nginx代理和负载均衡
目录
nginx代理
1.什么是代理
#代理一词往往并不陌生, 该服务我们常常用到如(代理理财、代理租房、代理收货等等),如下图所示

2.没有代理
#在没有代理模式的情况下,客户端和Nginx服务端,都是客户端直接请求服务端,服务端直接响应客户端。
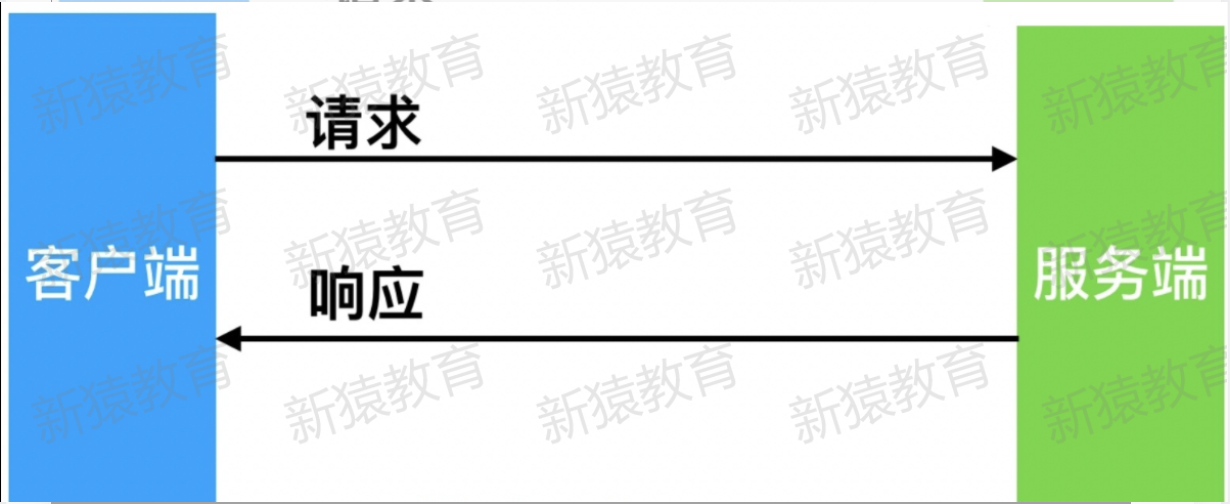
3.有代理
那么在互联网请求里面,为了安全客户端往往无法直接向服务端发起请求,就需要用到代理服务,来实现客户端和服务端通信,如下图所示

4.Nginx代理服务常见模式
#Nginx作为代理服务,按照应用场景模式进行总结,代理分为
1.正向代理
2.反向代理
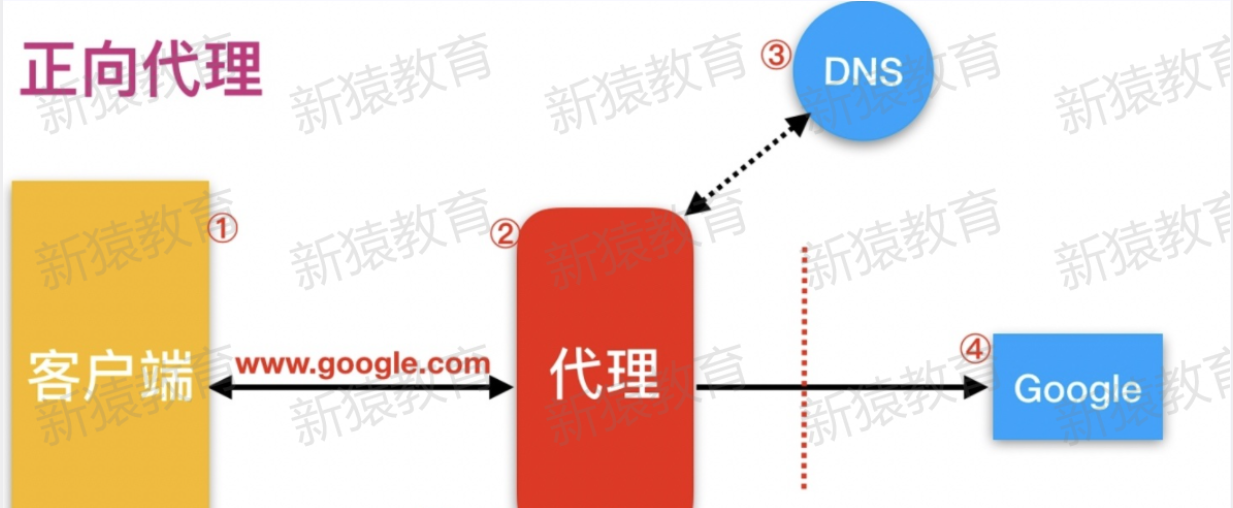
1)正向代理
#正向代理,(内部上网) 客户端 <—> 代理 -> 服务端
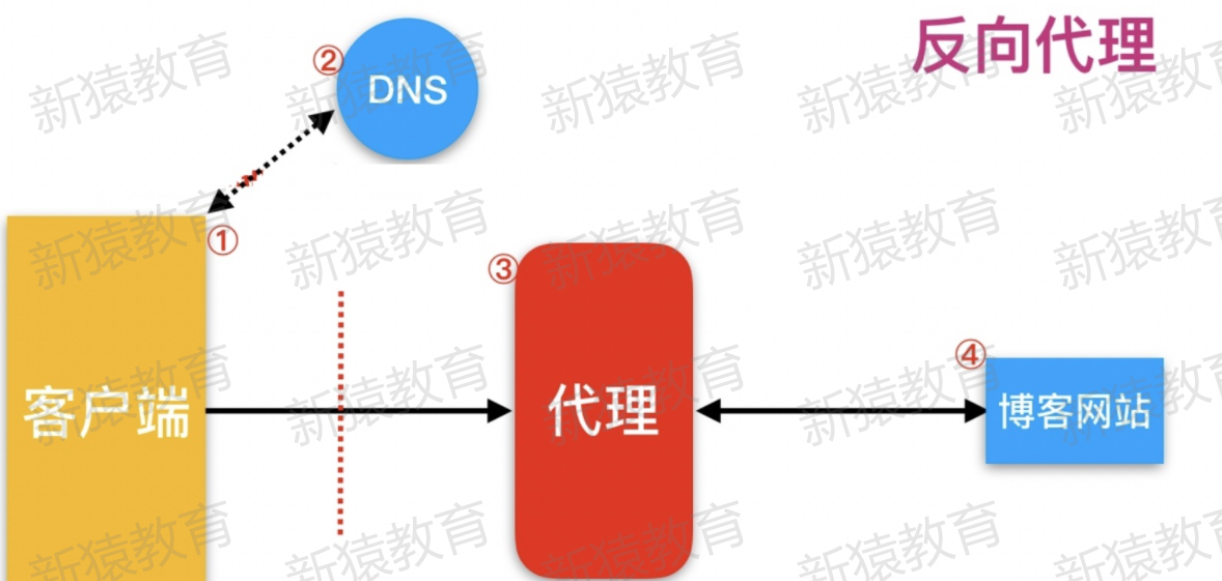
2)反向代理
#反向代理,用于公司集群架构中,客户端 -> 代理 <—> 服务端
3)正向代理与反向代理的区别
1.区别在于形式上服务的”对象”不一样
2.正向代理代理的对象是客户端,为客户端服务
3.反向代理代理的对象是服务端,为服务端服务
Nginx代理服务支持协议
1.支持的协议
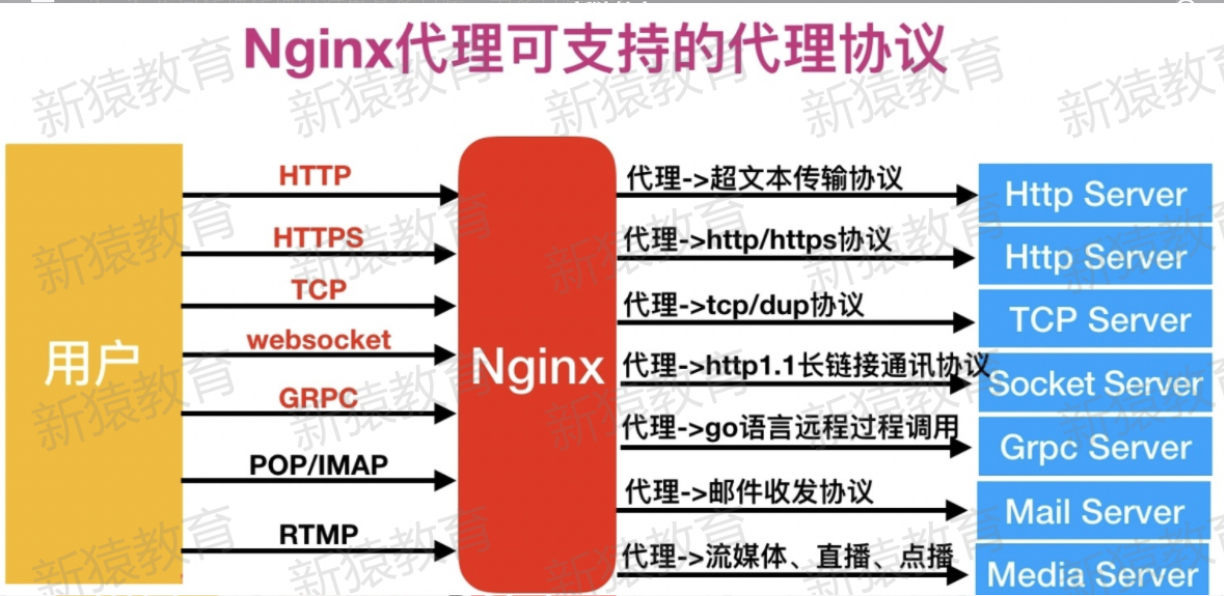
2.反向代理使用协议
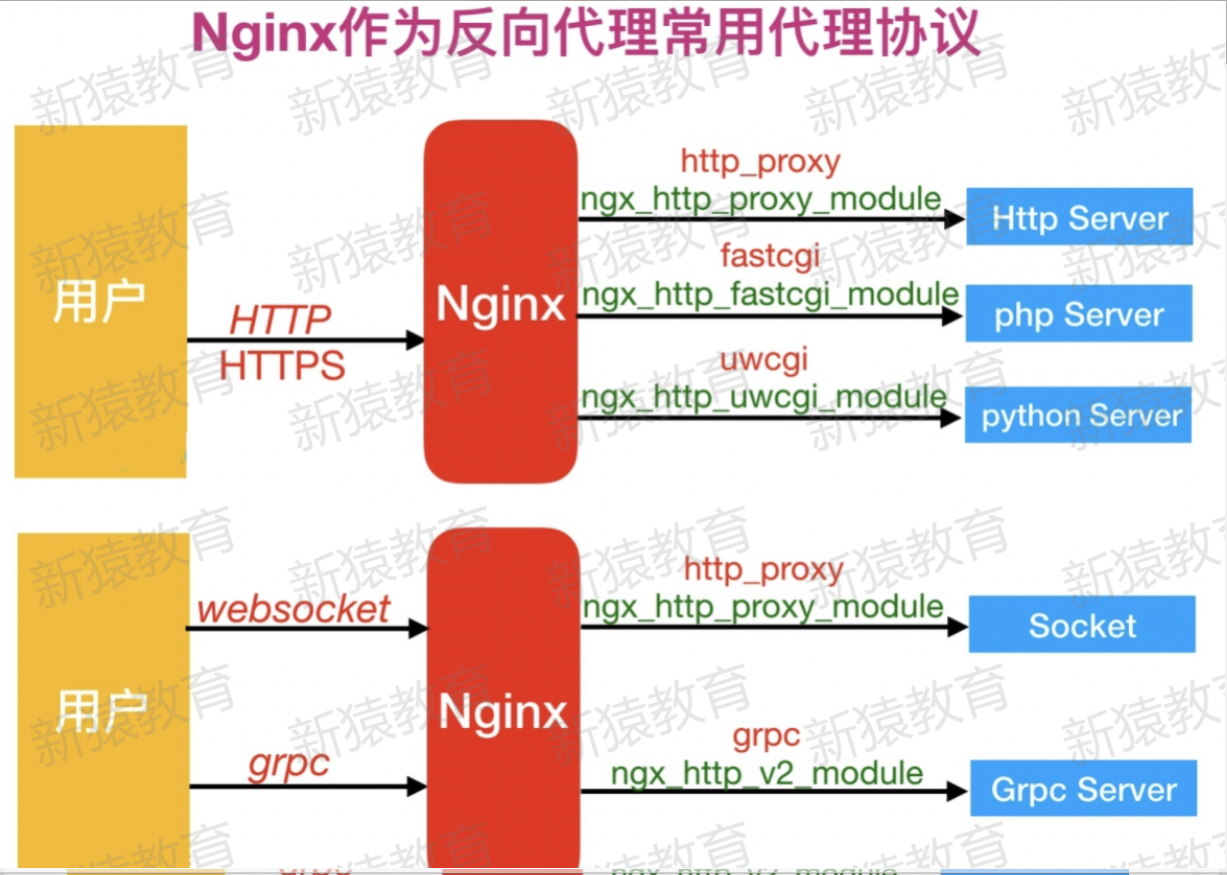
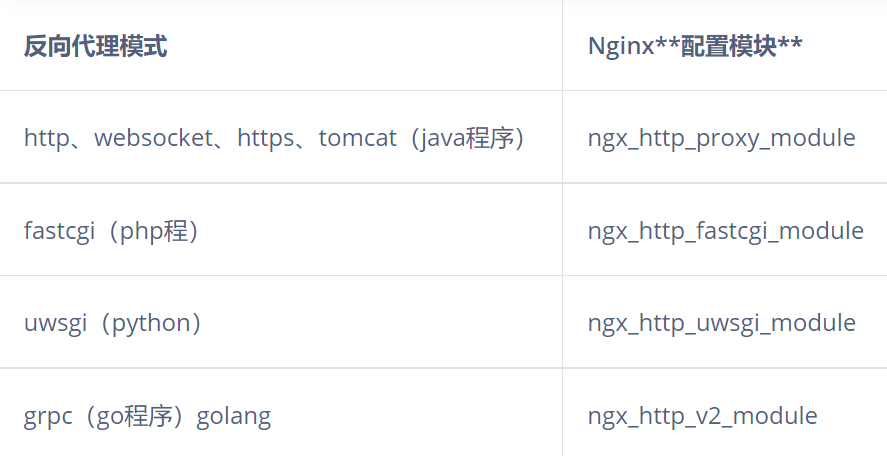
3.模块总结
#反向代理模式与Nginx代理模块总结如表格所示
nginx代理实践
1.环境准备
| 主机 | IP | 身份 |
| lb01 | 10.0.0.4 | 代理 |
| web01 | 172.16.1.7 | web服务端 |
2.代理语法
Syntax: proxy_pass URL;
Default: —
Context: location, if in location, limit_except
3.配置web01的nginx
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.proxy.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
root /code/proxy;
index index.html;
}
}
4.web01编写一个网站
[root@web01 ~]# mkdir /code/proxy
[root@web01 ~]# echo "web01 web01 web01 wbe01 ...." > /code/proxy/index.html
[root@web01 ~]# chown -R www.www /code/
5.访问测试
1.配置hosts
10.0.0.7 linux.proxy.com
2.重启
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
3.访问
linux.proxy.com
6.配置代理
1.安装nginx
2.配置nginx
3.创建用户
4.配置nginx代理
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.proxy.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://172.16.1.7:80;
}
}
7.重启代理nginx
[root@lb01 ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
8.访问页面测试
1.配置hosts
10.0.0.4 linux.proxy.com
2.访问测试
结果:访问的页面不是我们要的内容,返回了web端第一个配置文件的内容
#原因:代理请求web服务端时,没有使用域名,使用了IP,匹配时没有匹配到server_name,所以直接返回默认的第一个配置文件
9.配置代理携带域名访问web端
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.proxy.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://172.16.1.7:80;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
}
}
10.重启后再次访问
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
再次访问http://linux.proxy.com/,得到想要的内容
Nginx代理常用参数
1.添加发往后端服务器的请求头信息
Syntax: proxy_set_header field value;
Default: proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header Connection close;
Context: http, server, location
# 用户请求的时候HOST的值是linux.proxy.com, 那么代理服务会像后端传递请求的还是linux.proxy.com
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
# 将$remote_addr的值放进变量X-Real-IP中,$remote_addr的值为客户端的ip
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
# 客户端通过代理服务访问后端服务, 后端服务通过该变量会记录真实客户端地址
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
2.代理到后端的TCP连接、响应、返回等超时时间
#nginx代理与后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时)
Syntax: proxy_connect_timeout time;
Default: proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
Context: http, server, location
#nginx代理等待后端服务器的响应时间
Syntax: proxy_read_timeout time;
Default: proxy_read_timeout 60s;
Context: http, server, location
#后端服务器数据回传给nginx代理超时时间
Syntax: proxy_send_timeout time;
Default: proxy_send_timeout 60s;
Context: http, server, location
3.proxy_buffer代理缓冲区
#nignx会把后端返回的内容先放到缓冲区当中,然后再返回给客户端,边收边传, 不是全部接收完再传给客户端
Syntax: proxy_buffering on | off;
Default: proxy_buffering on;
Context: http, server, location
#设置nginx代理保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小
Syntax: proxy_buffer_size size;
Default: proxy_buffer_size 4k|8k;
Context: http, server, location
#proxy_buffers 缓冲区
Syntax: proxy_buffers number size;
Default: proxy_buffers 8 4k|8k;
Context: http, server, location
4.配置代理优化文件
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/proxy_params
proxy_set_header Host $http_host; #域名
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; #客户端的ip
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; # 客户端通过代理服务访问后端服务, 后端服务通过该变量会记录真实客户端地址
proxy_connect_timeout 10s; #nginx代理与后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时)
proxy_read_timeout 10s; #nginx代理等待后端服务器的响应时间
proxy_send_timeout 10s; #后端服务器数据回传给nginx代理超时时间
proxy_buffering on; #开启缓冲区(边收边传)
proxy_buffer_size 8k; #设置用户头信息的缓冲区大小
proxy_buffers 32 8k; #proxy_buffers 缓冲区
5.代理调用优化文件
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.proxy.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.proxy.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.0.0.7:80;
include proxy_params; # 调用上面proxy_params配置好的文件
}
}
负载均衡介绍
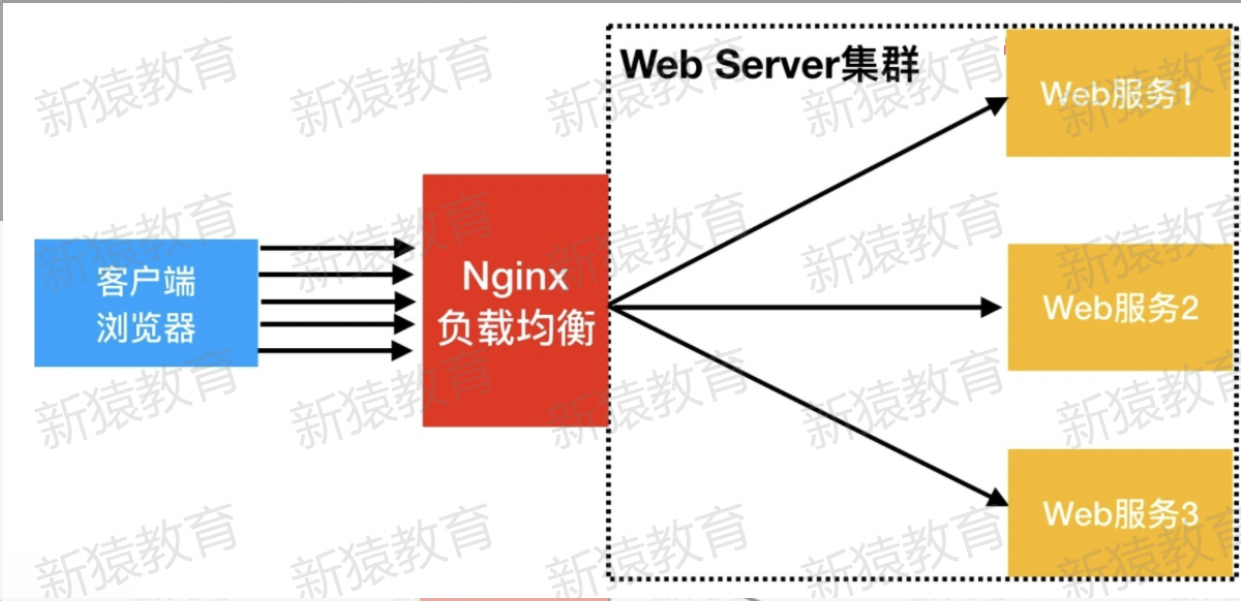
1.什么是负载均衡
将请求平均的分配给后端服务器
2.为什么要使用负载均衡
1. 当我们的Web服务器直接面向用户,往往要承载大量并发请求,单台服务器难以负荷,我使用多台Web服务器组成集群,前端使用Nginx负载均衡,将请求分散的打到我们的后端服务器集群中,实现负载的分发。那么会大大提升系统的吞吐率、请求性能、高容灾
2. 往往我们接触的最多的是SLB(Server Load Balance)负载均衡,实现最多的也是SLB、那么SLB它的调度节点和服务节点通常是在一个地域里面。那么它在这个小的逻辑地域里面决定了他对部分服务的实时性、响应性是非常好的。
3. 所以说当海量用户请求过来以后,它同样是请求调度节点,调度节点将用户的请求转发给后端对应的服务节点,服务节点处理完请求后在转发给调度节点,调度节点最后响应给用户节点。这样也能实现一个均衡的作用,那么Nginx则是一个典型的SLB
3.负载均衡的叫法
1.负载均衡
2.负载
3.LB
4.Load Balance
4.公有云中常见的负载均衡
1.SLB #阿里云产品
2.LB #青云产品
3.CLB #腾讯云产品
4.ULB #Ucloud产品
5.负载均衡软件
1.nginx
2.Haproxy
3.LVS
6.负载均衡类型
1.四层负载均衡
所谓四层负载均衡指的是OSI七层模型中的传输层,那么传输层Nginx已经能支持TCP/IP的控制,所以只需要对客户端的请求进行TCP/IP协议的包转发就可以实现负载均衡,那么它的好处是性能非常快、只需要底层进行应用处理,而不需要进行一些复杂的逻辑
2.七层负载均衡
七层负载均衡它是在应用层,那么它可以完成很多应用方面的协议请求,比如我们说的http应用的负载均衡,它可以实现http信息的改写、头信息的改写、安全应用规则控制、URL匹配规则控制、以及转发、rewrite等等的规则,所以在应用层的服务里面,我们可以做的内容就更多,那么Nginx则是一个典型的七层负载均衡SLB
3.四层和七层负载均衡的区别
四层负载均衡数据包在底层就进行了分发,而七层负载均衡数据包则是在最顶层进行分发、由此可以看出,七层负载均衡效率没有四负载均衡高。
但七层负载均衡更贴近于服务,如:http协议就是七层协议,我们可以用Nginx可以作会话保持,URL路径规则匹配、head头改写等等,这些是四层负载均衡无法实现的。
注意:四层负载均衡不识别域名,七层负载均衡识别域名
负载均衡实践
#1. Nginx要实现负载均衡需要用到proxy_pass代理模块配置
#2. Nginx负载均衡与Nginx代理不同地方在于,Nginx的一个location仅能代理一台服务器,而Nginx负载均衡则是将客户端请求代理转发至一组upstream虚拟服务池.
1.负载均衡模块
# ngx_http_upstream_module
#语法
Syntax: upstream name { ... }
Default: —
Context: http
#例子
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com weight=5;
server backend2.example.com:8080;
server backup1.example.com:8080 backup;
server backup2.example.com:8080 backup;
}
server {
... ...
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
2.环境准备
| 主机 | IP | 身份 |
| lb01 | 10.0.0.4,172.16.1.4 | 负载均衡 |
| web01 | 172.16.1.7 | web服务端 |
| web02 | 172.16.1.8 | web服务端 |
3.web01准备站点
1)配置nginx
[root@web01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.lb.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.lb.com;
charset utf8;
location / {
root /code/lb;
index index.html;
}
}
2)准备网站
[root@web01 ~]# mkdir /code/lb
[root@web01 ~]# echo "我是web0111111111111" > /code/lb/index.html
[root@web01 ~]# chown -R www.www /code/
3)配置hosts访问
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
10.0.0.7 linux.lb.com
访问
3.web01准备站点
1)配置nginx
[root@web02 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.lb.com.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.lb.com;
charset utf8;
location / {
root /code/lb;
index index.html;
}
}
2)准备网站
[root@web02 ~]# mkdir /code/lb
[root@web02 ~]# echo "我是web0222222222222" > /code/lb/index.html
[root@web02 ~]# chown -R www.www /code/
3)配置hosts访问
[root@web02 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
10.0.0.8 linux.lb.com
访问
4.配置负载均衡配置文件
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.lb.com.conf
upstream web_group {
server 172.16.1.7:80;
server 172.16.1.8;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.lb.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web_group;
include proxy_params;
}
}
5.准备代理优化文件
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/proxy_params
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_connect_timeout 10s;
proxy_read_timeout 10s;
proxy_send_timeout 10s;
proxy_buffering on;
proxy_buffer_size 8k;
proxy_buffers 8 8k;
6.重启访问测试
1.重启
[root@lb01 ~]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
2.配置hosts
10.0.0.4 linux.lb.com
负载均衡结合项目
1.配置wordpress负载均衡
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.wp.com.conf
upstream blog {
server 172.16.1.7;
server 172.16.1.8;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.wp.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://blog;
include proxy_params;
}
}
#重启
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
2.配置hosts查看网站
10.0.0.4 linux.wp.com
3.配置zh的负载均衡 # zh可以随意定义,server能调用就好
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.zh.com.conf
upstream zh {
server 172.16.1.7;
server 172.16.1.8;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.zh.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://zh;
include proxy_params;
}
}
4.负载均衡常见问题
1)问题
如果后端服务器出现问题,负载均衡仍然会将请求发送给相应机器
如果后台服务连接超时,Nginx是本身是有机制的,如果出现一个节点down掉的时候,Nginx会更据你具体负载均衡的设置,将请求转移到其他的节点上,但是,如果后台服务连接没有down掉,但是返回错误异常码了如:504、502、500,这个时候你需要加一个负载均衡的设置,如下:proxy_next_upstream http_500 | http_502 | http_503 | http_504 |http_404;意思是,当其中一台返回错误码404,500...等错误时,可以分配到下一台服务器程序继续处理,提高平台访问成功率。
2)解决问题的模块
Syntax: proxy_next_upstream error | timeout | invalid_header | http_500 | http_502 | http_503 | http_504 | http_403 | http_404 | http_429 | non_idempotent | off ...;
Default: proxy_next_upstream error timeout;
Context: http, server, location
3)配置
[root@lb01 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/linux.wp.com.conf
upstream blog {
server 172.16.1.7;
server 172.16.1.8;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.wp.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://blog;
include proxy_params;
#可以配置,可以写到include
proxy_next_upstream http_500 | http_502 | http_503 | http_504 | http_403 | http_404;
}
}
#重启
[root@lb01 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
负载均衡调度算法
| 调度算法 | 概述 |
| 轮询 | 按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器(默认) |
| weight | 加权轮询,weight值越大,分配到的访问几率越高 |
| ip_hash | 每个请求按访问IP的hash结果分配,这样来自同一IP的固定访问一个后端服务器|
| url_hash | 按照访问URL的hash结果来分配请求,是每个URL定向到同一个后端服务器 |
| least_conn | 最少链接数,哪个机器链接数少就分发 |
1.轮询的配置方法
upstream blog {
server 172.16.1.7;
server 172.16.1.8;
}
2.加权轮询配置 (weiht可以单独加一台机器)
upstream blog {
server 172.16.1.7 weight=1;
server 172.16.1.8 weight=2;
}
3.ip_bash配置方法
upstream web_group {
server 172.16.1.7:80;
server 172.16.1.8;
ip_hash;
}
#一般用来做会话保持
负载均衡后端状态
| 状态 | 概述 |
| down | 当前的server暂时不参与负载均衡 |
| backup | 预留的备份服务器 |
| max_fails | 允许请求失败的次数 |
| fail_timeout | 经过max_fails失败后, 服务暂停时间 |
| max_conns | 限制最大的接收连接数 |
1.down状态配置 (当前的server暂时不参与负载均衡 )
upstream blog {
#一般情况下,维护场景使用
server 172.16.1.7 down;
server 172.16.1.8;
}
2.backup状态配置(预留的备份服务器) (只有当所有的其他服务全部断开,才启用这个服务器)
upstream web_group {
server 172.16.1.7;
server 172.16.1.8 backup;
}
3.访问错误状态配置 (经过max_fails失败3次后, 服务暂停10秒)
upstream web_group {
server 172.16.1.7;
server 172.16.1.8 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=10s;
}
4.最大连接数配置 (限制最大的接收连接数100秒)
upstream web_group {
server 172.16.1.7;
server 172.16.1.8 max_conns=100;
}
Nginx负载均衡健康检查(扩展)
在Nginx官方模块提供的模块中,没有对负载均衡后端节点的健康检查模块,但可以使用第三方模块。
nginx_upstream_check_module来检测后端服务的健康状态。
1.安装依赖
[root@lb02 ~]# yum install -y gcc glibc gcc-c++ pcre-devel openssl-devel patch
2.下载第三方模块
[root@lb02 ~]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.14.2.tar.gz
[root@lb02 ~]# wget https://github.com/yaoweibin/nginx_upstream_check_module/archive/master.zip
3.解压及安装
[root@lb02 ~]# tar xf nginx-1.14.2.tar.gz
[root@lb02 ~]# unzip master.zip
4.进入nginx目录,打补丁(nginx的版本是1.14补丁就选择1.14的,p1代表在nginx目录,p0是不在nginx目录)
[root@lb02 ~]# cd nginx-1.14.2/
[root@lb02 nginx-1.14.2]# patch -p1 <../nginx_upstream_check_module-master/check_1.14.0+.patch
[root@lb02 nginx-1.14.2]# ./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-compat --with-file-aio --with-threads --with-http_addition_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_v2_module --with-mail --with-mail_ssl_module --with-stream --with-stream_realip_module --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_ssl_preread_module --add-module=/root/nginx_upstream_check_module-master --with-cc-opt='-O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -m64 -mtune=generic -fPIC' --with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -Wl,-z,now -pie'
[root@lb02 nginx-1.14.2]# make && make install
5.在已有的负载均衡上增加健康检查的功能
[root@lb01 conf.d]# cat proxy_web.conf
upstream web {
server 172.16.1.7:80 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=10s;
server 172.16.1.8:80 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=10s;
check interval=3000 rise=2 fall=3 timeout=1000 type=tcp;
#interval 检测间隔时间,单位为毫秒
#rise 表示请求2次正常,标记此后端的状态为up
#fall 表示请求3次失败,标记此后端的状态为down
#type 类型为tcp
#timeout 超时时间,单位为毫秒
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name linux.lb.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web;
include proxy_params;
}
location /upstream_check {
check_status;
}
}
6.重启访问页面
#重启
#配置hosts
#访问
http://linux.lb.com/upstream_check


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号