图算法
一.无向图
1.邻接表数据结构
1) 图中顶点用一个一维数组存储,当然也可以用单链表来存储,不过用数组可以较容易的读取顶点信息,更加方便。另外,对于顶点数组中,每个数据元素还需要存储指向第一个邻接点的指针,以便于查找该顶点的边信息。
2) 图中每个顶点vi的所有邻接点构成一个线性表,由于邻接点的个数不定,所以用单链表存储,无向图称为顶点vi的边表,有向图则称为以vi为弧尾的出边表。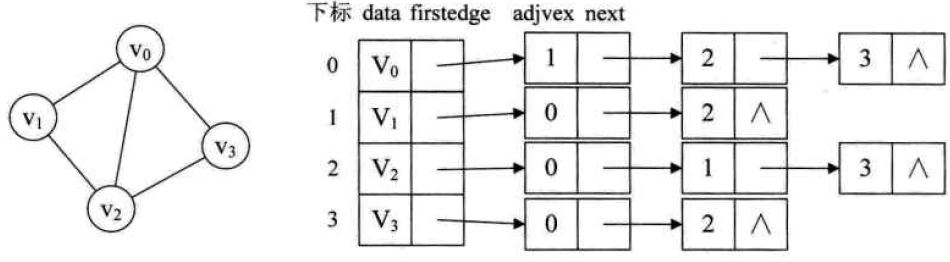
package sort; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Bag; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; import java.util.Stack; public class Graph { private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator"); private final int V; private int E; private Bag<Integer>[] adj; //创建一个含有V个顶点但不含有边的图 public Graph(int V) { if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices must be nonnegative"); this.V = V; this.E = 0; adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>(); } } //从标准输入流in读入一幅图 public Graph(In in) { if (in == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null"); try { this.V = in.readInt(); if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of vertices in a Graph must be nonnegative"); adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>(); } int E = in.readInt(); if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of edges in a Graph must be nonnegative"); for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int v = in.readInt(); int w = in.readInt(); validateVertex(v); validateVertex(w); addEdge(v, w); } } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in Graph constructor", e); } } //深拷贝一幅图 public Graph(Graph G) { this.V = G.V(); this.E = G.E(); if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices must be nonnegative"); // update adjacency lists adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>(); } for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { // reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original Stack<Integer> reverse = new Stack<Integer>(); for (int w : G.adj[v]) { reverse.push(w); } for (int w : reverse) { adj[v].add(w); } } } //返回顶点数 public int V() { return V; } //返回边数 public int E() { return E; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } //向图中添加一条边v-w public void addEdge(int v, int w) { validateVertex(v); validateVertex(w); E++; adj[v].add(w); adj[w].add(v); } //和v相邻的所有顶点 public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v) { validateVertex(v); return adj[v]; } //返回顶点v的度数 public int degree(int v) { validateVertex(v); return adj[v].size(); } public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); s.append(V + " vertices, " + E + " edges " + NEWLINE); for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { s.append(v + ": "); for (int w : adj[v]) { s.append(w + " "); } s.append(NEWLINE); } return s.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); Graph G = new Graph(in); StdOut.println(G); } }
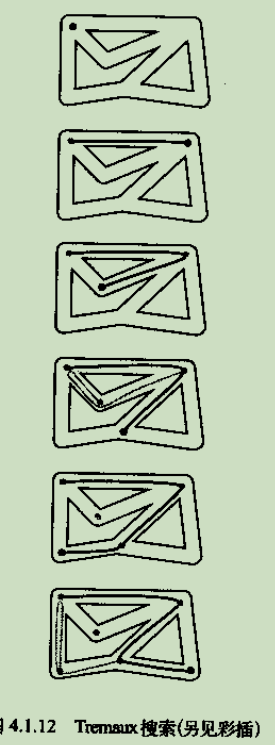
2.深度优先搜索
思路:将深度优先搜索比喻成走迷宫。
(1)选择一条没有标记过的通道,在你走过的路上铺上一条绳子。
(2)标记所有你第一次路过的路口和通道。
(3)当你来到一个你标记过的路口时,回退到上一个路口。
(4)当回退的路口已没有可走的通道时继续回退。
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class DepthFirstSearch { private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = is there an s-v path? private int count; // number of vertices connected to s public DepthFirstSearch(Graph G, int s) { marked = new boolean[G.V()]; validateVertex(s); dfs(G, s); } // 深度优先搜索v顶点 private void dfs(Graph G, int v) { count++; marked[v] = true; for (int w : G.adj(v)) { if (!marked[w]) { dfs(G, w); } } } //判断v和s是否连通 public boolean marked(int v) { validateVertex(v); return marked[v]; } //与s连通的顶点数 public int count() { return count; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = marked.length; if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); Graph G = new Graph(in); int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); DepthFirstSearch search = new DepthFirstSearch(G, s); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { if (search.marked(v)) StdOut.print(v + " "); } StdOut.println(); if (search.count() != G.V()) StdOut.println("NOT connected"); else StdOut.println("connected"); } }
3.使用深度优先搜索查找图中的路径
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import java.util.Stack; public class DepthFirstPaths { private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = is there an s-v path? private int[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on s-v path private final int s; // source vertex public DepthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s) { this.s = s; edgeTo = new int[G.V()]; marked = new boolean[G.V()]; validateVertex(s); dfs(G, s); } // 深度优先搜索 private void dfs(Graph G, int v) { marked[v] = true; for (int w : G.adj(v)) { if (!marked[w]) { edgeTo[w] = v; dfs(G, w); } } } //是否存在从s到v的路径 public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); return marked[v]; } //s到v的路径,如果不存在则返回null public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<Integer>(); for (int x = v; x != s; x = edgeTo[x]) path.push(x); path.push(s); return path; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = marked.length; if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); Graph G = new Graph(in); int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); DepthFirstPaths dfs = new DepthFirstPaths(G, s); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { if (dfs.hasPathTo(v)) { StdOut.printf("%d to %d: ", s, v); for (int x : dfs.pathTo(v)) { if (x == s) StdOut.print(x); else StdOut.print("-" + x); } StdOut.println(); } else { StdOut.printf("%d to %d: not connected\n", s, v); } } } }
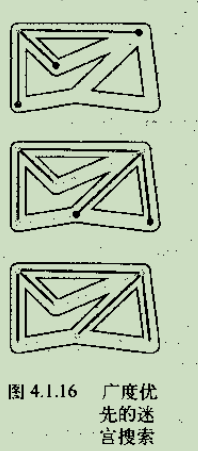
4.广度优先搜索(最短路径)
思路:广度优先搜索就像是一组人在一起朝各个方向走这座迷宫,每个人都有自己的绳子。当出现叉路时,可以假设一个探险者可以分裂为更多的人来搜索它们,当两个探险者相遇时,会合二为一。
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Queue; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import java.util.Stack; public class BreadthFirstPaths { private static final int INFINITY = Integer.MAX_VALUE; private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = is there an s-v path private int[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = previous edge on shortest s-v path private int[] distTo; // distTo[v] = number of edges shortest s-v path public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s) { marked = new boolean[G.V()]; distTo = new int[G.V()]; edgeTo = new int[G.V()]; validateVertex(s); bfs(G, s); assert check(G, s); } public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph G, Iterable<Integer> sources) { marked = new boolean[G.V()]; distTo = new int[G.V()]; edgeTo = new int[G.V()]; for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) distTo[v] = INFINITY; validateVertices(sources); bfs(G, sources); } // 广度优先搜索 private void bfs(Graph G, int s) { Queue<Integer> q = new Queue<Integer>(); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) distTo[v] = INFINITY; distTo[s] = 0; marked[s] = true; q.enqueue(s); while (!q.isEmpty()) { int v = q.dequeue(); for (int w : G.adj(v)) { if (!marked[w]) { edgeTo[w] = v; distTo[w] = distTo[v] + 1; marked[w] = true; q.enqueue(w); } } } } // breadth-first search from multiple sources private void bfs(Graph G, Iterable<Integer> sources) { Queue<Integer> q = new Queue<Integer>(); for (int s : sources) { marked[s] = true; distTo[s] = 0; q.enqueue(s); } while (!q.isEmpty()) { int v = q.dequeue(); for (int w : G.adj(v)) { if (!marked[w]) { edgeTo[w] = v; distTo[w] = distTo[v] + 1; marked[w] = true; q.enqueue(w); } } } } //判断v是否可达 public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); return marked[v]; } //返回顶点到v的边数 public int distTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); return distTo[v]; } //顶点到v的最短路径 public Iterable<Integer> pathTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<Integer>(); int x; for (x = v; distTo[x] != 0; x = edgeTo[x]) path.push(x); path.push(x); return path; } // check optimality conditions for single source private boolean check(Graph G, int s) { // check that the distance of s = 0 if (distTo[s] != 0) { StdOut.println("distance of source " + s + " to itself = " + distTo[s]); return false; } // check that for each edge v-w dist[w] <= dist[v] + 1 // provided v is reachable from s for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { for (int w : G.adj(v)) { if (hasPathTo(v) != hasPathTo(w)) { StdOut.println("edge " + v + "-" + w); StdOut.println("hasPathTo(" + v + ") = " + hasPathTo(v)); StdOut.println("hasPathTo(" + w + ") = " + hasPathTo(w)); return false; } if (hasPathTo(v) && (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + 1)) { StdOut.println("edge " + v + "-" + w); StdOut.println("distTo[" + v + "] = " + distTo[v]); StdOut.println("distTo[" + w + "] = " + distTo[w]); return false; } } } // check that v = edgeTo[w] satisfies distTo[w] = distTo[v] + 1 // provided v is reachable from s for (int w = 0; w < G.V(); w++) { if (!hasPathTo(w) || w == s) continue; int v = edgeTo[w]; if (distTo[w] != distTo[v] + 1) { StdOut.println("shortest path edge " + v + "-" + w); StdOut.println("distTo[" + v + "] = " + distTo[v]); StdOut.println("distTo[" + w + "] = " + distTo[w]); return false; } } return true; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = marked.length; if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertices(Iterable<Integer> vertices) { if (vertices == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null"); } int V = marked.length; for (int v : vertices) { if (v < 0 || v >= V) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); Graph G = new Graph(in); // StdOut.println(G); int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); BreadthFirstPaths bfs = new BreadthFirstPaths(G, s); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { if (bfs.hasPathTo(v)) { StdOut.printf("%d to %d (%d): ", s, v, bfs.distTo(v)); for (int x : bfs.pathTo(v)) { if (x == s) StdOut.print(x); else StdOut.print("-" + x); } StdOut.println(); } else { StdOut.printf("%d to %d (-): not connected\n", s, v); } } } }
5.使用深度优先搜索找出图中的所有连通分量
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*; public class CC { private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = has vertex v been marked? private int[] id; // id[v] = id of connected component containing v private int[] size; // size[id] = number of vertices in given component private int count; // number of connected components public CC(Graph G) { marked = new boolean[G.V()]; id = new int[G.V()]; size = new int[G.V()]; for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { if (!marked[v]) { dfs(G, v); count++; } } } public CC(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { marked = new boolean[G.V()]; id = new int[G.V()]; size = new int[G.V()]; for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { if (!marked[v]) { dfs(G, v); count++; } } } // depth-first search for a Graph private void dfs(Graph G, int v) { marked[v] = true; id[v] = count; size[count]++; for (int w : G.adj(v)) { if (!marked[w]) { dfs(G, w); } } } // depth-first search for an EdgeWeightedGraph private void dfs(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v) { marked[v] = true; id[v] = count; size[count]++; for (Edge e : G.adj(v)) { int w = e.other(v); if (!marked[w]) { dfs(G, w); } } } //v所在的连通分量的标识符 public int id(int v) { validateVertex(v); return id[v]; } public int size(int v) { validateVertex(v); return size[id[v]]; } //连通分量数 public int count() { return count; } //v和w连通吗 public boolean connected(int v, int w) { validateVertex(v); validateVertex(w); return id(v) == id(w); } @Deprecated public boolean areConnected(int v, int w) { validateVertex(v); validateVertex(w); return id(v) == id(w); } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = marked.length; if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); Graph G = new Graph(in); CC cc = new CC(G); // number of connected components int m = cc.count(); StdOut.println(m + " components"); // compute list of vertices in each connected component Queue<Integer>[] components = (Queue<Integer>[]) new Queue[m]; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { components[i] = new Queue<Integer>(); } for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { components[cc.id(v)].enqueue(v); } // print results for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int v : components[i]) { StdOut.print(v + " "); } StdOut.println(); } } }
6.符号图的数据结构
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*; public class SymbolGraph { private ST<String, Integer> st; // string -> index private String[] keys; // index -> string private Graph graph; // the underlying graph public SymbolGraph(String filename, String delimiter) { st = new ST<String, Integer>(); // First pass builds the index by reading strings to associate // distinct strings with an index In in = new In(filename); // while (in.hasNextLine()) { while (!in.isEmpty()) { String[] a = in.readLine().split(delimiter); for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { if (!st.contains(a[i])) st.put(a[i], st.size()); } } // inverted index to get string keys in an array keys = new String[st.size()]; for (String name : st.keys()) { keys[st.get(name)] = name; } // second pass builds the graph by connecting first vertex on each // line to all others graph = new Graph(st.size()); in = new In(filename); while (in.hasNextLine()) { String[] a = in.readLine().split(delimiter); int v = st.get(a[0]); for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) { int w = st.get(a[i]); graph.addEdge(v, w); } } } //s是一个顶点吗 public boolean contains(String s) { return st.contains(s); } @Deprecated public int index(String s) { return st.get(s); } //s的索引 public int indexOf(String s) { return st.get(s); } @Deprecated public String name(int v) { validateVertex(v); return keys[v]; } //索引v的顶点名 public String nameOf(int v) { validateVertex(v); return keys[v]; } @Deprecated public Graph G() { return graph; } public Graph graph() { return graph; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = graph.V(); if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } public static void main(String[] args) { String filename = args[0]; String delimiter = args[1]; SymbolGraph sg = new SymbolGraph(filename, delimiter); Graph graph = sg.graph(); while (StdIn.hasNextLine()) { String source = StdIn.readLine(); if (sg.contains(source)) { int s = sg.index(source); for (int v : graph.adj(s)) { StdOut.println(" " + sg.name(v)); } } else { StdOut.println("input not contain '" + source + "'"); } } } }
二.有向图
1.有向图数据结构
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Bag; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Stack; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class Digraph { private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator"); private final int V; // number of vertices in this digraph private int E; // number of edges in this digraph private Bag<Integer>[] adj; // adj[v] = adjacency list for vertex v private int[] indegree; // indegree[v] = indegree of vertex v public Digraph(int V) { if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative"); this.V = V; this.E = 0; indegree = new int[V]; adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>(); } } public Digraph(In in) { if (in == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null"); try { this.V = in.readInt(); if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative"); indegree = new int[V]; adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>(); } int E = in.readInt(); if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of edges in a Digraph must be nonnegative"); for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int v = in.readInt(); int w = in.readInt(); addEdge(v, w); } } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in Digraph constructor", e); } } public Digraph(Digraph G) { if (G == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null"); this.V = G.V(); this.E = G.E(); if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative"); // update indegrees indegree = new int[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) this.indegree[v] = G.indegree(v); // update adjacency lists adj = (Bag<Integer>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { adj[v] = new Bag<Integer>(); } for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { // reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original Stack<Integer> reverse = new Stack<Integer>(); for (int w : G.adj[v]) { reverse.push(w); } for (int w : reverse) { adj[v].add(w); } } } //顶点总数 public int V() { return V; } //边的总数 public int E() { return E; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } //向有向图中添加一条边v->w public void addEdge(int v, int w) { validateVertex(v); validateVertex(w); adj[v].add(w); indegree[w]++; E++; } //由v指出的边所连接的所有顶点 public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v) { validateVertex(v); return adj[v]; } public int outdegree(int v) { validateVertex(v); return adj[v].size(); } //到顶点v的有向边数 public int indegree(int v) { validateVertex(v); return indegree[v]; } //该图的反向图 public Digraph reverse() { Digraph reverse = new Digraph(V); for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { for (int w : adj(v)) { reverse.addEdge(w, v); } } return reverse; } public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); s.append(V + " vertices, " + E + " edges " + NEWLINE); for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { s.append(String.format("%d: ", v)); for (int w : adj[v]) { s.append(String.format("%d ", w)); } s.append(NEWLINE); } return s.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); Digraph G = new Digraph(in); StdOut.println(G); } }
2.有向图中的可达性
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Bag; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class DirectedDFS { private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = true iff v is reachable from source(s) private int count; // number of vertices reachable from source(s) public DirectedDFS(Digraph G, int s) { marked = new boolean[G.V()]; validateVertex(s); dfs(G, s); } public DirectedDFS(Digraph G, Iterable<Integer> sources) { marked = new boolean[G.V()]; validateVertices(sources); for (int v : sources) { if (!marked[v]) dfs(G, v); } } private void dfs(Digraph G, int v) { count++; marked[v] = true; for (int w : G.adj(v)) { if (!marked[w]) dfs(G, w); } } public boolean marked(int v) { validateVertex(v); return marked[v]; } public int count() { return count; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = marked.length; if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertices(Iterable<Integer> vertices) { if (vertices == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null"); } int V = marked.length; for (int v : vertices) { if (v < 0 || v >= V) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // read in digraph from command-line argument In in = new In(args[0]); Digraph G = new Digraph(in); // read in sources from command-line arguments Bag<Integer> sources = new Bag<Integer>(); for (int i = 1; i < args.length; i++) { int s = Integer.parseInt(args[i]); sources.add(s); } // multiple-source reachability DirectedDFS dfs = new DirectedDFS(G, sources); // print out vertices reachable from sources for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { if (dfs.marked(v)) StdOut.print(v + " "); } StdOut.println(); } }
3.寻找有向环
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Stack; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class DirectedCycle { private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = has vertex v been marked? private int[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = previous vertex on path to v private boolean[] onStack; // onStack[v] = is vertex on the stack? private Stack<Integer> cycle; // directed cycle (or null if no such cycle) public DirectedCycle(Digraph G) { marked = new boolean[G.V()]; onStack = new boolean[G.V()]; edgeTo = new int[G.V()]; for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) if (!marked[v] && cycle == null) dfs(G, v); } // check that algorithm computes either the topological order or finds a directed cycle private void dfs(Digraph G, int v) { onStack[v] = true; marked[v] = true; for (int w : G.adj(v)) { // short circuit if directed cycle found if (cycle != null) return; // found new vertex, so recur else if (!marked[w]) { edgeTo[w] = v; dfs(G, w); } // trace back directed cycle else if (onStack[w]) { cycle = new Stack<Integer>(); for (int x = v; x != w; x = edgeTo[x]) { cycle.push(x); } cycle.push(w); cycle.push(v); assert check(); } } onStack[v] = false; } //是否含有有向环 public boolean hasCycle() { return cycle != null; } //有向环中的所有顶点 public Iterable<Integer> cycle() { return cycle; } // certify that digraph has a directed cycle if it reports one private boolean check() { if (hasCycle()) { // verify cycle int first = -1, last = -1; for (int v : cycle()) { if (first == -1) first = v; last = v; } if (first != last) { System.err.printf("cycle begins with %d and ends with %d\n", first, last); return false; } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); Digraph G = new Digraph(in); DirectedCycle finder = new DirectedCycle(G); if (finder.hasCycle()) { StdOut.print("Directed cycle: "); for (int v : finder.cycle()) { StdOut.print(v + " "); } StdOut.println(); } else { StdOut.println("No directed cycle"); } StdOut.println(); } }
4.有向图中基于深度优先搜索的顶点排序
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*; public class DepthFirstOrder { private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = has v been marked in dfs? private int[] pre; // pre[v] = preorder number of v private int[] post; // post[v] = postorder number of v private Queue<Integer> preorder; // vertices in preorder private Queue<Integer> postorder; // vertices in postorder private int preCounter; // counter or preorder numbering private int postCounter; // counter for postorder numbering public DepthFirstOrder(Digraph G) { pre = new int[G.V()]; post = new int[G.V()]; postorder = new Queue<Integer>(); preorder = new Queue<Integer>(); marked = new boolean[G.V()]; for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) if (!marked[v]) dfs(G, v); assert check(); } public DepthFirstOrder(EdgeWeightedDigraph G) { pre = new int[G.V()]; post = new int[G.V()]; postorder = new Queue<Integer>(); preorder = new Queue<Integer>(); marked = new boolean[G.V()]; for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) if (!marked[v]) dfs(G, v); } // run DFS in digraph G from vertex v and compute preorder/postorder private void dfs(Digraph G, int v) { marked[v] = true; pre[v] = preCounter++; preorder.enqueue(v); for (int w : G.adj(v)) { if (!marked[w]) { dfs(G, w); } } postorder.enqueue(v); post[v] = postCounter++; } // run DFS in edge-weighted digraph G from vertex v and compute preorder/postorder private void dfs(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int v) { marked[v] = true; pre[v] = preCounter++; preorder.enqueue(v); for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) { int w = e.to(); if (!marked[w]) { dfs(G, w); } } postorder.enqueue(v); post[v] = postCounter++; } public int pre(int v) { validateVertex(v); return pre[v]; } public int post(int v) { validateVertex(v); return post[v]; } //所有顶点的后序排序 public Iterable<Integer> post() { return postorder; } //所有顶点的前序排序 public Iterable<Integer> pre() { return preorder; } //所有顶点的逆后序排序 public Iterable<Integer> reversePost() { Stack<Integer> reverse = new Stack<Integer>(); for (int v : postorder) reverse.push(v); return reverse; } // check that pre() and post() are consistent with pre(v) and post(v) private boolean check() { // check that post(v) is consistent with post() int r = 0; for (int v : post()) { if (post(v) != r) { StdOut.println("post(v) and post() inconsistent"); return false; } r++; } // check that pre(v) is consistent with pre() r = 0; for (int v : pre()) { if (pre(v) != r) { StdOut.println("pre(v) and pre() inconsistent"); return false; } r++; } return true; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = marked.length; if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); Digraph G = new Digraph(in); DepthFirstOrder dfs = new DepthFirstOrder(G); StdOut.println(" v pre post"); StdOut.println("--------------"); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { StdOut.printf("%4d %4d %4d\n", v, dfs.pre(v), dfs.post(v)); } StdOut.print("Preorder: "); for (int v : dfs.pre()) { StdOut.print(v + " "); } StdOut.println(); StdOut.print("Postorder: "); for (int v : dfs.post()) { StdOut.print(v + " "); } StdOut.println(); StdOut.print("Reverse postorder: "); for (int v : dfs.reversePost()) { StdOut.print(v + " "); } StdOut.println(); } }
5.拓扑排序
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.EdgeWeightedDigraph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.SymbolDigraph; public class Topological { private Iterable<Integer> order; // topological order private int[] rank; // rank[v] = rank of vertex v in order public Topological(Digraph G) { DirectedCycle finder = new DirectedCycle(G); if (!finder.hasCycle()) { DepthFirstOrder dfs = new DepthFirstOrder(G); order = dfs.reversePost(); rank = new int[G.V()]; int i = 0; for (int v : order) rank[v] = i++; } } public Topological(EdgeWeightedDigraph G) { EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle finder = new EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle(G); if (!finder.hasCycle()) { DepthFirstOrder dfs = new DepthFirstOrder(G); order = dfs.reversePost(); } } //拓扑有序的所有顶点 public Iterable<Integer> order() { return order; } public boolean hasOrder() { return order != null; } @Deprecated public boolean isDAG() { return hasOrder(); } public int rank(int v) { validateVertex(v); if (hasOrder()) return rank[v]; else return -1; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = rank.length; if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } public static void main(String[] args) { String filename = args[0]; String delimiter = args[1]; SymbolDigraph sg = new SymbolDigraph(filename, delimiter); Topological topological = new Topological(sg.digraph()); for (int v : topological.order()) { StdOut.println(sg.nameOf(v)); } } }
三.加权无向图
1.加权边数据结构
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> { private final int v; private final int w; private final double weight; public Edge(int v, int w, double weight) { if (v < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a nonnegative integer"); if (w < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex index must be a nonnegative integer"); if (Double.isNaN(weight)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Weight is NaN"); this.v = v; this.w = w; this.weight = weight; } //边的权重 public double weight() { return weight; } //边两边的顶点之一 public int either() { return v; } //另一个顶点 public int other(int vertex) { if (vertex == v) return w; else if (vertex == w) return v; else throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal endpoint"); } @Override public int compareTo(Edge that) { return Double.compare(this.weight, that.weight); } public String toString() { return String.format("%d-%d %.5f", v, w, weight); } public static void main(String[] args) { Edge e = new Edge(12, 34, 5.67); StdOut.println(e); } }
2.加权无向图数据结构
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class EdgeWeightedGraph { private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator"); private final int V; private int E; private Bag<Edge>[] adj; public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V) { if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices must be nonnegative"); this.V = V; this.E = 0; adj = (Bag<Edge>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { adj[v] = new Bag<Edge>(); } } public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V, int E) { this(V); if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative"); for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int v = StdRandom.uniform(V); int w = StdRandom.uniform(V); double weight = Math.round(100 * StdRandom.uniform()) / 100.0; Edge e = new Edge(v, w, weight); addEdge(e); } } public EdgeWeightedGraph(In in) { if (in == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null"); try { V = in.readInt(); adj = (Bag<Edge>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { adj[v] = new Bag<Edge>(); } int E = in.readInt(); if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative"); for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int v = in.readInt(); int w = in.readInt(); validateVertex(v); validateVertex(w); double weight = in.readDouble(); Edge e = new Edge(v, w, weight); addEdge(e); } } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in EdgeWeightedGraph constructor", e); } } public EdgeWeightedGraph(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { this(G.V()); this.E = G.E(); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { // reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original Stack<Edge> reverse = new Stack<Edge>(); for (Edge e : G.adj[v]) { reverse.push(e); } for (Edge e : reverse) { adj[v].add(e); } } } //图的顶点数 public int V() { return V; } //图的边数 public int E() { return E; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } //向图中添加一条边 public void addEdge(Edge e) { int v = e.either(); int w = e.other(v); validateVertex(v); validateVertex(w); adj[v].add(e); adj[w].add(e); E++; } //和v相关联的所有边 public Iterable<Edge> adj(int v) { validateVertex(v); return adj[v]; } public int degree(int v) { validateVertex(v); return adj[v].size(); } //图的所有边 public Iterable<Edge> edges() { Bag<Edge> list = new Bag<Edge>(); for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { int selfLoops = 0; for (Edge e : adj(v)) { if (e.other(v) > v) { list.add(e); } // add only one copy of each self loop (self loops will be consecutive) else if (e.other(v) == v) { if (selfLoops % 2 == 0) list.add(e); selfLoops++; } } } return list; } public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); s.append(V + " " + E + NEWLINE); for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { s.append(v + ": "); for (Edge e : adj[v]) { s.append(e + " "); } s.append(NEWLINE); } return s.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in); StdOut.println(G); } }
3.最小生成树的Prim算法的延时实现
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*; public class LazyPrimMST { private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12; private double weight; // total weight of MST private Queue<Edge> mst; // edges in the MST private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = true iff v on tree private MinPQ<Edge> pq; // edges with one endpoint in tree public LazyPrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { mst = new Queue<Edge>(); pq = new MinPQ<Edge>(); marked = new boolean[G.V()]; for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) // run Prim from all vertices to if (!marked[v]) prim(G, v); // get a minimum spanning forest // check optimality conditions assert check(G); } // run Prim's algorithm private void prim(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int s) { scan(G, s); while (!pq.isEmpty()) { // better to stop when mst has V-1 edges Edge e = pq.delMin(); // smallest edge on pq int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v); // two endpoints assert marked[v] || marked[w]; if (marked[v] && marked[w]) continue; // lazy, both v and w already scanned mst.enqueue(e); // add e to MST weight += e.weight(); if (!marked[v]) scan(G, v); // v becomes part of tree if (!marked[w]) scan(G, w); // w becomes part of tree } } // add all edges e incident to v onto pq if the other endpoint has not yet been scanned private void scan(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v) { assert !marked[v]; marked[v] = true; for (Edge e : G.adj(v)) if (!marked[e.other(v)]) pq.insert(e); } public Iterable<Edge> edges() { return mst; } public double weight() { return weight; } // check optimality conditions (takes time proportional to E V lg* V) private boolean check(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { // check weight double totalWeight = 0.0; for (Edge e : edges()) { totalWeight += e.weight(); } if (Math.abs(totalWeight - weight()) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) { System.err.printf("Weight of edges does not equal weight(): %f vs. %f\n", totalWeight, weight()); return false; } // check that it is acyclic UF uf = new UF(G.V()); for (Edge e : edges()) { int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v); if (uf.find(v) == uf.find(w)) { System.err.println("Not a forest"); return false; } uf.union(v, w); } // check that it is a spanning forest for (Edge e : G.edges()) { int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v); if (uf.find(v) != uf.find(w)) { System.err.println("Not a spanning forest"); return false; } } // check that it is a minimal spanning forest (cut optimality conditions) for (Edge e : edges()) { // all edges in MST except e uf = new UF(G.V()); for (Edge f : mst) { int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x); if (f != e) uf.union(x, y); } // check that e is min weight edge in crossing cut for (Edge f : G.edges()) { int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x); if (uf.find(x) != uf.find(y)) { if (f.weight() < e.weight()) { System.err.println("Edge " + f + " violates cut optimality conditions"); return false; } } } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in); LazyPrimMST mst = new LazyPrimMST(G); for (Edge e : mst.edges()) { StdOut.println(e); } StdOut.printf("%.5f\n", mst.weight()); } }
4.最小生成树的Prim算法(即时版本)
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*; public class PrimMST { private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12; private Edge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = shortest edge from tree vertex to non-tree vertex private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = weight of shortest such edge private boolean[] marked; // marked[v] = true if v on tree, false otherwise private IndexMinPQ<Double> pq; public PrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { edgeTo = new Edge[G.V()]; distTo = new double[G.V()]; marked = new boolean[G.V()]; pq = new IndexMinPQ<Double>(G.V()); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) // run from each vertex to find if (!marked[v]) prim(G, v); // minimum spanning forest // check optimality conditions assert check(G); } // run Prim's algorithm in graph G, starting from vertex s private void prim(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int s) { distTo[s] = 0.0; pq.insert(s, distTo[s]); while (!pq.isEmpty()) { int v = pq.delMin(); scan(G, v); } } // scan vertex v private void scan(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v) { marked[v] = true; for (Edge e : G.adj(v)) { int w = e.other(v); if (marked[w]) continue; // v-w is obsolete edge if (e.weight() < distTo[w]) { distTo[w] = e.weight(); edgeTo[w] = e; if (pq.contains(w)) pq.decreaseKey(w, distTo[w]); else pq.insert(w, distTo[w]); } } } public Iterable<Edge> edges() { Queue<Edge> mst = new Queue<Edge>(); for (int v = 0; v < edgeTo.length; v++) { Edge e = edgeTo[v]; if (e != null) { mst.enqueue(e); } } return mst; } public double weight() { double weight = 0.0; for (Edge e : edges()) weight += e.weight(); return weight; } // check optimality conditions (takes time proportional to E V lg* V) private boolean check(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { // check weight double totalWeight = 0.0; for (Edge e : edges()) { totalWeight += e.weight(); } if (Math.abs(totalWeight - weight()) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) { System.err.printf("Weight of edges does not equal weight(): %f vs. %f\n", totalWeight, weight()); return false; } // check that it is acyclic UF uf = new UF(G.V()); for (Edge e : edges()) { int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v); if (uf.find(v) == uf.find(w)) { System.err.println("Not a forest"); return false; } uf.union(v, w); } // check that it is a spanning forest for (Edge e : G.edges()) { int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v); if (uf.find(v) != uf.find(w)) { System.err.println("Not a spanning forest"); return false; } } // check that it is a minimal spanning forest (cut optimality conditions) for (Edge e : edges()) { // all edges in MST except e uf = new UF(G.V()); for (Edge f : edges()) { int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x); if (f != e) uf.union(x, y); } // check that e is min weight edge in crossing cut for (Edge f : G.edges()) { int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x); if (uf.find(x) != uf.find(y)) { if (f.weight() < e.weight()) { System.err.println("Edge " + f + " violates cut optimality conditions"); return false; } } } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in); PrimMST mst = new PrimMST(G); for (Edge e : mst.edges()) { StdOut.println(e); } StdOut.printf("%.5f\n", mst.weight()); } }
5.最小生成树的Kruskal算法
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*; public class KruskalMST { private static final double FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON = 1E-12; private double weight; // weight of MST private Queue<Edge> mst = new Queue<Edge>(); // edges in MST public KruskalMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { // more efficient to build heap by passing array of edges MinPQ<Edge> pq = new MinPQ<Edge>(); for (Edge e : G.edges()) { pq.insert(e); } // run greedy algorithm UF uf = new UF(G.V()); while (!pq.isEmpty() && mst.size() < G.V() - 1) { Edge e = pq.delMin(); int v = e.either(); int w = e.other(v); if (uf.find(v) != uf.find(w)) { // v-w does not create a cycle uf.union(v, w); // merge v and w components mst.enqueue(e); // add edge e to mst weight += e.weight(); } } // check optimality conditions assert check(G); } public Iterable<Edge> edges() { return mst; } public double weight() { return weight; } // check optimality conditions (takes time proportional to E V lg* V) private boolean check(EdgeWeightedGraph G) { // check total weight double total = 0.0; for (Edge e : edges()) { total += e.weight(); } if (Math.abs(total - weight()) > FLOATING_POINT_EPSILON) { System.err.printf("Weight of edges does not equal weight(): %f vs. %f\n", total, weight()); return false; } // check that it is acyclic UF uf = new UF(G.V()); for (Edge e : edges()) { int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v); if (uf.find(v) == uf.find(w)) { System.err.println("Not a forest"); return false; } uf.union(v, w); } // check that it is a spanning forest for (Edge e : G.edges()) { int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v); if (uf.find(v) != uf.find(w)) { System.err.println("Not a spanning forest"); return false; } } // check that it is a minimal spanning forest (cut optimality conditions) for (Edge e : edges()) { // all edges in MST except e uf = new UF(G.V()); for (Edge f : mst) { int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x); if (f != e) uf.union(x, y); } // check that e is min weight edge in crossing cut for (Edge f : G.edges()) { int x = f.either(), y = f.other(x); if (uf.find(x) != uf.find(y)) { if (f.weight() < e.weight()) { System.err.println("Edge " + f + " violates cut optimality conditions"); return false; } } } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); EdgeWeightedGraph G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in); KruskalMST mst = new KruskalMST(G); for (Edge e : mst.edges()) { StdOut.println(e); } StdOut.printf("%.5f\n", mst.weight()); } }
四.加权有向图
1.加权有向边的数据结构
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class DirectedEdge { private final int v; private final int w; private final double weight; public DirectedEdge(int v, int w, double weight) { if (v < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vertex names must be nonnegative integers"); if (w < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vertex names must be nonnegative integers"); if (Double.isNaN(weight)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Weight is NaN"); this.v = v; this.w = w; this.weight = weight; } public int from() { return v; } public int to() { return w; } public double weight() { return weight; } public String toString() { return v + "->" + w + " " + String.format("%5.2f", weight); } public static void main(String[] args) { DirectedEdge e = new DirectedEdge(12, 34, 5.67); StdOut.println(e); } }
2.加权有向图的数据结构
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class EdgeWeightedDigraph { private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator"); private final int V; // number of vertices in this digraph private int E; // number of edges in this digraph private Bag<DirectedEdge>[] adj; // adj[v] = adjacency list for vertex v private int[] indegree; // indegree[v] = indegree of vertex v public EdgeWeightedDigraph(int V) { if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative"); this.V = V; this.E = 0; this.indegree = new int[V]; adj = (Bag<DirectedEdge>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) adj[v] = new Bag<DirectedEdge>(); } public EdgeWeightedDigraph(int V, int E) { this(V); if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges in a Digraph must be nonnegative"); for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int v = StdRandom.uniform(V); int w = StdRandom.uniform(V); double weight = 0.01 * StdRandom.uniform(100); DirectedEdge e = new DirectedEdge(v, w, weight); addEdge(e); } } public EdgeWeightedDigraph(In in) { if (in == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null"); try { this.V = in.readInt(); if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative"); indegree = new int[V]; adj = (Bag<DirectedEdge>[]) new Bag[V]; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { adj[v] = new Bag<DirectedEdge>(); } int E = in.readInt(); if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative"); for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int v = in.readInt(); int w = in.readInt(); validateVertex(v); validateVertex(w); double weight = in.readDouble(); addEdge(new DirectedEdge(v, w, weight)); } } catch (NoSuchElementException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in EdgeWeightedDigraph constructor", e); } } public EdgeWeightedDigraph(EdgeWeightedDigraph G) { this(G.V()); this.E = G.E(); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) this.indegree[v] = G.indegree(v); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { // reverse so that adjacency list is in same order as original Stack<DirectedEdge> reverse = new Stack<DirectedEdge>(); for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj[v]) { reverse.push(e); } for (DirectedEdge e : reverse) { adj[v].add(e); } } } public int V() { return V; } public int E() { return E; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } public void addEdge(DirectedEdge e) { int v = e.from(); int w = e.to(); validateVertex(v); validateVertex(w); adj[v].add(e); indegree[w]++; E++; } public Iterable<DirectedEdge> adj(int v) { validateVertex(v); return adj[v]; } public int outdegree(int v) { validateVertex(v); return adj[v].size(); } public int indegree(int v) { validateVertex(v); return indegree[v]; } public Iterable<DirectedEdge> edges() { Bag<DirectedEdge> list = new Bag<DirectedEdge>(); for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { for (DirectedEdge e : adj(v)) { list.add(e); } } return list; } public String toString() { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); s.append(V + " " + E + NEWLINE); for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) { s.append(v + ": "); for (DirectedEdge e : adj[v]) { s.append(e + " "); } s.append(NEWLINE); } return s.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in); StdOut.println(G); } }
3.最短路径的Dijkstra算法
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.IndexMinPQ; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Stack; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class DijkstraSP { private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = distance of shortest s->v path private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on shortest s->v path private IndexMinPQ<Double> pq; // priority queue of vertices public DijkstraSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) { for (DirectedEdge e : G.edges()) { if (e.weight() < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("edge " + e + " has negative weight"); } distTo = new double[G.V()]; edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.V()]; validateVertex(s); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; distTo[s] = 0.0; // relax vertices in order of distance from s pq = new IndexMinPQ<Double>(G.V()); pq.insert(s, distTo[s]); while (!pq.isEmpty()) { int v = pq.delMin(); for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) relax(e); } // check optimality conditions assert check(G, s); } // relax edge e and update pq if changed private void relax(DirectedEdge e) { int v = e.from(), w = e.to(); if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.weight()) { distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.weight(); edgeTo[w] = e; if (pq.contains(w)) pq.decreaseKey(w, distTo[w]); else pq.insert(w, distTo[w]); } } public double distTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); return distTo[v]; } public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); return distTo[v] < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; } public Iterable<DirectedEdge> pathTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<DirectedEdge> path = new Stack<DirectedEdge>(); for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.from()]) { path.push(e); } return path; } // check optimality conditions: // (i) for all edges e: distTo[e.to()] <= distTo[e.from()] + e.weight() // (ii) for all edge e on the SPT: distTo[e.to()] == distTo[e.from()] + e.weight() private boolean check(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) { // check that edge weights are nonnegative for (DirectedEdge e : G.edges()) { if (e.weight() < 0) { System.err.println("negative edge weight detected"); return false; } } // check that distTo[v] and edgeTo[v] are consistent if (distTo[s] != 0.0 || edgeTo[s] != null) { System.err.println("distTo[s] and edgeTo[s] inconsistent"); return false; } for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { if (v == s) continue; if (edgeTo[v] == null && distTo[v] != Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY) { System.err.println("distTo[] and edgeTo[] inconsistent"); return false; } } // check that all edges e = v->w satisfy distTo[w] <= distTo[v] + e.weight() for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) { int w = e.to(); if (distTo[v] + e.weight() < distTo[w]) { System.err.println("edge " + e + " not relaxed"); return false; } } } // check that all edges e = v->w on SPT satisfy distTo[w] == distTo[v] + e.weight() for (int w = 0; w < G.V(); w++) { if (edgeTo[w] == null) continue; DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[w]; int v = e.from(); if (w != e.to()) return false; if (distTo[v] + e.weight() != distTo[w]) { System.err.println("edge " + e + " on shortest path not tight"); return false; } } return true; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = distTo.length; if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in); int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); // compute shortest paths DijkstraSP sp = new DijkstraSP(G, s); for (int t = 0; t < G.V(); t++) { if (sp.hasPathTo(t)) { StdOut.printf("%d to %d (%.2f) ", s, t, sp.distTo(t)); for (DirectedEdge e : sp.pathTo(t)) { StdOut.print(e + " "); } StdOut.println(); } else { StdOut.printf("%d to %d no path\n", s, t); } } } }
4.无环加权有向图的最短路径算法
package graph; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Stack; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; public class AcyclicSP { private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = distance of shortest s->v path private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = last edge on shortest s->v path public AcyclicSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) { distTo = new double[G.V()]; edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.V()]; validateVertex(s); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; distTo[s] = 0.0; // visit vertices in topological order Topological topological = new Topological(G); if (!topological.hasOrder()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Digraph is not acyclic."); for (int v : topological.order()) { for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) relax(e); } } // relax edge e private void relax(DirectedEdge e) { int v = e.from(), w = e.to(); if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.weight()) { distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.weight(); edgeTo[w] = e; } } public double distTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); return distTo[v]; } public boolean hasPathTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); return distTo[v] < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; } public Iterable<DirectedEdge> pathTo(int v) { validateVertex(v); if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null; Stack<DirectedEdge> path = new Stack<DirectedEdge>(); for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.from()]) { path.push(e); } return path; } // throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V} private void validateVertex(int v) { int V = distTo.length; if (v < 0 || v >= V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1)); } public static void main(String[] args) { In in = new In(args[0]); int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in); // find shortest path from s to each other vertex in DAG AcyclicSP sp = new AcyclicSP(G, s); for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) { if (sp.hasPathTo(v)) { StdOut.printf("%d to %d (%.2f) ", s, v, sp.distTo(v)); for (DirectedEdge e : sp.pathTo(v)) { StdOut.print(e + " "); } StdOut.println(); } else { StdOut.printf("%d to %d no path\n", s, v); } } } }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架