struts2拦截器的使用
拦截器的使用
转自http://blog.csdn.net/woshisap/article/details/7271854
1:拦截器(Interceptor)
拦截器是Struts2最强大的特性之一,它是一种可以让用户在Action执行之前和Result执行之后进行一些功能处理的机制。

图中示意了三个拦截器,Interceptor1、Interceptor2、Interceptor3,注意的是他们的执行顺序,在Action运行之前是按照Interceptor1、Inteceptor2和Inteceptor3的顺序,而在Result执行之后,再次运行拦截器的时候是按照Interceptor3、Interceptor2和Interceptor1的顺序执行的,顺序刚好相反。
2:拦截器的优点
a:简化了Action的实现。拦截器能把很多功能从Action中独立出来,大量减少了Action的代码
b:功能更单一。按照上面的描述,把功能从Action中分离出来,分散到不同的拦截器中,这样每个拦截器的功能,以及Action本身的功能就更单一了。
c:通用代码模块化。从Action中把功能分离出来,放到拦截器中去实现,这样能把一些在多个Action中通用的代码进行模块化,封装在一个或者几个拦截器中。
d:提高重用性。当通用的功能代码被封装在拦截器中,实现了代码模块化过程之后,就可以对不同的Action,根据功能需要,来配置相同的拦截器了。
e:实现AOP。
拦截器相比Filter具有更强大的功能,比如拦截器与Servlet的API无关,比如拦截器可以访问到值栈等。
3:拦截器的的调用顺序
a:首先,要找到它自己有没有声明拦截器的引用,即<action>元素有没有<interceptor-ref>子元素,如果有,则不用继续寻找,直接使用这些拦截器,如果没有进行下一步的查找。
b:其次,找到这个<action>所在包有没有声明默认的拦截器引用,即<package>元素的<default-interceptor-ref>子元素,如果有,则不用继续再找,直接使用这些拦截器,如果没有,则进行下一步的查找。
c:递归的查找这个包的父包,看看有没有声明默认的拦截器引用,直到找到默认的拦截器引用为止。
4:开发自定义的拦截器
开发自定义的拦截器,要实现Interceptor接口,还要使用到ActionInvocation接口,现在对ActionInvocation接口进行简单的介绍。
它里面有一些方法,如下:
a:getAction,获得这次请求准备执行的Action对象。
b:getProxy,返回这次请求的ActionProxy对象,可以在这个对象上获得要运行Action的哪个方法。
c:getInvocationContext,返回这个Action执行的上下文(ActionContext),可以在这个上下文对象中获得大量的数据,比如请求的parameter值,session的值等。
d:在ActionContext中取到的parameter值是一个Map<String, Object>,其中以String为key,以String[]为value,这个Map记录了所有的request参数。
e:getResult方法,返回Result运行之后代表结果的Result对象。
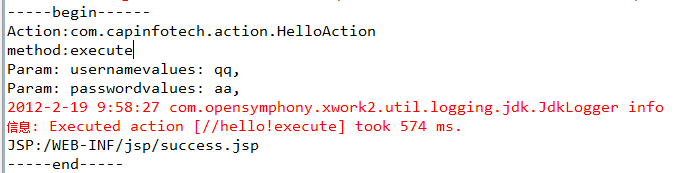
我们要实现这样一个Aciton,要求拦截器输出如下的信息:运行哪个Action类,运行哪个方法,请求的参数和Action运行完要跳转到哪个JSP。
- import java.util.Map;
- import org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ServletDispatcherResult;
- import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionInvocation;
- import com.opensymphony.xwork2.Result;
- import com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.Interceptor;
- public class LoggerInterceptor implements Interceptor {
- @Override
- public void destroy() {
- }
- @Override
- public void init() {
- }
- @Override
- public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
- System.out.println("-----begin------");
- //运行的action的名字
- String actionName = invocation.getAction().getClass().getName();
- System.out.println("Action:" + actionName);
- //执行的action的方法
- String method = invocation.getProxy().getMethod();
- System.out.println("method:" + method);
- //获得这次请求的parameter对象,并打印
- Map<String, Object> params = invocation.getInvocationContext().getParameters();
- for(String key : params.keySet()) {
- Object obj = params.get(key);
- if(obj instanceof String[]) {
- String[] array = (String[])obj;
- System.out.print("Param: " + key + "values: ");
- for(String value : array) {
- System.out.print(value + ", ") ;
- }
- System.out.print("\n");
- }
- }
- //运行后续的拦截器、Action和Result
- String resultCode = invocation.invoke();
- //在Action和Result运行之后,得到Result对象,并且可以强制转换成ServletDispatcherResult
- //打印其下一个jsp的位置
- Result result = invocation.getResult();
- if(result instanceof ServletDispatcherResult) {
- ServletDispatcherResult dispatcherResult = (ServletDispatcherResult)result;
- System.out.println("JSP:" + dispatcherResult.getLastFinalLocation());
- }
- System.out.println("-----end-----");
- return resultCode;
- }
- }
5:一个重要的拦截器timer
timer拦截器是Struts2的预定义拦截器之一,可以用来记录Action运行的时间。
配置:在struts.xml中写入配置信息,如下所示,
- <package name="hello" namespace="/" extends="struts-default">
- <interceptors>
- <interceptor name="MyLogger" class="com.capinfotech.inteceptor.LoggerInterceptor">
- </interceptor>
- </interceptors>
- <action name="hello" class="com.capinfotech.action.HelloAction">
- <interceptor-ref name="MyLogger"></interceptor-ref>
- <interceptor-ref name="timer"></interceptor-ref>
- <interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"></interceptor-ref>
- <result name="success">/WEB-INF/jsp/success.jsp</result>
- </action>
- </package>
程序运行输入信息如下:
6:Struts2的预定义拦截器
a:params拦截器
把请求参数设置进Action的相应属性,并自动进行类型转换
b:staticParams拦截器
将struts.xml配置文件里定义的Action参数,设置到对应的Action实例中,Action参数使用<param>标签,是<action>标签的子元素。
<action name="hello" class="HelloAction">
<param name="account">test</param>
</action>
这要求action中有一个account属性,并有相应的setter和getter方法,运行的时候,action的account属性在初始化过后,会接到这里的赋值test。
c:prepare拦截器
在action执行之前调用Action的prepare方法,这个方法是用来准备action之前要做的工作,它要求用户必须实现com.opensymphony.xwork2.Preparable接口。
d:modelDriven拦截器
如果action实现了ModelDriven接口,它将getModel方法取得的模型对象存入OgnlValueStack中。
e:chain拦截器
chain拦截器,将前一个执行结束的Action属性设置到当前的action中,它被用在ResultType为"chain"所指定的结果的Action中,该结果Action对象会从值栈获得前一个Action对应的属性,它实现Action链之间的数据传递。
f:exception拦截器
在抛出异常的时候,这个拦截器起作用,任何应用都应该引用这个拦截器,而且引用的时候,最好把它放在第一位,让它能捕获所有的异常。
g:validation拦截器
调用验证框架读取*-validation.xml文件,并且应用在这些文件中声明的校验。
h:token拦截器
核对当前Action请求(request)的有效标识,防止重复提交Action请求,使用标签<s:token>可以生成表单令牌,该标签会在Session中设置一个预期的值,并且在表单中创建一个隐藏的input字段,Token拦截器会检查这个令牌,如果不合法,将不会执行Action,这个拦截器是手工添加的,还需要一个invalide.token的result。
i:conversionError拦截器
用来处理框架进行类型转化(Type Conversion)时的出错信息,它将存储在ActionContext中的类型转化错误信息转化成相应的Action字段的错误信息,保存在堆栈中。根据需要,可以将这些错误信息在视图中显示出来。
j:fileUpload拦截器
用来处理上传文件
k:workflow拦截器
Action默认的工作流,如果Action实现了Validateable接口,那么interceptor会调用action的validate()方法,如果Action实现了ValidateAware接口,那么interceptor将会检查Action是否包含错误信息,如果包含错误信息,那么Interceptor将会返回input,而不让Action继续执行。
l:servletConfig拦截器
这个拦截器提供Action直接对Servlet API的调用,把Servlet API的对象注入到Action中,包括ServletRequestAware,ServletResponseAware,ParameterAware,SessionAware和ApplicationAware
m:timer拦截器
记录ActionInvocation剩余部分执行的时间,并作为日志信息记录下来,便于寻找性能瓶颈。
n:logger拦截器
在日志信息中输出要执行的Action信息,这样,在调试的时候,就能很快的定位到这个对应的Action中了。
o:tokenSession拦截器
扩展了token拦截器的功能,当提交无效的Action请求标识时,它会跳转到第一次成功后的页面



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号