第三周期大作业总结
--wudibaolongsho
前言
这么快就到了java课程的结尾了,第三次大作业已经结束了。总感觉时间飞逝,我回首往事,其实java给我带来的不仅是编程技术的提升,还有的是对编程语言中大的内核的体会,这是我觉得在Java课程中体会到的,让就来看看我这最后一次大作业的提升和感悟吧。
第七次大作业总结
这一次大作业明显比上一次更加的有难度,在题目上看仅仅加上了一个互斥开关,但是对题目难度的提升是立竿见影的,因为在前几次的题目中的解析输入的数据是十分的简单的,但这一次我不仅要解析输入的数据,还要将互斥开关出现的两条的语句合并成一条语句。但最难的是将互斥开关放到干路上处理还是将其放到支路上去处理,因为在我设计的代码中我将支路和干路做出了严格的区分。但在输入样例中互斥开关有时接点在前有时节点在后这是我必须重新改变我的解析规则和我的电路的判定规则。
所以我索性将支路和干路的划分给模糊掉,将用一个更加大的电路给代替。这样就可以灵活的加装互斥开关的代码。
之后,在这一启发下,我又接着寻找到了解决互斥开关节点不定的问题。在此之后我决定用先分割在比对的方法。这样两种最难处理的数据类型都解决了。剩下的只要交给时间就行了。
那我们来看看我这个思路的圈复杂度:
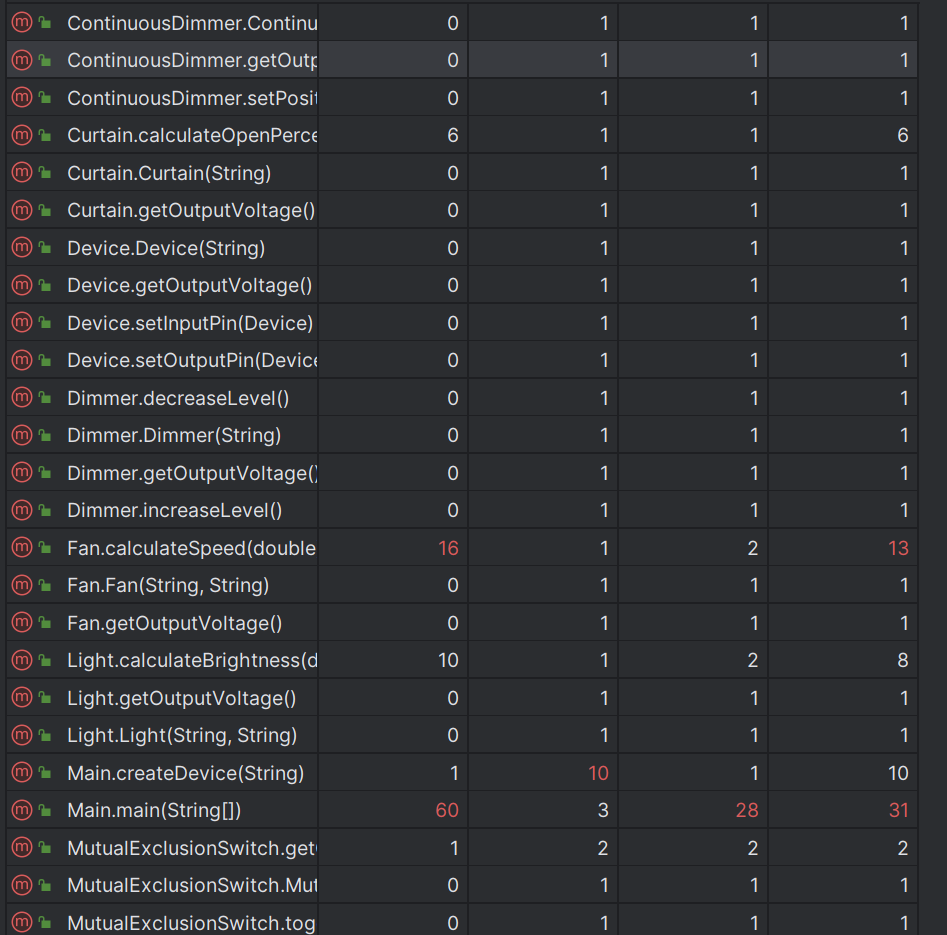
这个圈复杂度虽然没有达到理想的状态,但毕竟是我自己独立想出的我还是十分满意的。
在来看看我的代码吧
点击查看代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Device {
String id;
Device inputPin;
Device outputPin;
public Device(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setInputPin(Device pin) {
this.inputPin = pin;
}
public void setOutputPin(Device pin) {
this.outputPin = pin;
}
public double getOutputVoltage() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not implemented");
}
}
class Switch extends Device {
int state; // 0: turned on, 1: closed
public Switch(String id) {
super(id);
this.state = 0;
}
public void toggle() {
this.state = 1 - this.state;
}
@Override
public double getOutputVoltage() {
if (this.state == 0) {
return 0;
}
return this.inputPin.getOutputVoltage();
}
}
class MutualExclusionSwitch extends Device {
int state; // 0: 1-2 closed, 1: 1-3 closed
int[] resistances = {5, 10};
public MutualExclusionSwitch(String id) {
super(id);
this.state = 0;
}
public void toggle() {
this.state = 1 - this.state;
}
@Override
public double getOutputVoltage() {
if (this.state == 0) {
return this.inputPin.getOutputVoltage() * (resistances[0] / (resistances[0] + resistances[1]));
}
return this.inputPin.getOutputVoltage() * (resistances[1] / (resistances[0] + resistances[1]));
}
}
class Dimmer extends Device {
int level;
double[] levels = {0, 0.3, 0.6, 0.9};
public Dimmer(String id) {
super(id);
this.level = 0;
}
public void increaseLevel() {
this.level = Math.min(this.level + 1, levels.length - 1);
}
public void decreaseLevel() {
this.level = Math.max(this.level - 1, 0);
}
@Override
public double getOutputVoltage() {
return this.inputPin.getOutputVoltage() * levels[this.level];
}
}
class ContinuousDimmer extends Device {
double position;
public ContinuousDimmer(String id) {
super(id);
this.position = 0.0;
}
public void setPosition(double position) {
this.position = position;
}
@Override
public double getOutputVoltage() {
return this.inputPin.getOutputVoltage() * this.position;
}
}
class Light extends Device {
String type;
int brightness;
public Light(String id, String type) {
super(id);
this.type = type;
this.brightness = 0;
}
public void calculateBrightness(double voltageDiff) {
if (this.type.equals("incandescent")) {
if (voltageDiff == 0) {
this.brightness = 0;
} else if (voltageDiff < 10) {
this.brightness = 0;
} else if (voltageDiff == 10) {
this.brightness = 50;
} else if (voltageDiff == 220) {
this.brightness = 200;
} else {
this.brightness = (int) (50 + (voltageDiff - 10) * (150 / 210));
}
} else if (this.type.equals("fluorescent")) {
this.brightness = voltageDiff > 0 ? 180 : 0;
}
}
@Override
public double getOutputVoltage() {
return this.inputPin.getOutputVoltage();
}
}
class Fan extends Device {
String type;
int speed;
public Fan(String id, String type) {
super(id);
this.type = type;
this.speed = 0;
}
public void calculateSpeed(double voltageDiff) {
if (this.type.equals("ceiling")) {
if (voltageDiff < 80) {
this.speed = 0;
} else if (voltageDiff >= 80 && voltageDiff < 150) {
this.speed = (int) (80 + (voltageDiff - 80) * (280 / 70));
} else {
this.speed = 360;
}
} else if (this.type.equals("floor")) {
if (voltageDiff < 80) {
this.speed = 0;
} else if (voltageDiff >= 80 && voltageDiff < 100) {
this.speed = 80;
} else if (voltageDiff >= 100 && voltageDiff < 120) {
this.speed = 160;
} else if (voltageDiff >= 120 && voltageDiff < 140) {
this.speed = 260;
} else {
this.speed = 360;
}
}
}
@Override
public double getOutputVoltage() {
return this.inputPin.getOutputVoltage();
}
}
class Curtain extends Device {
int openPercentage;
public Curtain(String id) {
super(id);
this.openPercentage = 100;
}
public void calculateOpenPercentage(int totalBrightness) {
if (totalBrightness < 50) {
this.openPercentage = 100;
} else if (totalBrightness < 100) {
this.openPercentage = 80;
} else if (totalBrightness < 200) {
this.openPercentage = 60;
} else if (totalBrightness < 300) {
this.openPercentage = 40;
} else if (totalBrightness < 400) {
this.openPercentage = 20;
} else {
this.openPercentage = 0;
}
}
@Override
public double getOutputVoltage() {
return this.inputPin.getOutputVoltage();
}
}
class SeriesCircuit extends Device {
List<Device> devices;
public SeriesCircuit(String id) {
super(id);
this.devices = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addDevice(Device device) {
this.devices.add(device);
}
@Override
public double getOutputVoltage() {
double voltage = 220; // Start with the input voltage
for (Device device : this.devices) {
voltage = device.getOutputVoltage();
}
return voltage;
}
}
class ParallelCircuit extends Device {
List<Device> circuits;
public ParallelCircuit(String id) {
super(id);
this.circuits = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addCircuit(Device circuit) {
this.circuits.add(circuit);
}
@Override
public double getOutputVoltage() {
double[] voltages = new double[this.circuits.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < this.circuits.size(); i++) {
voltages[i] = this.circuits.get(i).getOutputVoltage();
}
return Math.min(voltages[0], voltages[1]); // Simplified for demonstration
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
List<String> inputLines = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println("请输入电路信息和设备控制信息,输入 'end' 结束输入:");
while (true) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
if (line.trim().toLowerCase().equals("end")) {
break;
}
inputLines.add(line);
}
scanner.close();
Map<String, Device> devices = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Device> circuits = new HashMap<>();
for (String line : inputLines) {
if (line.startsWith("#T")) {
// 处理串联电路
String[] parts = line.split(":");
String circuitId = parts[0].substring(2);
SeriesCircuit circuit = new SeriesCircuit(circuitId);
String[] connections = parts[1].trim().split(" ");
for (String connection : connections) {
if (connection.contains("[") && connection.contains("]")) {
connection = connection.replace("[", "").replace("]", "");
String[] pins = connection.split(" ");
String deviceId = pins[1].split("-")[0];
if (!devices.containsKey(deviceId)) {
devices.put(deviceId, createDevice(deviceId));
}
circuit.addDevice(devices.get(deviceId));
}
}
circuits.put(circuitId, circuit);
} else if (line.startsWith("#M")) {
// 处理并联电路
String[] parts = line.split(":");
String circuitId = parts[0].substring(2);
ParallelCircuit circuit = new ParallelCircuit(circuitId);
String[] connections = parts[1].trim().split(" ");
for (String connection : connections) {
if (connection.contains("[") && connection.contains("]")) {
connection = connection.replace("[", "").replace("]", "");
String[] subCircuitIds = connection.split(" ");
for (String subCircuitId : subCircuitIds) {
circuit.addCircuit(circuits.get(subCircuitId));
}
}
}
circuits.put(circuitId, circuit);
} else if (line.startsWith("#")) {
// 处理设备控制信息
String controlInfo = line.substring(1).trim();
if (controlInfo.charAt(0) == 'K') {
String deviceId = controlInfo.substring(1);
((Switch) devices.get(deviceId)).toggle();
} else if (controlInfo.charAt(0) == 'H') {
String deviceId = controlInfo.substring(1);
((MutualExclusionSwitch) devices.get(deviceId)).toggle();
} else if (controlInfo.charAt(0) == 'F') {
String deviceId = controlInfo.substring(1).split("\\\\+|-")[0];
if (controlInfo.contains("+")) {
((Dimmer) devices.get(deviceId)).increaseLevel();
} else if (controlInfo.contains("-")) {
((Dimmer) devices.get(deviceId)).decreaseLevel();
}
} else if (controlInfo.charAt(0) == 'L') {
String deviceId = controlInfo.split(":")[0];
double position = Double.parseDouble(controlInfo.split(":")[1]);
((ContinuousDimmer) devices.get(deviceId)).setPosition(position);
}
}
}
// 输出结果
for (Map.Entry<String, Device> entry : devices.entrySet()) {
Device device = entry.getValue();
if (device instanceof Switch) {
String state = ((Switch) device).state == 1 ? "closed" : "turned on";
System.out.println("@" + device.id + ":" + state);
} else if (device instanceof MutualExclusionSwitch) {
String state = ((MutualExclusionSwitch) device).state == 1 ? "closed" : "turned on";
System.out.println("@" + device.id + ":" + state);
} else if (device instanceof Dimmer) {
System.out.println("@" + device.id + ":" + ((Dimmer) device).levels[((Dimmer) device).level]);
} else if (device instanceof ContinuousDimmer) {
System.out.println("@" + device.id + ":" + String.format("%.2f", ((ContinuousDimmer) device).position));
} else if (device instanceof Light) {
System.out.println("@" + device.id + ":" + ((Light) device).brightness);
} else if (device instanceof Fan) {
System.out.println("@" + device.id + ":" + ((Fan) device).speed);
} else if (device instanceof Curtain) {
System.out.println("@" + device.id + ":" + ((Curtain) device).openPercentage + "%");
}
}
}
public static Device createDevice(String deviceId) {
char deviceType = deviceId.charAt(0);
switch (deviceType) {
case 'K':
return new Switch(deviceId);
case 'H':
return new MutualExclusionSwitch(deviceId);
case 'F':
return new Dimmer(deviceId);
case 'L':
return new ContinuousDimmer(deviceId);
case 'B':
return new Light(deviceId, "incandescent");
case 'R':
return new Light(deviceId, "fluorescent");
case 'D':
return new Fan(deviceId, "ceiling");
case 'A':
return new Fan(deviceId, "floor");
case 'S':
return new Curtain(deviceId);
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown device type: " + deviceType);
}
}
}
收获与想法
另外这次大作业的新语法其实没有多少也就是类继承的运用,但特别考验对过去知识的掌握。
这次大作业对我的影响蛮大的,在往后的大作业的时候,我都将优先考虑对类的设计。
在这次大作业的完成后,我在思考将tool类的功能分散到其他的属性定义类中,再者我也注意到main方法中的排序算法可以独立,我也想将它里面的功能放在其他的类中,使其只承担调用方法的作用,更好的保持面向对象的编程语言的特点,也更方便迭代。
第八次大作业总结
这次大作业是本学期最后一次大作业,也是将本学期的知识结合的集大成者。但其实我在写这道题时我还是犯了难,我在之前的我对引脚这一感念不清,所以在之前的迭代中我都是尽量不去使用它,但在这次的迭代中却必须要输出引脚两端的电压,这使得我有些束手无策。所以我只能重新的去设计代码来实现引脚电压的输出。这也让我知道题目中的每一个细节都有可能成为题目的考点。这让我对设计一个工程时要更加的注重各方面的细节。
在其后的思考中我想出了一个方案,就是将每个电子元件再加上一个属性,其实是本元件所占有的电压。这样就可以顺藤摸瓜的找出每个引脚的电压了。而后就是多并联的问题,我是这样解决的:我将子并联电路单独的设立成一个集成的电子元件,这样就可以解决多并联电路的问题。
那就让我们来看看这次我的代码的圈复杂度吧
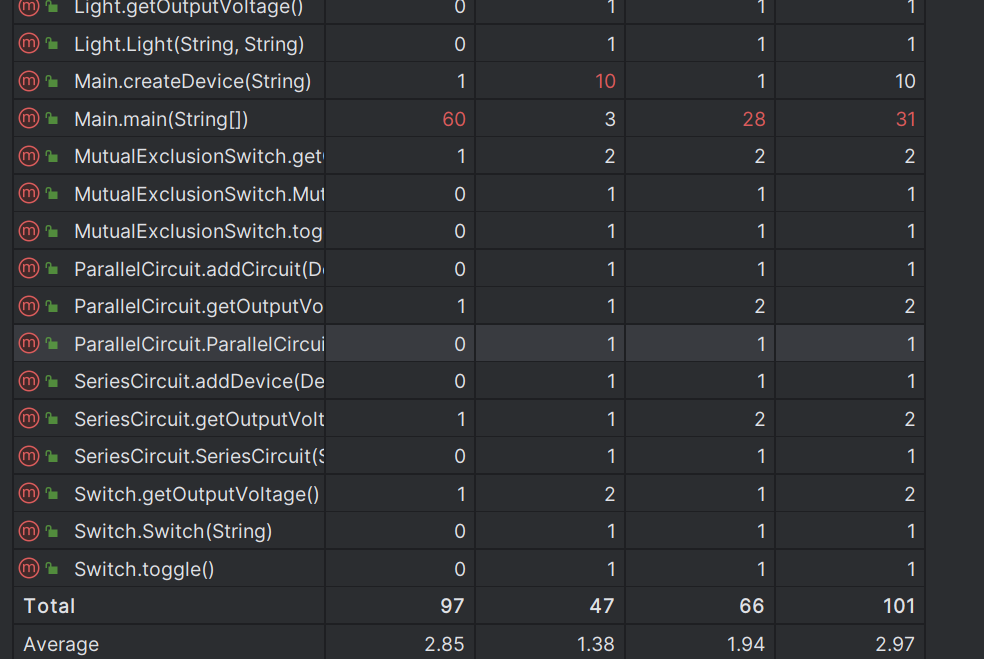
这次为了将引脚上的电压给输出,我费了许多的力气,所以没有太多的时间来琢磨如何将圈复杂度降低。这也算是我的失误吧。
接下是我对我代码的理解:
类定义:
CircuitElement:电路元件的基类,包含每个元件的基本属性,如标识符、类型、电阻、电压、电流和最大电流限制。
Switch:继承自CircuitElement,代表电路中的开关,具有开关状态和切换功能。
Diode:继承自CircuitElement,代表电路中的二极管,具有正向和反向接入状态。
Circuit:代表整个电路,包含所有电路元件和线路的集合,提供添加元件和线路的方法以及处理电路和打印状态的功能。
电路元件处理:
每个电路元件在创建时都会被添加到Circuit类的元件映射中,便于后续处理。
线路解析与处理:
该框架预留了process方法用于解析线路和计算电压电流,但具体实现需要根据电路的具体连接和规则来完成。
输出:
printStatus方法负责输出电路中每个元件的状态信息,包括元件类型、状态、电压、电流以及是否超出电流限制的错误提示。
主程序流程:
main方法读取用户输入,处理命令,添加线路和开关操作,最后处理电路并打印状态。
待完成和扩展的部分:
实现具体的线路解析逻辑,包括处理主线路和复线路、并联操作以及元件之间的电压和电流传递。
扩展更多的电路元件类,如互斥开关、白炽灯、日光灯等,并在CircuitElement基类中添加相应的计算方法。
添加操作指令的处理,如分档调速器和连续调速器的调节操作。
处理短路情况,检测无穷大电流并输出错误提示。
这些就是我的全部总结了.



