张量 矩阵乘法优化
张量 矩阵乘法优化
在SIMT架构下, 不使用TensorCore进行矩阵乘法,计算所需要的访存相关的优化。通过逐步迭代优化,深入理解GPU的性能特征和内存访问优化。
测试环境为一块A10 GPU, 驱动版本: 550.54.15, CUDA版本: 12.4 . 矩阵M=N=K=4092,见表6-5。
表6-5 cuBLAS调用,在每种大小下调用的内核
|
内核 |
GFLOPs/s |
相对于cuBLAS的性能 |
|
0: cuBLAS |
|
100.0% |
|
1: Naive |
|
3.9% |
|
2: GMEM Coalescing |
|
7.9% |
|
3: SMEM Caching |
|
14.6% |
|
4: 1D Blocktiling |
|
41.2% |
|
5: 2D Blocktiling |
|
76.4% |
|
6: Vectorized Mem Access |
|
87.1% |
|
7: WarpTiling |
|
100.0% |
6.4.1 cuBLAS基线
1. cuBLAS基线概述
采用cuBLAS作为性能测试基线, 测试环境是一张A10的推理卡, 测试矩阵规模如下:

(6-11)
const int M = 4092;
const int K = 4092;
const int N = 4092;
float alpha = 1.0f;
float beta = 0.5f;
const int K = 4092;
const int N = 4092;
float alpha = 1.0f;
float beta = 0.5f;
cuBLAS测试代码如下所示:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cublas_v2.h>
#include "util.h"
int main()
{
cudaError_t cudaStat; // cudaMalloc status
cublasStatus_t stat; // cuBLAS functions status
cublasHandle_t handle; // cuBLAS context
stat = cublasCreate(&handle); // initialize CUBLAS context
float *d_a, *d_b, *d_c;
cudaMalloc(&d_a, M * K * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&d_b, K * N * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&d_c, M * N * sizeof(float));
cudaEvent_t start, end;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&end);
cudaEventRecord(start);
for (int i = 0; i < ITER; i++)
stat = cublasSgemm(handle,
CUBLAS_OP_N, CUBLAS_OP_N,
N, M, K,
&alpha, d_b, N,
d_a, K, &beta, d_c, N);
cudaEventRecord(end);
cudaEventSynchronize(end);
float msec;
cudaEventElapsedTime(&msec, start, end);
long workload = long(M) * N * K * 2 * ITER;
double avg_Gflops = ((double)workload / 1e9) / (double(msec) / 1e3);
printf("cuBLAS AveragePerformance %10.1lf Gflops\n", avg_Gflops);
cudaFree(d_a);
cudaFree(d_b);
cudaFree(d_c);
cublasDestroy(handle); // destroy CUBLAS context
}
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cublas_v2.h>
#include "util.h"
int main()
{
cudaError_t cudaStat; // cudaMalloc status
cublasStatus_t stat; // cuBLAS functions status
cublasHandle_t handle; // cuBLAS context
stat = cublasCreate(&handle); // initialize CUBLAS context
float *d_a, *d_b, *d_c;
cudaMalloc(&d_a, M * K * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&d_b, K * N * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&d_c, M * N * sizeof(float));
cudaEvent_t start, end;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&end);
cudaEventRecord(start);
for (int i = 0; i < ITER; i++)
stat = cublasSgemm(handle,
CUBLAS_OP_N, CUBLAS_OP_N,
N, M, K,
&alpha, d_b, N,
d_a, K, &beta, d_c, N);
cudaEventRecord(end);
cudaEventSynchronize(end);
float msec;
cudaEventElapsedTime(&msec, start, end);
long workload = long(M) * N * K * 2 * ITER;
double avg_Gflops = ((double)workload / 1e9) / (double(msec) / 1e3);
printf("cuBLAS AveragePerformance %10.1lf Gflops\n", avg_Gflops);
cudaFree(d_a);
cudaFree(d_b);
cudaFree(d_c);
cublasDestroy(handle); // destroy CUBLAS context
}
2. 简单实现
按照三层的循环结构进行编程。从结果C矩阵来看,
可以编排每个线程负责一个位置的值。

(6-12)
__global__ void gmem_coalescing_gemm(int M, int N, int K, float alpha, const float *A,
float beta, float *C)
{
//交换矩阵C的X/Y索引
const uint y = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
const uint x = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if (x < M && y < N)
{
float tmp = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i)
{
tmp += A[x * K + i] * B[i * N + y];
}
// C = α*(A@B)+β*C
C[x * N + y] = alpha * tmp + beta * C[x * N + y];
}
}
void launch_gemm(int M, int N, int K, float alpha, const float *A,
const float *B, float beta, float *C)
{
//交换Grid编排
dim3 gridDim(ceil(N / 32), ceil(M / 32), 1);
dim3 blockDim(32, 32, 1);
gmem_coalescing_gemm<<<gridDim, blockDim>>>(M, N, K, alpha, A, B, beta, C);
}
{
//交换矩阵C的X/Y索引
const uint y = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
const uint x = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if (x < M && y < N)
{
float tmp = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i)
{
tmp += A[x * K + i] * B[i * N + y];
}
// C = α*(A@B)+β*C
C[x * N + y] = alpha * tmp + beta * C[x * N + y];
}
}
void launch_gemm(int M, int N, int K, float alpha, const float *A,
const float *B, float beta, float *C)
{
//交换Grid编排
dim3 gridDim(ceil(N / 32), ceil(M / 32), 1);
dim3 blockDim(32, 32, 1);
gmem_coalescing_gemm<<<gridDim, blockDim>>>(M, N, K, alpha, A, B, beta, C);
}
简单交换一下后性能可以提升到1165.7GFlops. 通过Profiling可以看到,在简单实现中访问内存带宽为52.29GB/s。
将沿着 A 的列和 B 的行移动块,对 C 执行部分求和,直到计算出结果。
template <const int CHUNK_SIZE>
__global__ void sgemm_shared_mem_block(int M, int N, int K, float alpha,
const float *A, const float *B,
float beta, float *C) {
// 矩阵C按照BLOCK划分, cRow和cCol为该线程对应块的行号和列号
const uint cRow = blockIdx.x;
const uint cCol = blockIdx.y;
// 分配共享内存, 共享内存可以被Block内所有的线程访问
__shared__ float As[CHUNK_SIZE * CHUNK_SIZE];
__shared__ float Bs[CHUNK_SIZE * CHUNK_SIZE];
// BLOCK内线程在启动内核的时候分配的blockdim仅有一个维度
// 通过threadIdx找到线程在BLOCK内部对应的行和列
const uint threadCol = threadIdx.x % CHUNK_SIZE;
const uint threadRow = threadIdx.x / CHUNK_SIZE;
// 基于cRow和cCol计算矩阵开始的指针位置
A += cRow * CHUNK_SIZE * K; // row=cRow, col=0
B += cCol * CHUNK_SIZE; // row=0, col=cCol
C += cRow * CHUNK_SIZE * N + cCol * CHUNK_SIZE; // row=cRow, col=cCol
float tmp = 0.0;
for (int bkIdx = 0; bkIdx < K; bkIdx += CHUNK_SIZE) {
// 每个线程加载A和B的一个元素, 由于threadIdx.x是一个连续的分布
// 因此访问GMEM是可以合并的
As[threadRow * CHUNK_SIZE + threadCol] = A[threadRow * K + threadCol];
Bs[threadRow * CHUNK_SIZE + threadCol] = B[threadRow * N + threadCol];
// 同步等待所有thread完成数据加载
__syncthreads();
//将数据移动到下一个CHUNK
A += CHUNK_SIZE;
B += CHUNK_SIZE * N;
// 进行BLOCK Level的内积计算
for (int dotIdx = 0; dotIdx < CHUNK_SIZE; ++dotIdx) {
tmp += As[threadRow * CHUNK_SIZE + dotIdx] *
Bs[dotIdx * CHUNK_SIZE + threadCol];
}
// 考虑Cache影响, 需要在执行下一次加载时再进行一次同步
__syncthreads();
}
C[threadRow * N + threadCol] =
alpha * tmp + beta * C[threadRow * N + threadCol];
}
__global__ void sgemm_shared_mem_block(int M, int N, int K, float alpha,
const float *A, const float *B,
float beta, float *C) {
// 矩阵C按照BLOCK划分, cRow和cCol为该线程对应块的行号和列号
const uint cRow = blockIdx.x;
const uint cCol = blockIdx.y;
// 分配共享内存, 共享内存可以被Block内所有的线程访问
__shared__ float As[CHUNK_SIZE * CHUNK_SIZE];
__shared__ float Bs[CHUNK_SIZE * CHUNK_SIZE];
// BLOCK内线程在启动内核的时候分配的blockdim仅有一个维度
// 通过threadIdx找到线程在BLOCK内部对应的行和列
const uint threadCol = threadIdx.x % CHUNK_SIZE;
const uint threadRow = threadIdx.x / CHUNK_SIZE;
// 基于cRow和cCol计算矩阵开始的指针位置
A += cRow * CHUNK_SIZE * K; // row=cRow, col=0
B += cCol * CHUNK_SIZE; // row=0, col=cCol
C += cRow * CHUNK_SIZE * N + cCol * CHUNK_SIZE; // row=cRow, col=cCol
float tmp = 0.0;
for (int bkIdx = 0; bkIdx < K; bkIdx += CHUNK_SIZE) {
// 每个线程加载A和B的一个元素, 由于threadIdx.x是一个连续的分布
// 因此访问GMEM是可以合并的
As[threadRow * CHUNK_SIZE + threadCol] = A[threadRow * K + threadCol];
Bs[threadRow * CHUNK_SIZE + threadCol] = B[threadRow * N + threadCol];
// 同步等待所有thread完成数据加载
__syncthreads();
//将数据移动到下一个CHUNK
A += CHUNK_SIZE;
B += CHUNK_SIZE * N;
// 进行BLOCK Level的内积计算
for (int dotIdx = 0; dotIdx < CHUNK_SIZE; ++dotIdx) {
tmp += As[threadRow * CHUNK_SIZE + dotIdx] *
Bs[dotIdx * CHUNK_SIZE + threadCol];
}
// 考虑Cache影响, 需要在执行下一次加载时再进行一次同步
__syncthreads();
}
C[threadRow * N + threadCol] =
alpha * tmp + beta * C[threadRow * N + threadCol];
}
void launch_gemm(int M, int N, int K,
float alpha, const float *A,
const float *B, float beta,
float *C)
{
dim3 gridDim(CEIL_DIV(M, 32), CEIL_DIV(N, 32));
dim3 blockDim(32 * 32);
sgemm_shared_mem_block<32>
<<<gridDim, blockDim>>>(M, N, K, alpha, A, B, beta, C);
}
dim3 gridDim(CEIL_DIV(M, 32), CEIL_DIV(N, 32));
dim3 blockDim(32 * 32);
sgemm_shared_mem_block<32>
<<<gridDim, blockDim>>>(M, N, K, alpha, A, B, beta, C);
}
测试可以看到性能提升到2166GFLOPS, 同时,通过Profiling看到,访问内存的请求转移到了SMEM,如图6-38所示。
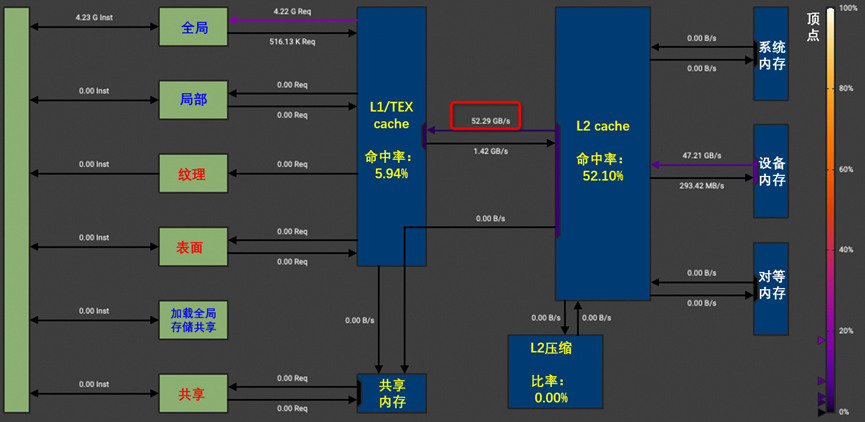
图6-38 代码测试性能模块分析
人工智能芯片与自动驾驶





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)
2023-09-20 SIMD和SIMT技术分析
2022-09-20 SSD, Redis多线程与云服务器架构,PC处理器
2021-09-20 传统编译原理