ThreadLocal 使用和源码分析
前言
ThreadLocal 线程本地变量/线程本地存储
用来提供线程内部的局部变量(ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类对象),将一个共用的ThreadLocal静态实例作为key,通过get或set方法访问时能保证各个线程里的变量相对独立于其他线程内的变量;在线程执行的各处通过这个静态ThreadLocal实例,用于关联线程和线程的上下文,避免了将这个对象作为参数传递的麻烦。
基本操作
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
/**
* ThreadLocals rely on per-thread linear-probe hash maps attached
* to each thread (Thread.threadLocals and
* inheritableThreadLocals). The ThreadLocal objects act as keys,
* searched via threadLocalHashCode. This is a custom hash code
* (useful only within ThreadLocalMaps) that eliminates collisions
* in the common case where consecutively constructed ThreadLocals
* are used by the same threads, while remaining well-behaved in
* less common cases.
*/
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
/**
* The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at
* zero.
*/
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =
new AtomicInteger();
/**
* The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns
* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread
* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.
*/
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
.....
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
....
}
}
ThreadLocal三个变量threadLocalHashCode final属性,用来区分不同的ThreadLocal实例
nextHashCode 递增计数器,AtomicInteger保证了nextHashCode自增的原子性
HASH_INCREMENT 两个ThreadLocal实例的threadLocalHashCode值之间的增量
//返回下一个HashCode
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}ThreadLocal的get 方法,获取当前线程中的ThreadLocalMap,value不为空返回
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); //ThreadLocal为key
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}ThreadLocal为key的原因是一个thread中可能有多个ThreadLocal,所以不能以thread的id为keyThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
public class Thread implements Runnable {
....
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null; //即ThreadLocal的类对象ThreadLocalMap
}
value为空调用setInitialValue,判断ThreadLocalMap是否为空,为空则创建/**
* Variant of set() to establish initialValue. Used instead
* of set() in case user has overridden the set() method.
*
* @return the initial value
*/
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}initialValue函数用来设置ThreadLocal的初始值,可以重写protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}/**
* Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}set /**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}remove
/**
* Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local
* variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently
* {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be
* reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method,
* unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread
* in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the
* {@code initialValue} method in the current thread.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}内存泄露问题
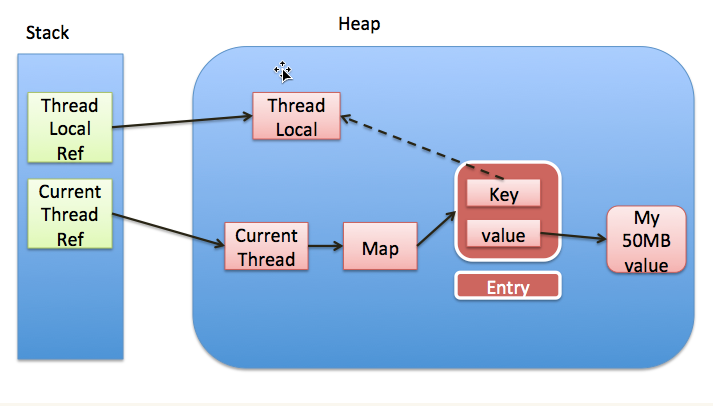
threadlocal里面使用了一个存在弱引用的map,当释放掉threadlocal的强引用以后,map里面的value却没有被回收.而这块value永远不会被访问到了. 所以存在着内存泄露. 最好的做法是将调用threadlocal的remove方法.每个thread中都存在一个map, map的类型是ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap. Map中的key为一个threadlocal实例. 这个Map的确使用了弱引用,不过弱引用只是针对key. 每个key都弱引用指向threadlocal. 当把threadlocal实例置为null以后,没有任何强引用指向threadlocal实例,所以threadlocal将会被gc回收. 但是,我们的value却不能回收,因为存在一条从current thread连接过来的强引用. 只有当前thread结束以后, current thread就不会存在栈中,强引用断开, Current Thread, Map, value将全部被GC回收.
ThreadLocal Ref -> Thread -> ThreaLocalMap -> Entry -> value
此处参考:https://link.zhihu.com/?target=http%3A//qifuguang.me/2015/09/02/
其实,在JDK的ThreadLocalMap的设计中已经考虑到这种情况,也加上了一些防护措施,下面是ThreadLocalMap的getEntry方法的源码
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// expunge entry at staleSlot
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
size--;
// Rehash until we encounter null
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) {
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}整理一下ThreadLocalMap的getEntry函数的流程:
- 首先从ThreadLocal的直接索引位置(通过ThreadLocal.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1)运算得到)获取Entry e,如果e不为null并且key相同则返回e;
- 如果e为null或者key不一致则向下一个位置查询,如果下一个位置的key和当前需要查询的key相等,则返回对应的Entry,否则,如果key值为null,则擦除该位置的Entry,否则继续向下一个位置查询
在这个过程中遇到的key为null的Entry都会被擦除,那么Entry内的value也就没有强引用链,自然会被回收。仔细研究代码可以发现,set操作也有类似的思想,将key为null的这些Entry都删除,防止内存泄露。 但是光这样还是不够的,上面的设计思路依赖一个前提条件:要调用ThreadLocalMap的getEntry函数或者set函数。这当然是不可能任何情况都成立的,所以很多情况下需要使用者手动调用ThreadLocal的remove函数,手动删除不再需要的ThreadLocal,防止内存泄露。所以JDK建议将ThreadLocal变量定义成private static的,这样的话ThreadLocal的生命周期就更长,由于一直存在ThreadLocal的强引用,所以ThreadLocal也就不会被回收,也就能保证任何时候都能根据ThreadLocal的弱引用访问到Entry的value值,然后remove它,防止内存泄露。