springboot整合shiro、redis及相关优化
shrio官网:https://shiro.apache.org/
Apache Shiro是一个功能强大且易于使用的Java安全框架,可执行身份验证,授权,加密和会话管理。借助Shiro易于理解的API,您可以快速轻松地保护任何应用程序 - 从最小的移动应用程序到最大的Web和企业应用程序。spring中也有自带的安全框架spring security。shrio是通过对其的再封装,实现了自己的一套全新架构。话不多说,直接进入正题:
1.出了springboot的依赖之外,还需要导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--redis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2..直接上配置类:下面会对配置的一些重要bean进行稍加解释
import org.apache.shiro.crypto.hash.SimpleHash;
import org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.SessionManager;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.LifecycleBeanPostProcessor;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.security.interceptor.AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean;
import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.web.session.mgt.DefaultWebSessionManager;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.DependsOn;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
/**
* LifecycleBeanPostProcessor,这是个DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor的子类,
* 负责org.apache.shiro.util.Initializable类型bean的生命周期的,初始化和销毁。
* 主要是AuthorizingRealm类的子类,以及EhCacheManager类。
*/
@Bean(name = "lifecycleBeanPostProcessor")
public LifecycleBeanPostProcessor lifecycleBeanPostProcessor() {
return new LifecycleBeanPostProcessor();
}
/**
* HashedCredentialsMatcher,这个类是为了对密码进行编码的,
* 防止密码在数据库里明码保存,当然在登陆认证的时候,
* 这个类也负责对form里输入的密码进行编码。
*/
@Bean(name = "hashedCredentialsMatcher")
public HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher() {
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
credentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("MD5");
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
credentialsMatcher.setStoredCredentialsHexEncoded(true);
return credentialsMatcher;
}
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// String hashAlgorithmName = "MD5";
// String credentials = "123456";
// int hashIterations = 1024;
// Object obj = new SimpleHash(hashAlgorithmName, credentials, null, hashIterations);
// System.out.println(obj);
// }
/**
* ShiroRealm,这是个自定义的认证类,继承自AuthorizingRealm,
* 负责用户的认证和权限的处理,可以参考JdbcRealm的实现。
*/
@Bean(name = "shiroRealm")
@DependsOn("lifecycleBeanPostProcessor")
public CustomRealm shiroRealm() {
CustomRealm realm = new CustomRealm();//这个类需要自己编写 下面会贴出其实现
// realm.setCredentialsMatcher(hashedCredentialsMatcher());
return realm;
}
/**
* EhCacheManager,缓存管理,用户登陆成功后,把用户信息和权限信息缓存起来,
* 然后每次用户请求时,放入用户的session中,如果不设置这个bean,每个请求都会查询一次数据库。
*/
// @Bean(name = "ehCacheManager")
// @DependsOn("lifecycleBeanPostProcessor")
// public EhCacheManager getEhCacheManager(){
// EhCacheManager ehcacheManager = new EhCacheManager();
// ehcacheManager.setCacheManagerConfigFile("classpath:ehcache.xml");
// return ehcacheManager;
// }
/**
* SecurityManager,权限管理,这个类组合了登陆,登出,权限,session的处理,是个比较重要的类。
* //
*/
@Bean(name = "securityManager")
public DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager(@Qualifier("shiroRealm") CustomRealm shiroRealm, @Qualifier("defaultWebSessionManager") SessionManager sessionManager) {
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
securityManager.setRealm(shiroRealm);
// securityManager.setCacheManager(getEhCacheManager());
securityManager.setSessionManager(sessionManager);
return securityManager;
}
/**
* ShiroFilterFactoryBean,是个factorybean,为了生成ShiroFilter。
* 它主要保持了三项数据,securityManager,filters,filterChainDefinitionManager。
*/
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
Map<String, Filter> filters = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// filters.put("user",new ShiroUserFilter());
// LogoutFilter logoutFilter = new LogoutFilter();
// logoutFilter.setRedirectUrl("/api/1.0/loginout");
// filters.put("logout",null);
// shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilters(filters);
Map<String, String> filterChainDefinitionManager = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
// filterChainDefinitionManager.put("/logout", "logout");//登出URL
filterChainDefinitionManager.put("/login", "anon");//登陆URL
filterChainDefinitionManager.put("/nologin", "anon");//未登录跳转的URL
filterChainDefinitionManager.put("/test", "anon");
// filterChainDefinitionManager.put("/user/edit/**", "authc,perms[user:edit]");// 这里为了测试,固定写死的值,也可以从数据库或其他配置中读取,此处是用权限控制
// filterChainDefinitionManager.put("/**", "authc");
filterChainDefinitionManager.put("/**", "user");
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterChainDefinitionManager);
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login");
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilters(filters);
// shiroFilterFactoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/api/1.0/unauth");
return shiroFilterFactoryBean;
}
/**
* DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,Spring的一个bean,由Advisor决定对哪些类的方法进行AOP代理。
*/
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator defaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator() {
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator defaultAAP = new DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator();
defaultAAP.setProxyTargetClass(true);
return defaultAAP;
}
/**
* AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor,shiro里实现的Advisor类,
* 内部使用AopAllianceAnnotationsAuthorizingMethodInterceptor来拦截用以下注解的方法。
*/
@Bean
public AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor authorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor(org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager) {
AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor aASA = new AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor();
aASA.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
return aASA;
}
@Bean("defaultWebSessionManager")
public DefaultWebSessionManager configWebSessionManager(@Qualifier("redisSessionDao") RedisSessionDao sessionDao) {
MySessionManager manager = new MySessionManager();
manager.setSessionDAO(sessionDao);// 设置SessionDao
manager.setDeleteInvalidSessions(true);// 删除过期的session
manager.setSessionValidationSchedulerEnabled(false);// 是否定时检查session
return manager;
}
}
LifecycleBeanPostProcessor: 这个类 实现了DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口,而DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor接口继承了spring的 BeanPostProcessor。知道LifecycleBeanPostProcessor将Initializable和Destroyable的实现类统一在其内部自动分别调用了Initializable.init()和Destroyable.destroy()方法,从而达到管理shiro bean生命周期的目的。
public class LifecycleBeanPostProcessor implements DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LifecycleBeanPostProcessor.class);
private int order;
public LifecycleBeanPostProcessor() {
this(LOWEST_PRECEDENCE);
}
public LifecycleBeanPostProcessor(int order) {
this.order = order;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object object, String name) throws BeansException {
if (object instanceof Initializable) {
try {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Initializing bean [" + name + "]...");
}
((Initializable) object).init();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new FatalBeanException("Error initializing bean [" + name + "]", e);
}
}
return object;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object object, String name) throws BeansException {
// Does nothing after initialization
return object;
}
public void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object object, String name) throws BeansException {
if (object instanceof Destroyable) {
try {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Destroying bean [" + name + "]...");
}
((Destroyable) object).destroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new FatalBeanException("Error destroying bean [" + name + "]", e);
}
}
}
public int getOrder() {
// LifecycleBeanPostProcessor needs Order. See https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/SHIRO-222
return order;
}
}
spring的后置处理器BeanPostProcessor的作用是在spring初始化bean的前后进行一些特定操作。如果自己实现了多个后置处理器,并想按照自己的意愿顺序去执行这些处理器,那么这时候可以通过getOrder()方法去实现。order越小,执行优先级越高。
- DefaultWebSecurityManager: shiro的默认安全管理器,是整个配置的核心,必不可少的。可以通过设置自定义的realm,缓存管理器,会话管理器等等。
- ShiroFilterFactoryBean:核心过滤工厂类,里面可以配置需要过滤的路径,以及未登录,登陆等跳转地址。
- DefaultWebSessionManager:会话管理器。可以设置自定义的sessionDao sessionManager。
配置过程中涉及了自定义的sessionDao,自定义realm,自定义的sessionManager.其中的会话管理是通过redis去实现的,下面先贴出这3个实现类的 代码。
3.RedisSessionDao:实现自己的sessionDao的管理需要继承AbstractSessionDAO类,实现其中对于Session的增删改查的一些基本功能,并将该sessionDao配置好:
import org.apache.shiro.session.Session;
import org.apache.shiro.session.UnknownSessionException;
import org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.eis.AbstractSessionDAO;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Component("redisSessionDao")
public class RedisSessionDao extends AbstractSessionDAO {
@Value("${session.expireTime}")
private long expireTime;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
// 创建session,保存到数据库
@Override
protected Serializable doCreate(Session session) throws UnknownSessionException {
System.out.println("创建Session.......");
Assert.notNull(session);
if (session.getId() == null) {
Serializable sessionId = generateSessionId(session);
assignSessionId(session, sessionId);
}
String sessionId = session.getId().toString();
//判断session是否已经存在
Boolean exist = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Boolean>() {
public Boolean doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) {
Boolean result = connection.exists(sessionId.getBytes());
return result;
}
});
if (exist) {
throw new RuntimeException("session " + sessionId + "已经存在");
}
Boolean success = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Boolean>() {
public Boolean doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) {
Boolean result = connection.setNX(sessionId.getBytes(), sessionToByte(session));
return result;
}
});
if (!success) {
throw new RuntimeException("session " + sessionId + "创建失败");
}
//设置Session超时间间
redisTemplate.expire(sessionId, expireTime, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
return session.getId();
}
// 获取session
@Override
protected Session doReadSession(Serializable sessionId) {
System.out.println("查询Session.......");
Session session = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Session>() {
public Session doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) {
byte[] bytes = connection.get(sessionId.toString().getBytes());
if (null == bytes || bytes.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return ByteToSession(bytes);
}
});
return session;
}
// 更新session的最后一次访问时间
@Override
public void update(Session session) {
Assert.notNull(session);
if (session.getId() == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("sessionId is null");
}
String sessionId = session.getId().toString();
//判断session是否已经存在
Boolean exist = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Boolean>() {
public Boolean doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) {
Boolean result = connection.exists(sessionId.getBytes());
return result;
}
});
if (!exist) {
throw new RuntimeException("session " + sessionId + "不存在");
}
Boolean success = redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback<Boolean>() {
public Boolean doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) {
try {
connection.set(sessionId.getBytes(), sessionToByte(session));
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
});
if (!success) {
throw new RuntimeException("session " + sessionId + "更新失败");
}
System.out.println("更新Session.......");
//设置Session超时间间
redisTemplate.expire(sessionId, expireTime, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
// 删除session
@Override
public void delete(Session session) {
System.out.println("删除Session.......");
redisTemplate.delete(session.getId().toString());
}
@Override
public Collection<Session> getActiveSessions() {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
/**
* session转成字节数组流
*
* @param session
* @return
*/
private byte[] sessionToByte(Session session) {
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = null;
try {
ObjectOutput oo = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oo.writeObject(session);
bytes = bo.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bytes;
}
/**
* 获取redis中的流转session
*
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
private Session ByteToSession(byte[] bytes) {
Session session = null;
try {
ByteArrayInputStream bi = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(bi);
Object o = oi.readObject();
session = (Session) o;
bi.close();
oi.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("translation" + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
return session;
}
}
4.CustomRealm :该类是实现自己的认证(doGetAuthorizationInfo()方法)及登陆(doGetAuthenticationInfo()方法); 有了这个实现类,才能自己对登录和权限进行控制
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.crypto.hash.SimpleHash;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
private LoginServiceImpl loginServiceImpl;
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
//获取登录用户名
String name = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
//根据用户名去数据库查询用户信息
User user = loginServiceImpl.getUserByName(name);
//添加角色和权限
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
for (Role role : user.getRoles()) {
//添加角色
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole(role.getRoleName());
//添加权限
for (Permissions permissions : role.getPermissions()) {
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission(permissions.getPermissionsName());
}
}
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
//加这一步的目的是在Post请求的时候会先进认证,然后在到请求
if (authenticationToken.getPrincipal() == null) {
return null;
}
//获取用户信息
String name = authenticationToken.getPrincipal().toString();
User user = loginServiceImpl.getUserByName(name);
if (user == null) {
//这里返回后会报出对应异常
return null;
} else {
//这里验证authenticationToken和simpleAuthenticationInfo的信息
String hashAlgorithmName = "MD5";
int hashIterations = 1024;
Object obj = new SimpleHash(hashAlgorithmName, user.getPassword(), null, hashIterations);
SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(name, user.getPassword().toString(), getName());
return simpleAuthenticationInfo;
}
}
}
5.MySessionManager :实现默认的session管理器DefaultWebSessionManager,复写了其中的getSessionId方法。
import org.apache.shiro.session.Session;
import org.apache.shiro.session.UnknownSessionException;
import org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.SessionKey;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean;
import org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.ShiroHttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.shiro.web.session.mgt.DefaultWebSessionManager;
import org.apache.shiro.web.session.mgt.WebSessionKey;
import org.apache.shiro.web.util.WebUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class MySessionManager extends DefaultWebSessionManager {
public static final String AUTHORIZATION = "token";
private static final String REFERENCED_SESSION_ID_SOURCE = "Stateless request";
@Autowired
private RedisSessionDao redisSessionDao;
public MySessionManager() {
super();
}
/**
* 获取session
* 优化单次请求需要多次访问redis的问题
* @param sessionKey
* @return
* @throws UnknownSessionException
*/
@Override
protected Session retrieveSession(SessionKey sessionKey) throws UnknownSessionException {
Serializable sessionId = getSessionId(sessionKey);
ServletRequest request = null;
if (sessionKey instanceof WebSessionKey) {
request = ((WebSessionKey) sessionKey).getServletRequest();
}
if (request != null && null != sessionId) {
Object sessionObj = request.getAttribute(sessionId.toString());
if (sessionObj != null) {
System.out.println("read session from request");
return (Session) sessionObj;
}
}
Session session = super.retrieveSession(sessionKey);
if (request != null && null != sessionId) {
request.setAttribute(sessionId.toString(), session);
}
return session;
}
@Override
protected Serializable getSessionId(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) {
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
String id = WebUtils.toHttp(request).getHeader(AUTHORIZATION);
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = ApplicationContextUtils.getBean(ShiroFilterFactoryBean.class);
String loginUrl = bean.getLoginUrl();
String requestURI = req.getRequestURI();
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(id) && !requestURI.equals(loginUrl)) {
//可以使用全局异常捕获返回到前端
throw new RuntimeException("请登录");
}
//避免sessionId过期自动创建session问题
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(id)) {
Session session = redisSessionDao.doReadSession(id);
if (session ==null) {
throw new RuntimeException("There is no session with id [" + id + "]");
}
}
request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID_SOURCE, REFERENCED_SESSION_ID_SOURCE);
request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID, id);
request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID_IS_VALID, Boolean.TRUE);
return id;
}
}
6.配置 application.properties:
spring.redis.database=0
spring.redis.host=192.168.1.101
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=wuzhenzhao
session.expireTime=30
通过以上的配置,就可以进行登陆了,demo中用到的类如下:
//*******************************************************
// ********************用户--角色--权限**********************
ublic class User {
private String id;
private String username;
private String password;
/**
* 用户对应的角色集合
*/
private Set<Role> roles;
//省略get/set/构造
}
public class Role {
private String id;
private String roleName;
/**
* 角色对应权限集合
*/
private Set<Permissions> permissions;
//省略get/set/构造
}
public class Permissions {
private String id;
private String permissionsName;
//省略get/set/构造
}
//********************************************************
//************************登录服务************************
@Service("loginServiceImpl")
public class LoginServiceImpl {
public User getUserByName(String getMapByName) {
//模拟数据库查询,正常情况此处是从数据库或者缓存查询。
return getMapByName(getMapByName);
}
/**
* 模拟数据库查询
* @param userName
* @return
*/
private User getMapByName(String userName){
//共添加两个用户,两个用户都是admin一个角色,
//wsl有query和add权限,zhangsan只有一个query权限
Permissions permissions1 = new Permissions("1","query");
Permissions permissions2 = new Permissions("2","add");
Set<Permissions> permissionsSet = new HashSet<>();
permissionsSet.add(permissions1);
permissionsSet.add(permissions2);
Role role = new Role("1","admin",permissionsSet);
Set<Role> roleSet = new HashSet<>();
roleSet.add(role);
User user = new User("1","wuzz","123456",roleSet);
Map<String ,User> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(user.getUsername(), user);
Permissions permissions3 = new Permissions("3","query");
Set<Permissions> permissionsSet1 = new HashSet<>();
permissionsSet1.add(permissions3);
Role role1 = new Role("2","user",permissionsSet1);
Set<Role> roleSet1 = new HashSet<>();
roleSet1.add(role1);
User user1 = new User("2","zhangsan","123456",roleSet1);
map.put(user1.getUsername(), user1);
return map.get(userName);
}
}
//*****************************************************
//*************************上下文帮助类**********************
@Component
public class ApplicationContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {
/**
* 上下文对象实例
*/
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Autowired
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
/**
* 获取applicationContext
*
* @return
*/
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
/**
* 通过name获取 Bean.
*
* @param name 参数传入要获取的实例的类名 首字母小写,这是默认的
* @return
*/
public static Object getBean(String name) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name);
}
/**
* 通过class获取Bean.
*
* @param clazz
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(clazz);
}
/**
* 通过name,以及Clazz返回指定的Bean
*
* @param name
* @param clazz
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
public static <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name, clazz);
}
}
//****************************************************
//************************接口测试类*************************
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String login(User user) {
//添加用户认证信息
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken(
user.getUsername(),
user.getPassword()
);
try {
//进行验证,这里可以捕获异常,然后返回对应信息
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
// subject.checkRole("admin");
// subject.checkPermissions("query", "add");
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "账号或密码错误!";
} catch (AuthorizationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "没有权限";
}
String id = (String) subject.getSession().getId();
return id;
}
//注解验角色和权限
// @RequiresRoles("admin")
@RequiresPermissions("add")
@RequestMapping(value = "/index", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String index() {
return "index!";
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/logout", method = RequestMethod.GET)
// public String logout() {
// Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// subject.logout();
// return "redirect:/login";
// }
@RequestMapping(value = "/nologin", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String nologin() {
return "nologin!";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String tttt() {
String id = (String) SecurityUtils.getSubject().getSession().getId();
return id;
}
@RequestMapping("/wuzz/logout")
public String logout() {
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.logout();
return "login out.....";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test() {
return "test!";
}
}
权限控制可以通过shiro的注解进行对对应的角色,或者权限的控制。shiro整合中 Subject 与 principal 是比较重要的两个名词,个人理解前者像是一系列的登陆用户组成的一个实体,就好比一个人有多种登陆账号,而后者便是实际登陆该系统的账号密码。 跟其源码可以发现 Subject 的创建时通过 org.apache.shiro.subject 接口里面的内部类Builder里的这个方法去创建,
public Subject buildSubject() {
return this.securityManager.createSubject(this.subjectContext);
}
而实际上创建subject的是DefaultSecurityManager类,也就是我们配置的DefaultWebSecurityManager类的父类里面的
public Subject createSubject(SubjectContext subjectContext) {
//create a copy so we don't modify the argument's backing map:
SubjectContext context = copy(subjectContext);
//ensure that the context has a SecurityManager instance, and if not, add one:
context = ensureSecurityManager(context);
//Resolve an associated Session (usually based on a referenced session ID), and place it in the context before
//sending to the SubjectFactory. The SubjectFactory should not need to know how to acquire sessions as the
//process is often environment specific - better to shield the SF from these details:
context = resolveSession(context);
//Similarly, the SubjectFactory should not require any concept of RememberMe - translate that here first
//if possible before handing off to the SubjectFactory:
context = resolvePrincipals(context);
Subject subject = doCreateSubject(context);
//save this subject for future reference if necessary:
//(this is needed here in case rememberMe principals were resolved and they need to be stored in the
//session, so we don't constantly rehydrate the rememberMe PrincipalCollection on every operation).
//Added in 1.2:
save(subject);
return subject;
}
通过该方法去绑定session,principl...等等需要绑定的信息。注:需要满足自己的业务需求。可以通过重写shiro里面的一些列管理器,过滤器,再配置进指定的管理器中就可以。这些过滤器如下图:
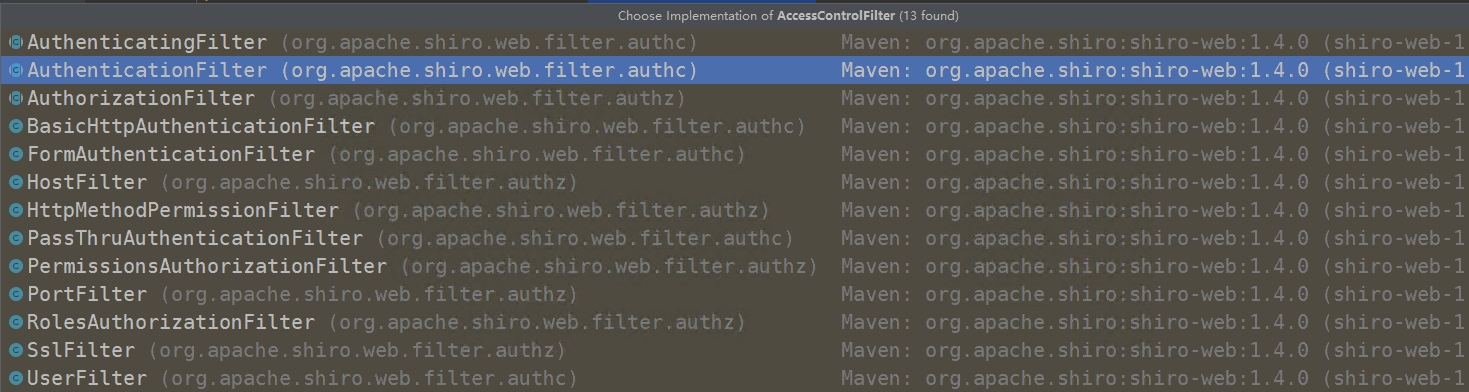
通过集成对应的过滤器,重写方法,例如:
public class ShiroUserFilter extends UserFilter {
@Override
protected boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) {
if (isLoginRequest(request, response)) {
return super.isAccessAllowed(request, response, mappedValue);
} else {
String id = WebUtils.toHttp(request).getHeader(MySessionManager.AUTHORIZATION);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(id)) {
try {
super.redirectToLogin(request,response);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Subject subject = getSubject(request, response);
// If principal is not null, then the user is known and should be allowed access.
return subject.getPrincipal() != null;
}
}
}
然后通过以下方式注入:
Map<String, Filter> filters = new LinkedHashMap<>();
filters.put("user",new ShiroUserFilter());
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilters(filters);





