NetworkX系列教程(8)-Drawing Graph
如果只是简单使用nx.draw,是无法定制出自己需要的graph,并且这样的graph内的点坐标的不定的,运行一次变一次,实际中一般是要求固定的位置,这就需要到布局的概念了.详细的画图信息可以看这里,代码中的关键部分使用了英文进行注释,不在另外注释.
目录:
注意:如果代码出现找不库,请返回第一个教程,把库文件导入.
9.Drawing Graph
9.1使用Matplotlib
- #定义graph
- nodes=[0,1,2,3,4,5,'a','b','c']
- edges=[(0,1),(0,5),(1,2),(1,4),(2,1),(2,4),('a','b'),('b','c'),('c','a')]
- G=nx.Graph()
- G.add_nodes_from(nodes)
- G.add_edges_from(edges)
- #使用spring_layout布局
- pos=nx.spring_layout(G)
- plt.subplots(2,4,figsize=(18,6))
- plt.subplot(241)
- plt.title('spring_layout')
- nx.draw(G, with_labels=True, font_weight='bold') #Draw the graph G with Matplotlib.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(242)
- plt.title('draw_networkx')
- nx.draw_networkx(G) #Draw the graph G using Matplotlib.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(243)
- plt.title('draw_networkx_nodes')
- nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G,pos) #Draw the nodes of the graph G.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(244)
- plt.title('draw_networkx_edges')
- nx.draw_networkx_edges(G,pos) #Draw the edges of the graph G.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(245)
- plt.title('draw_networkx_labels')
- nx.draw_networkx_labels(G,pos) #Draw node labels on the graph G.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(246)
- plt.title('draw_networkx_edge_labels')
- nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G,pos) #Draw edge labels.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(247)
- plt.title('draw_circular')
- nx.draw_circular(G,) #Draw the graph G with a circular layout.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(248)
- plt.title('draw_kamada_kawai')
- nx.draw_kamada_kawai(G) #Draw the graph G with a Kamada-Kawai force-directed layout.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.show()
- plt.close()
- plt.subplots(1,4,figsize=(18,3))
- plt.subplot(141)
- plt.title('draw_random')
- nx.draw_random(G) #Draw the graph G with a random layout.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(142)
- plt.title('draw_spectral')
- nx.draw_spectral(G,) #Draw the graph G with a spectral layout.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(143)
- plt.title('draw_spring')
- nx.draw_spring(G) #Draw the graph G with a spring layout.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(144)
- plt.title('draw_shell')
- nx.draw_shell(G) #Draw networkx graph with shell layout.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.show()
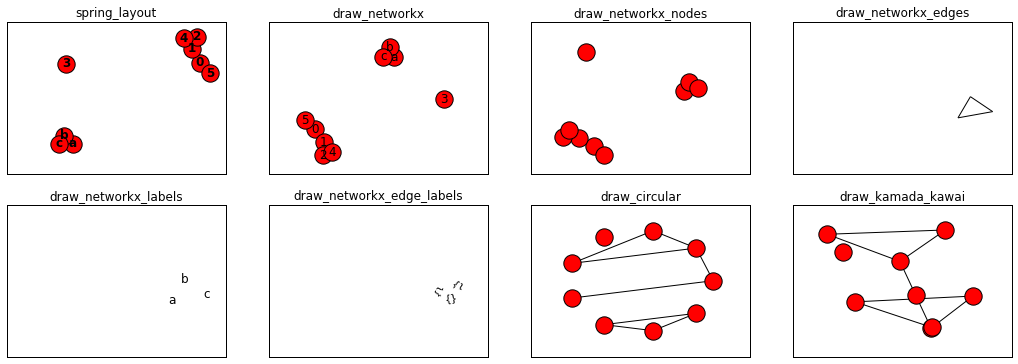
Matplotlib布局1
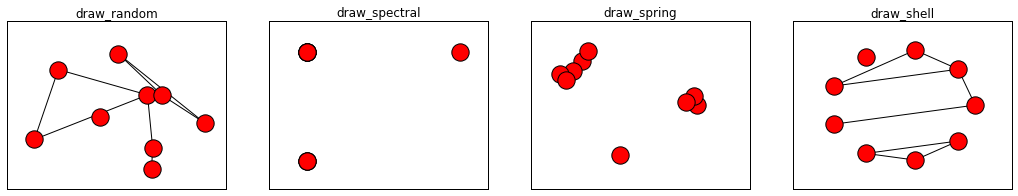
Matplotlib布局2
9.2使用Graphviz AGraph (dot)
有些同学不知道如何安装Graphviz,我在这里作一个说明:
1.linux是安装graphviz即可,我使用的命令是:
- sudo apt install graphviz
2.Windows我没用实践过,不过我查到Graphviz有官网,里面有windows安装包,地址看下:
http://www.graphviz.org/download/
- G.clear()
- from networkx.drawing.nx_pydot import write_dot,read_dot
- plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(15,5))
- K5 = nx.complete_graph(5)
- A = nx.nx_agraph.to_agraph(K5) #Return a pygraphviz graph from a NetworkX graph N.
- G1 = nx.nx_agraph.from_agraph(A) #Return a NetworkX Graph or DiGraph from a PyGraphviz graph.
- plt.subplot(131)
- plt.title('原图',fontproperties=myfont)
- nx.draw_random(G1) #Draw the graph G with a random layout.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- write_dot(G1, 'graph.test') #Write NetworkX graph G to Graphviz dot format on path.
- G2=read_dot('graph.test') #Return a NetworkX graph from a dot file on path.
- plt.subplot(132)
- plt.title('保存原图后并读取',fontproperties=myfont)
- nx.draw_random(G2) #Draw the graph G with a random layout.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- G3 = nx.petersen_graph()
- pos = nx.nx_agraph.graphviz_layout(G3) #Create node positions for G using Graphviz.
- plt.subplot(133)
- plt.title('graphviz_layout',fontproperties=myfont)
- nx.draw_random(G3) #Draw the graph G with a random layout.
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.show()
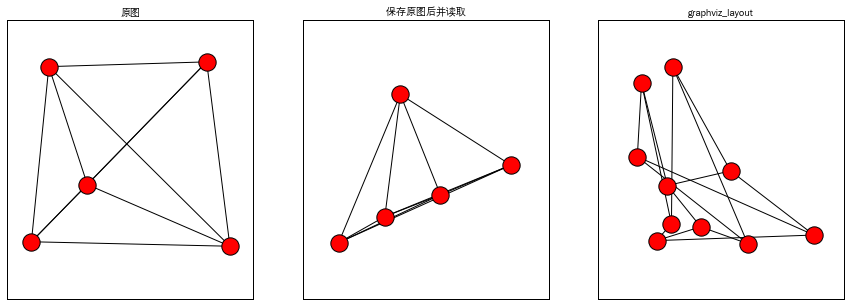
Graphviz画图
9.3图布局
- #定义graph
- nodes=[0,1,2,3,4,5,'a','b','c']
- edges=[(0,1),(0,5),(1,2),(1,4),(2,1),(2,4),('a','b'),('b','c'),('c','a')]
- G=nx.Graph()
- G.add_nodes_from(nodes)
- G.add_edges_from(edges)
- plt.subplots(2,3,figsize=(18,6))
- plt.subplot(231)
- plt.title('circular_layout')
- pos=nx.circular_layout(G) #Position nodes on a circle.
- nx.draw(G,pos, with_labels=True, font_weight='bold')
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(232)
- plt.title('kamada_kawai_layout')
- pos=nx.kamada_kawai_layout(G) #Position nodes using Kamada-Kawai path-length cost-function.
- nx.draw(G, pos,with_labels=True, font_weight='bold')
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(233)
- plt.title('random_layout')
- pos=nx.random_layout(G) #Position nodes uniformly at random in the unit square.
- nx.draw(G, pos,with_labels=True, font_weight='bold')
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(234)
- plt.title('shell_layout')
- pos=nx.shell_layout(G) #Position nodes in concentric circles.
- nx.draw(G, pos,with_labels=True, font_weight='bold')
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(235)
- plt.title('spring_layout')
- pos=nx.spring_layout(G)#Position nodes using Fruchterman-Reingold force-directed algorithm.
- nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True, font_weight='bold')
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.subplot(236)
- plt.title('spectral_layout')
- pos=nx.spectral_layout(G) #Position nodes using the eigenvectors of the graph Laplacian.
- nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True, font_weight='bold')
- plt.axis('on')
- plt.xticks([])
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.show()
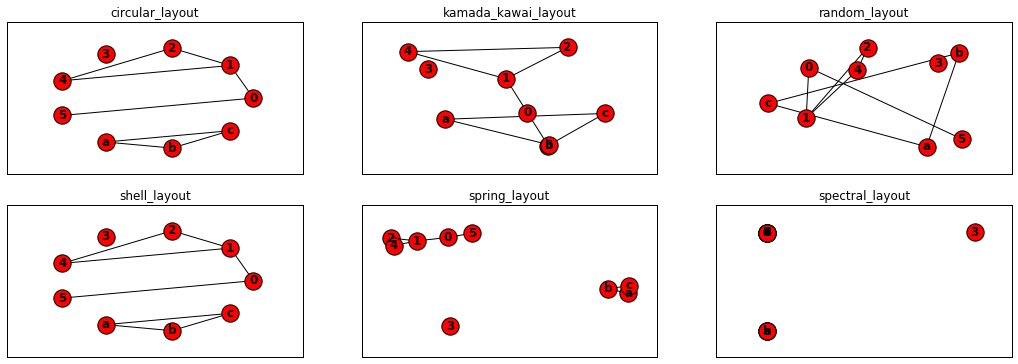
图布局
学技术之路太难,唯有坚持不懈!!!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号