第6章 梯度下降法
梯度下降法:(Gradient Descent),梯度法用来求一个函数的最优值
 ,
,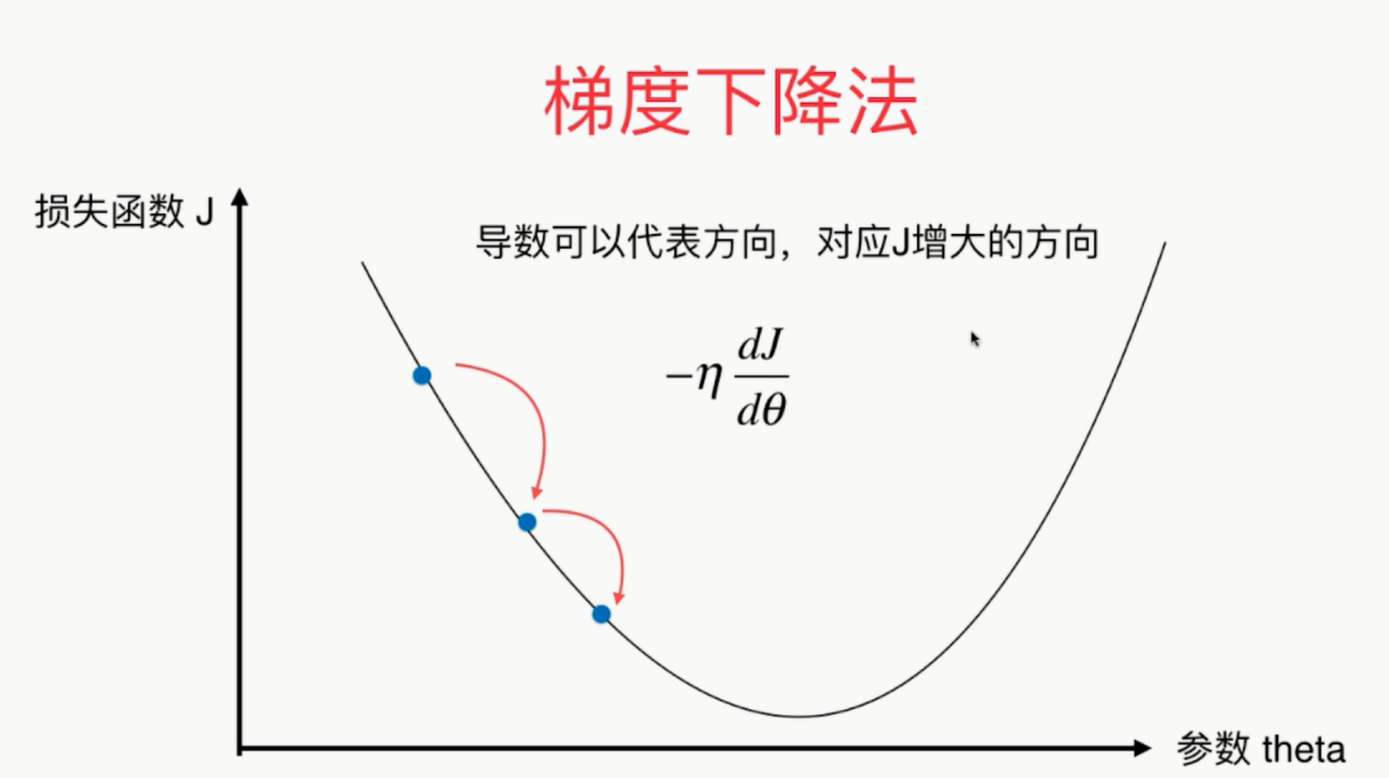
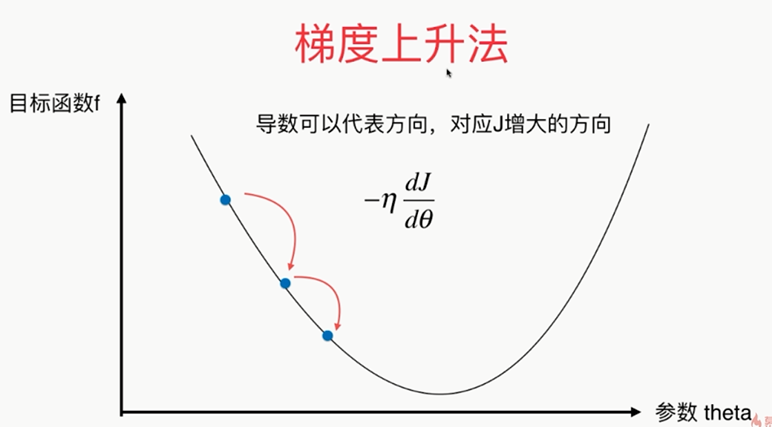
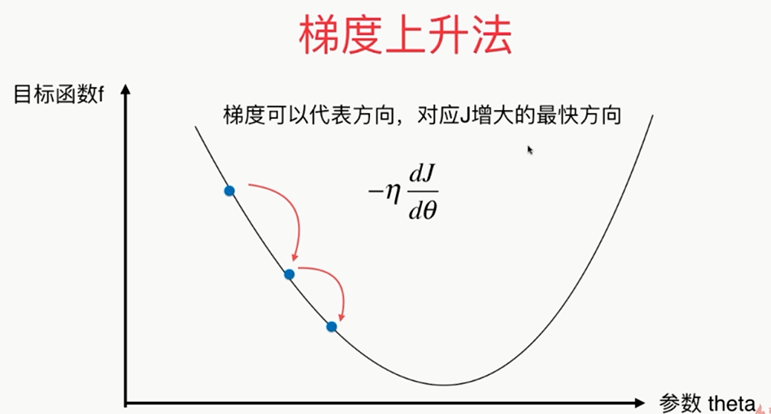
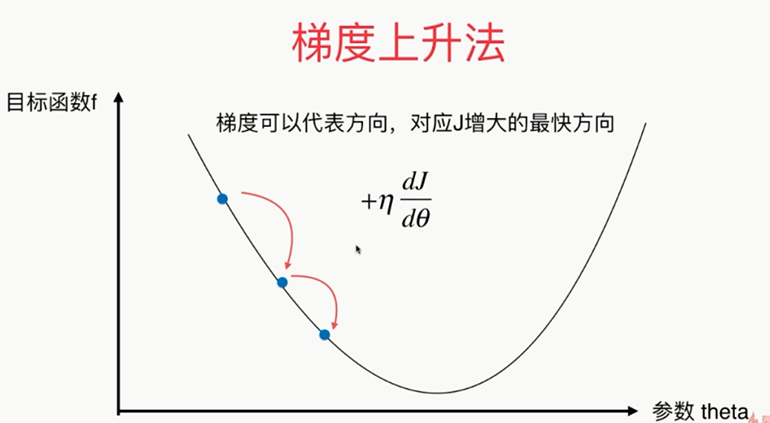
如果第一个点导数不为零的话,那么这点肯定不在极值点上!
有时候一上来η的取值不是很准确,需要通过调参的方式来找到适合的η值

 ,
, 
 ,
, 


import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plot_x=np.linspace(-1,6,141) plot_x plot_y=(plot_x-2.5)**2-1 plt.plot(plot_x,plot_y) plt.show() def dJ(theta): return 2*(theta-2.5) def J(theta): return (theta-2.5)**2-1 def gradient_descent(initial_theta,eta,n_iters = 1e4,epsilon=1e-8): theta = initial_theta theta_history.append(initial_theta) i_iter=0 while i_iter<n_iters: gradient=dJ(theta) last_theta=theta theta=theta-eta*gradient theta_history.append(theta) if (abs(J(theta)-J(last_theta))<epsilon): break i_iter+=1 def plot_theta_history(): plt.plot(plot_x,J(plot_x)) plt.plot(np.array(theta_history),J(np.array(theta_history)),color='r',marker='+') plt.show() eta=1.1 theta_history=[] gradient_descent(0,eta,n_iters=10) plot_theta_history()
 ,
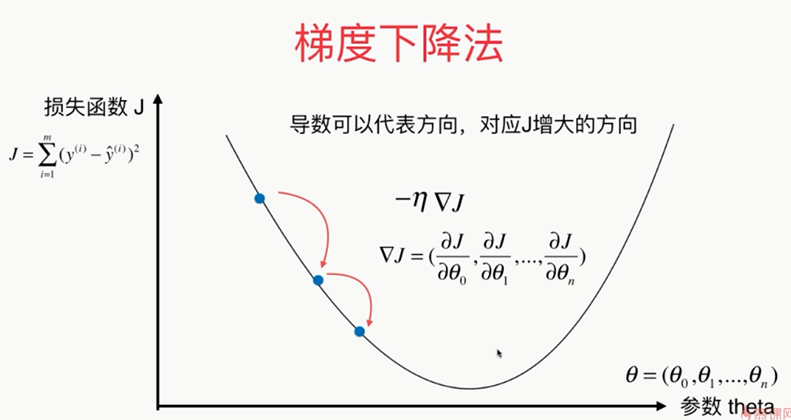
, 

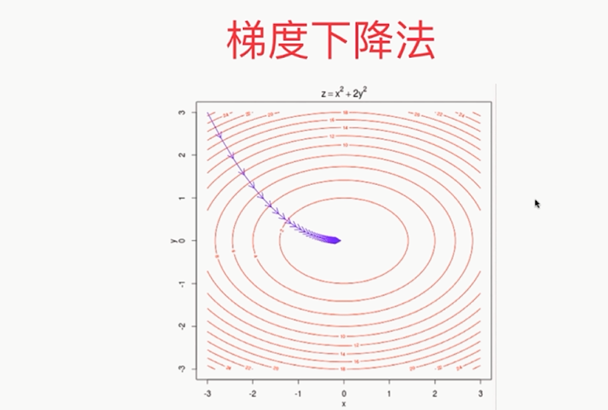
 ,
,
 , ,
, ,
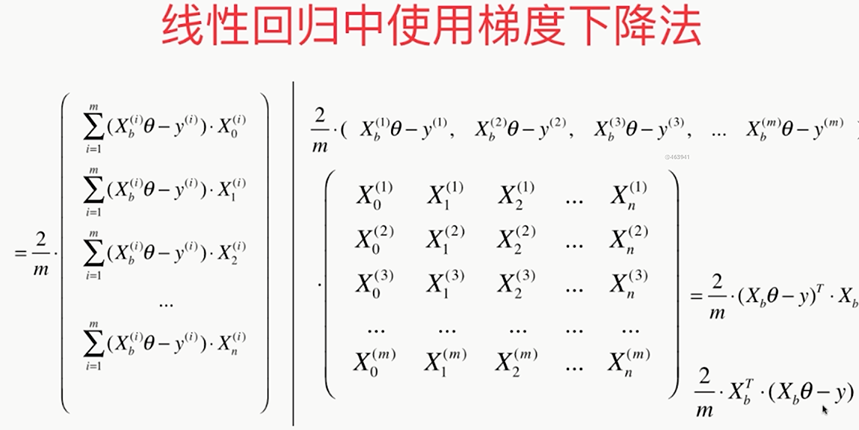
线性回归中梯度下降法的向量化
假设:X0恒等于1
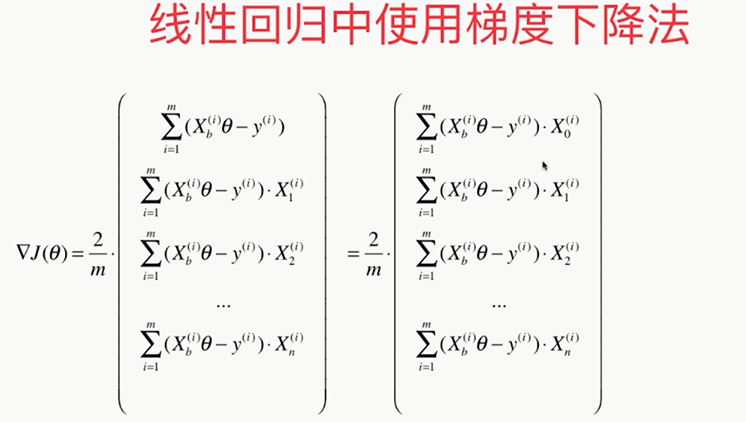 ,
, 
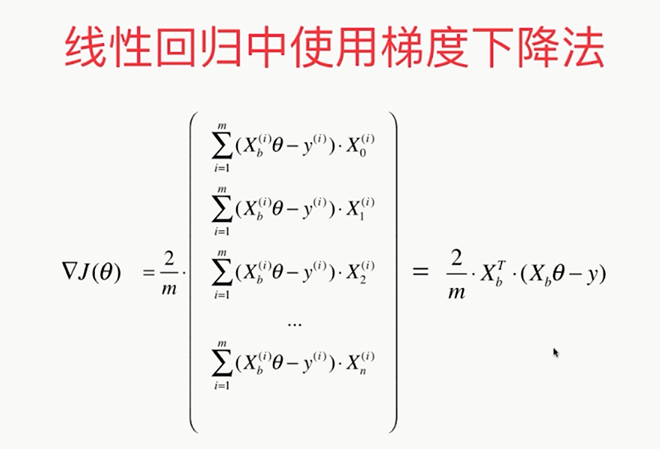 ,
,
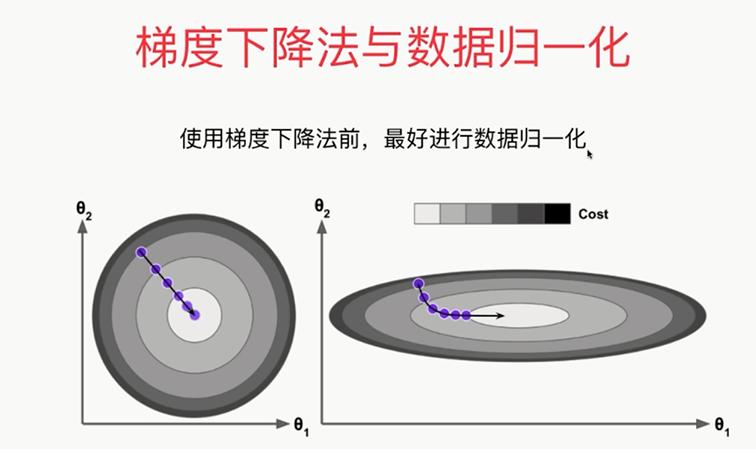

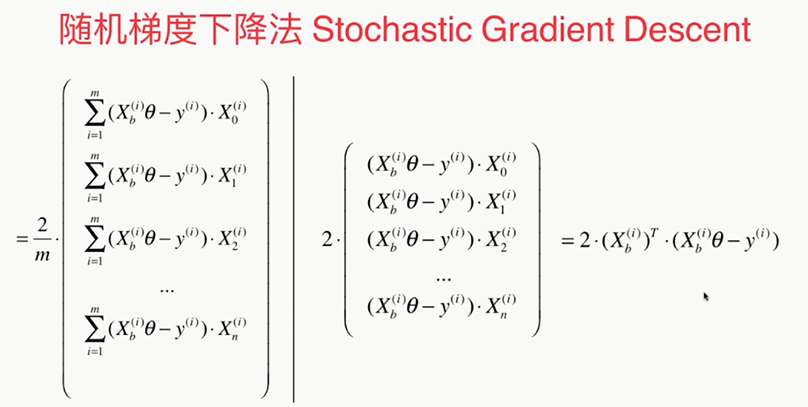 ,
, 
取值a=5,b=50

 ,
, 

 ,
, 
 ,
, 
 ,
, 



