vue、入门
入门vue
v-on:click:chang 绑定事件点击
生面周期,整个vue的执行过程,他的应用执行了生面周期,也就是执行过程,这个执行过程如下图表,我们可以参考下图,也可以访问官方网址:https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/instance.html。
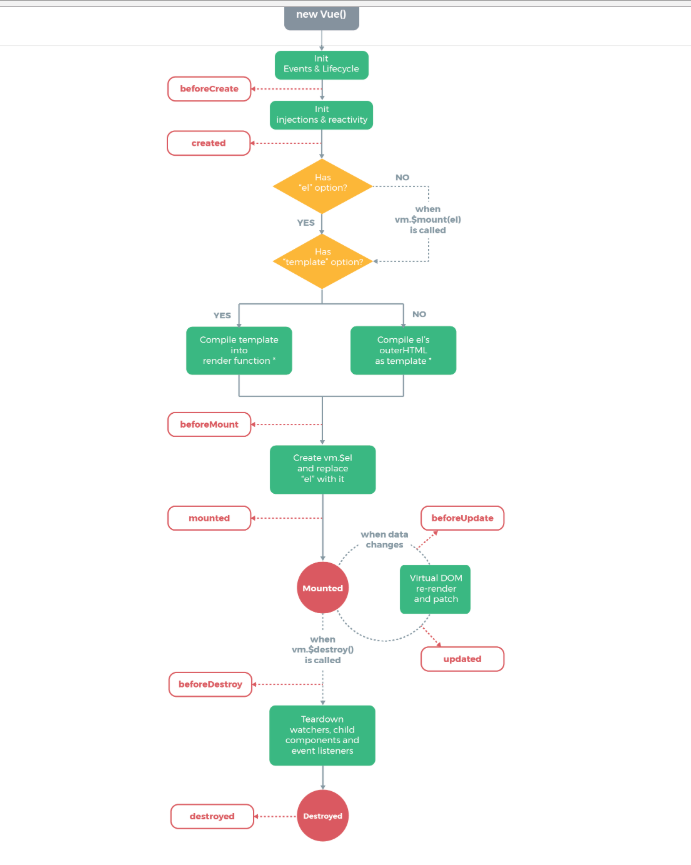
当变量进来的时候我们就要调用模板进行渲染等等。
初始化--->boeforecreate--->created--->beforeMout(渲染之前、挂载之前)--->mounted---->beforeupdate -----> updated --这就是一个生命周期的流程。
实际上中间的很多东西我们是操作不了的,因为别人已经写好了固定的模型,所以我们只要懂得业务逻辑就可以很好的做开发了。总体还有没有了解透的可以点击进去官方网址看看,我这里只是统计一个大概内容而已,并没有完善整个资料。我们可以在它的整个生命周期来调用不同的函数和方法来执行我们所需求的业务逻辑等,比如在挂载之前我们发起ajax去请求,等等度可以,这些代码库都是相互并用的,并不是一山不容二虎,恰好在他们并用的时候才能发挥更大的作用。
比如我们在某个过程中我们可以使用ajax发起http请求json文件,调用网址等等。生命周期的一点小理解:就是在他的某个阶段前,操作某个事件,
条件渲染:
(1)、视图的变化就是由数据来决定的。
v-if:渲染一个
v-show:渲染多个

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> <script src="js/vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script> <script src="js/jquery-1.11.0.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script> </head> <body> <!-- 1、仅仅只需要关注数据、业务逻辑和事件,dom直接的操作隐藏起来,不用再重复去做这个事情。 2、大大增加团队效率,团队协作能力 3、模块化,降低耦合度 4、数据的双向绑定,视图和模型的数据是绑定在一起的,变更1个,那么所有都变更 --> <!--视图--> <div id="app"> <h1>{{jsonMsg}}</h1> <p>{{jsonContent}}</p> <h1> 这是H1内容: {{ isA ? a : b}}</h1> <!--将变量绑定到属性上--> <a v-bind:href="httpUrl">链接地址</a> <a :href="httpUrl">链接地址</a> <div> {{htmlElement}} </div> <div v-html='htmlElement'></div> <h1>{{msg}}</h1> <h1 v-once>{{msg}}</h1> <input type="text" v-model='msg' name="" id="" value="" /> <button v-on:click='changeUrl'>更改为淘宝地址</button> <!-- v-on:可以缩写成@ --> <button @click='changeMsg'>更改msg</button> </div> <!-- vue模板: 1、变量放在{{}}里面,里面可以正常运行JS表达式 2、变量如果要放在HTML的属性里面,那么就需要使用v-bind,缩写即前面加冒号 3、默认是将HTML以字符串的形式输出到视图,如果想要以HTML的形式输出到视图,那么需要使用v-html这个指令 4、v-once只渲染1次 5、绑定事件的书写方式:v-on, vue应用生命周期(即执行过程) new Vue(配置变量) ---》初始化 ---》beforecreate ---》created --》beforeMount(渲染之前、挂载之前) ---》mounted --》beforeupdate ---》updated ---》beforeDestory ---》destoryed 条件渲染: --> <script type="text/javascript"> var obj = { el:'#app', data:{ msg:'helloworld', num:'123456778', isA:false, a:8, b:4, httpUrl:'http://www.baidu.com', htmlElement:'<button>这是一个按钮</button>', jsonMsg:'', jsonContent:'' }, methods:{ changeMsg:function(){ this.msg = '今天天气不错' }, changeUrl:function(){ this.httpUrl = 'http://www.taobao.com' } }, beforeCreate:function(){ console.log('创造之前执行的函数') }, created:function(){ console.log('创造之后') }, beforeMount:function(){ console.log('挂载之前') var that = this $.ajax({ url:'abc.json', success:function(res){ console.log(res) that.jsonMsg = res.msg that.jsonContent = res.content } }) }, mounted:function(){ console.log('挂载之后') }, beforeUpdate:function(){ console.log('更新之前') }, updated:function(){ console.log('更新之后') } } var app = new Vue(obj) console.log(app) </script> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <script src="js/vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h1>{{ isLogin ? '登录' : '注册' }}</h1> <form action="" v-if='isLogin' > <input type="text" placeholder="请输入用户名" /> <input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" /> <input type="submit" name="" id="" value="登录" /> </form> <form action="" v-if='!isLogin'> <input type="text" placeholder="请输入用户名" /> <input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" /> <input type="password" placeholder="请再次输入密码" /> <input type="submit" name="" id="" value="注册" /> </form> <hr /> <hr /> <form action="" v-show='isLogin' > <input type="text" placeholder="请输入用户名" /> <input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" /> <input type="submit" name="" id="" value="登录" /> </form> <form action="" v-show='!isLogin'> <input type="text" placeholder="请输入用户名" /> <input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" /> <input type="password" placeholder="请再次输入密码" /> <input type="submit" name="" id="" value="注册" /> </form> <!-- 条件渲染: v-if:在只渲染一次的情况下,那么性能最佳 v-show:在频繁切换的情况下,那么性能最佳,因为v-show,所有都生成出来,通过display来决定是否显示 --> <button @click='login'>登录</button> <button @click='register'>注册</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ isLogin:true }, methods:{ register:function(){ this.isLogin = false }, login:function(){ this.isLogin = true } } }) </script> </body> </html>
自动化学习。



