情感分析:基于循环神经网络
情感分析:基于循环神经网络
Sentiment Analysis: Using Recurrent Neural Networks
与搜索同义词和类比词类似,文本分类也是单词嵌入的一个下游应用。在本文中,将应用预训练的词向量(glow)和具有多个隐藏层的双向递归神经网络,如图1所示。将使用该模型来判断长度不定的文本序列是包含积极情绪还是消极情绪。
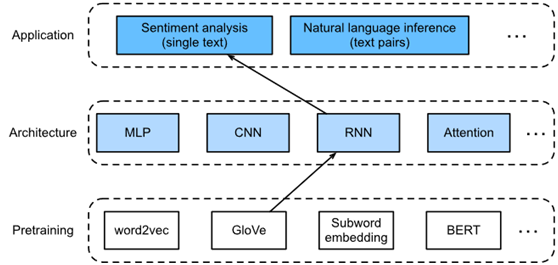
图1. 本节将经过预训练的GloVe to RNN-based提供给基于RNN的体系结构,用于情感分析。
from d2l import mxnet as d2l
from mxnet import gluon, init, np, npx
from mxnet.gluon import nn, rnn
npx.set_np()
batch_size = 64
train_iter, test_iter, vocab = d2l.load_data_imdb(batch_size)
1. Using a Recurrent Neural Network Model
在该模型中,每个词首先从嵌入层获得一个特征向量。然后,利用双向递归神经网络对特征序列进行编码,得到序列信息。最后,将编码后的序列信息通过全连通层输出。具体来说,可以将双向长短期存储器的隐藏状态连接在初始时间步和最终时间步中,并将其作为编码的特征序列信息传递给输出层分类。在下面实现的BiRNN类中,嵌入实例是嵌入层,LSTM实例是序列编码的隐藏层,密集实例是生成分类结果的输出层。
class BiRNN(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens,
num_layers, **kwargs):
super(BiRNN, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
# Set Bidirectional to True to get a bidirectional recurrent neural
# network
self.encoder = rnn.LSTM(num_hiddens, num_layers=num_layers,
bidirectional=True, input_size=embed_size)
self.decoder = nn.Dense(2)
def forward(self, inputs):
# The shape of inputs is (batch size, number of words). Because LSTM
# needs to use sequence as the first dimension, the input is
# transformed and the word feature is then extracted. The output shape
# is (number of words, batch size, word vector dimension).
embeddings = self.embedding(inputs.T)
# Since the input (embeddings) is the only argument passed into
# rnn.LSTM, it only returns the hidden states of the last hidden layer
# at different timestep (outputs). The shape of outputs is
# (number of words, batch size, 2 * number of hidden units).
outputs = self.encoder(embeddings)
# Concatenate the hidden states of the initial timestep and final
# timestep to use as the input of the fully connected layer. Its
# shape is (batch size, 4 * number of hidden units)
encoding = np.concatenate((outputs[0], outputs[-1]), axis=1)
outs = self.decoder(encoding)
return outs
创建一个具有两个隐藏层的双向递归神经网络。
embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers, ctx = 100, 100, 2, d2l.try_all_gpus()
net = BiRNN(len(vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers)
net.initialize(init.Xavier(), ctx=ctx)
1.1. Loading Pre-trained Word Vectors
由于用于情感分类的训练数据集不是很大,为了处理过拟合,将直接使用在较大语料库上预先训练的词向量作为所有词的特征向量。这里,为字典vocab中的每个单词加载一个100维的GloVe词向量。
glove_embedding = d2l.TokenEmbedding('glove.6b.100d')
查询词汇表中的单词向量。
embeds = glove_embedding[vocab.idx_to_token]
embeds.shape
(49339, 100)
然后,将这些词向量作为评论中每个词的特征向量。请注意,预先训练的词向量的维数需要与创建的模型中的嵌入层输出大小embed_size一致。此外,不再在训练期间更新这些词向量。
net.embedding.weight.set_data(embeds)
net.embedding.collect_params().setattr('grad_req', 'null')
2. Training and Evaluating the Model
现在,可以开始训练了。
lr, num_epochs = 0.01, 5
trainer = gluon.Trainer(net.collect_params(), 'adam', {'learning_rate': lr})
loss = gluon.loss.SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss()
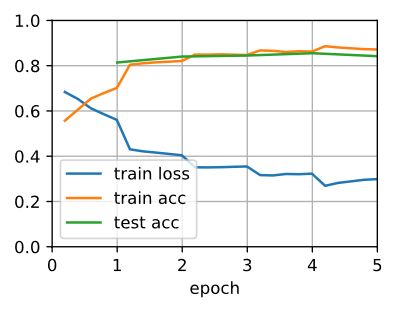
d2l.train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs, ctx)
loss 0.299, train acc 0.872, test acc 0.842
626.7 examples/sec on [gpu(0), gpu(1)]
最后,定义了预测函数。
#@save
def predict_sentiment(net, vocab, sentence):
sentence = np.array(vocab[sentence.split()], ctx=d2l.try_gpu())
label = np.argmax(net(sentence.reshape(1, -1)), axis=1)
return 'positive' if label == 1 else 'negative'
然后,利用训练好的模型对两个简单句子的情感进行分类。
predict_sentiment(net, vocab, 'this movie is so great')
'positive'
predict_sentiment(net, vocab, 'this movie is so bad')
'negative'
2. Summary
- Text classification transforms a sequence of text of indefinite length into a category of text. This is a downstream application of word embedding.
- We can apply pre-trained word vectors and recurrent neural networks to classify the emotions in a text.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号