java8引入了stream流和并行流,极大的简化了多线程的操作,但是有一点要注意,parallelStream和completablefuture默认都是使用commonPool,参考源码:ForkJoinPool.commonPool();
项目所有流操作都是共享该池,当频繁的用于阻塞型任务(IO流:http请求等)时会导致整个项目卡顿,parallelStream只适用于cpu密集型的任务,但是我们可以将parallelStream使用自定义线程就可以避免这个问题。
1.使用自定义线程池作为并行流的线程池。
public static void main(String[] args) { String[] firstRange = new String[100]; String[] secondRange = new String[100];
//线程池1 ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(3); forkJoinPool.submit(() -> { Stream.of(firstRange).parallel().forEach((number) -> { try { System.out.println("任务1的线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); // do something slow Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }); }); //线程池2 ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool2 = new ForkJoinPool(2); forkJoinPool2.submit(() -> { Stream.of(secondRange).parallel().forEach((number) -> { try { System.out.println("任务2的线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); // do something slow Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }); }); System.out.println("ok!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"); try { Thread.sleep(1000000); } catch (Exception e) { } }
执行结果
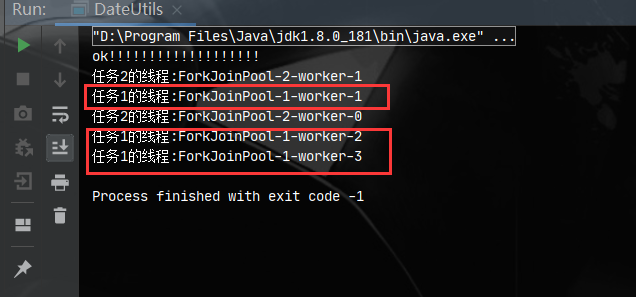
可以看到第一个线程池使用了3个线程,第二个线程池使用了2个线程,线程数量可以自己指定,commonPool的默认线程数为cpu的核心数。
这样IO密集型的多线程操作就可以不占用commonPool线程池了。
2.当我们想对并行计算的结果进行处理时:
方式1:在ForkJoinPool池中处理,即submit方法内部处理(即上面的示例代码)。
方式2:当我们想把处理结果传递给主线程时,由于submit方法传递的是Runnable对象,没有返回值,那么我们可以用对象数组配合join方法处理,比如以下代码:
说明:该方式和CompletableFuture区别是:
CompletableFuture先提交异步线程执行任务,接下来可以做其他事情,需要得到结果的时候再通过CompletableFuture的返回参数得到。
该方式:提交异步线程并立即等待结果(这里只是示例代码,可以做其他调整)
public static void main(String[] args) { final Integer[] result = new Integer[1]; String[] firstRange = new String[100000000]; ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(16); forkJoinPool.submit(() -> { Optional<Integer> reduce = Stream.of(firstRange).parallel().map((number) -> { return 1; }).reduce((integer, integer2) -> { //累加总次数 return integer + integer2; }); Integer integer = reduce.get(); result[0] = integer; System.out.println("count:" + integer); }).join(); System.out.println("并行计算结果:" + result[0]); System.out.println("ok!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"); }
执行结果

以下是基于上面方式整理的工具类,可以简化多线程执行。
和与CompletableFuture区别: CompletableFuture可以在“提交执行任务”和“获取结果”之间可以做其他事情。
package xxx; import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask; /** * 多线程异步编程工具类 * * @author wulingming **/ public class StreamUtils { /**cpu线程数*/ public static final int AVAILABLE_PROCESSORS = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); /** * io密集型任务可以多分配点线程 * 这里不使用AVAILABLE_PROCESSORS - 1,是因为只有stream原始方式,main主线程才参与forkjoin。所以这里总线程数即为cpu核心线程数 */ public static final int DEFAULT_PARALLELISM = AVAILABLE_PROCESSORS <= 0 ? 1 : AVAILABLE_PROCESSORS; /**io密集型线程池*/ public static final ForkJoinPool FORK_JOIN_POOL_IO = new ForkJoinPool(DEFAULT_PARALLELISM); /** * 执行任务(主线程 等待 任务完成) * 不使用默认的线程池,避免导致整个项目卡顿{@link ForkJoinPool#commonPool()} * 适用于IO密集型任务,比如:io流操作、http请求等。 * * @param runnable 执行任务 **/ public static void run(Runnable runnable) { ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(DEFAULT_PARALLELISM); execute(forkJoinPool, runnable, false); forkJoinPool.shutdown(); } /** * 执行任务(主线程 等待 任务完成) * 不使用默认的线程池,避免导致整个项目卡顿{@link ForkJoinPool#commonPool()} * 适用于IO密集型任务,比如:io流操作、http请求等。 * * @param forkJoinPool 线程池 * @param runnable 执行任务 **/ public static void run(ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool, Runnable runnable) { execute(forkJoinPool, runnable, false); //不关闭ForkJoinPool,由外部自己管理 } /** * 执行任务(主线程 不等待 任务完成) * 不使用默认的线程池,避免导致整个项目卡顿{@link ForkJoinPool#commonPool()} * 适用于IO密集型任务,比如:io流操作、http请求等。 * * @param runnable 执行任务 **/ public static void runAsync(Runnable runnable) { ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(DEFAULT_PARALLELISM); execute(forkJoinPool, runnable, true); } /** * 执行任务(主线程 不等待 任务完成) * 不使用默认的线程池,避免导致整个项目卡顿{@link ForkJoinPool#commonPool()} * 适用于IO密集型任务,比如:io流操作、http请求等。 * * @param forkJoinPool 线程池 * @param runnable 执行任务 **/ public static void runAsync(ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool, Runnable runnable) { execute(forkJoinPool, runnable, true); } /** * 使用jdk默认的线程池执行任务(主线程 不等待 任务完成) * 不适用于IO密集型任务,比如:io流操作、http请求等。 * 该方式总线程数比cpu核心线程数少1,是因为主线程不参与执行。原始stream并行下,主线程参与并行 * * @param runnable 执行任务 **/ public static void runAsyncByCommonPool(Runnable runnable) { execute(ForkJoinPool.commonPool(), runnable, true); } /** * 执行 * * @param forkJoinPool 线程池 * @param runnable 执行任务 * @param isAsync 是否异步,true:异步,false:同步(等待任务完成) **/ private static void execute(ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool, Runnable runnable, boolean isAsync) { Assert.isTrue(forkJoinPool != null, "forkJoinPool不能为空!!!"); Assert.isTrue(runnable != null, "runnable不能为空!!!"); ForkJoinTask<?> forkJoinTask = forkJoinPool.submit(runnable); if (!isAsync) { //等待子线程任务完成 forkJoinTask.join(); } } // public static void main(String[] args) { // final Integer[] result = new Integer[1]; // String[] firstRange = new String[50]; // // runAsyncByCommonPool(() -> { // //累加总次数 // Integer r = Stream.of(firstRange).parallel().map((number) -> { // System.out.println("线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); // return 1; // }).reduce(Integer::sum).orElse(0); // // result[0] = r; // // System.out.println("count:" + r); // // }); // // try { // Thread.sleep(3000); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // System.out.println("并行计算结果:" + result[0]); // // System.out.println("ok!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!"); // } // public static void main2(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { // // 没有返回值 // CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync = // CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("已执行runAsync 200")); // runAsync.get(); // 获取结果值,如果一直执行不完,该方法就会被阻塞,一直等待去get // // // 有返回值 // CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // System.out.println("准备等待"); // // System.out.println(19/0); // try { // Thread.sleep(5000); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // return 200; // }); // //System.out.println(supplyAsync.get()); // // // try { // Thread.sleep(5000); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // // // 当成功完成 // Integer info = supplyAsync.whenComplete((t, e) -> { // System.out.println(t); // 获得成功执行完成的返回值,如果执行出错为null // System.out.println(e); // 如果执行不成功,获取异常信息,如果没有异常为null // }).exceptionally((e) -> { // 如果没有异常不执行 // e.getMessage(); // 将执行失败的异常信息获取出来 // return 404; // 有返回值 // }).get(); // // System.out.println(info); // // } }
github:https://github.com/JonSnow592622272/sweet-util


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号