学习RabbitMQ(三)
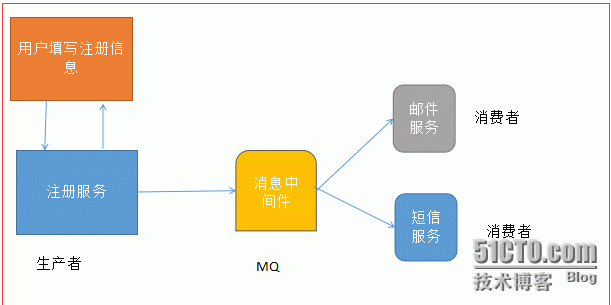
1 用户注册后(会立即提示注册成功),过一会发送短信和邮件通知
发布/订阅模型
以上模式一般是用户注册成功后,写入一条数据到mysql,在发送一条消息到MQ!
如果不用消息中间件(或者简单的做成异步发送),做成了用户提交了注册之后,成功后,就同步立即执行发送邮件和短信服务脚本(这样耗时间),这样用户体验不好时间慢!
术语: SOA
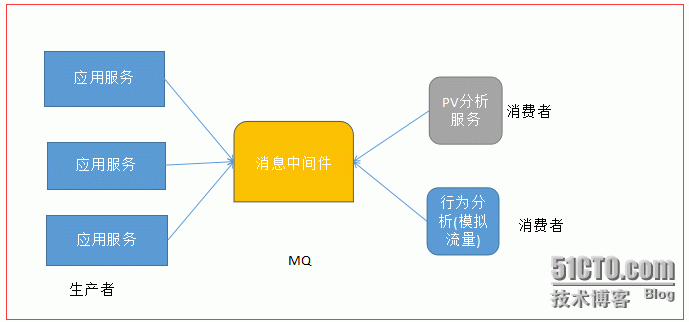
2 把日志进行集中收集,用于日志分析和流量回放分析
术语:灰度发布,小流量
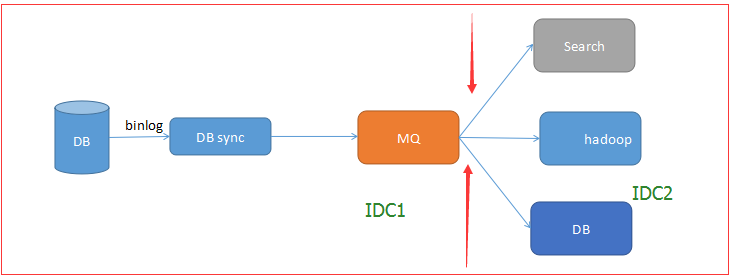
3 将数据源头复制到多个目的地,一般是要求顺序或者因果关系序的
用于跨机房数据传输,搜索 离线数据和其他DB等
术语:
AOP
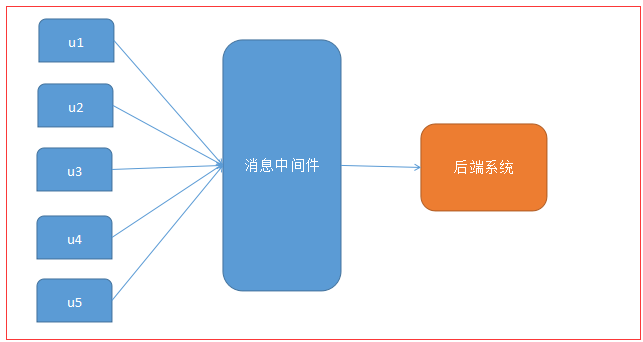
4 消息暂存地
把消息中间件当成可靠的消息暂存地
定时进行消息投递,比如模拟用户秒杀访问,进行系统性能压测
消费者消费完后不删除消息! 这种压测方式比较真实,比一般的并发压测软件更符合真实环境!
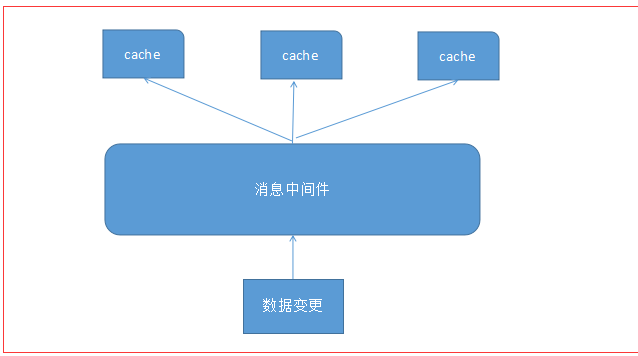
5 缓存数据同步更新 往应用推送数据
就像很多数据都是缓存在本地的应用中的如tomcat应用,如一个数据价格缓存,当有数据更新的时候,就需要及时(而不是通过租约到期去解决) 这个时候就需要中间件,不是一个一个去通知更新
##################################################################################################
【介绍】
RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完整的,可复用的企业消息系统。他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议。
RabbitMQ是流行的开源消息队列系统,用erlang语言开发
RabbitMQ是AMQP(高级消息队列协议)的标准实现
【安装】
方式:yum/rpm
系统环境
[root@log_server scripts]# ifconfig | sed -n 's#.*inet addr:\(.*\) B.*#\1#gp'
192.168.100.20
[root@log_server scripts]# cat /etc/issue | grep -i cent
CentOS release 6.4 (Final)
[root@log_server scripts]# yum repolist |grep epel
* epel: mirrors.aliyun.com
epel Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 6 - x86_64 12,244
[root@log_server scripts]#
yum install -y rabbitmq-server
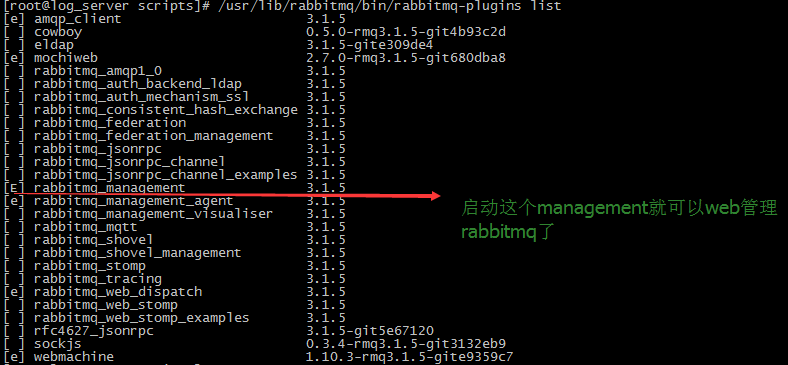
安装成功后,查看插件列表
/usr/lib/rabbitmq/bin/rabbitmq-plugins list
启动rabbitmq_management插件
/usr/lib/rabbitmq/bin/rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
启动程序
/etc/init.d/rabbitmq-server start
【验证】
[root@log_server scripts]# netstat -tulnp |grep 15672 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15672 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3877/beam.smp [root@log_server scripts]# ps -ef |grep rabbit root 3837 1 0 11:30 pts/2 00:00:00 /bin/sh /etc/init.d/rabbitmq-server start root 3868 3837 0 11:30 pts/2 00:00:00 /bin/bash -c ulimit -S -c 0 >/dev/null 2>&1 ; /usr/sbin/rabbitmq-server root 3869 3868 0 11:30 pts/2 00:00:00 /bin/sh /usr/sbin/rabbitmq-server root 3876 3869 0 11:30 pts/2 00:00:00 su rabbitmq -s /bin/sh -c /usr/lib/rabbitmq/bin/rabbitmq-server rabbitmq 3877 3876 0 11:30 ? 00:00:55 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-5.8.5/bin/beam.smp -W w -K true -A30 -P 1048576 -- -root /usr/lib64/erlang -progname erl -- -home /var/lib/rabbitmq -- -pa /usr/lib/rabbitmq/lib/rabbitmq_server-3.1.5/sbin/../ebin -noshell -noinput -s rabbit boot -sname rabbit@log_server -boot start_sasl -kernel inet_default_connect_options [{nodelay,true}] -sasl errlog_type error -sasl sasl_error_logger false -rabbit error_logger {file,"/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@log_server.log"} -rabbit sasl_error_logger {file,"/var/log/rabbitmq/rabbit@log_server-sasl.log"} -rabbit enabled_plugins_file "/etc/rabbitmq/enabled_plugins" -rabbit plugins_dir "/usr/lib/rabbitmq/lib/rabbitmq_server-3.1.5/sbin/../plugins" -rabbit plugins_expand_dir "/var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia/rabbit@log_server-plugins-expand" -os_mon start_cpu_sup false -os_mon start_disksup false -os_mon start_memsup false -mnesia dir "/var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia/rabbit@log_server" rabbitmq 3951 3877 0 11:30 ? 00:00:00 inet_gethost 4 rabbitmq 3952 3951 0 11:30 ? 00:00:00 inet_gethost 4 root 19143 1770 0 14:02 pts/2 00:00:00 grep rabbit [root@log_server scripts]#
【配置】
默认配置不需要配置
如果有需要/etc/rabbitmq/ 下可以创建
【常见命令】
查看列队列表
rabbitmqctl list_queues
查看默认 vhost为 "/"下的列队
rabbitmqctl list_queues -p "/"
查看vhost列表
rabbitmqctl list_vhosts
增加/删除vhost
rabbitmqctl add_vhost vhost_andy
rabbitmqctl delete_vhost <VHostPath>
增加用户
rabbitmqctl add_user andy '12qwaszx'
查看用户
rabbitmqctl list_users
[root@log_server scripts]# rabbitmqctl list_users
Listing users ...
andy []
guest [administrator]
查看用户权限
rabbitmqctl list_user_permissions andy
[root@log_server scripts]# rabbitmqctl list_user_permissions andy
Listing permissions for user "andy" ...
vhost_andy .* .* .*
...done.
【web管理连接】
guest/guest登入
【python程序模拟生产者】
参考官网:http://www.rabbitmq.com/tutorials/tutorial-one-python.html
来自最简单的模型P-mq--C
cat send.py
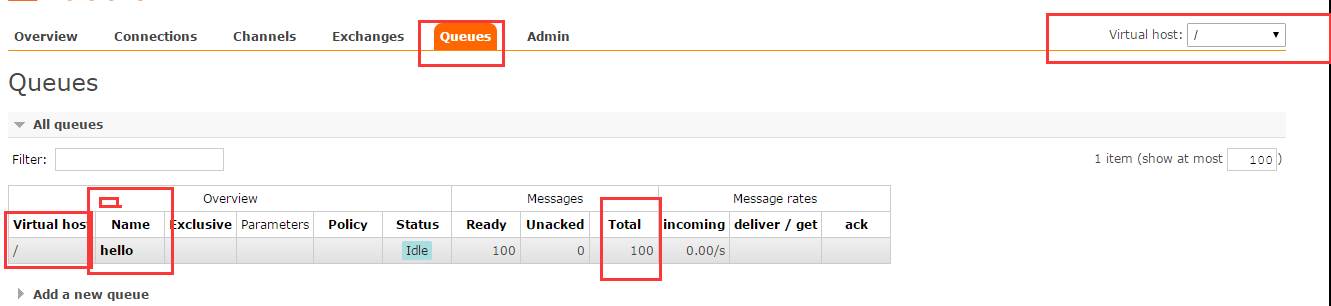
模拟发送100条消息到queue=hello的这个列队中
命令查看队列:(不指定vhost 列队在默认的vhost "/"中)
[root@log_server scripts]# rabbitmqctl list_queues -p "/"
Listing queues ...
hello 100
...done.
web端查看
【python程序模拟消费者进行消费】
[root@log_server scripts]# cat receive.py
执行消费,并等待messages! 直到ctrl+c 终止
再次查看队列
[root@log_server scripts]# rabbitmqctl list_queues -p "/"
Listing queues ...
hello 0
...done.
【常见启动报错】
/etc/init.d/rabbitmq-server 脚本调用的是 rabbitmqctl
常见问题:
root@log_server scripts]# /etc/init.d/rabbitmq-server stop
Stopping rabbitmq-server: RabbitMQ is not running
rabbitmq-server.
[root@log_server scripts]# rabbitmqctl stop
Stopping and halting node rabbit@log_server ...
Error: unable to connect to node rabbit@log_server: nodedown
DIAGNOSTICS
===========
nodes in question: [rabbit@log_server]
hosts, their running nodes and ports:
- unable to connect to epmd on log_server: address (cannot connect to host/port)
current node details:
- node name: rabbitmqctl23829@log_server
- home dir: /var/lib/rabbitmq
- cookie hash: UtT55njEKHItAnmjDeoV+A==
解释原因:
分析 rabbitmqctl --help 中的第一段
Usage:
rabbitmqctl [-n <node>] [-q] <command> [<command options>]
Options:
-n node
-q
Default node is "rabbit@server", where server is the local host. On a host
named "server.example.com", the node name of the RabbitMQ Erlang node will
usually be rabbit@server (unless RABBITMQ_NODENAME has been set to some
non-default value at broker startup time). The output of hostname -s is usually
the correct suffix to use after the "@" sign. See rabbitmq-server(1) for
details of configuring the RabbitMQ broker.
Quiet output mode is selected with the "-q" flag. Informational messages are
suppressed when quiet mode is in effect.
Commands:
stop [<pid_file>]
stop_app
start_app
wait <pid_file>
reset
force_reset
rotate_logs <suffix>
原因是不能解析 本主机,原因是 默认作为解析的节点和 本机的hostname -s 结果一致
解决方法:只要把hostname -s的结果 加入到/etc/hosts中即可
[root@log_server ~]# hostname -s
log_server
正常停止的结果:
[root@log_server ~]# rabbitmqctl stop
Stopping and halting node rabbit@log_server ...
...done.
正常启动的结果:
[root@log_server ~]# /etc/init.d/rabbitmq-server start
Starting rabbitmq-server: SUCCESS
rabbitmq-server.
可以查看的日志
/var/log/rabbit/
##################################################################################################3
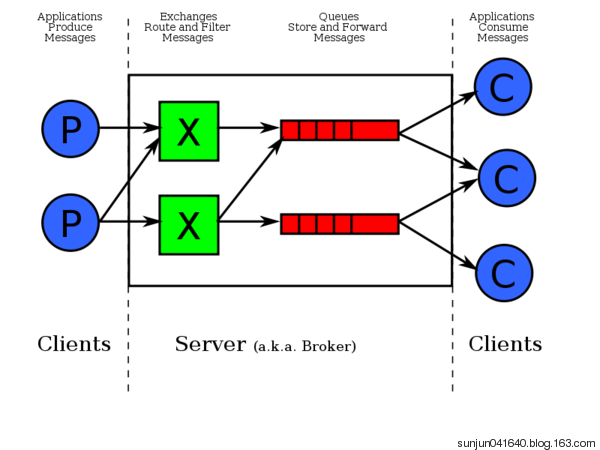
AMQ结构图,工作原理图
重要术语
Server(broker):接收客户端连接,实现AMQP消息队列的路由功能的进程.简单来说就是消息队列服务器实体。
Vhost:虚拟主机,一个broker里可以开设多个vhost,用作不同用户的权限分离。权限控制组,用户只能关联到一个vhost上,一个vhost中可以有若干个Exchange和Queue,默认的vhost是"/"
Exchange:接收生产者发送的消息,并根据Binding规则将消息路由给服务器中的队列 Exchange Type决定了Exchange路由消息额行为,例如,在RabbitMQ中,ExchangeType有Direct、Fanout和Topic三种,不同类型的Exchange路由得到行为是不一样的
queue:用于存储还未消费的消息。消息队列载体,每个消息都会被投入到一个或多个队列。
Message:由Header和Body组成,Header是由生产者添加到各种属性的集合,包括Message是否被持久化,是由哪个Message Queue接收优先级是多少等,而Body是真正需要传输的APP数据
Binding: 绑定,它的作用就是把exchange和queue按照路由规则绑定起来。:
BindingKey: 在mq中设置的绑定key
Routing Key:路由关键字,exchange根据这个关键字进行消息投递。
producer:消息生产者,就是投递消息的程序。
consumer:消息消费者,就是接受消息的程序。
channel:消息通道,在客户端的每个连接里,可建立多个channel,每个channel代表一个会话任务
消息队列的使用过程大概如下:
(1)客户端(生产者)连接到消息队列服务器,打开一个channel。
(2)客户端声明一个exchange,并设置相关属性。
(3)客户端声明一个queue,并设置相关属性。
(4)客户端使用routing key,在exchange和queue之间建立好绑定关系。
(5)客户端投递消息到exchange。
exchange接收到消息后,就根据消息的key和已经设置的binding,进行消息路由,将消息投递到一个或多个队列里。
exchange也有几个类型,完全根据key进行投递的叫做Direct交换机,例如,绑定时设置了routing key为”abc”,那么客户端提交的消息,只有设置了key为”abc”的才会投递到队列。对key进行模式匹配后进行投递的叫做Topic交换机,符号”#”匹配一个或多个词,符号”*”匹配正好一个词。例如”abc.#”匹配”abc.def.ghi”,”abc.*”只匹配”abc.def”。还有一种不需要key的,叫做Fanout交换机,它采取广播模式,一个消息进来时,投递到与该交换机绑定的所有队列。
Direct:
任何发送到Direct Exchange的消息都会被转发到routing_key中指定的Queue
1.一般情况可以使用rabbitMQ自带的Exchange:””(该Exchange的名字为空字符串);
2.这种模式下不需要将Exchange进行任何绑定(bind)操作;
3.消息传递时需要一个“routing_key”,可以简单的理解为要发送到的队列名字;
4.如果vhost中不存在routing_key中指定的队列名,则该消息会被抛弃。
如代码发送
Topic:
任何发送到Topic Exchange的消息都会被转发到所有关心routing_key中指定话题的Queue上
1.这种模式较为复杂,简单来说,就是每个队列都有其关心的主题,所有的消息都带有一个“标题”(routing_key),Exchange会将消息转发到所有关注主题能与routing_key模糊匹配的队列。
2.这种模式需要routing_key,也许要提前绑定Exchange与Queue。
3.在进行绑定时,要提供一个该队列关心的主题,如“#.log.#”表示该队列关心所有涉及log的消息(一个routing_key为”MQ.log.error”的消息会被转发到该队列)。
4.“#”表示0个或若干个关键字,“*”表示一个关键字。如“log.*”能与“log.warn”匹配,无法与“log.warn.timeout”匹配;但是“log.#”能与上述两者匹配。
5.同样,如果Exchange没有发现能够与routing_key匹配的Queue,则会抛弃此消息。
Fanout:
任何发送到Fanout Exchange的消息都会被转发到与该Exchange绑定(Binding)的所有Queue上
1.可以理解为路由表的模式
2.这种模式不需要routing_key
3.这种模式需要提前将Exchange与Queue进行绑定,一个Exchange可以绑定多个Queue,一个Queue可以同多个Exchange进行绑定。
4.如果接受到消息的Exchange没有与任何Queue绑定,则消息会被抛弃。
Demo中创建了一个将一个exchange和一个queue进行fanout类型的bind.但是发送信息时没有用到它,如果要用到它,只要在发送消息时指定该exchange的名称即可,该exchange就会将消息发送到所有和它bind的队列中。在fanout模式下,指定的routing_key是无效的 。
rabbitMQ的两个核心组件是exchange和queue
运行原理如下图: