; } public void setBirthday(Date birthday) { this.birthday = birthday; } @Override public String toString() { return "ConfigInjectBean{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", arrays=" + Arrays.toString(arrays) + ", lists=" + lists + ", maps=" + maps + ", sets=" + sets + ", birthday=" + birthday + '}'; } } @SpringBootTest public class AnnotationTest { /* 测试方法 */ @Test public void configInjectBeanPrint(){ System.out.println(configInjectBean.toString()); } }
application.yml 配置方式。
需要注意的是,SpingBoot中 application.properties 优先级比 application.yml 高,所以两个都配置了的话,优先读取application.properties
 View Code
View Code 上面这种配置文件注入方式必须有get() set() ,还可以通过 @Value 注解注入配置信息,不需要写 get() set()
@Value和 @ConfigurationProperties 区别:前者是主动到IOC容器里寻找值,后者被被动的被IOC容器注入。

configbeans.id=123 configbeans.name=zhangsan configbeans.arrays=1,2,3 configbeans.lists=jinan,qingdao,weifang #configbeans.maps.name1=zhangsan #configbeans.maps.name2=lisi #configbeans.maps.name3=wangerma configbeans.maps={key1: 'value1', key2: 'value2'} configbeans.sets=shandong,shanxi,bejing,shanghai configbeans.birthday=2020/03/19 22:22:10

/* 注入的Bean对象 */ @Component public class ConfigInjectBean { @Value("${configbeans.id}") private Integer id; @Value("${configbeans.name}") private String name; @Value("${configbeans.arrays}") private String[] arrays; @Value("${configbeans.lists}") private List<String> lists; @Value("#{${configbeans.maps}}") private Map<String, String> maps; @Value("${configbeans.sets}") private Set<String> sets; @Value("${configbeans.birthday}") private Date birthday; @Override public String toString() { return "ConfigInjectBean{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", arrays=" + Arrays.toString(arrays) + ", lists=" + lists + ", maps=" + maps + ", sets=" + sets + ", birthday=" + birthday + '}'; } } @SpringBootTest public class AnnotationTest { /* 测试方法 */ @Test public void configInjectBeanPrint(){ System.out.println(configInjectBean.toString()); } }
@ImportResource()
SpringBoot不推荐使用xml配置文件,但是实际上SpringBoot是支持XML配置文件的。在实际开发中,用 @ImportResource 来导入一个传统的XML配置文件,将配置文件内对象交由Spring进行管理。
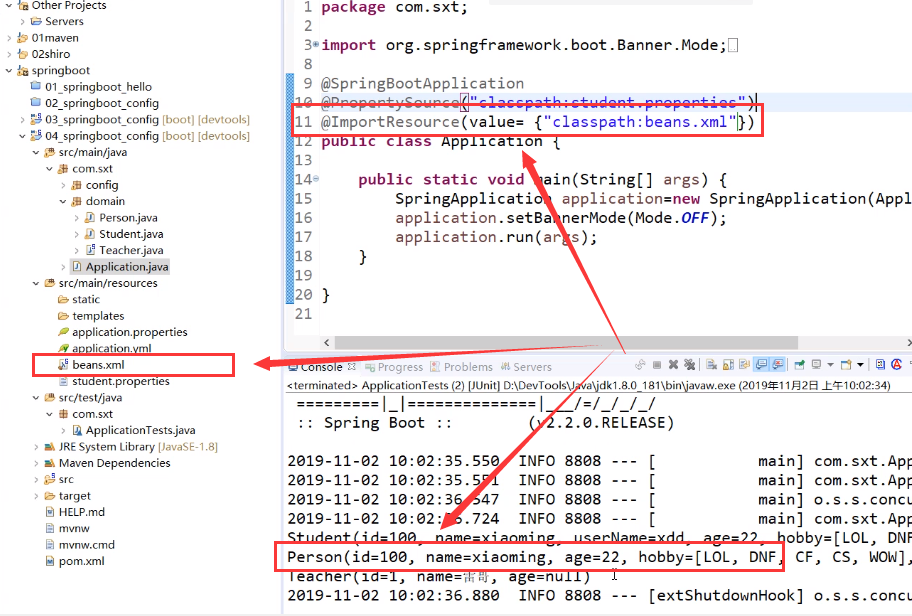
@Inherited
@Inherited 元注解是一个标记注解,
@Inherited阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。 如果一个使用了@Inherited 修饰的annotation类型被用于一个class,则这个annotation将被用于该class的子类。
注意:@Inherited annotation 类型是被标注过的class的子类所继承。类并不从它所实现的接口继承 annotation, 方法并不从它所重载的方法继承annotation。
当 @Inherited annotation 类型标注的annotation的Retention是 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME,则反射API增强了这种继承性。
如果我们使用 java.lang.reflect 去查询一个@Inherited annotation类型的annotation时,反射代码检查将展开工作: 检查class和其父类,直到发现指定的annotation类型被发现,或者到达类继承结构的顶层。
@Repository:
用于标注数据访问组件,即 DAO组件。
@Service:
用于标注业务层组件。
@RestController:
用于标注控制层组件(如struts中的action),包含 @Controller 和 @ResponseBody。
@ResponseBody:
表示该方法的返回结果直接写入HTTP response body中
一般在异步获取数据时使用,在使用 @RequestMapping 后,返回值通常解析为跳转路径,加上@responsebody 后返回结果不会被解析为跳转路径,而是直接写入HTTP response body中。比如异步获取json数据,加上@Responsebody() 后,会直接返回json数据。
@Component:
泛指组件,当组件不好归类的时候,我们可以使用这个注解进行标注。
@AutoWired:
byType方式。把配置好的Bean拿来用,完成属性、方法的组装,它可以对类成员变量、方法及构造函数进行标注,完成自动装配的工作。
当加上(required=false)时,就算找不到bean也不报错。
@Qualifier:
当有多个同一类型的Bean时,可以用 @Qualifier("name") 来指定。与 @Autowired 配合使用
@Resource(name="name",type="type"):
没有括号内内容的话,默认byName,否则 Type。与 @Autowired 干类似的事。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
修饰注解的注解。用来指定注解修饰类的哪个成员。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //接口、类、枚举 @Target(ElementType.FIELD) //字段、枚举的常量 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) //方法 @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) //方法参数 @Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) //构造函数 @Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)//局部变量 @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)//注解 @Target(ElementType.PACKAGE) ///包
@RequestMapping:
RequestMapping 是一个用来处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于类或方法上。用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径。
该注解有六个属性:
params:指定request中必须包含某些参数值是,才让该方法处理。
headers:指定request中必须包含某些指定的header值,才能让该方法处理请求。
value:指定请求的实际地址,指定的地址可以是URI Template 模式
method:指定请求的method类型, GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等
consumes:指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),如application/json,text/html;
produces:指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回
@RequestParam:
用在方法的参数前面。
@RequestParam String a =request.getParameter("a")。
@PathVariable:
路径变量。参数与大括号里的名字一样要相同。
RequestMapping("user/get/mac/{macAddress}")
public String getByMacAddress(@PathVariable String macAddress){
//do something;
}
@Profiles
Spring Profiles提供了一种隔离应用程序配置的方式,并让这些配置只能在特定的环境下生效。
任何 @Component 或 @Configuration 都能被 @Profile 标记,从而限制加载它的时机。
@Configuration @Profile("prod") public class ProductionConfiguration { // ... }
@ConfigurationProperties
Spring Boot将尝试校验外部的配置,默认使用JSR-303(如果在classpath 路径中)。
你可以轻松的为你的 @ConfigurationProperties 类添加 JSR-303 javax.validation 约束注解:
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix="connection") public class ConnectionSettings { @NotNull private InetAddress remoteAddress; // ... getters and setters }
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
实体向前端返回 Json 时的时间日期格式,timezone 表示为东八区。
public class CompanyModel { public String companyCode; public String companyName; @JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8") private Date addTime; public String getCompanyCode() { return companyCode; } public void setCompanyCode(String companyCode) { this.companyCode = companyCode; } public String getCompanyName() { return companyName; } public void setCompanyName(String companyName) { this.companyName = companyName; } public Date getAddTime() { return addTime; } public void setAddTime(Date addTime) { this.addTime = addTime; } }
@DateTimeFormat()
@DateTimeFormat(pattern ="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
和 @JsonFormat()注解相反,@DateTimeFormat()注解是前端往后端接收日期的数据格式。
()








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?