Spring in action读书笔记(二) Spring Profile注解应用 ----- 根据不同环境(如开发环境、测试环境)装配bean
依赖的jar包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
1、 profile设置
像某些配置,如数据库连接,可能需要根据开发环境和生产环境选择对应的配置文件,这时可使
用Spring profile功能:根据不同的环境加载不同的配置文件,创建对应的bean。
这个定义一个环境类MyEnvironment.java
package profile; public class MyEnvironment { private String name; public MyEnvironment(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "MyEnvironment{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
创建类DevelopmentConfig.java, 配置开发环境, profile值为dev
package profile; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; @Configuration @Profile("dev") public class DevelopmentConfig { @Bean public MyEnvironment getEnvironment() { return new MyEnvironment("dev"); } }
创建ProductConfig.java, 配置生产环境, profile值为prod
package profile; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; @Configuration @Profile("prod") public class ProductConfig { @Bean public MyEnvironment getEnvironment() { return new MyEnvironment("prod"); } }
Spring 3.1 版本及以前只能在类级别使用@Profile注解,从Spring 3.2开始, 可以在方法级别上使用@Profile注解,@Bean注解一同使用,
这样可以将两个bean的声明放到同一个配置类中
package profile; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile; @Configuration public class MyEnvironmentConfig { @Bean @Profile("dev") public MyEnvironment getEnvironment1() { return new MyEnvironment("dev"); } @Bean @Profile("prod") public MyEnvironment getEnvironment2() { return new MyEnvironment("prod"); } }
2、 profile激活
Spring在确定那个profile处于激活状态时,需要依赖两个独立的属性: spring.profiles.active 和 spring.profiles.default, spring.profile.active优先级最高, spring.profiles.default次之
有多重方式设置这两个属性:
(1)作为DispatcherServlet的初始化参数
(2) 作为Web应用的上下文参数
在web.xml中设置上下文默认的profile
<context-param>
<param-name>spring.profiles.default</param-name>
<param-value>dev</param-value>
</context-param>
(3) 作为JNDI条目
(4) 作为环境变量;
(5) 作为JVM的系统属性
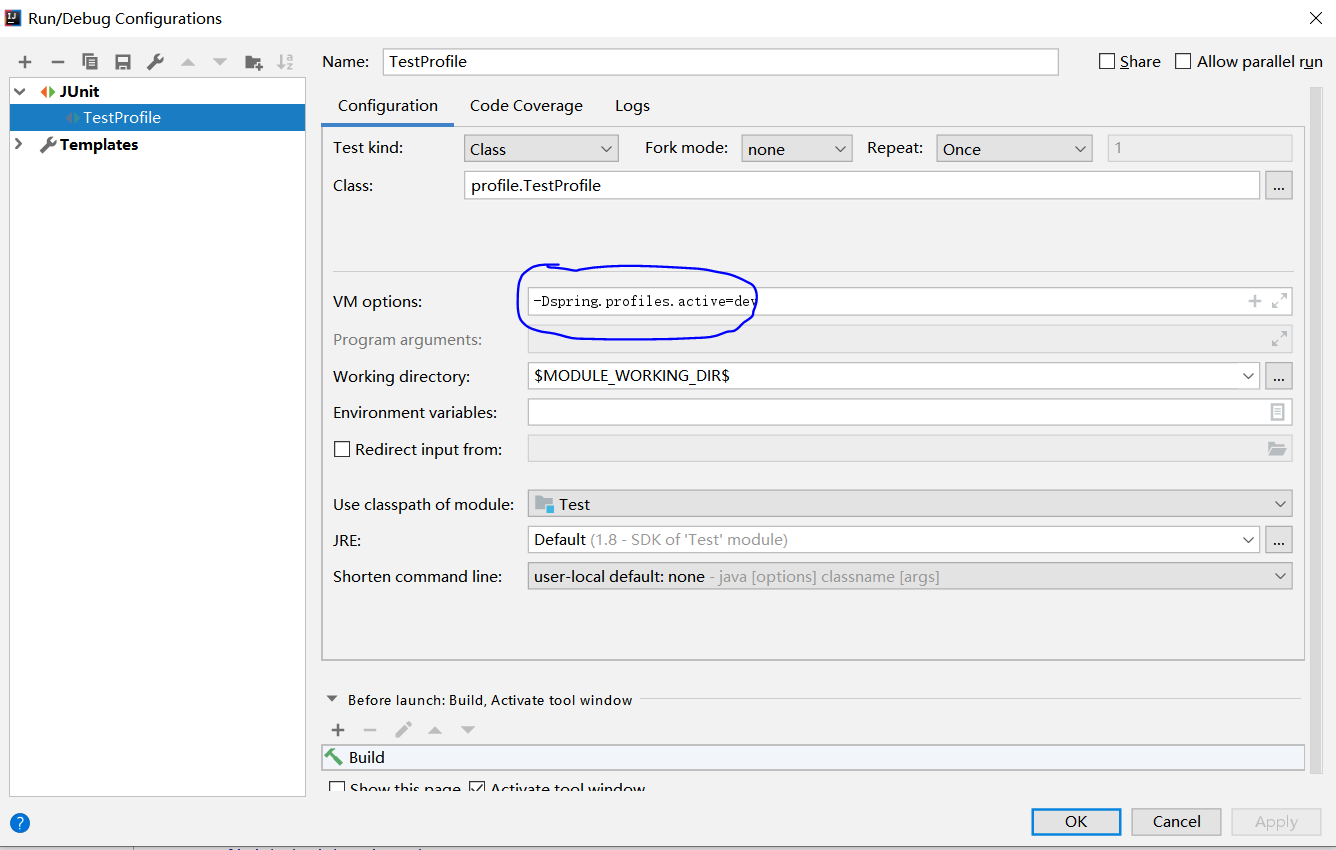
(6) 在测试类中使用@ActivieProfiles注解设置
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {DevelopmentConfig.class, ProductConfig.class}) 可以换成
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {MyEnvironmentConfig.class})
package profile; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = {DevelopmentConfig.class, ProductConfig.class}) @ActiveProfiles("prod") public class TestProfile { @Autowired private MyEnvironment myEnvironment; @Test public void test() { System.out.println(myEnvironment); } }

