Linux I2C驱动程序设计
1. Linux I2C子系统概述
① Linux将I2C总线驱动进行结构化,将该子系统分成3个部分:I2C核心层、I2C总线驱动和I2C设备驱动。
(1)I2C核心层:提供了I2C总线驱动和设备驱动的注册、注销方法,I2C通信方法(algorithm)上层的、与具体适配器无关的代码以及探测设备、检测设备地址的上层代码等。
(2)I2C总线驱动:I2C总线驱动是对I2C硬件体系结构中适配器端的实现,适配器可由CPU控制,甚至可以直接集成在CPU内部。I2C总线驱动主要包含了I2C适配器数据结构i2c_adapter、I2C适配器的
algorithm数据结构i2c_algorithm和控制I2C适配器产生通信信号的函数。经由I2C总线驱动的代码,我们可以控制I2C适配器以主控方式产生开始位、停止位、读写周期,以及以从设备方式被读写、产生
ACK等。
(3)I2C设备驱动:I2C设备驱动是对I2C硬件体系结构中设备端的实现,设备一般挂接在首CPU控制的I2C适配器上,通过I2C适配器与CPU交换数据。I2C设备驱动主要包含了数据结构i2c_driver和i2c_client,
我们需要根据具体设备实现其中的成员函数。
② Linux I2C 子系统体系架构

2. Linux I2C子系统重要数据结构
① i2c_adapter结构:I2C适配器对象描述结构
struct i2c_adapter { struct module *owner; unsigned int id; unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */ const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */ void *algo_data; /* --- administration stuff. */ int (*client_register)(struct i2c_client *); int (*client_unregister)(struct i2c_client *); /* data fields that are valid for all devices */ u8 level; /* nesting level for lockdep */ struct mutex bus_lock; struct mutex clist_lock; int timeout; /* in jiffies */ int retries; struct device dev; /* the adapter device */ int nr; struct list_head clients; /* DEPRECATED */ char name[48]; struct completion dev_released; };
(1)nr:总线编号,对应设备结点/dev/i2c-x中的x
(2)i2c_adapter注册、注销函数
int i2c_add_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adapter); int i2c_del_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap); int i2c_add_numbered_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap);
② i2c_algorithm结构:I2C适配器的操作方法结构
struct i2c_algorithm { /* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated using common I2C messages */ /* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully processed, or a negative value on error */ int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num); int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr, unsigned short flags, char read_write, u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data); /* To determine what the adapter supports */ u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adapter *); };
③ i2c_msg结构
struct i2c_msg { __u16 addr; /* slave address */ __u16 flags; __u16 len; /* msg length */ __u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */ };
④ i2c_driver结构
struct i2c_driver { int id; unsigned int class; int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *); int (*detach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *);
int (*detach_client)(struct i2c_client *) __deprecated; int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *); int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *); /* driver model interfaces that don't relate to enumeration */ void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *); int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_message_t mesg); int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *); /* a ioctl like command that can be used to perform specific functions * with the device. */ int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg); struct device_driver driver; const struct i2c_device_id *id_table; /* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */ int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, int kind, struct i2c_board_info *); const struct i2c_client_address_data *address_data; struct list_head clients; };
⑤ i2c_client结构:I2C设备对象描述结构
struct i2c_client { unsigned short flags; /* div., see below */ unsigned short addr; /* chip address - NOTE: 7bit */ /* addresses are stored in the */ /* _LOWER_ 7 bits */ char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE]; struct i2c_adapter *adapter; /* the adapter we sit on */ struct i2c_driver *driver; /* and our access routines */ struct device dev; /* the device structure */ int irq; /* irq issued by device */ struct list_head list; /* DEPRECATED */ struct list_head detected; struct completion released; };
3. I2C适配器的设备接口(drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c)
① I2C模块初始化函数i2c_dev_init()主要完成3种操作:
static int __init i2c_dev_init(void) { int res; ... res = register_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c", &i2cdev_fops); ... i2c_dev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "i2c-dev");
... res = i2c_add_driver(&i2cdev_driver);
...
(1)注册字符设备,其中主设备号为I2C_MAJOR(89)、次设备号范围为0~255、文件操作集合为i2cdev_fops
(2)注册设备类
(3)添加I2C适配器设备驱动i2cdev_driver
② 当I2C适配器驱动(i2c_driver结构)和适配器(i2c_adapter结构)匹配时,会调用i2cdev_driver(i2c_driver结构)的i2cdev_attach_adapter()成员函数,该函数主要执行两种操作:
static int i2cdev_attach_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap) { struct i2c_dev *i2c_dev; i2c_dev = get_free_i2c_dev(adap); ... /* register this i2c device with the driver core */ i2c_dev->dev = device_create(i2c_dev_class, &adap->dev, MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, adap->nr), NULL, "i2c-%d", adap->nr);
... }
(1)分配一个与I2C设备对应的i2c_dev对象,并将该对象添加到全局链表i2c_dev_list
(2)创建设备对象并在sysfs中注册
③ I2C适配器字符设备操作方法
static const struct file_operations i2cdev_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .llseek = no_llseek, .read = i2cdev_read, .write = i2cdev_write, .unlocked_ioctl = i2cdev_ioctl, .open = i2cdev_open, .release = i2cdev_release, };
(1)i2cdev_open()函数:
* 获得次设备号,通过i2c_dev_get_by_minor(minor)函数,从链表i2c_dev_list中获取与minor对应的i2c_dev对象
* 通过i2c_get_adapter(i2c->adap->nr)函数获得ID为i2c->adap->nr的适配器对象
* 分配一个i2c_client对象,并用adap、i2c_driver初始化其成员adapter、driver成员,绑定设备与相应适配器和驱动
* 将i2c_client对象作为file结构体的私有数据(file->private_data)保存
static int i2cdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { unsigned int minor = iminor(inode); struct i2c_client *client; struct i2c_adapter *adap; struct i2c_dev *i2c_dev; int ret = 0; lock_kernel(); i2c_dev = i2c_dev_get_by_minor(minor);
adap = i2c_get_adapter(i2c_dev->adap->nr); client = kzalloc(sizeof(*client), GFP_KERNEL); snprintf(client->name, I2C_NAME_SIZE, "i2c-dev %d", adap->nr); client->driver = &i2cdev_driver; client->adapter = adap; file->private_data = client; return ret; }
(2)i2cdev_read()函数:
* 从file结构的私有数据成员获取i2c_client对象,然后调用i2c_master_recv()函数进行接收数据,最后把数据拷贝到用户空间
static ssize_t i2cdev_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *offset) { char *tmp; int ret; struct i2c_client *client = (struct i2c_client *)file->private_data; if (count > 8192) count = 8192; tmp = kmalloc(count,GFP_KERNEL); if (tmp==NULL) return -ENOMEM; pr_debug("i2c-dev: i2c-%d reading %zu bytes.\n", iminor(file->f_path.dentry->d_inode), count); ret = i2c_master_recv(client,tmp,count); if (ret >= 0) ret = copy_to_user(buf,tmp,count)?-EFAULT:ret; kfree(tmp); return ret; }
* i2c_master_recv()函数通过填充i2c_msg结构,然后调用i2c_transfer()来实现传输的。i2c_transfer()则通过调用适配器通信方法master_xfer()将消息发送出去。
int i2c_master_recv(struct i2c_client *client, char *buf ,int count) { struct i2c_adapter *adap=client->adapter; struct i2c_msg msg; int ret; msg.addr = client->addr; msg.flags = client->flags & I2C_M_TEN; msg.flags |= I2C_M_RD; msg.len = count; msg.buf = buf; ret = i2c_transfer(adap, &msg, 1); /* If everything went ok (i.e. 1 msg transmitted), return #bytes transmitted, else error code. */ return (ret == 1) ? count : ret; } int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter * adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num) { ... ret = adap->algo->master_xfer(adap,msgs,num); ... }
注:msg.addr表示的设备地址是由client->addr初始化的,而在之前open()方法中并未填充client->addr,所以在应用层打开设备之后并不能立即调用read或者write进行数据传输,需要用ioctl方法设置设备地址。
(3)i2cdev_ioctl()函数:
static long i2cdev_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) { struct i2c_client *client = (struct i2c_client *)file->private_data; ... switch ( cmd ) { case I2C_SLAVE: case I2C_SLAVE_FORCE: ... case I2C_TENBIT: ... case I2C_PEC: ... case I2C_FUNCS: ... case I2C_RDWR: ...case I2C_SMBUS: ...case I2C_RETRIES: ...case I2C_TIMEOUT: ... default: return -ENOTTY; } return 0; }
4. I2C适配器驱动的实现
① 最终目标是要为硬件适配器注册i2c_adapter对象,在注册前需对其成员进行初始化
② 初始化的核心是实现其通信方法,需要一个i2c_algorithm对象并实现其成员方法:master_xfer、sumbus_xfer等
③ 硬件适配器可能属于片上资源,总线驱动的实现可基于platform驱动模型,一般在platform驱动的probe方法中分配、初始化并注册这个i2c_adapter对象
5. S3C2440 I2C适配器驱动分析
① MINI2440的I2C总线驱动位于文件drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-s3c2410.c,由于I2C适配器属于片上资源,驱动的实现采用了platform驱动模型:
static struct platform_driver s3c2440_i2c_driver = { .probe = s3c24xx_i2c_probe, .remove = s3c24xx_i2c_remove, .suspend_late = s3c24xx_i2c_suspend_late, .resume = s3c24xx_i2c_resume, .driver = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .name = "s3c2440-i2c", }, }; static int __init i2c_adap_s3c_init(void) { int ret; ret = platform_driver_register(&s3c2410_i2c_driver); if (ret == 0) { ret = platform_driver_register(&s3c2440_i2c_driver); if (ret) platform_driver_unregister(&s3c2410_i2c_driver); } return ret; }
② s3c24xx_i2c用于描述S3C2440的I2C适配器(在实现一个具体驱动时,要定义一个结构体来描述它,这个结构体往往内嵌一个描述这类驱动的通用成员和一些该驱动所特有的成员)
struct s3c24xx_i2c { spinlock_t lock; wait_queue_head_t wait; unsigned int suspended:1; struct i2c_msg *msg; unsigned int msg_num; unsigned int msg_idx; unsigned int msg_ptr; unsigned int tx_setup; unsigned int irq; enum s3c24xx_i2c_state state; unsigned long clkrate; void __iomem *regs; struct clk *clk; struct device *dev; struct resource *ioarea; struct i2c_adapter adap; }
③ s3c24xx_i2c_probe 的作用是i2c适配器对象(s3c24xx_i2c )分配、初始化和注册。如前面分析,注册适配器时会遍历I2C总线上的所有驱动,然后调用相应驱动的attach_adapter方法(分配一个i2c_dev结构,并把它注册进全局链表i2c_dev_list,然后在sysfs中注册)。
注:s3c24xx_i2c_probe 最重要的作用是初始化适配器的通信方法s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm
static int s3c24xx_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) { struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c; struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata; struct resource *res; int ret; pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data; i2c = kzalloc(sizeof(struct s3c24xx_i2c), GFP_KERNEL); strlcpy(i2c->adap.name, "s3c2410-i2c", sizeof(i2c->adap.name)); i2c->adap.owner = THIS_MODULE; i2c->adap.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm; i2c->adap.retries = 2; i2c->adap.class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON | I2C_CLASS_SPD; i2c->tx_setup = 50; spin_lock_init(&i2c->lock); init_waitqueue_head(&i2c->wait); /* find the clock and enable it */ i2c->dev = &pdev->dev; i2c->clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "i2c"); clk_enable(i2c->clk); /* map the registers */ res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0); i2c->ioarea = request_mem_region(res->start, (res->end-res->start)+1, pdev->name); i2c->regs = ioremap(res->start, (res->end-res->start)+1); /* setup info block for the i2c core */ i2c->adap.algo_data = i2c; i2c->adap.dev.parent = &pdev->dev; /* initialise the i2c controller */ ret = s3c24xx_i2c_init(i2c); /* find the IRQ for this unit (note, this relies on the init call to * ensure no current IRQs pending */ i2c->irq = ret = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0); ret = request_irq(i2c->irq, s3c24xx_i2c_irq, IRQF_DISABLED, dev_name(&pdev->dev), i2c); ret = s3c24xx_i2c_register_cpufreq(i2c); /* Note, previous versions of the driver used i2c_add_adapter() * to add the bus at any number. We now pass the bus number via * the platform data, so if unset it will now default to always * being bus 0. */ i2c->adap.nr = pdata->bus_num; ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&i2c->adap); ... }
④ S3C2440总线通信方法
(1)S3C2440 I2C总线通信方法:
static const struct i2c_algorithm s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm = { .master_xfer = s3c24xx_i2c_xfer, .functionality = s3c24xx_i2c_func, };
(2)s3c24xx_i2c_xfer()调用函数s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()进行真正的数据传输
(3)s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer()传输数据的大致流程:
* 记录待传输数据的信息
* 调用s3cc24xx_i2c_enable_irq()使能I2C中断
* 设置I2C传输状态位STATE_START
* 调用s3cc24xx_i2c_message_start()启动本次传输
static int s3c24xx_i2c_doxfer(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num) { ... ret = s3c24xx_i2c_set_master(i2c); spin_lock_irq(&i2c->lock); i2c->msg = msgs; i2c->msg_num = num; i2c->msg_ptr = 0; i2c->msg_idx = 0; i2c->state = STATE_START; s3c24xx_i2c_enable_irq(i2c); s3c24xx_i2c_message_start(i2c, msgs); spin_unlock_irq(&i2c->lock); timeout = wait_event_timeout(i2c->wait, i2c->msg_num == 0, HZ * 5); ... }
(4)启动传输后,调用进程会在等待队列i2c->wait中挂起,接下来的数据传输将由I2C中断处理完成(中断完成后将调用wake_up()唤醒在i2c->wait中挂起的进程)。
(5)s3cc24xx_i2c_message_start()的实现涉及S3C2440 I2C适配器的硬件操作:
* 根据i2c->flags标识设置传输方向
* 使能ACK
* 将i2c->addr记录的设备地址写入IICDS寄存器
* 将IICSTAT寄存器的START/STOP条件置位,启动传输
(6)I2C中断处理程序s3c24xx_i2c_irq是处理传输的核心部分:该函数首先判断总线状态,如果正常,则调用i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte()
(7)i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte()中case STATE_START分支即为数据传输部分核心
static int i2s_s3c_irq_nextbyte(struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c, unsigned long iicstat) { unsigned long tmp; unsigned char byte; int ret = 0; switch (i2c->state) { case STATE_IDLE: ... case STATE_STOP: ... case STATE_START: /* last thing we did was send a start condition on the * bus, or started a new i2c message */ if (iicstat & S3C2410_IICSTAT_LASTBIT && !(i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK)) { /* ack was not received... */ dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "ack was not received\n"); s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, -ENXIO); goto out_ack; } if (i2c->msg->flags & I2C_M_RD) i2c->state = STATE_READ; else i2c->state = STATE_WRITE; /* terminate the transfer if there is nothing to do * as this is used by the i2c probe to find devices. */ if (is_lastmsg(i2c) && i2c->msg->len == 0) { s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0); goto out_ack; } if (i2c->state == STATE_READ) goto prepare_read; /* fall through to the write state, as we will need to * send a byte as well */ case STATE_WRITE: ... case STATE_READ: /* we have a byte of data in the data register, do * something with it, and then work out wether we are * going to do any more read/write */ byte = readb(i2c->regs + S3C2410_IICDS); i2c->msg->buf[i2c->msg_ptr++] = byte; prepare_read: if (is_msglast(i2c)) { /* last byte of buffer */ if (is_lastmsg(i2c)) s3c24xx_i2c_disable_ack(i2c); } else if (is_msgend(i2c)) { /* ok, we've read the entire buffer, see if there * is anything else we need to do */ if (is_lastmsg(i2c)) { /* last message, send stop and complete */ dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "READ: Send Stop\n"); s3c24xx_i2c_stop(i2c, 0); } else { /* go to the next transfer */ dev_dbg(i2c->dev, "READ: Next Transfer\n"); i2c->msg_ptr = 0; i2c->msg_idx++; i2c->msg++; } } break; } ... }
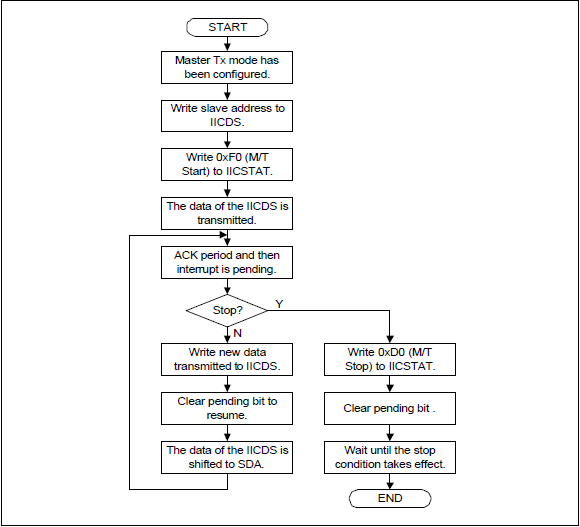
6. 详细的流程可以参考S3C2440芯片手册的流程图
① Operations for Master/Transmitter Mode
② Operations for Master/Receiver Mode



