Elasticsearch 之(4)kibana集群健康检查,文档 CRUD
简单的集群管理
(1)快速检查集群的健康状况
es提供了一套api,叫做cat api,可以查看es中各种各样的数据
GET /_cat/health?v
epoch timestamp cluster status node.total node.data shards pri relo init unassign pending_tasks max_task_wait_time active_shards_percent 1488006741 15:12:21 elasticsearch yellow 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 - 50.0% epoch timestamp cluster status node.total node.data shards pri relo init unassign pending_tasks max_task_wait_time active_shards_percent 1488007113 15:18:33 elasticsearch green 2 2 2 1 0 0 0 0 - 100.0% epoch timestamp cluster status node.total node.data shards pri relo init unassign pending_tasks max_task_wait_time active_shards_percent 1488007216 15:20:16 elasticsearch yellow 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 - 50.0%
如何快速了解集群的健康状况?green、yellow、red?
green:每个索引的primary shard和replica shard都是active状态的
yellow:每个索引的primary shard都是active状态的,但是部分replica shard不是active状态,处于不可用的状态
red:不是所有索引的primary shard都是active状态的,部分索引有数据丢失了
为什么现在会处于一个yellow状态?
我们现在就一个笔记本电脑,就启动了一个es进程,相当于就只有一个node。现在es中有一个index,就是kibana自己内置建立的index。由于默认的配置是给每个index分配5个primary shard和5个replica shard,而且primary shard和replica shard不能在同一台机器上(为了容错)。现在kibana自己建立的index是1个primary shard和1个replica shard。当前就一个node,所以只有1个primary shard被分配了和启动了,但是一个replica shard没有第二台机器去启动。
做一个小实验:此时只要启动第二个es进程,就会在es集群中有2个node,然后那1个replica shard就会自动分配过去,然后cluster status就会变成green状态。
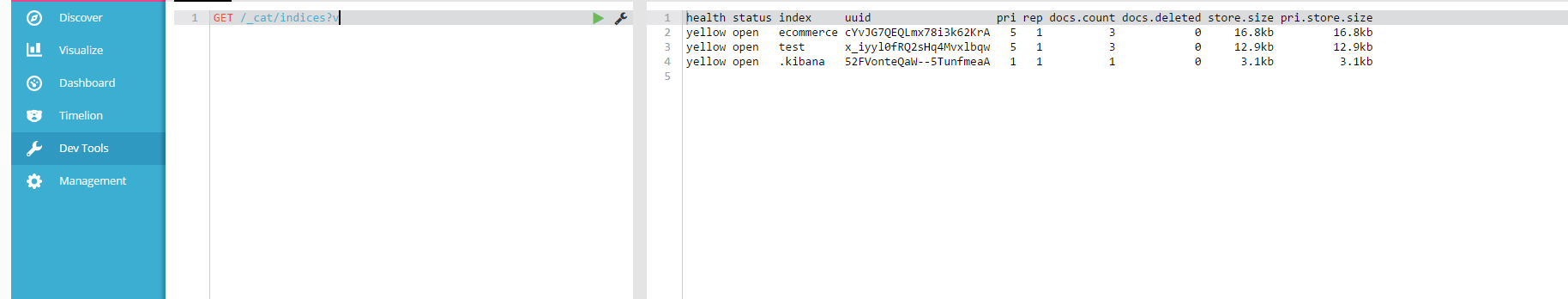
(2)快速查看集群中有哪些索引
(3)简单的索引操作
创建索引:PUT /test_index?pretty
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size yellow open test_index XmS9DTAtSkSZSwWhhGEKkQ 5 1 0 0 650b 650b yellow open .kibana rUm9n9wMRQCCrRDEhqneBg 1 1 1 0 3.1kb 3.1kb
删除索引:DELETE /test_index?pretty
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size yellow open .kibana rUm9n9wMRQCCrRDEhqneBg 1 1 1 0 3.1kb 3.1kb
document数据格式
面向文档的搜索分析引擎
(1)应用系统的数据结构都是面向对象的,复杂的
(2)对象数据存储到数据库中,只能拆解开来,变为扁平的多张表,每次查询的时候还得还原回对象格式,相当麻烦
(3)ES是面向文档的,文档中存储的数据结构,与面向对象的数据结构是一样的,基于这种文档数据结构,es可以提供复杂的索引,全文检索,分析聚合等功能
(4)es的document用json数据格式来表达
public class Employee {
private String email;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private EmployeeInfo info;
private Date joinDate;
}
private class EmployeeInfo {
private String bio; // 性格
private Integer age;
private String[] interests; // 兴趣爱好
}
EmployeeInfo info = new EmployeeInfo();
info.setBio("curious and modest");
info.setAge(30);
info.setInterests(new String[]{"bike", "climb"});
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setEmail("zhangsan@sina.com");
employee.setFirstName("san");
employee.setLastName("zhang");
employee.setInfo(info);
employee.setJoinDate(new Date());employee对象:里面包含了Employee类自己的属性,还有一个EmployeeInfo对象
两张表:employee表,employee_info表,将employee对象的数据重新拆开来,变成Employee数据和EmployeeInfo数据
employee表:email,first_name,last_name,join_date,4个字段
employee_info表:bio,age,interests,3个字段;此外还有一个外键字段,比如employee_id,关联着employee表
{
"email": "zhangsan@sina.com",
"first_name": "san",
"last_name": "zhang",
"info": {
"bio": "curious and modest",
"age": 30,
"interests": [ "bike", "climb" ]
},
"join_date": "2017/01/01"
}我们就明白了es的document数据格式和数据库的关系型数据格式的区别
商品的CRUD操作
(1)新增商品:新增文档,建立索引
PUT /index/type/id
{
"json数据"
}
PUT /ecommerce/product/1
{
"name" : "gaolujie yagao",
"desc" : "gaoxiao meibai",
"price" : 30,
"producer" : "gaolujie producer",
"tags": [ "meibai", "fangzhu" ]
}
{
"_index": "ecommerce",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"created": true
}
PUT /ecommerce/product/2
{
"name" : "jiajieshi yagao",
"desc" : "youxiao fangzhu",
"price" : 25,
"producer" : "jiajieshi producer",
"tags": [ "fangzhu" ]
}
PUT /ecommerce/product/3
{
"name" : "zhonghua yagao",
"desc" : "caoben zhiwu",
"price" : 40,
"producer" : "zhonghua producer",
"tags": [ "qingxin" ]
}es会自动建立index和type,不需要提前创建,而且es默认会对document每个field都建立倒排索引,让其可以被搜索
根据应用情况来说,是否满足手动指定document id的前提:
一般来说,是从某些其他的系统中,导入一些数据到es时,会采取这种方式,就是使用系统中已有数据的唯一标识,作为es中document的id。举个例子,比如说,我们现在在开发一个电商网站,做搜索功能,或者是OA系统,做员工检索功能。这个时候,数据首先会在网站系统或者IT系统内部的数据库中,会先有一份,此时就肯定会有一个数据库的primary key(自增长,UUID,或者是业务编号)。如果将数据导入到es中,此时就比较适合采用数据在数据库中已有的primary key。
如果说,我们是在做一个系统,这个系统主要的数据存储就是es一种,也就是说,数据产生出来以后,可能就没有id,直接就放es一个存储,那么这个时候,可能就不太适合说手动指定document id的形式了,因为你也不知道id应该是什么,此时可以采取下面要讲解的让es自动生成id的方式。
POST/index/type
POST /test_index/test_type
{
"test_content": "my test"
}
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "test_type",
"_id": "AVp4RN0bhjxldOOnBxaE",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"created": true
}自动生成的id,长度为20个字符,URL安全,base64编码,GUID,分布式系统并行生成时不可能会发生冲突

(2)查询商品:检索文档
GET /index/type/id
GET /ecommerce/product/1
{
"_index": "ecommerce",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "gaolujie yagao",
"desc": "gaoxiao meibai",
"price": 30,
"producer": "gaolujie producer",
"tags": [
"meibai",
"fangzhu"
]
}
}(3)修改商品:替换文档
PUT /ecommerce/product/1
{
"name" : "jiaqiangban gaolujie yagao",
"desc" : "gaoxiao meibai",
"price" : 30,
"producer" : "gaolujie producer",
"tags": [ "meibai", "fangzhu" ]
}
{
"_index": "ecommerce",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"created": true
}
{
"_index": "ecommerce",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 2,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"created": false
}document的全量替换
(1)语法与创建文档是一样的,如果document id不存在,那么就是创建;如果document id已经存在,那么就是全量替换操作,替换document的json串内容
(2)document是不可变的,如果要修改document的内容,第一种方式就是全量替换,直接对document重新建立索引,替换里面所有的内容
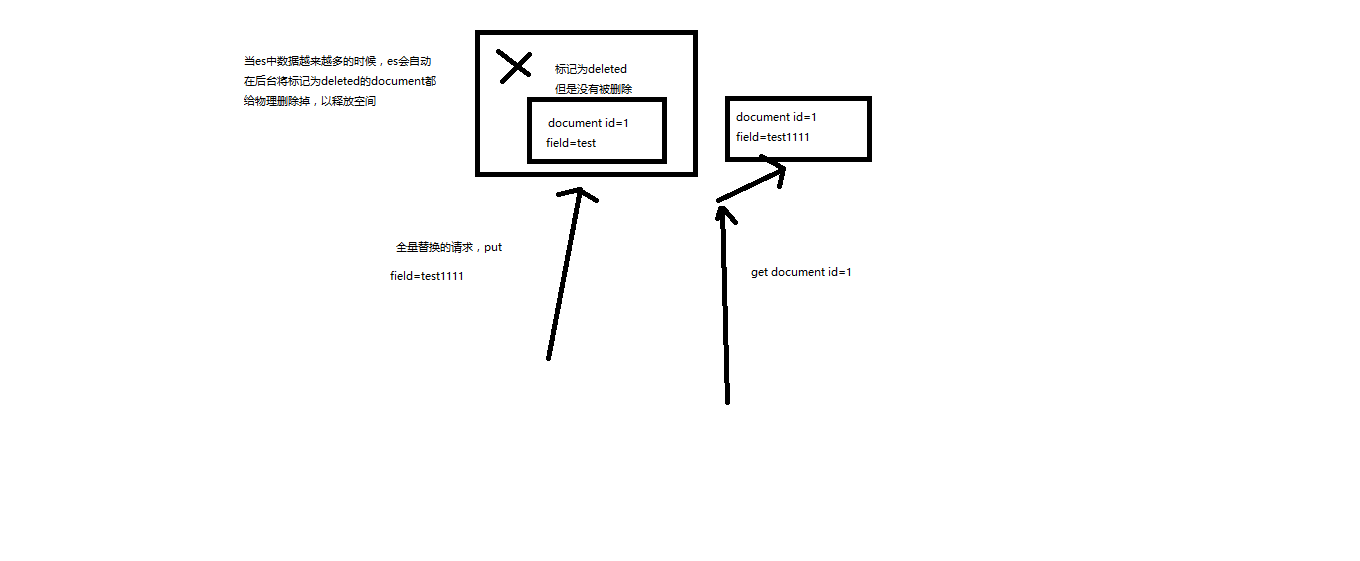
(3)es会将老的document标记为deleted,然后新增我们给定的一个document,当我们创建越来越多的document的时候,es会在适当的时机在后台自动删除标记为deleted的document
PUT /ecommerce/product/1
{
"name" : "jiaqiangban gaolujie yagao"
}
替换方式有一个不好,即使必须带上所有的field,才能去进行信息的修改(4)修改商品:更新文档
POST /ecommerce/product/1/_update
{
"doc": {
"name": "jiaqiangban gaolujie yagao"
}
}
{
"_index": "ecommerce",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 8,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
}
}(5)删除商品:删除文档
DELETE /ecommerce/product/1
{
"found": true,
"_index": "ecommerce",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 9,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
}
}
{
"_index": "ecommerce",
"_type": "product",
"_id": "1",
"found": false
}不会理解物理删除,只会将其标记为deleted,当数据越来越多的时候,在后台自动删除


