用个骰子
课程理解
再次翻阅
- 深入理解Java面向对象三大特性 封装 继承 多态
- UML类图(上):类、继承和实现
- UML类图几种关系的总结
大致理解:泛化,实现,依赖,关联,聚合,组合,之间的关系。以及类图的画法。理清关系,画好类图,这样会起到事半功倍的效果,对写程序的效率也有提高。
设计实现
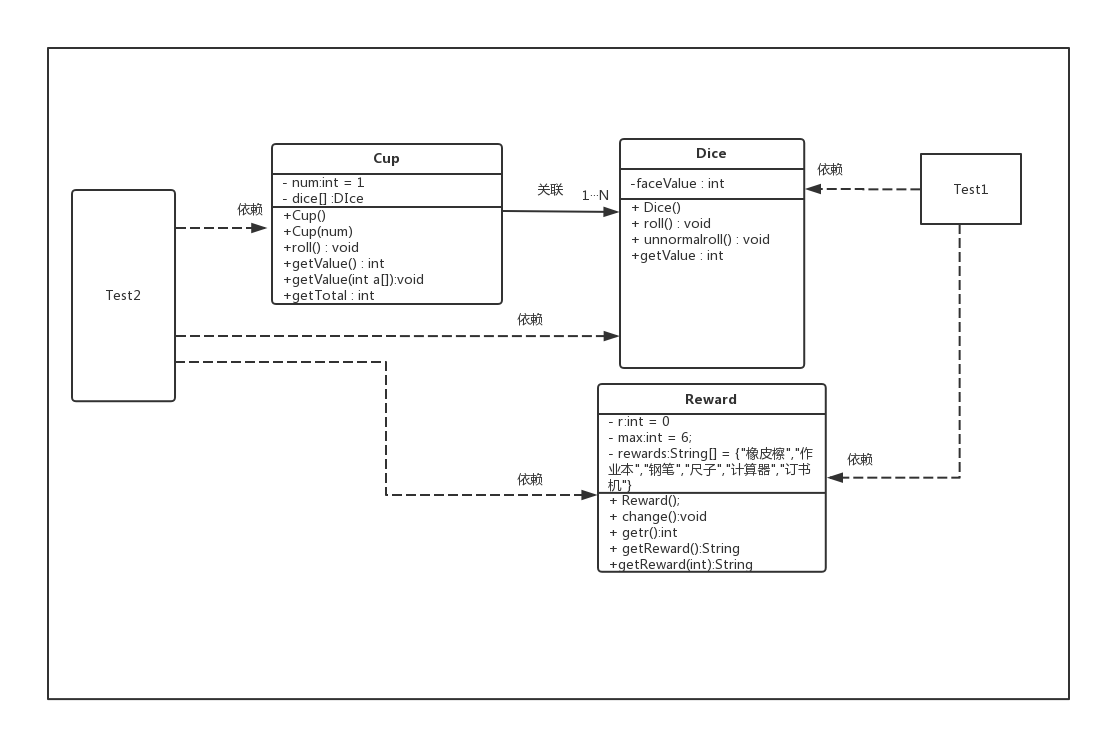
如图所示的各类间关系,当Test1(图形化)直接使用两个Dice类的方法;当Test2(控制台)通过使用骰盅Cup类调用Dice类的方法来随机选择学生,直接用Dice类随机选择奖品。
代码说明
1.Dice.java
//骰子类的实现
public class Dice {
private int faceValue; //定义骰子面值
public Dice(){
faceValue = (int)(Math.random() * 6) + 1; //获得一 个1-6的随机数
}
public void roll(){ //摇骰子
faceValue = (int)(Math.random() * 6) + 1;
}
public void unnormalroll(){ //摇不出4的骰子
while(faceValue==4){
faceValue = (int)(Math.random() * 6) + 1;
}
}
public int getValue(){ //获得骰子数值
return faceValue;
}
}
2.Cup.java
//骰盅类的实现:可以放入多个骰子。
public class Cup {
private int num=1;// num记录骰子的个数,默认为一个
private Dice dice[]; //声明骰子数组
public Cup(){ //往骰盅放入一个骰子
dice = new Dice[num];
}
public Cup(int num){ //往骰盅放入多个骰子
this.num = num;
dice = new Dice[num];
}
public void roll(){ //摇动骰盅
int i;
for(i=0;i<num;i++){
dice[i] = new Dice();
}
}
public int getValue(){ //一个骰子开盅看大小,并返回该数值
return (dice[0].getValue());
}
public void getValues(int a[]){ //多个骰子开盅看大小。并将每个骰子的数值通过整型数组传出
int i;
for(i = 0;i < num;i++)
a[i]=dice[i].getValue();
}
public int getTotal(){ //返回多个骰子的总数值
int sum=0,i;
for(i=0;i<num;i++){
sum += dice[i].getValue();
}
return sum;
}
}
3.Reward.java
public class Reward {
private int r =0;
private int max = 6;
String[] rewards ={"橡皮檫","作业本","钢笔","尺子","计算器","订书机"};
public Reward(){
r = (int)(Math.random() * (max-1) ) ; //获得一个0-(max-1)的随机数
}
public void change(){
r = (int)(Math.random() * (max-1) ) ;
}
public String getReward(){
return rewards[r];
}
public int getr(){
return r;
}
public String getReward(int num) {
return rewards[num];
}
}
4.Test1.java
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.Image;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.JEditorPane;
import java.awt.Canvas;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
public class Test1 {
private JFrame frame;
/**
* Launch the application.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
Test1 window = new Test1();
window.frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the application.
*/
public Test1() {
initialize();
}
/**
* Initialize the contents of the frame.*/
private void initialize() {
//Dice pdice = new Dice();
Reward reward = new Reward();
frame = new JFrame();
frame.setTitle("小公鸡点到谁");
frame.setResizable(false);
frame.setBounds(100, 100, 450, 300);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
ImageIcon[] image = new ImageIcon[15];
image[0] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\0.gif");
image[1] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\1.png");
image[2] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\2.png");
image[3] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\3.png");
image[4] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\4.png");
image[5] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\5.png");
image[6] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\6.png");
image[7] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\jl1.jpg");
image[8] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\jl2.jpg");
image[9] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\jl3.jpg");
image[10] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\jl4.jpg");
image[11] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\jl5.jpg");
image[12] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\jl6.jpg");
image[13] = new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\sorry.jpg");
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
frame.getContentPane().add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
panel.setLayout(null);
JLabel[] Jdice = new JLabel[2];
Jdice[0] = new JLabel(" ");
Jdice[0].setIcon(new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\0.gif"));
Jdice[0].setBounds(68, 14, 117, 111);
panel.add(Jdice[0]);
Jdice[1] = new JLabel(" ");
Jdice[1].setIcon(new ImageIcon("D:\\Desktop\\dice\\0.gif"));
Jdice[1].setBounds(257, 14, 117, 111);
panel.add(Jdice[1]);
JLabel pLabel = new JLabel(" ");
pLabel.setVisible(false);
pLabel.setBounds(68, 154, 225, 128);
panel.add(pLabel);
JLabel pLabel2 = new JLabel(" ");
pLabel2.setVisible(true);
pLabel2.setBounds(68, 104, 225, 128);
panel.add(pLabel2);
JLabel pLabel3 = new JLabel(" ");
pLabel3.setVisible(false);
pLabel3.setBounds(68, 14, 225, 111);
panel.add(pLabel3);
JButton usebutton = new JButton("开骰子"); //抽取一名学生
usebutton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
Dice[] dice = new Dice[2];
Jdice[0].setVisible(true);
Jdice[1].setVisible(true);
for(int i= 0;i < 2;i++){
dice[i] = new Dice();
Jdice[i].setIcon(image[dice[i].getValue()]);
}
pLabel2.setVisible(true);
pLabel2.setText("有请:第 " + dice[0].getValue() + " 组第 " + dice[1].getValue() +" 位同学上台回答问题");
}
});
usebutton.setBounds(18, 125, 93, 23);
panel.add(usebutton);
JButton retbutton = new JButton("重新摇"); //重置筛子
retbutton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Jdice[0].setIcon(image[0]);
Jdice[1].setIcon(image[0]);
Jdice[0].setVisible(true);
Jdice[1].setVisible(true);
pLabel.setVisible(false);
pLabel2.setVisible(false);
pLabel3.setVisible(false);
}
});
retbutton.setBounds(121, 125, 93, 23);
panel.add(retbutton);
JButton quebutton = new JButton("√"); //选取奖品
quebutton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Jdice[0].setVisible(false);
Jdice[1].setVisible(false);
pLabel.setVisible(true);
pLabel3.setVisible(true);
reward.change();
pLabel3.setIcon(image[reward.getr()+7]);
pLabel.setText("恭喜你答对了,奖励"+reward.getReward());
}
});
quebutton.setBounds(224, 125, 93, 23);
panel.add(quebutton);
JButton ansbutton = new JButton("×"); //答错了
ansbutton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Jdice[0].setVisible(false);
Jdice[1].setVisible(false);
pLabel.setVisible(true);
pLabel3.setVisible(true);
pLabel3.setIcon(image[13]);
pLabel.setText("很遗憾你答错了,再接再厉。");
}
});
ansbutton.setBounds(327, 125, 93, 23);
panel.add(ansbutton);
}
}
5.Test2.java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("小公鸡点到谁?");
int flag = 1;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Cup cup = new Cup(2);
int[] myValue = new int[2];
cup.roll();
cup.getValues(myValue);
do{
System.out.println("有请:第 " + myValue[0] + " 组第 " + myValue[1] +" 位同学上台回答问题");
flag = input.nextInt();
//判断正误,输入1正确,输入0错误
if(flag==1) {
Dice dice = new Dice();
Reward reward = new Reward();
reward.change();
System.out.println("恭喜你答对了,奖励"+reward.getReward());
}else{
System.out.println("很遗憾你答错了,再接再厉");
}
System.out.println("1--继续,0--结束");
flag = input.nextInt();
}while(flag==1);
}
}
测试运行
1.图形化界面




2.控制界面

总结
对于的图形化的界面接触较少,预估完成控制台界面30分,而图形化界面只能一脸懵懂的状态,最后参照@稽美大学小学生 大佬的程序,模仿着弄出一个小成品。总的来说,大致一个下午的时间,在模仿着弄出的时间比较多。

