实验1 现代C++编程初体验
实验任务1:
task1.cpp:
1 // 现代C++标准库、算法库体验 2 // 本例用到以下内容: 3 // 1. 字符串string, 动态数组容器类vector、迭代器 4 // 2. 算法库:反转元素次序、旋转元素 5 // 3. 函数模板、const引用作为形参 6 7 #include <iostream> 8 #include <string> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <algorithm> 11 12 using namespace std; 13 14 // 声明 15 // 模板函数声明 16 template<typename T> 17 void output(const T &c); 18 19 // 普通函数声明 20 void test1(); 21 void test2(); 22 void test3(); 23 24 int main() { 25 cout << "测试1: \n"; 26 test1(); 27 28 cout << "\n测试2: \n"; 29 test2(); 30 31 cout << "\n测试3: \n"; 32 test3(); 33 } 34 35 // 函数实现 36 // 输出容器对象c中的元素 37 template <typename T> 38 void output(const T &c) { 39 for(auto &i: c) 40 cout << i << " "; 41 cout << endl; 42 } 43 44 // 测试1 45 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、string反转字符串 46 void test1() { 47 string s0{"0123456789"}; 48 cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl; 49 50 string s1{s0}; 51 reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end()); // 反转指定迭代器区间的元素 52 cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl; 53 54 string s2{s0}; 55 reverse_copy(s0.begin(), s0.end(), s2.begin()); // 将指定迭代区间的元素拷贝到指定迭代器开始的目标区间,并且在复制过程中反转次序 56 cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl; 57 } 58 59 // 测试2 60 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector反转动态数组对象vector内数据 61 void test2() { 62 vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9}; 63 cout << "v0: "; 64 output(v0); 65 66 vector<int> v1{v0}; 67 reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end()); 68 cout << "v1: "; 69 output(v1); 70 71 vector<int> v2{v0}; 72 reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin()); 73 cout << "v2: "; 74 output(v2); 75 } 76 77 // 测试3 78 // 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector实现元素旋转移位 79 void test3() { 80 vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; 81 cout << "v0: "; 82 output(v0); 83 84 vector<int> v1{v0}; 85 rotate(v1.begin(), v1.begin()+1, v1.end()); // 旋转指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(), v1.end())之间的数据项,旋转后从迭代器v1.begin()+1位置的数据项开始 86 cout << "v1: "; 87 output(v1); 88 89 vector<int> v2{v0}; 90 rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin()+2, v2.end()); 91 cout << "v2: "; 92 output(v2); 93 94 vector<int> v3{v0}; 95 rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end()-1, v3.end()); 96 cout << "v3: "; 97 output(v3); 98 99 vector<int> v4{v0}; 100 rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end()-2, v4.end()); 101 cout << "v4: "; 102 output(v4); 103 }
运行测试截图:
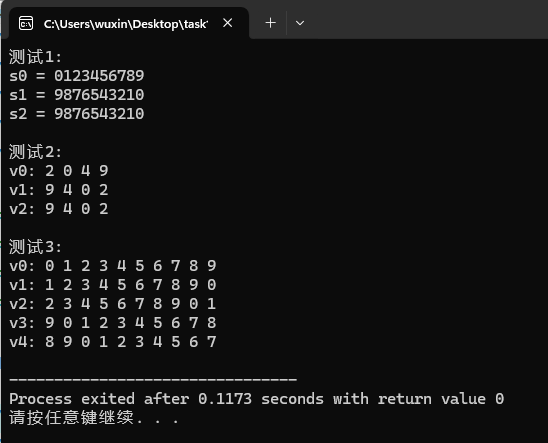
实验任务2:
task2.cpp:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <numeric> 6 #include <iomanip> 7 8 using namespace std; 9 10 // 函数声明 11 // 模板函数声明 12 template<typename T> 13 void output(const T &c); 14 15 // 普通函数声明 16 int rand_int_100(); 17 void test1(); 18 void test2(); 19 20 int main() { 21 cout << "测试1: \n"; 22 test1(); 23 24 cout << "\n测试2: \n"; 25 test2(); 26 } 27 28 // 函数实现 29 // 输出容器对象c中的元素 30 template <typename T> 31 void output(const T &c) { 32 for(auto &i: c) 33 cout << i << " "; 34 cout << endl; 35 } 36 37 // 返回[0, 100]区间内的一个随机整数 38 int rand_int_100() { 39 return rand() % 101; 40 } 41 42 // 测试1 43 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、排序 44 void test1() { 45 vector<int> v0(10); // 创建一个动态数组对象v0, 对象大小为10 46 generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); // 产生[0, 100]之间的随机整数赋值给指定迭代器区间[v0.begin(), v0.end())内的每个数据项 47 cout << "v0: "; 48 output(v0); 49 50 vector<int> v1{v0}; 51 sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(), v1.end())内数据项进行升序排序 52 cout << "v1: "; 53 output(v1); 54 55 vector<int> v2{v0}; 56 sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1)内数据项进行升序排序 57 cout << "v2: "; 58 output(v2); 59 } 60 61 // 测试2 62 // 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、计算最大值/最小值/均值 63 void test2() { 64 vector<int> v0(10); 65 generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); 66 cout << "v0: "; 67 output(v0); 68 69 auto iter1 = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); 70 cout << "最小值: " << *iter1 << endl; 71 72 auto iter2 = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); 73 cout << "最大值: " << *iter2 << endl; 74 75 auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end()); 76 cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl; 77 cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl; 78 double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0)/v0.size(); 79 cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl; 80 81 cout << endl; 82 83 vector<int> v1{v0}; 84 cout << "v0: "; 85 output(v0); 86 sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); 87 double avg2 = accumulate(v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1, 0)/(v1.size()-2); 88 cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl; 89 }
运行测试截图:
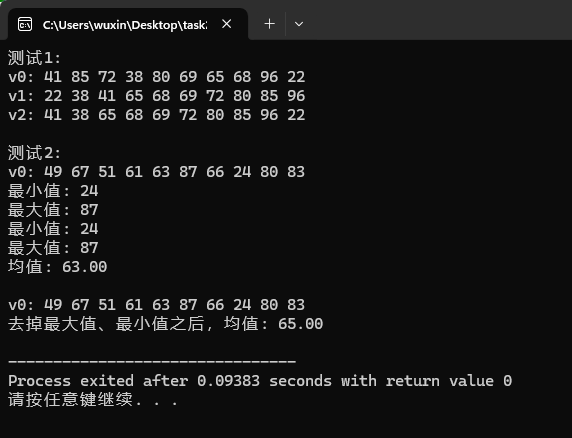
实验任务3:
task3.cpp:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 5 bool is_palindrome(std::string s); 6 7 int main() { 8 using namespace std; 9 string s; 10 11 while(cin >> s) // 多组输入,直到按下Ctrl+Z后结束测试 12 cout << boolalpha << is_palindrome(s) << endl; 13 } 14 15 // 函数is_palindrom定义 16 // 待补足 17 // ××× 18 bool is_palindrome(std::string s) 19 { 20 using namespace std; 21 string vec; 22 23 vec = s; 24 reverse(vec.begin(), vec.end()); 25 bool is_equal = equal(s.begin(), s.end(), vec.begin()); 26 27 return is_equal; 28 }
运行测试截图:
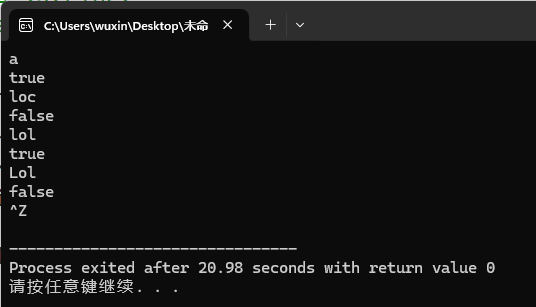
实验任务4:
task4.cpp:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 5 std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2); 6 7 int main() { 8 using namespace std; 9 10 int x; 11 while(cin >> x) { 12 cout << "十进制: " << x << endl; 13 cout << "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << endl; 14 cout << "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << endl; 15 cout << "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << endl << endl; 16 } 17 } 18 19 // 函数dec2n定义 20 // 待补足 21 // ××× 22 std::string dec2n(int x, int n) 23 { 24 using namespace std; 25 26 string result; 27 string str = "0123456789ABCDEF"; 28 29 while (x / n) 30 { 31 result.append(str, x % n, 1); 32 x /= n; 33 } 34 result.append(str, x % n, 1); 35 reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); 36 37 return result; 38 }
运行测试截图:
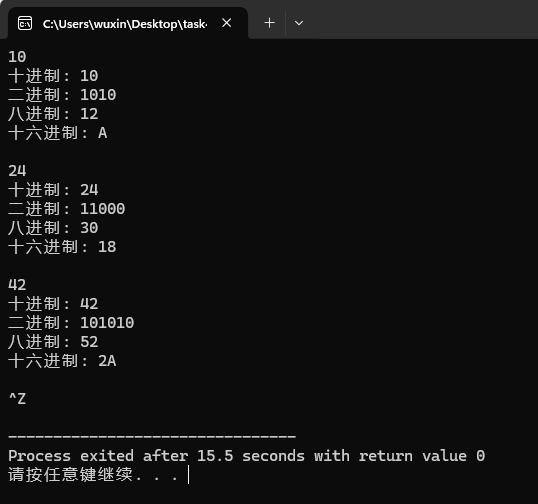
实验任务5:
task5.cpp:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <iomanip> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int i, j; 9 10 cout << " "; 11 for (i = 0;i < 26;i++) 12 cout << setw(2) << (char)('a' + i); 13 cout << endl; 14 15 for (i = 1;i < 27;i++) 16 { 17 cout << setw(2) << i; 18 for (j = 0;j < 26;j++) 19 { 20 if ('A' + i +j <= 'Z') 21 cout << setw(2) << (char)('A' + i + j); 22 else 23 cout << setw(2) << (char)('A' + i + j - 26); 24 } 25 cout << endl; 26 } 27 28 return 0; 29 }
运行测试截图:

实验任务6:
task6.cpp:
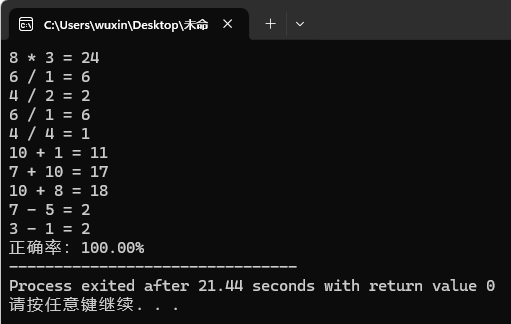
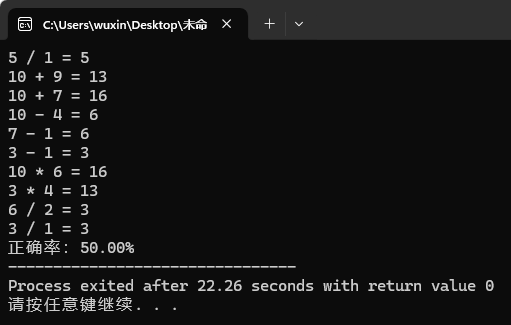
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <ctime> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 int i = 10, j = 0; 10 int num1, num2, func, answer, right; 11 12 while(i--) 13 { 14 srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); 15 num1 = rand() % 10 + 1; 16 num2 = rand() % 10 + 1; 17 func = rand() % 4 + 1; 18 19 if(func == 1) 20 { 21 right = num1 + num2; 22 cout << num1 << " + " << num2 << " = "; 23 } 24 else if(func == 2) 25 { 26 while(num1 == 1) 27 num1 = rand() % 10 + 1; 28 while(num2 >= num1) 29 num2 = rand() % 10 + 1; 30 right = num1 - num2; 31 cout << num1 << " - " << num2 << " = "; 32 } 33 else if(func == 3) 34 { 35 right = num1 * num2; 36 cout << num1 << " * " << num2 << " = "; 37 } 38 else if(func == 4) 39 { 40 while(num1 % num2 !=0) 41 { 42 num1 = rand() % 10 + 1; 43 num2 = rand() % 10 + 1; 44 } 45 right = num1 / num2; 46 cout << num1 << " / " << num2 << " = "; 47 } 48 49 cin >> answer; 50 if(answer == right) 51 j++; 52 } 53 54 cout << "正确率:" << j << "0.00%"; 55 return 0; 56 }
运行测试截图:
实验总结:
对于C++的语言特性,在C的基础上增加了很多库函数,让C更易于使用,当你知道那些函数怎么用,你就能节约大量时间来做更多的事情!
6个实验任务让我还是有比较深的体验到了C++的标准库、算法库的使用的。毕竟不断的查找资料嘛。当然,网站是个好东西,后面一定得多用!


