[HAOI2007]理想的正方形 st表 || 单调队列
题解:
因为数据范围不大,而且题目要求的是正方形,所以这道题有2种解法。
1,st表。
这种解法暴力好写好理解,但是较慢。我们设st[i][j][k]表示以(i, j)为左端点,向下/向右分别扩展$2^k$格的最大值,最小值同理,处理完后$n^2$枚举左端点取最优值即可。
(此为早期代码,写丑了不要介意)

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define R register int 4 #define AC 1010 5 #define ac 110 6 //#define getchar() *S ++ 7 //char READ[1250000],*S = READ; 8 int n,a,b,ans = INT_MAX; 9 int st_max[AC][AC][7], st_min[AC][AC][7]; 10 int k, q = 1; 11 //二维ST表emmmm 12 13 inline int read() 14 { 15 int x = 0;char c = getchar(); 16 while(c > '9' || c < '0') c = getchar(); 17 while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar(); 18 return x; 19 } 20 21 inline int Max(int a, int b, int c, int d) 22 { 23 if(a > b && a > c && a > d) return a; 24 else if(b > c && b > d) return b; 25 else if(c > d) return c; 26 else return d; 27 } 28 29 inline int Min(int a, int b, int c, int d) 30 { 31 if(a < b && a < c && a < d) return a; 32 else if(b < c && b < d) return b; 33 else if(c < d) return c; 34 else return d; 35 } 36 37 void pre() 38 { 39 a = read(), b = read(), n = read(); 40 for(R i = 1; i <= a; i ++) 41 for(R j = 1; j <= b; j ++) 42 st_max[i][j][0] = st_min[i][j][0] = read(); 43 } 44 45 void check() 46 { 47 for(R i = 1; i <= a; i ++) 48 for(R j = 1; j <= b; j ++) 49 { 50 printf("!!!(%d , %d)\nst_max:\n", i, j); 51 for(R l = 1; l <= k; l ++) 52 printf("2^%d = %d\n", l, st_max[i][j][l]); 53 printf("\n"); 54 printf("st_min:\n"); 55 for(R l = 1; l <= k; l ++) 56 printf("2^%d = %d\n", l, st_min[i][j][l]); 57 printf("\n\n"); 58 } 59 } 60 61 void build() 62 { 63 while(n > q) q <<= 1, ++ k; 64 -- k, q >>= 1; 65 int pos=1; 66 for(R l = 1; l <= k; l ++) 67 { 68 for(R i = pos + 1; i <= a; i ++) 69 { 70 for(R j = pos + 1; j <= b; j ++) 71 { 72 st_max[i][j][l] = Max(st_max[i - pos][j][l - 1], st_max[i][j - pos][l - 1], st_max[i - pos][j - pos][l - 1], st_max[i][j][l - 1]); 73 st_min[i][j][l] = Min(st_min[i - pos][j][l - 1], st_min[i][j - pos][l - 1], st_min[i - pos][j - pos][l - 1], st_min[i][j][l - 1]); 74 } 75 } 76 pos <<= 1; 77 } 78 } 79 80 void work() 81 { 82 int maxn, minn; 83 for(R i = n; i <= a; i ++) 84 for(R j = n; j <= b; j ++) 85 { 86 maxn = Max(st_max[i][j][k], st_max[i - n + q][j - n + q][k], st_max[i - n + q][j][k], st_max[i][j - n + q][k]); 87 minn = Min(st_min[i][j][k], st_min[i - n + q][j - n + q][k], st_min[i - n + q][j][k], st_min[i][j - n + q][k]); 88 ans = min(ans, maxn - minn); 89 } 90 printf("%d\n", ans); 91 } 92 93 int main() 94 { 95 // freopen("in.in", "r", stdin); 96 //fread(READ, 1, 1200000, stdin); 97 pre(); 98 build(); 99 //check(); 100 work(); 101 // fclose(stdin); 102 return 0; 103 }
2,单调队列。
其实也好理解,,,但是感觉很多博客没有图所以意思讲的不是很清晰,这里就详细讲一下吧。
类似于滑动窗口,如果没做过这题建议先理解这题的做法。
可以看做此题就是滑动窗口的二维扩展版。那么我们已经有了在序列上获取指定区间大小的最大最小值的方法,要如何才能扩展到二维平面上呢?
其实画个图就很好理解了。
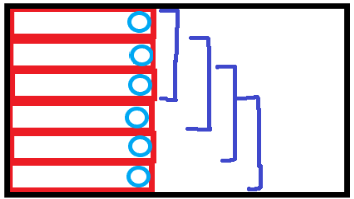
如果我们将每个红色区间的最大最小值都存在蓝色点上,那么只需要对蓝色点做一次滑动窗口,就可以获得指定大小的矩形最大最小值了。
因为每个蓝色点已经代表了指定区间大小的行的最大最小值,所以再在这个基础上查询蓝点指定区间的最大最小值就相当于是在查询一个矩形了。

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define R register int 4 #define AC 1100 5 #define LL long long 6 7 int n, m, k, ans = INT_MAX; 8 int s[AC][AC], g[AC][AC], f[AC][AC]; 9 10 struct node{ 11 int x, id; 12 }; 13 14 struct que{ 15 node q[AC];int head, tail; 16 void init() 17 { 18 head = 1, tail = 0; 19 } 20 21 void add_max(int x, int id) 22 { 23 while(head <= tail && q[head].id <= id - k) ++ head; 24 while(head <= tail && q[tail].x <= x) -- tail; 25 q[++tail] = (node){x, id}; 26 } 27 28 void add_min(int x, int id) 29 { 30 while(head <= tail && q[head].id <= id - k) ++ head; 31 while(head <= tail && q[tail].x >= x) -- tail; 32 q[++tail] = (node){x, id}; 33 } 34 35 int top() {return q[head].x;} 36 }q1, q2; 37 38 inline void upmin(int &a, int b) 39 { 40 if(b < a) a = b; 41 } 42 43 inline int read() 44 { 45 int x = 0;char c = getchar(); 46 while(c > '9' || c < '0') c = getchar(); 47 while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar(); 48 return x; 49 } 50 51 void pre() 52 { 53 n = read(), m = read(), k = read(); 54 for(R i = 1; i <= n; i ++) 55 for(R j = 1; j <= m; j ++) s[i][j] = read(); 56 } 57 58 void build()//先对每一行求出来 59 { 60 for(R i = 1; i <= n; i ++)//枚举行 61 { 62 q1.init(), q2.init(); 63 for(R j = 1; j <= m; j ++)//枚举列 64 { 65 q1.add_min(s[i][j], j), q2.add_max(s[i][j], j); 66 if(j >= k) f[i][j] = q1.top(), g[i][j] = q2.top(); 67 } 68 } 69 } 70 71 void work()//再求整体的 72 { 73 for(R i = k; i <= m; i ++)//先枚举列,再枚举行 74 { 75 q1.init(), q2.init(); 76 for(R j = 1; j <= n; j ++) 77 { 78 q1.add_min(f[j][i], j), q2.add_max(g[j][i], j); 79 if(j >= k) upmin(ans, q2.top() - q1.top()); 80 } 81 } 82 printf("%d\n", ans); 83 } 84 85 int main() 86 { 87 // freopen("in.in", "r", stdin); 88 pre(); 89 build(); 90 work(); 91 // fclose(stdin); 92 return 0; 93 }



