SpringMvc工作原理及手写源码流程
使用过spring mvc的小伙伴都知道,mvc在使用的时候,我们只需要在controller上注解上@controller跟@requestMapping(“URL”),当我们访问对应的路径的时候,框架便会帮我们去映射到指定的controller里面的指定方法,那么这一切都是怎么做到的呢?还有我们所传递过去的参数,为什么通过request.getParam就能轻易地 拿到呢?大家都知道mvc的核心控制器DispacherServlet的基本运行流程,那么他的内部是怎么运行的呢,我们来做一下简单的实现,让我们能进一步的了解MVC。以助于我们今后的开发。
SpringMVC流程:
1、 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet。
2、 DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
3、 处理器映射器找到具体的处理器(可以根据xml配置、注解进行查找),生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
4、 DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器。
5、 HandlerAdapter经过适配调用具体的处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
6、 Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView。
7、 HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet。
8、 DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。
9、 ViewReslover解析后返回具体View。
10、DispatcherServlet根据View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
11、 DispatcherServlet响应用户。
此次实现基于Servlet 3.0,SpringBoot 2.0.1,采用注解的方式实现.这里我先把我的demo的工程包结构先贴出来:
pom文件:
<dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> </dependency>
首先,我们先从注解入手,为什么在类上面标注一下@controller以及@RequestMapping,他就能其效果呢? 我们先来定义出这两个注解 @Controller :
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)//表示注解运行在哪里 这里表示只能注解再类上面 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//表示注解的(生命周期)哪来出现 public @interface WuzzController { }
@RequestMapping :
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface WuzzRequestMapping { String value(); }
@Service
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface WuzzService { String value() default ""; }
@Autowired
@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface WuzzAutowired { String value() default ""; }
定义完注解后,那么我们创建一个TestController 来测试一下我们自己定义的注解
@WuzzController @WuzzRequestMapping("/wuzz") public class TestController extends BaseController{ @WuzzAutowired private ServiceDemo serviceDemo; @WuzzRequestMapping("/index.do") public void index() { try { response.getWriter().write("index"+serviceDemo.get("wuzz")); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @WuzzRequestMapping("/index1.do") public void index1() { try { response.getWriter().write("index1"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @WuzzRequestMapping("/index2.do") public void index2() { try { response.getWriter().write("index2"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @WuzzRequestMapping("/index3.do") public void index3() { try { response.getWriter().write("index3"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Service:
public interface ServiceDemo { String get(String name); } @WuzzService public class ServiceDemoImpl implements ServiceDemo { @Override public String get(String name) { return "service demo" + name; } }
很显然,现在我们虽然能在类,方法上注解上我们自己定义的注解,但是他们现在是起不到我们MVC框架中的效果的,在框架的内部肯定是需要有一系列操作,才能使得这些注解起效果,我们注意到,要使用MVC的时候我们通常需要配置一个注解扫描包。然后肯定是将有这些特定注解的类扫描出来,并创建出映射的路径,才能达到我们预期的效果。
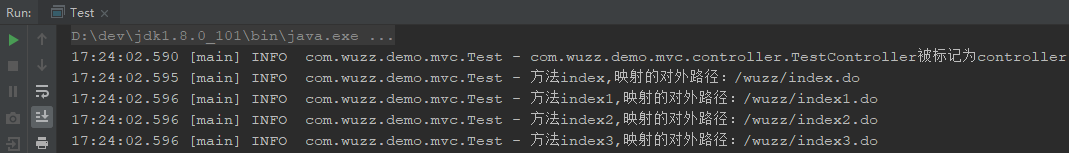
现在我们可以做一个小小的测试:所以我这里建了一个Test类来做简单的获取指定类(TestController)里面有没有我们的注解:
public class Test { private static final Logger LOGGER = LogManager.getLogger(Test.class); public static void main(String[] args) { // Class Class clazz = TestController.class; //判断这个类是否存在 @WuzzController if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(WuzzController.class)) { LOGGER.info(clazz.getName() + "被标记为controller"); String path = ""; //判断clazz是否存在注解@WuzzRequestMapping if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(WuzzRequestMapping.class)) { //取出注解的值 放入path WuzzRequestMapping reqAnno =
(WuzzRequestMapping)clazz.getAnnotation(WuzzRequestMapping.class); path = reqAnno.value().toString(); } Method[] ms = clazz.getMethods();//拿到控制类所有公开方法遍历 for (Method method : ms) { //如果不存在该注解 就进入下一轮 if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(WuzzRequestMapping.class)) { continue; } LOGGER.info("方法"+method.getName()+",映射的对外路径:" + path
+ method.getAnnotation(WuzzRequestMapping.class).value().toString()); } } } }
这里我们运行后的结果为:
这样我们就可以拿到指定的类里面的指定的一些注解的值,还可以做一系列的操作。好,那么现在我们需要想到的就是核心控制器DispacherServlet了。既然是servlet,我们先来看一下servlet的生命周期。Servlet 生命周期可被定义为从创建直到毁灭的整个过程。以下是 Servlet 遵循的过程:
- Servlet 通过调用 init () 方法进行初始化。
- Servlet 调用 service() 方法来处理客户端的请求。
- Servlet 通过调用 destroy() 方法终止(结束)。
- 最后,Servlet 是由 JVM 的垃圾回收器进行垃圾回收的。
既然知道了servlet的生命周期,那就好办了,我们可以通过servlet的初始化,将指定包下的类都扫描起来,然后再重写service()方法去处理这些请求,不久可以了么?接下去我们试一试。
创建自己的DispacherServlet:我是再spring boot环境下去操作的。我们要配置好拦截路径,基准包并重写init(),service()方法
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = {"*.do"},loadOnStartup = 1,initParams = {@WebInitParam(name = "basePackage", value = "com.wuzz.demo")})
public class WuzzDispacherServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//保存url和Method的对应关系
private Map<String, Method> handlerMapping = new HashMap<String, Method>();
//保存扫描的所有的类名
private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<String>();
//存放所扫描出来的类及其实例
private Map<String, Object> ioc = new HashMap<String, Object>();
public WuzzDispacherServlet() {
super();
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.doGet(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//访问地址http://localhost:8081/wuzz/index.do
//这里拿到uri : /wuzz/index.do
String uri = req.getRequestURI();
//从方法map里获取到映射到的方法实例 : public void com.example.demo.annotation.TestController.index()
//处理成相对路径
if (!this.handlerMapping.containsKey(uri)) {
resp.getWriter().write("404 Not Found!!!");
return;
}
Method method = this.handlerMapping.get(uri);
//通过反射拿到method所在class,拿到class之后还是拿到class的名称
//再调用toLowerFirstCase获得beanName
String beanName = toLowerFirstCase(method.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName());
BaseController controller;
try {
//获取实例
controller = (BaseController) ioc.get(beanName);
//初始化该controller的请求与响应
//也就是我们的请求中参数怎么通过requset.getParam方法拿到的原因
System.out.println(req.getRequestURI());
controller.init(req, resp);
//然后调用该方法
method.invoke(controller);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
//获取基础扫描包: 这里设定为com.wuzz.demo
String basePackage = config.getInitParameter("basePackage");
//1 扫描包得到所有的class 并且注入ioc
doScanner(basePackage);
//2、初始化扫描到的类,并且将它们放入到ICO容器之中
doInstance();
//3.实际上这里中间可以扫描@Service @Autowired 注解实现自动的依赖注入
//可参考DispacherServlet 的初始化流程
//可参考DispacherServlet#initStrategies(ApplicationContext context)
doAutowired();
//4、初始化HandlerMapping
initHandlerMapping();
}
//扫描出相关的类
private void doScanner(String scanPackage) {
//scanPackage = com.gupaoedu.demo ,存储的是包路径
//转换为文件路径,实际上就是把.替换为/就OK了
//classpath
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("" + scanPackage.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File classPath = new File(url.getFile());
for (File file : classPath.listFiles()) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
doScanner(scanPackage + "." + file.getName());
} else {
if (!file.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
continue;
}
String className = (scanPackage + "." + file.getName().replace(".class", ""));
classNames.add(className);
}
}
}
private void doInstance() {
//初始化,为DI做准备
if (classNames.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
try {
for (String className : classNames) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
//什么样的类才需要初始化呢?
//加了注解的类,才初始化,怎么判断?
//为了简化代码逻辑,主要体会设计思想,只举例 @Controller和@Service,
// @Componment...就一一举例了
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(WuzzController.class)) {
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
//Spring默认类名首字母小写
String beanName = toLowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
ioc.put(beanName, instance);
} else if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(WuzzService.class)) {
//1、自定义的beanName
WuzzService service = clazz.getAnnotation(WuzzService.class);
String beanName = service.value();
//2、默认类名首字母小写
if ("".equals(beanName.trim())) {
beanName = toLowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
ioc.put(beanName, instance);
//3、根据类型自动赋值,投机取巧的方式
for (Class<?> i : clazz.getInterfaces()) {
if (ioc.containsKey(i.getName())) {//接口若有多个实现
throw new Exception("The “" + i.getName() + "” is exists!!");
}
//把接口的类型直接当成key了
ioc.put(i.getName(), instance);
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果类名本身是小写字母,确实会出问题
//但是我要说明的是:这个方法是我自己用,private的
//传值也是自己传,类也都遵循了驼峰命名法
//默认传入的值,存在首字母小写的情况,也不可能出现非字母的情况
//为了简化程序逻辑,就不做其他判断了,大家了解就OK
//其实用写注释的时间都能够把逻辑写完了
private String toLowerFirstCase(String simpleName) {
char[] chars = simpleName.toCharArray();
//之所以加,是因为大小写字母的ASCII码相差32,
// 而且大写字母的ASCII码要小于小写字母的ASCII码
//在Java中,对char做算学运算,实际上就是对ASCII码做算学运算
chars[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(chars);
}
//自动依赖注入
private void doAutowired() {
if (ioc.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) {
//Declared 所有的,特定的 字段,包括private/protected/default
//正常来说,普通的OOP编程只能拿到public的属性
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (!field.isAnnotationPresent(WuzzAutowired.class)) {
continue;
}
WuzzAutowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(WuzzAutowired.class);
//如果用户没有自定义beanName,默认就根据类型注入
//这个地方省去了对类名首字母小写的情况的判断,这个作为课后作业
//小伙伴们自己去完善
String beanName = autowired.value().trim();
if ("".equals(beanName)) {
//获得接口的类型,作为key待会拿这个key到ioc容器中去取值
beanName = field.getType().getName();
}
//如果是public以外的修饰符,只要加了@Autowired注解,都要强制赋值
//反射中叫做暴力访问, 强吻
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
//用反射机制,动态给字段赋值
field.set(entry.getValue(), ioc.get(beanName));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//初始化url和Method的一对一对应关系
private void initHandlerMapping() {
if (ioc.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) {
Class<?> clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(WuzzController.class)) {
continue;
}
//保存写在类上面的@GPRequestMapping("/demo")
String baseUrl = "";
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(WuzzRequestMapping.class)) {
WuzzRequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(WuzzRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl = requestMapping.value();
}
//默认获取所有的public方法
for (Method method : clazz.getMethods()) {
if (!method.isAnnotationPresent(WuzzRequestMapping.class)) {
continue;
}
WuzzRequestMapping requestMapping = method.getAnnotation(WuzzRequestMapping.class);
//优化
// //demo///query
String url = ("/" + baseUrl + "/" + requestMapping.value())
.replaceAll("/+", "/");
handlerMapping.put(url, method);
System.out.println("Mapped :" + url + "," + method);
}
}
}
}
最后要使这个@WebServlet 起效果,需要配置启动类:
@SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan public class App { private final static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(App.class); public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); log.info("服务启动成功"); } }
经过以上的这些操作,我们自己定义的注解就能生效了,那么现在我们需要考虑的是,这个controller里面,我需要获取请求参数和响应要怎么做呢,其实,我们只要在初始化controller的时候将requset跟response给他塞进去不久好了嘛?我们可以创建一个controller的基类
public class BaseController { protected HttpServletRequest request; protected HttpServletResponse response; public void init(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { this.request = request; this.response = response; } public HttpServletRequest getRequest() { return request; } public void setRequest(HttpServletRequest request) { this.request = request; } public HttpServletResponse getResponse() { return response; } public void setResponse(HttpServletResponse response) { this.response = response; } }
这样子,我们在service()方法内去获取该controller实例的时候controller.init(req, resp); 给他插进去这两个东西,就完事了。最后启动主类,你会发现它真的就调用了controller下的方法。
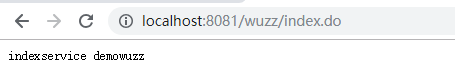
如果启用XML的形式去做的话,大致大逻辑还是一样的,只不过需要如下修改:
1.添加web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:javaee="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd" version="2.4"> <display-name>Gupao Web Application</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>gpmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.gupaoedu.mvcframework.v2.servlet.GPDispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>application.properties</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>gpmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
2.去掉 @WebServlet 注解,添加 application.properties 内容如下:
basePackage = com.wuzz.demo
3.既然添加了配置文件,那么我们需要扫描配置文件获取配置信息
//保存application.properties配置文件中的内容 private Properties contextConfig = new Properties(); //加载配置文件 private void doLoadConfig(String contextConfigLocation) { //直接从类路径下找到Spring主配置文件所在的路径 //并且将其读取出来放到Properties对象中 //相对于scanPackage=com.gupaoedu.demo 从文件中保存到了内存中 InputStream fis = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(contextConfigLocation); try { contextConfig.load(fis); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if(null != fis){ try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
加载配置文件
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
扫描相关的类
doScanner(contextConfig.getProperty("scanPackage"));
4.修改pom文件为war包形式
contextConfigLocation 是我们在web.xml中配置的。然后用Tomcat启动即可。




