Spring Security Oauth2 之 架构源码解读
本篇追踪源码阐述获Security的认证的基本流程
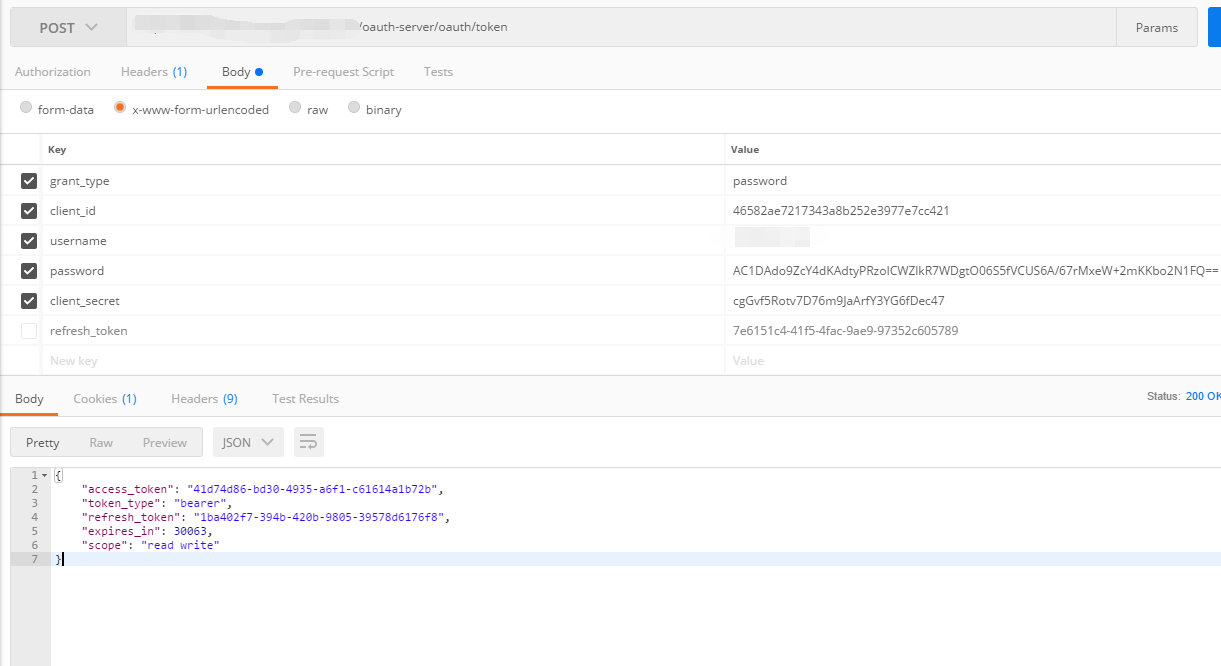
密码模式请求/oauth/token ,获取令牌(access_token)
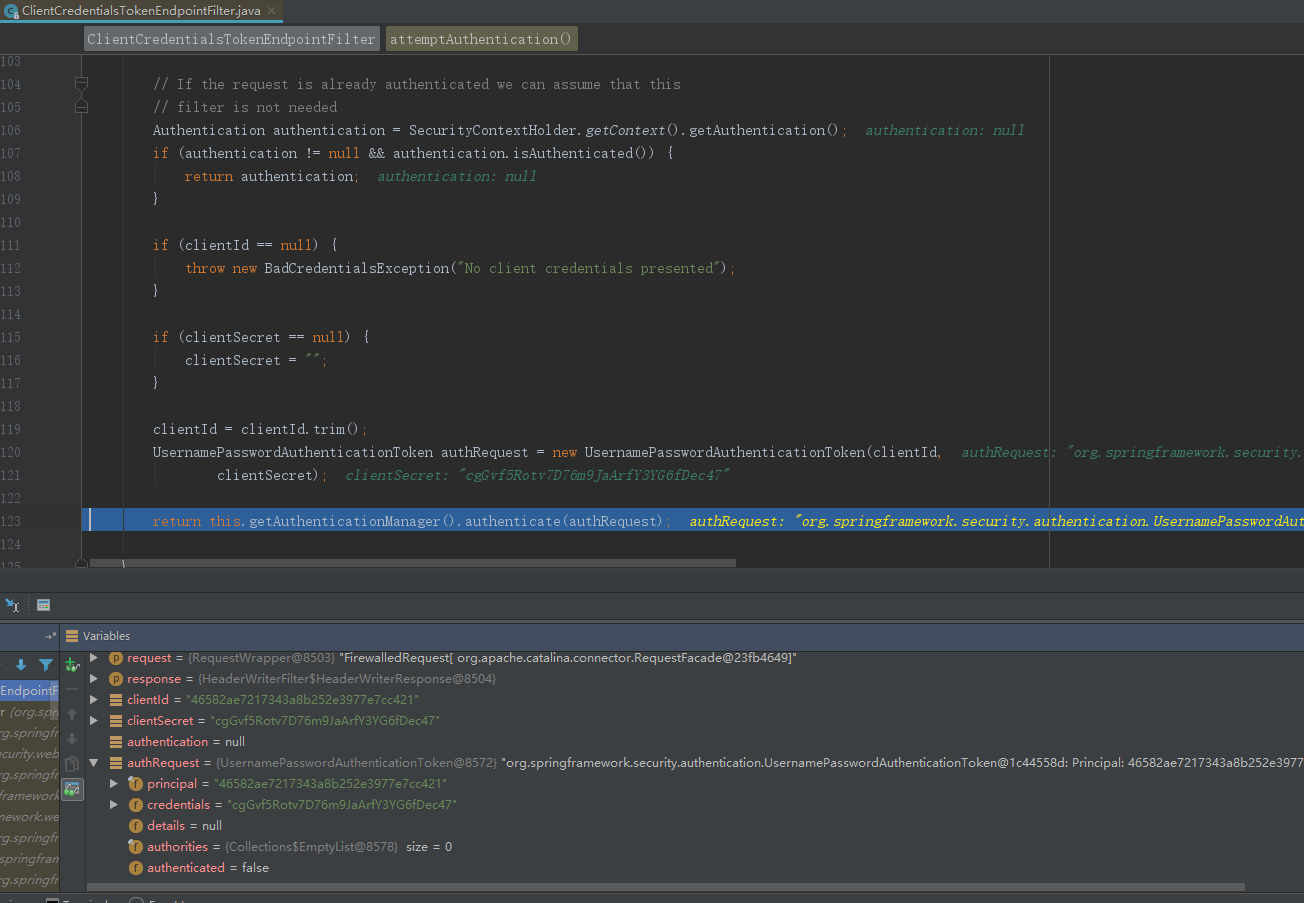
经过客户端认证核心过滤器ClientCredentialsTokenEndpointFilter(attemptAuthentication)
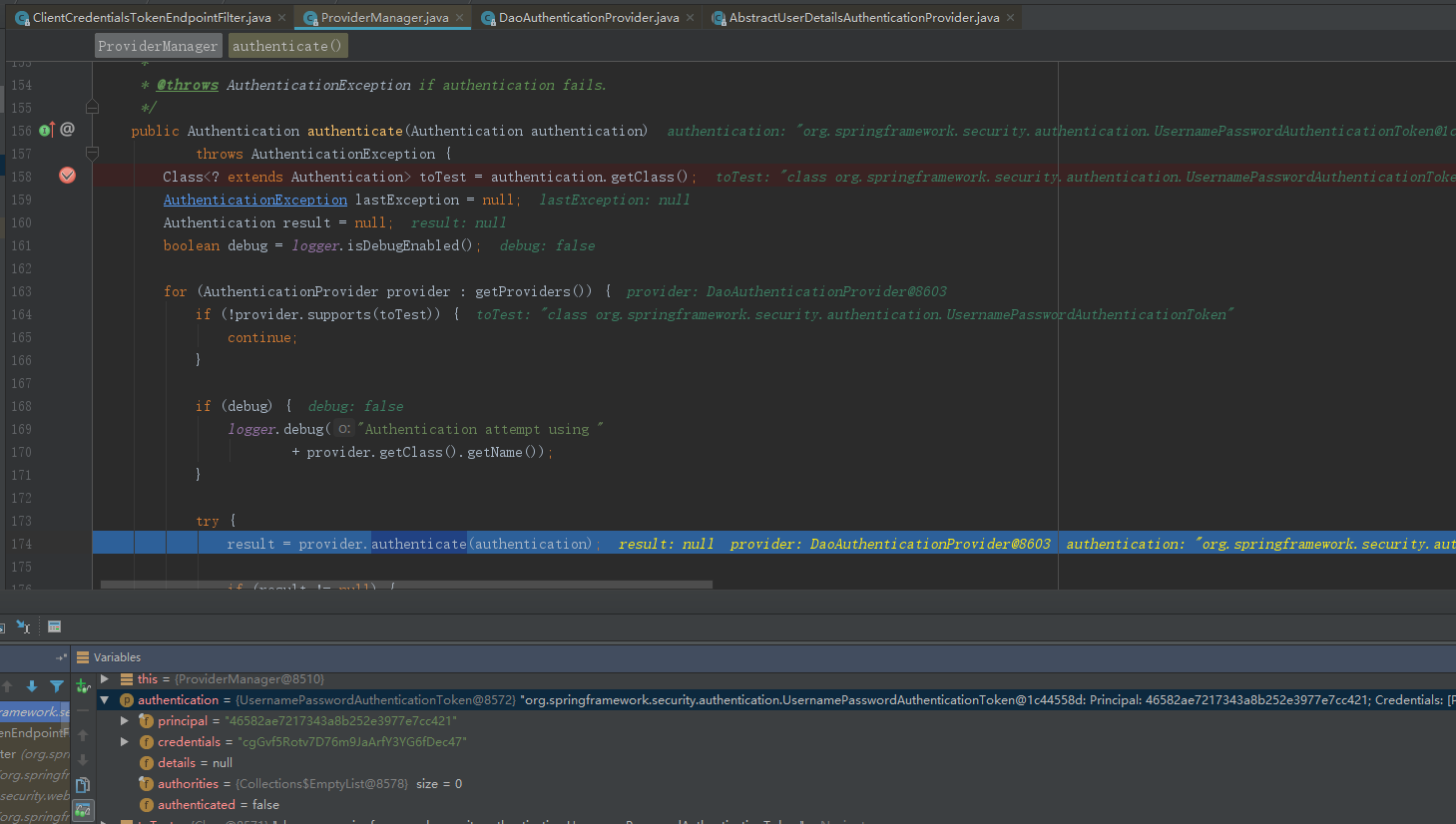
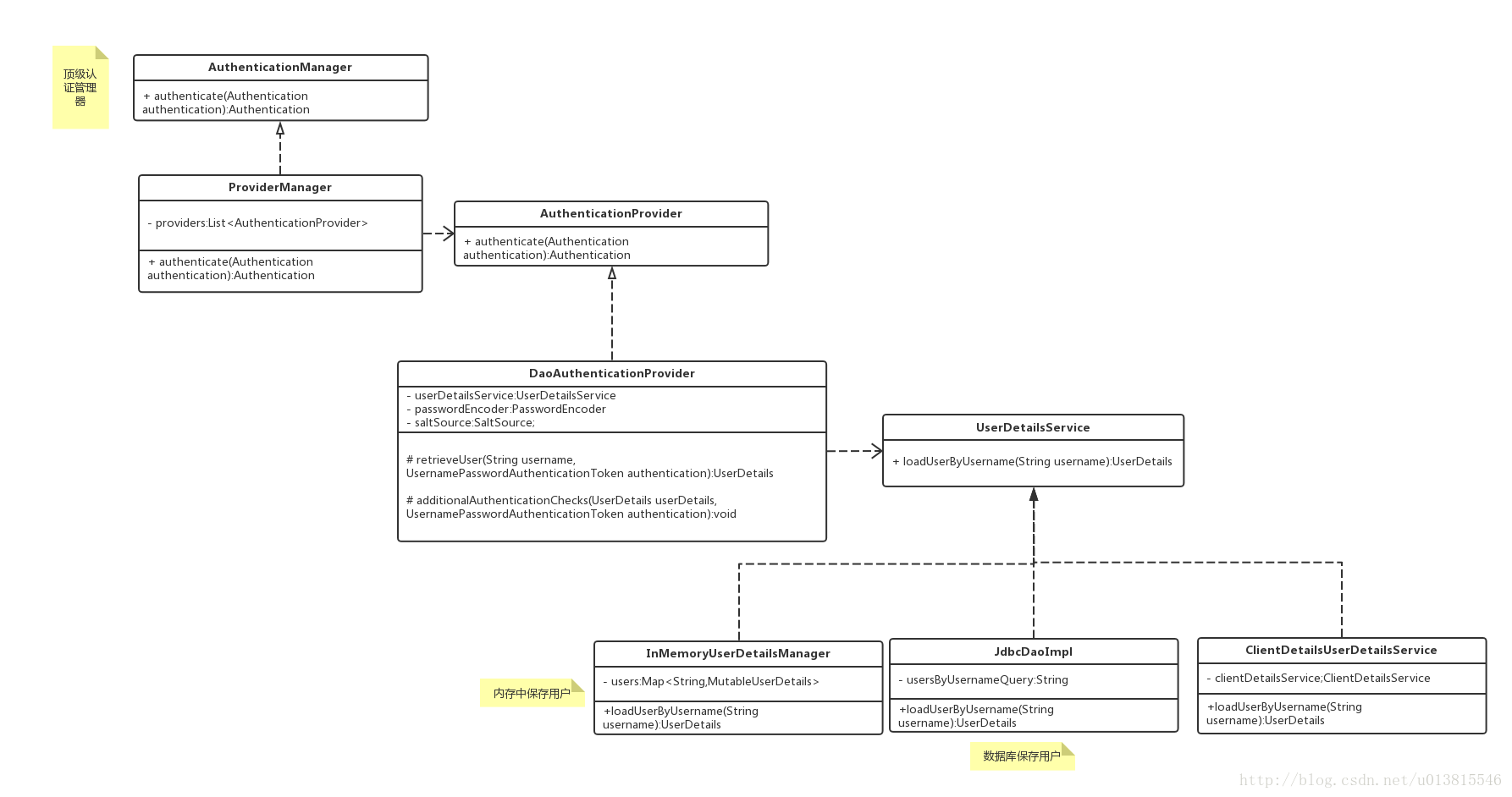
获取clientId,clientSecret组装成一个UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken作为身份标识,经过容器中的认证管理器 AuthenticationManager 进行身份认证。AuthenticationManager 核心实现由ProviderManager完成。
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
} ProviderManager内部管理一系列真正的身份认证AuthenticationProvider,ProviderManager利用反射 根据选择参数类型对应的provider。
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
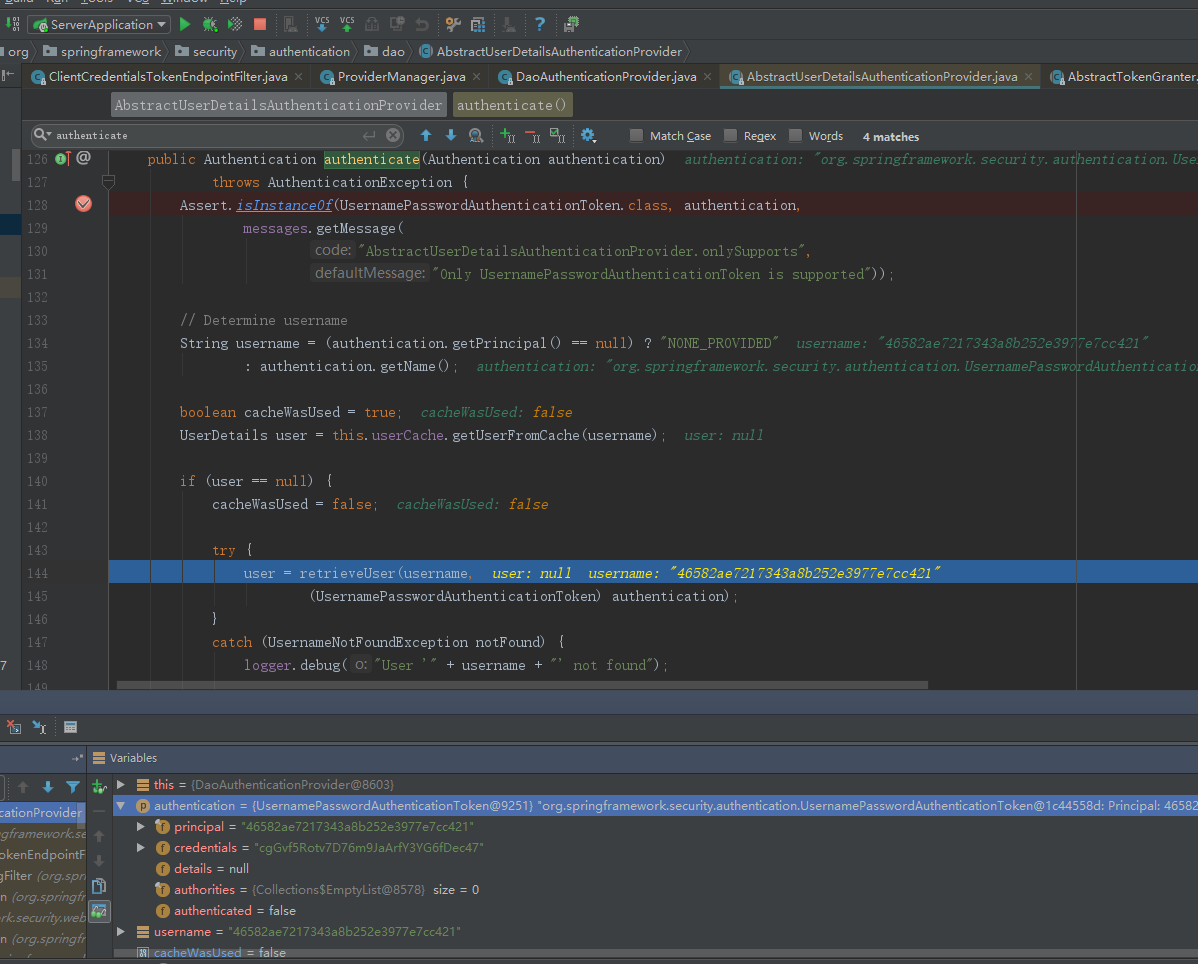
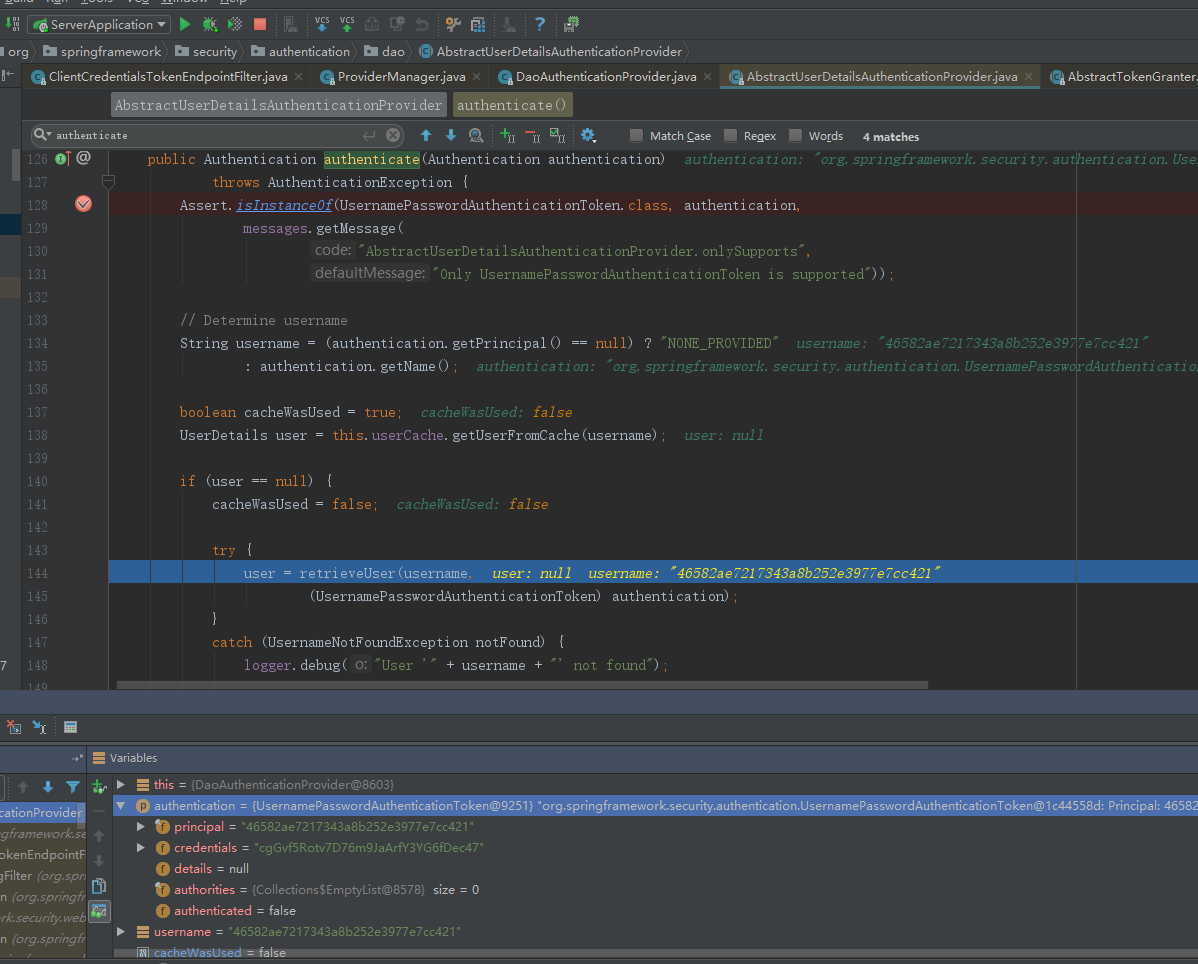
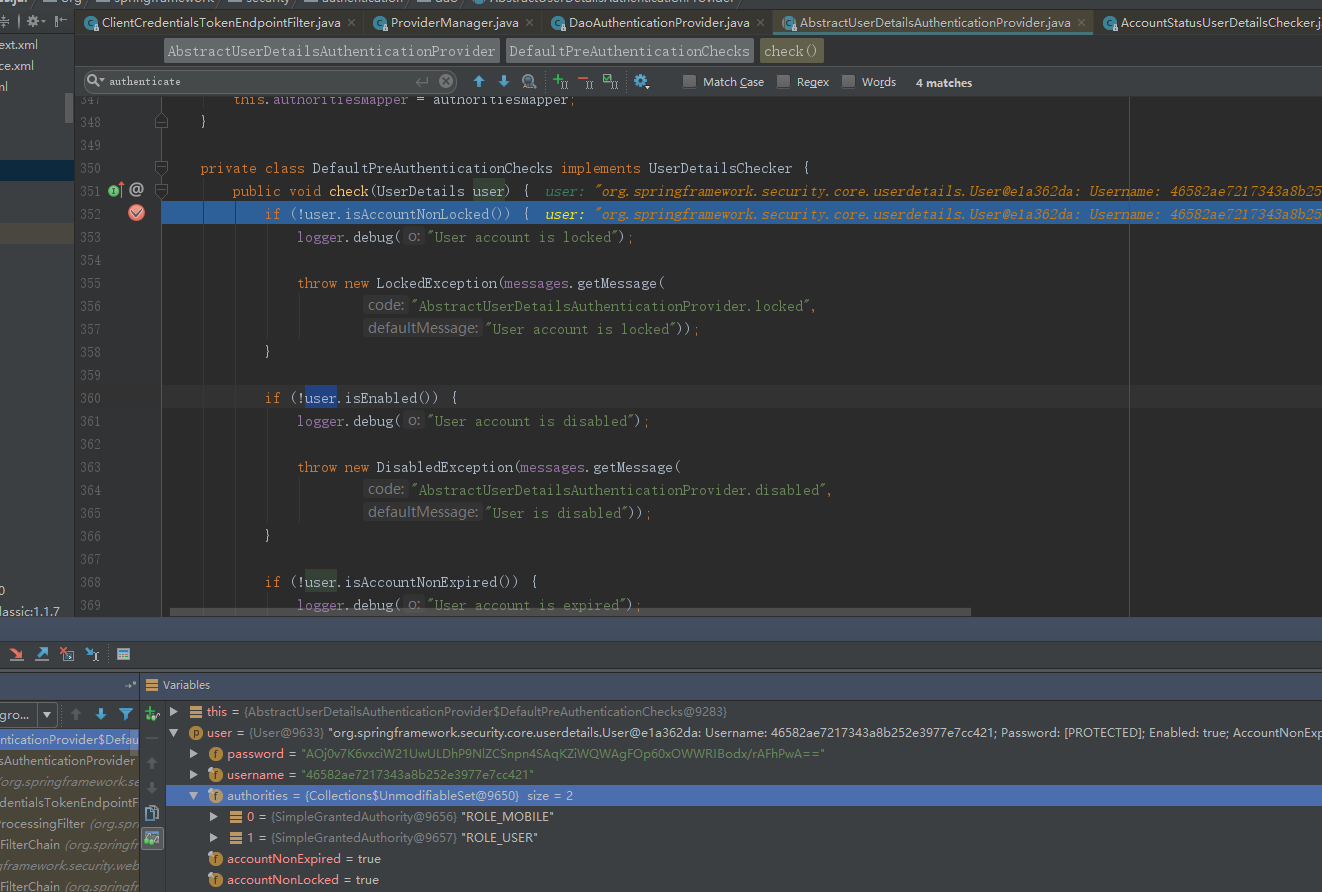
而AuthenticationProvider的常用实现类则是DaoAuthenticationProvider,此处DaoAuthenticationProvider调用父类AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider的authentic方法。
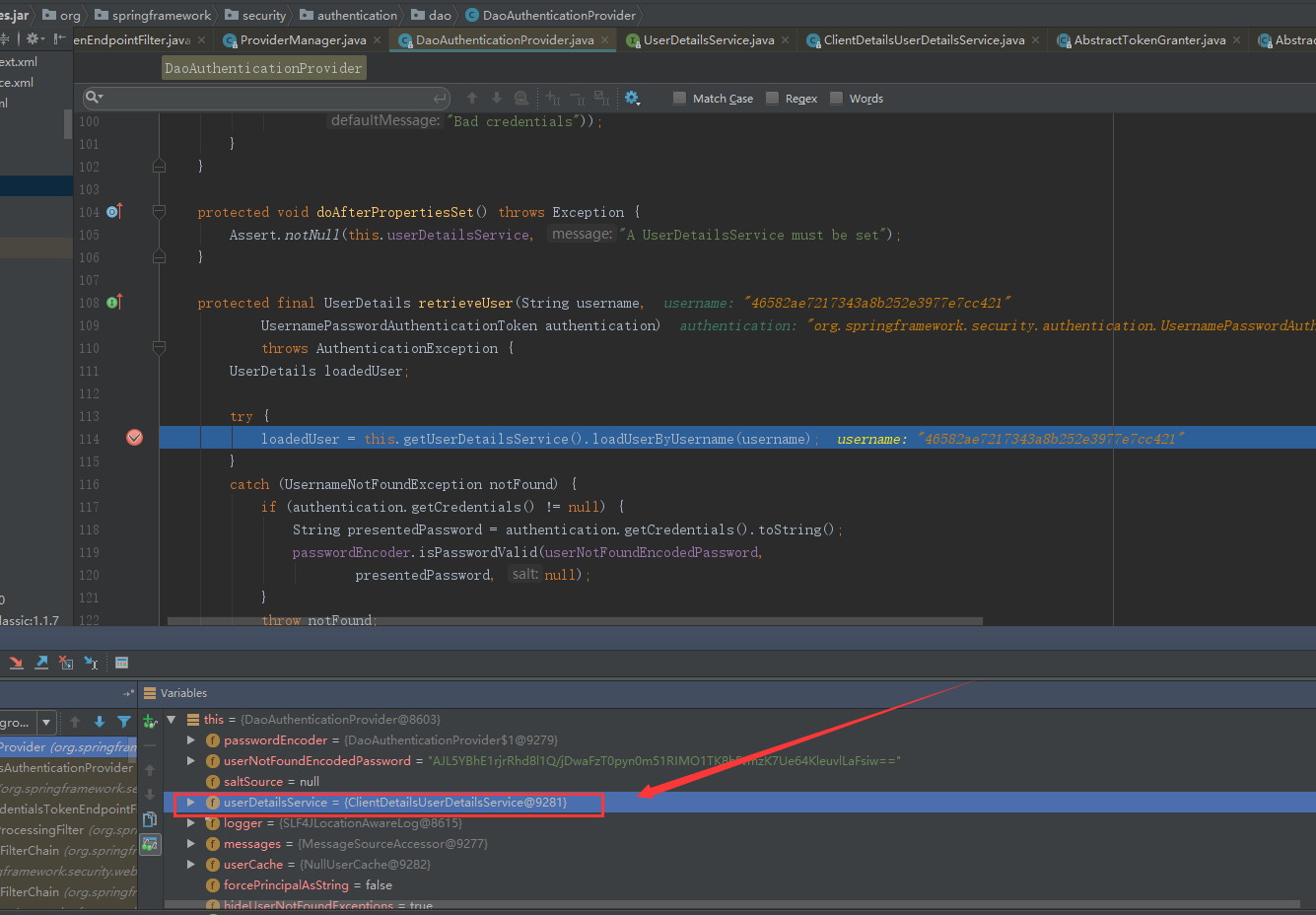
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider执行子类DaoAuthenticationProvider的retrieveUser方法。
获取完信息后,开始认证流程
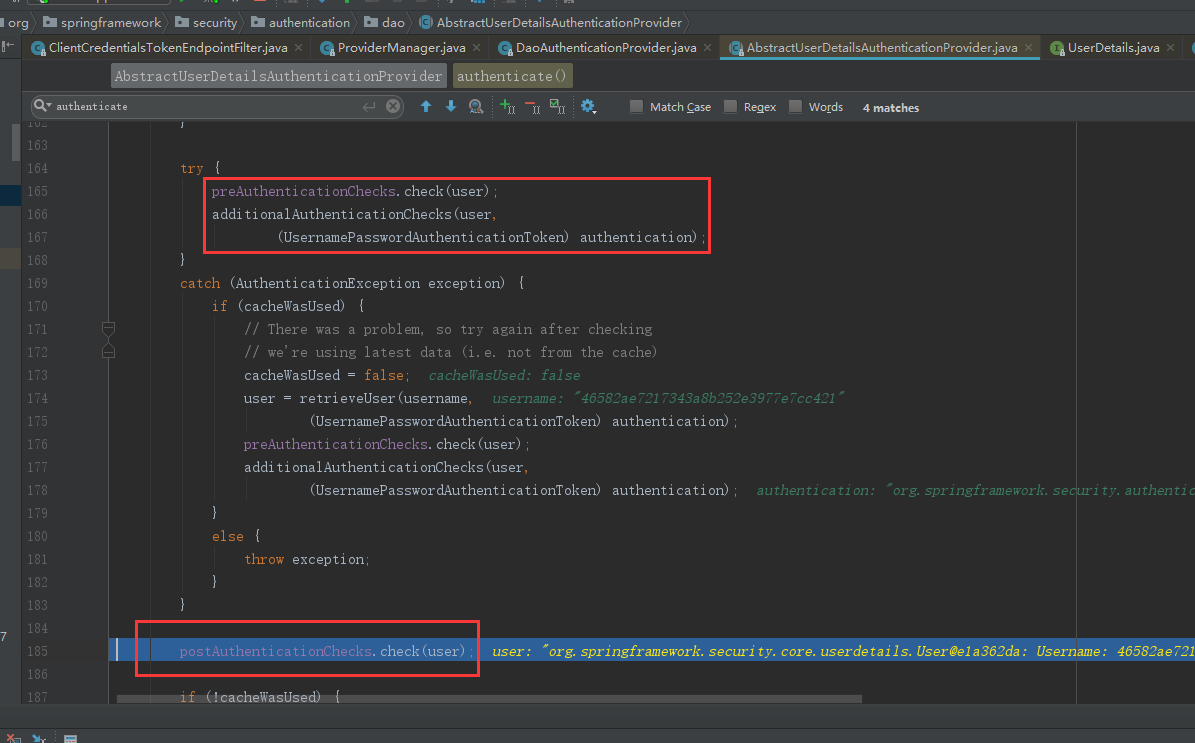
然后进入 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 验证 信息是否可用,过期
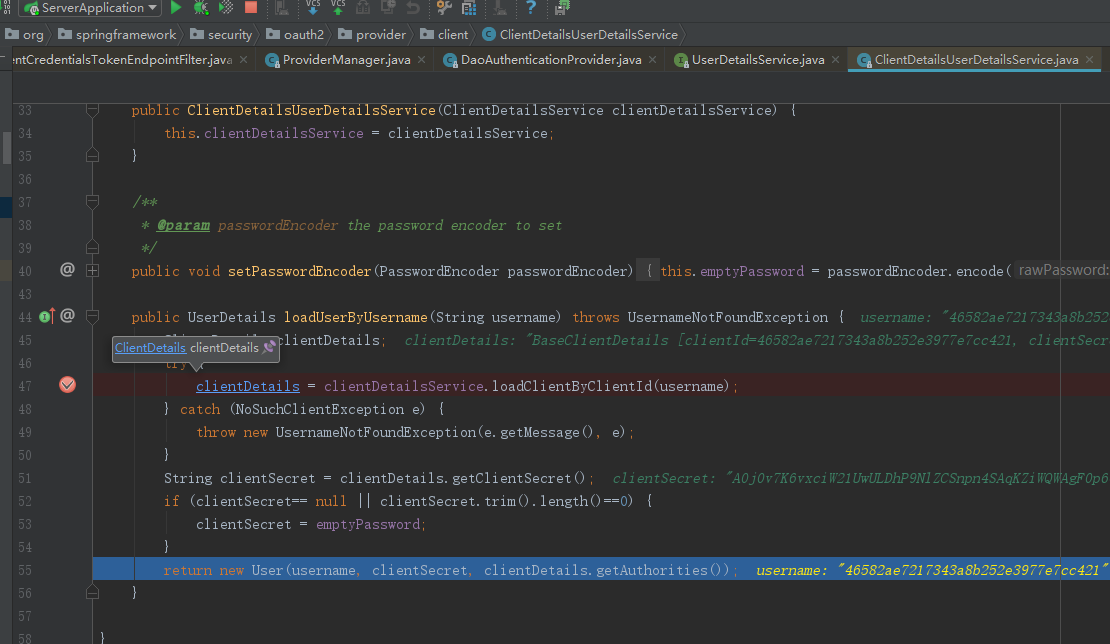
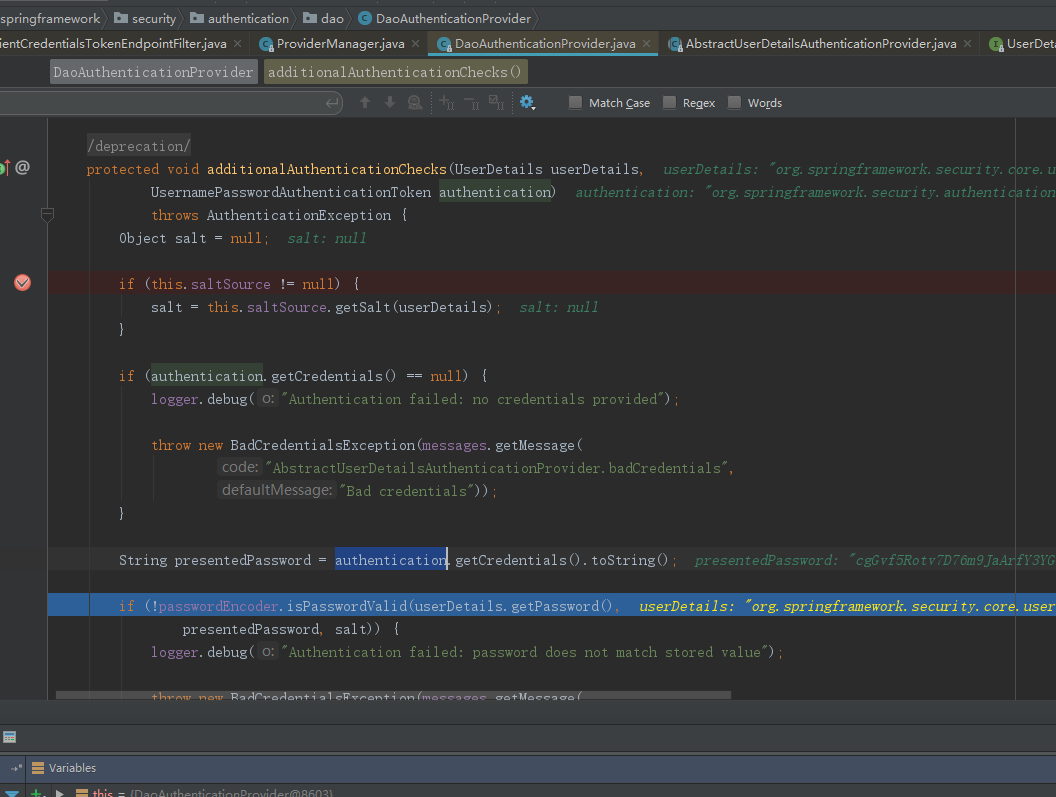
之后,再次进如DaoAuthenticationProvider 认证clientId和clientSecret
再次进入 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider 验证 是否过期
.... 这边就不一一阐述了
UML类图
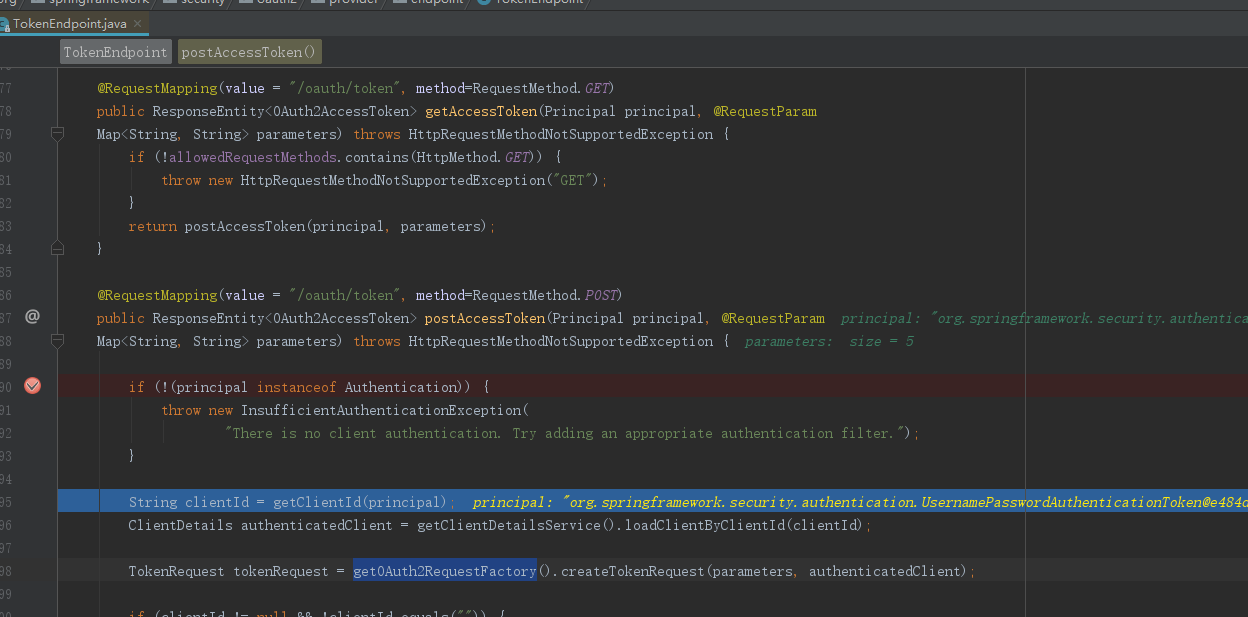
根据clientId查询client具体信息
工厂模式创建TokenRequest
校验params:授权码模式必传code;刷新令牌必传refresh_token等
源码:
@FrameworkEndpoint
public class TokenEndpoint extends AbstractEndpoint {
private OAuth2RequestValidator oAuth2RequestValidator = new DefaultOAuth2RequestValidator();
private Set<HttpMethod> allowedRequestMethods = new HashSet<HttpMethod>(Arrays.asList(HttpMethod.POST));
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<OAuth2AccessToken> getAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map<String, String> parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
if (!allowedRequestMethods.contains(HttpMethod.GET)) {
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException("GET");
}
return postAccessToken(principal, parameters);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<OAuth2AccessToken> postAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map<String, String> parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication)) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"There is no client authentication. Try adding an appropriate authentication filter.");
}
String clientId = getClientId(principal);
ClientDetails authenticatedClient = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(clientId);
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(parameters, authenticatedClient);
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals("")) {
// Only validate the client details if a client authenticated during this
// request.
if (!clientId.equals(tokenRequest.getClientId())) {
// double check to make sure that the client ID in the token request is the same as that in the
// authenticated client
throw new InvalidClientException("Given client ID does not match authenticated client");
}
}
if (authenticatedClient != null) {
oAuth2RequestValidator.validateScope(tokenRequest, authenticatedClient);
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(tokenRequest.getGrantType())) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("Missing grant type");
}
if (tokenRequest.getGrantType().equals("implicit")) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Implicit grant type not supported from token endpoint");
}
if (isAuthCodeRequest(parameters)) {
// The scope was requested or determined during the authorization step
if (!tokenRequest.getScope().isEmpty()) {
logger.debug("Clearing scope of incoming token request");
tokenRequest.setScope(Collections.<String> emptySet());
}
}
if (isRefreshTokenRequest(parameters)) {
// A refresh token has its own default scopes, so we should ignore any added by the factory here.
tokenRequest.setScope(OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE)));
}
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type: " + tokenRequest.getGrantType());
}
return getResponse(token);
}
....
}调用接口TokenGranter构建令牌OAuth2AccessToken
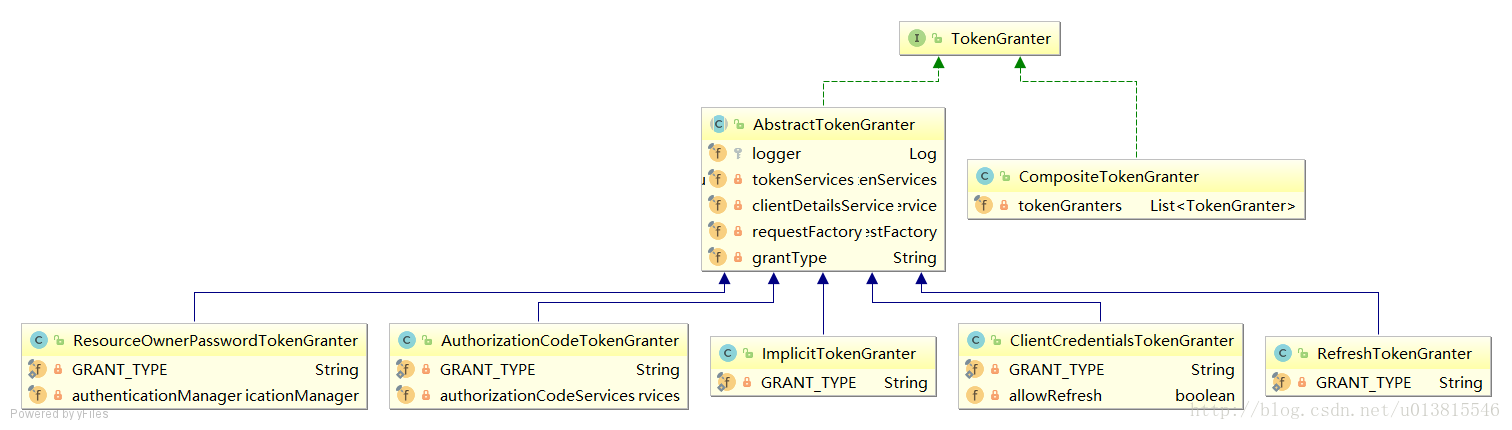
public interface TokenGranter {
OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest);
}调用CompositeTokenGranter,获取相对应的TokenGranter(共五种)ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter password密码模式
AuthorizationCodeTokenGranter authorization_code授权码模式
ClientCredentialsTokenGranter client_credentials客户端模式
ImplicitTokenGranter implicit简化模式
RefreshTokenGranter refresh_token 刷新token
public class CompositeTokenGranter implements TokenGranter {
private final List<TokenGranter> tokenGranters;
public CompositeTokenGranter(List<TokenGranter> tokenGranters) {
this.tokenGranters = new ArrayList<TokenGranter>(tokenGranters);
}
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
for (TokenGranter granter : tokenGranters) {
OAuth2AccessToken grant = granter.grant(grantType, tokenRequest);
if (grant!=null) {
return grant;
}
}
return null;
}
public void addTokenGranter(TokenGranter tokenGranter) {
if (tokenGranter == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Token granter is null");
}
tokenGranters.add(tokenGranter);
}
} AbstractTokenGranter根据 grantType选择对应TokenGranter 调用子类的getAccessTokenpublic OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
if (!this.grantType.equals(grantType)) {
return null;
}
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
ClientDetails client = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
validateGrantType(grantType, client);
logger.debug("Getting access token for: " + clientId);
return getAccessToken(client, tokenRequest);
}密码模式调用ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter 校验username,password流程和clientId,clientSecret一致,区别于UserDetailsService实现类是JdbcDaoImpl。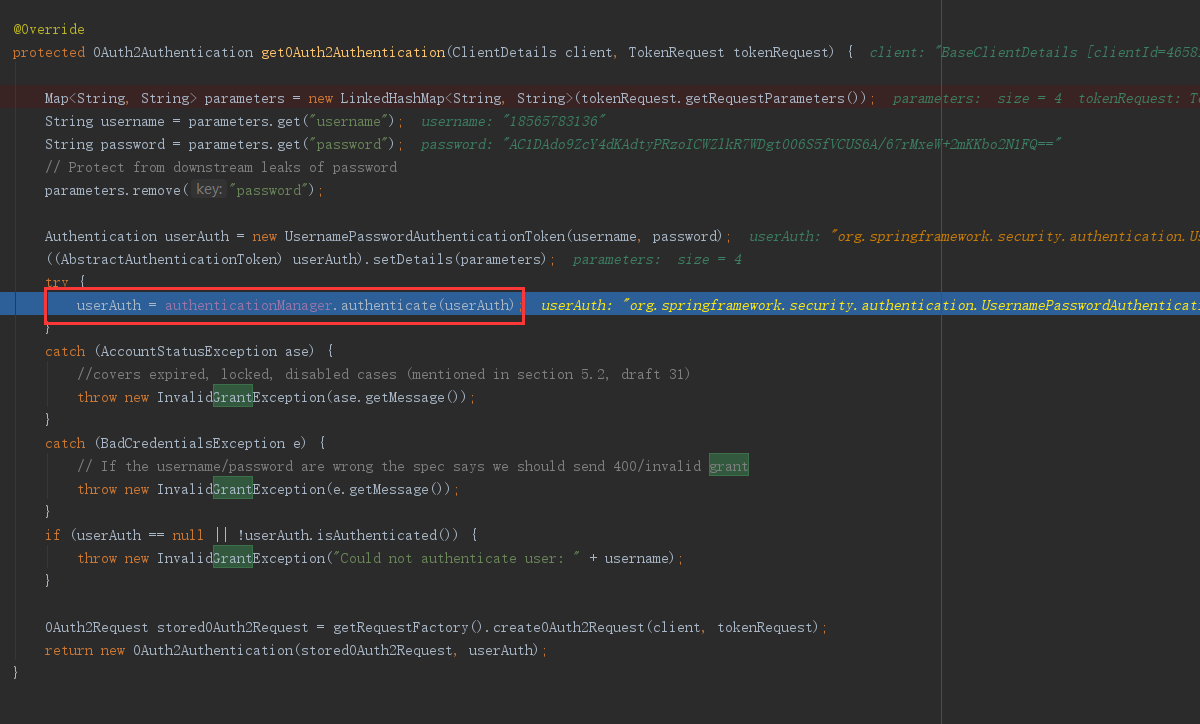
调用AuthorizationServerTokenServices.createAccessToken 创建 OAuth2AccessToken
public interface AuthorizationServerTokenServices {
/**
* Create an access token associated with the specified credentials.
* @param authentication The credentials associated with the access token.
* @return The access token.
* @throws AuthenticationException If the credentials are inadequate.
*/
OAuth2AccessToken createAccessToken(OAuth2Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
/**
* Refresh an access token. The authorization request should be used for 2 things (at least): to validate that the
* client id of the original access token is the same as the one requesting the refresh, and to narrow the scopes
* (if provided).
*
* @param refreshToken The details about the refresh token.
* @param tokenRequest The incoming token request.
* @return The (new) access token.
* @throws AuthenticationException If the refresh token is invalid or expired.
*/
OAuth2AccessToken refreshAccessToken(String refreshToken, TokenRequest tokenRequest)
throws AuthenticationException;
/**
* Retrieve an access token stored against the provided authentication key, if it exists.
*
* @param authentication the authentication key for the access token
*
* @return the access token or null if there was none
*/
OAuth2AccessToken getAccessToken(OAuth2Authentication authentication);
}public class DefaultTokenServices implements AuthorizationServerTokenServices, ResourceServerTokenServices,
ConsumerTokenServices, InitializingBean {
private int refreshTokenValiditySeconds = 60 * 60 * 24 * 30; // default 30 days.
private int accessTokenValiditySeconds = 60 * 60 * 12; // default 12 hours.
private boolean supportRefreshToken = false;
private boolean reuseRefreshToken = true;
private TokenStore tokenStore;
private ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService;
private TokenEnhancer accessTokenEnhancer;
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
/**
* Initialize these token services. If no random generator is set, one will be created.
*/
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(tokenStore, "tokenStore must be set");
}
@Transactional
public OAuth2AccessToken createAccessToken(OAuth2Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
OAuth2AccessToken existingAccessToken = tokenStore.getAccessToken(authentication);
OAuth2RefreshToken refreshToken = null;
if (existingAccessToken != null) {
if (existingAccessToken.isExpired()) {
if (existingAccessToken.getRefreshToken() != null) {
refreshToken = existingAccessToken.getRefreshToken();
// The token store could remove the refresh token when the
// access token is removed, but we want to
// be sure...
tokenStore.removeRefreshToken(refreshToken);
}
tokenStore.removeAccessToken(existingAccessToken);
}
else {
// Re-store the access token in case the authentication has changed
tokenStore.storeAccessToken(existingAccessToken, authentication);
return existingAccessToken;
}
}
// Only create a new refresh token if there wasn't an existing one
// associated with an expired access token.
// Clients might be holding existing refresh tokens, so we re-use it in
// the case that the old access token
// expired.
if (refreshToken == null) {
refreshToken = createRefreshToken(authentication);
}
// But the refresh token itself might need to be re-issued if it has
// expired.
else if (refreshToken instanceof ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) {
ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken expiring = (ExpiringOAuth2RefreshToken) refreshToken;
if (System.currentTimeMillis() > expiring.getExpiration().getTime()) {
refreshToken = createRefreshToken(authentication);
}
}
OAuth2AccessToken accessToken = createAccessToken(authentication, refreshToken);
tokenStore.storeAccessToken(accessToken, authentication);
// In case it was modified
refreshToken = accessToken.getRefreshToken();
if (refreshToken != null) {
tokenStore.storeRefreshToken(refreshToken, authentication);
}
return accessToken;
}tokenStore (四种):
InMemoryTokenStore 基于内存
JdbcTokenStore 基于数据库
JwtTokenStore 基于Jwt
RedisTokenStore 基于redis
userDetailsService,tokenStore 等一些配置化信息,下一篇详解