java设计模式之单例设计模式
1.定义
保证一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点.
2.意识图
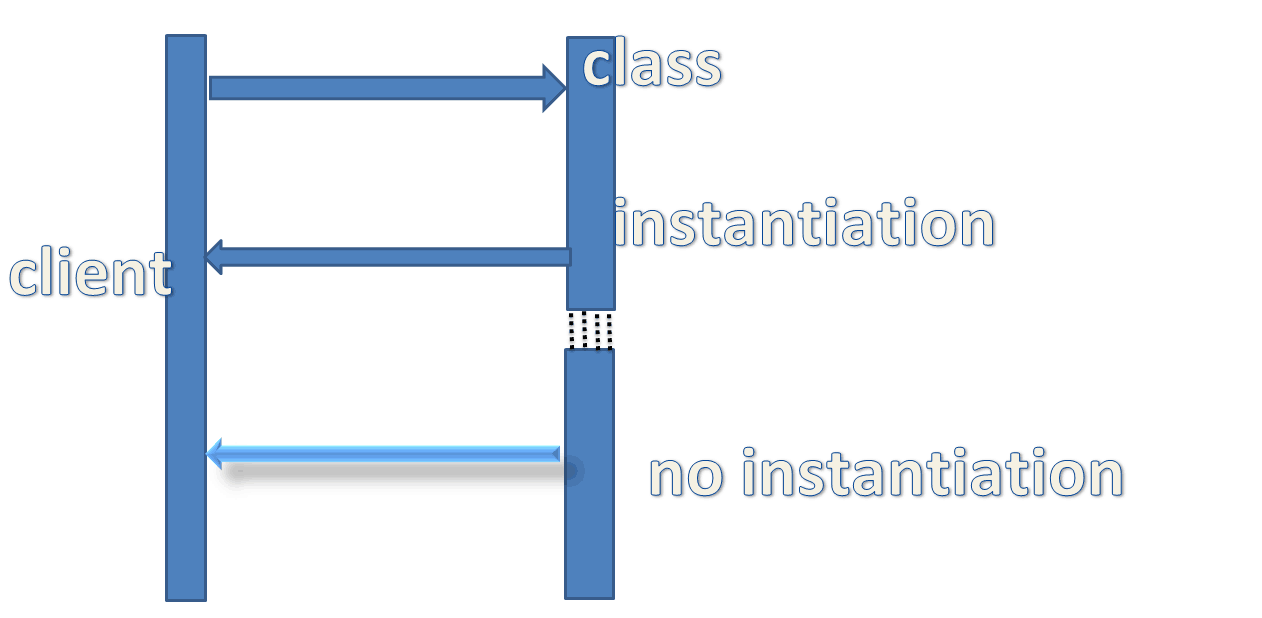
3.实例代码
1).懒汉式
package com.wyl.singleton;
/**
* 单例模式--懒汉式
* wuyanlin2016@163.com
* 2017年12月26日
*/
public class Example {
/**
* 懒汉式的特点:不得已时才创建对象
*/
//私有构造函数
private Example() {}
//成员变量
private static volatile Example instance;
//提供对外获取对象的方法
public static synchronized final Example getInstance() {
if(instance!=null) return instance;
synchronized (instance) {return new Example(); }
}
}
2).饿汉式
package com.wyl.singleton;
/**
* 单例模式--饿汉式
* wuyanlin2016@163.com
* 2017年12月26日
*/
public class Model {
/**
* 特点:开始就创建对象,比较饥饿
*/
//私有构造函数
private Model() {}
//初始化对象
private static final Model INSTANCE=new Model();
//提供对外访问方法
public static final Model getInstance() {return INSTANCE;}
}
3).静态内部类式
package com.wyl.singleton;
/**
* 单例模式--内部类
* wuyanlin2016@163.com
* 2017年12月26日
*/
public class Mode {
/**
* 特点:有效防止线程安全问题
*/
//私有构造方法
private Mode() {}
//静态内部类
private static class Inner {
private static final Mode INSTANCE = new Mode();
}
//提供对外访问的方法
public static final Mode getInstance() {return Inner.INSTANCE;}
}
4).枚举式
package com.wyl.singleton;
/**
* 单利模式--枚举
* wuyanlin2016@163.com
* 2017年12月26日
*/
public enum EnumModel {
INSTANCE;
public void execute() {
//execute other things
}
}
//使用
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
EnumModel.INSTANCE.execute();
}
}
5).单例与缓存
package com.wyl.singleton;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 单例模式与缓存 wuyanlin2016@163.com 2017年12月26日
*/
public class Extend {
/**
* map模拟缓存,控制实例个数
*/
// 私有构造方法
private Extend() {
}
// 默认key
private static String DEFAULT_KEY = "CACHE";
// 最大索引
private static int MAX_INDEX = 3;
// 初始索引
private static int num = 1;
// map充当缓存
private static Map<String, Extend> caches = new HashMap<>();
// 提供对外访问方法
public static final Extend getInstance() {
String realKey = DEFAULT_KEY + num;
if (caches.get(realKey) == null)
caches.put(realKey, new Extend());
if (num++ > MAX_INDEX)
num = 1;
return caches.get(realKey);
}
// 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("class1:" + Extend.getInstance());
System.out.println("class2:" + Extend.getInstance());
System.out.println("class3:" + Extend.getInstance());
System.out.println("class4:" + Extend.getInstance());
System.out.println("class5:" + Extend.getInstance());
System.out.println("class6:" + Extend.getInstance());
}
}
6).单例与缓存打印结果
class1:com.wyl.singleton.Extend@4a6ca1a6
class2:com.wyl.singleton.Extend@21e8bf76
class3:com.wyl.singleton.Extend@3771ed5e
class4:com.wyl.singleton.Extend@1896d2c2
class5:com.wyl.singleton.Extend@4a6ca1a6
class6:com.wyl.singleton.Extend@21e8bf76
4.总结
何时选用?
当一个类的实例只要一个,且外部只能通过一个访问点访问的时候.



