第1次作业
要求0:作业要求地址:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/nenu/2016CS/homework/2110
要求1:GIT仓库地址:https://git.coding.net/wudb527/wf.git (master2为中间的过程,V1.0为最终提交的版本,随后对V1.0和主分支master进行了合并)
要求2:PSP阶段表格
| SP2.1 | 预估时间600(min) | 实际开发时间1043(min) |
| 计划 | 20 | 40 |
| ·明确需求和其他相关因素,估计每段时间成本 | 20 | 40 |
| 开发 | 490 | 903 |
| ·需求分析 | 20 | 60 |
| ·生成设计文档 | 30 | 0 |
| ·设计复审(和同学审核设计文档) | 20 | 0 |
| ·代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 30 |
| ·具体设计 | 50 | 60 |
| ·具体编码 | 300 | 673 |
| ·代码复审 | 20 | 40 |
| ·测试(自测、修改代码、提交修改) | 40 | 40 |
| 报告 | 90 | 100 |
| ·测试报告 | 30 | 35 |
| ·计算工作量 | 30 | 35 |
| ·事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 40 |
| 功能模块 | 具体阶段 | 预计时间(min) | 实际时间(min) |
| 功能1 | 具体设计 | 15 | 20 |
| 具体编码 | 50 | 130 | |
| 测试完善 | 10 | 12 | |
| 功能2 | 具体设计 | 15 | 20 |
| 具体编码 | 70 | 246 | |
| 测试完善 | 15 | 13 | |
| 功能三 | 具体设计 | 20 | 20 |
| 具体编码 | 180 | 290 | |
| 测试完善 | 15 | 15 |
分析差距原因:
(1):没有完全按照软件开发的流程来,比如因为感觉是小程序,设计文档就没有做,虽然这一项我没有花时间,但是实际中我却在其他地方饶了弯路。
(2):我对C++的语法没有足够的熟悉,有些数据类型的内置函数不够了解(比如string.c_str()),导致在应用的时候还要上网查询。
(3):在之前没有对题目要求做足够的了解,导致,一边写代码还要返回去看题目要求,花费了不少时间。
要求3:
1.解题思路描述
我觉得这个程序的流程大概就是读取文件获得字符串,然后对字符串进行操作获得符合题目要要求的字符,而后进行字符串计数,然后按照题目要求输出就可以了。当第一眼看到这个题目的时候我觉得难点在打开文件、路径输入保存以及进行文件夹下的文件查询,而重点点我觉得有正则表达式的应用。我一开始就打算用C++里STL里面的map容器来实现字符串的计数。但是文件的打开以及文件夹下面的文件读取卡了不少时间,本来打算用C的fopen实现,但是fopen打开文件后获得是字符数组,我打算用string类型保存的单词的,所以还要把字符数组转为字符串,有点繁琐,后来我查找资料知道了C++的文件流,这是一大突破,而在文件夹内部的文件遍历上我查资料知道了 _findfirst()函数可以实现问价的查询。
2.代码解释
难点1:文件的打开
用文件流的话,我们使用流提取运算符( >> )从文件读取信息,就像使用该运算符从键盘输入信息一样。唯一不同的是,在这里您使用的是 ifstream 或 fstream 对象,而不是 cin 对象。
下面是文件流的使用方法,用于对某一个文件进行读取然后输出。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<fstream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 // 以读模式打开文件 7 ifstream infile; 8 string path = "D:\\codeblocks\\wf\\input.txt"; 9 //打开文件 10 infile.open(path.c_str()); 11 //括号里应该是字符串类型,所以要用到string.c_str()进行转换 12 string str; 13 while(infile>>str) 14 { 15 cout<<str<<endl; 16 } 17 return 0; 18 }
难点2:路径内文件夹的遍历,文件的查找
_findfirst是按照文件名的字典序查找的,所以题目要求的文件名排序问题直接解决了,只要能找到文件那就是符合要求的。
这两个函数均在io.h里面。
首先了解一下一个文件结构体:
struct _finddata_t {
unsigned attrib;
time_t time_create;
time_t time_access;
time_t time_write;
_fsize_t size;
char name[260];
};
time_t,其实就是long
而_fsize_t,就是unsigned long
现在来解释一下结构体的数据成员吧。
attrib,就是所查找文件的属性:_A_ARCH(存档)、_A_HIDDEN(隐藏)、_A_NORMAL(正常)、_A_RDONLY(只读)、_A_SUBDIR(文件夹)、_A_SYSTEM(系统)。
time_create、time_access和time_write分别是创建文件的时间、最后一次访问文件的时间和文件最后被修改的时间。
size:文件大小
name:文件名。
再来看一下_findfirst函数:long _findfirst(const char *, struct _finddata_t *);
第一个参数为文件名,可以用"*.*"来查找所有文件,也可以用"*.cpp"来查找.cpp文件。第二个参数是_finddata_t结构体指针。若查找成功,返回文件句柄,若失败,返回-1。
然后,_findnext函数:int _findnext(long, struct _finddata_t *);
第一个参数为文件句柄,第二个参数同样为_finddata_t结构体指针。若查找成功,返回0,失败返回-1。
最后:_findclose()函数:int _findclose(long);
只有一个参数,文件句柄。若关闭成功返回0,失败返回-1。
资料源自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_67e046d10100jwdo.html
下面是小的使用方法:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<io.h>//_findfirst的头文件 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 string path = "D:\\codeblocks\\wf\\"; 7 path += "*.txt";//.txt是文件类型 8 _finddata_t openfile; 9 long HANDLE;//_findfirst的返回值,若找到为0,找不到为-1 10 HANDLE = _findfirst( path.c_str(), &openfile ); 11 string file_name = openfile.name;//openfile的name成员是找到的文件名 12 cout<<file_name<<endl; 13 return 0; 14 }
难点3:把一行字符串按照空格分割开来
在这里我想到了stringstream来进行数据流的重定向。下面是我对stringstream的测试:
#include<iostream> #include<sstream>//stringstream的头文件 using namespace std; int main() { string str = "aaa bbb ccc ddd eee fff"; stringstream ss(str); string t; while(ss>>t) cout<<t<<endl; return 0; }
输出为:
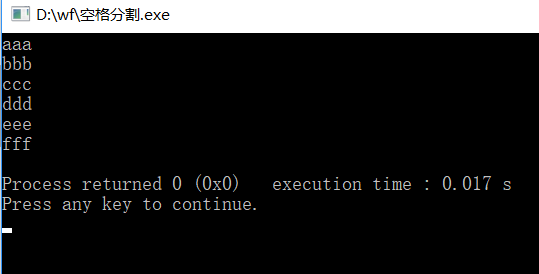
可以看到实现了用空格分割字符串。
要点1:由于功能1在输出时要求与输入时的顺序一致,所以我用一个vector<string>依次保存了输入时的字符串。在输出时只要依次取出即可。
1 vector<string>Vstr; 2 map<string,int>Map; 3 int Max_wordsize = 0; 4 while(ss>>str) 5 { 6 if(str[0] >= '0' && str[0] <= '9') continue; 7 Max_wordsize = Max(Max_wordsize,str.size());//寻找最长单词的长度 8 if(Map[str] == 0) Vstr.push_back(str);//把每一个单词不重复的保存起来 9 Map[str]++; 10 }
要点2:功能2在输出时要求字符串按照字典序输出,所以要对vector进行排序,我自定义了cmp函数。
1 bool cmp2(string a, string b) 2 { 3 return a < b; 4 }
sort(Vstr.begin(),Vstr.end(),cmp2);
要点3:在功能3输出时,要求先按照单词数量降序排序,对于数量一致的再按照单词的字典序升序排序,所以我构建了结构体,里面有成员str和num,然后在功能3中把每个结构踢对象存入vector中,然后自定义排序函数。
struct Node { string str; int num; };
1 for(int i = 0; i < total;++i) 2 { 3 node.str = Vstr[i]; 4 node.num = Map[Vstr[i]]; 5 V_node.push_back(node); 6 }
vector<Node>V_node; ///////////// bool cmp3(Node a, Node b) { if(a.num == b.num) return a.str < b.str; return a.num > b.num; } ///////////////////////// sort(V_node.begin(),V_node.end(),cmp3);
(1)下面是我的完整代码,对功能1,功能2,功能3的判别是根据控制台输入的字符串个数,如果是5段那肯定是功能3,如果不是那就是功能1或功能2,然后查询是有-c还是-f即可判断。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<map> 3 #include<vector> 4 #include<sstream> 5 #include<string> 6 #include<fstream> 7 #include<cstring> 8 #include<cstdio> 9 #include<cstdlib> 10 #include<algorithm> 11 #include<io.h> 12 using namespace std; 13 int Max(int a,int b) 14 { 15 return a > b ? a : b; 16 } 17 int Min(int a,int b) 18 { 19 return a < b ? a : b; 20 } 21 struct Node 22 { 23 string str; 24 int num; 25 }; 26 bool Get_FileName(string Path_Name,string &File_Name) 27 { 28 struct _finddata_t FileInfo; 29 long Handle; 30 Handle = _findfirst((Path_Name+"\\*.txt").c_str(),&FileInfo);//对文件夹下的文件筛选出.txt文件 31 if(Handle == -1) return 0; 32 else 33 { 34 string temp = FileInfo.name; 35 File_Name = Path_Name + "\\" + temp; 36 return true; 37 } 38 } 39 bool cmp2(string a, string b) 40 { 41 return a < b; 42 } 43 bool cmp3(Node a, Node b) 44 { 45 if(a.num == b.num) return a.str < b.str; 46 return a.num > b.num; 47 } 48 void solve(string File_Name,int num)//实际执行文件打开和输出的函数,num = 5为功能2,num= -1 为功能1,num= -2为功能2 49 { 50 ifstream infile; 51 string file_txt = "",str; 52 infile.open(File_Name.c_str());//打开文件 53 while(getline(infile,str)) 54 { 55 file_txt = file_txt + str + ' '; 56 } 57 infile.close(); 58 for(string::iterator it = file_txt.begin();it < file_txt.end();it++)//把大写转为小写,并且把非字母数字转为空格 59 { 60 if(*it >='A'&&*it<='Z') *it += 32; 61 else if(*it >='a' && *it <='z') continue; 62 else if(*it >='0' && *it <='9') continue; 63 else *it = ' '; 64 } 65 stringstream ss(file_txt); 66 vector<string>Vstr; 67 map<string,int>Map; 68 int Max_wordsize = 0; 69 while(ss>>str) 70 { 71 if(str[0] >= '0' && str[0] <= '9') continue; 72 Max_wordsize = Max(Max_wordsize,str.size());//寻找最长单词的长度 73 if(Map[str] == 0) Vstr.push_back(str);//把每一个单词不重复的保存起来 74 Map[str]++; 75 } 76 int total = Vstr.size(); 77 if(num == -1)//功能1 78 { 79 cout<<"total"<<" "<<total<<endl; 80 cout<<endl; 81 for(int i = 0;i < total;i++) 82 { 83 cout<<Vstr[i]; 84 int wordsize = Vstr[i].size(); 85 for(int j = 1; j <= Max_wordsize - wordsize;++j) cout<<" "; 86 cout<<" "<<Map[Vstr[i]]<<endl; 87 } 88 } 89 else if(num == -2)//功能2 90 { 91 cout<<"total"<<" "<<total<<" word"; 92 if(total > 1) cout<<'s'; 93 cout<<endl; 94 sort(Vstr.begin(),Vstr.end(),cmp2); 95 for(int i = 0;i < total;i++) 96 { 97 cout<<Vstr[i]; 98 int wordsize = Vstr[i].size(); 99 for(int j = 1; j <= Max_wordsize - wordsize;++j) cout<<" "; 100 cout<<" "<<Map[Vstr[i]]<<endl; 101 } 102 } 103 else//功能3 104 { 105 Max_wordsize = 0; 106 cout<<"Total word"; 107 if(total > 1) cout<<'s'; 108 cout<<" is "<<total<<endl; 109 cout<<"----------"<<endl; 110 vector<Node>V_node; 111 Node node; 112 for(int i = 0; i < total;++i) 113 { 114 node.str = Vstr[i]; 115 node.num = Map[Vstr[i]]; 116 V_node.push_back(node); 117 } 118 sort(V_node.begin(),V_node.end(),cmp3); 119 num = Min(num,total); 120 for(int i = 0; i < num;++i) 121 { 122 Max_wordsize = Max(V_node[i].str.size(),Max_wordsize); 123 } 124 for(int i = 0;i < num;++i) 125 { 126 cout<<V_node[i].str; 127 int wordsize = V_node[i].str.size(); 128 for(int j = 1; j <= Max_wordsize - wordsize;++j) cout<<" "; 129 cout<<" "<<V_node[i].num<<endl; 130 } 131 } 132 133 } 134 int main() 135 { 136 string str_input,Path_Name,File_Name;//控制台输入的内容,实际路径,实际文件名 137 bool havePath = false,haveFile = false;//判断是有路径还是有文件名 138 getline(cin,str_input); 139 vector<string>input; 140 stringstream ss(str_input);//对控制台输入的文字按照空格分割 141 string str; 142 while(ss>>str) 143 { 144 if(str == "-c") haveFile = true;//判断是否有文件名 145 if(str == "-f") havePath = true;//判断是否有判断是否有路径 146 input.push_back(str); 147 } 148 int len = input.size(); 149 if(havePath)//如果存在的是路径 150 { 151 152 for(int i = 0;i < len;i++) 153 { 154 if(input[i] == "-f") {Path_Name = input[i+1];break;} 155 } 156 string temp = ""; 157 //因为C++'\'的转义 158 for(string::iterator it = Path_Name.begin();it < Path_Name.end();it++) 159 { 160 if(*it == '\\') temp += "\\"; 161 else temp+=*it; 162 } 163 Path_Name = temp; 164 bool is = Get_FileName(Path_Name,File_Name);//获取文件名 165 if(is == false) {cout<<"路径下找不到.txt文件!"<<endl;return 0;}//获取失败,输出 166 } 167 else 168 { 169 for(int i = 0;i < len;i++) 170 { 171 if(input[i] == "-c") {File_Name = input[i+1];break;} 172 } 173 } 174 int num; 175 if(len == 5) 176 { 177 for(int i = 0;i < len ;i++) 178 if(input[i] == "-n") 179 num = atoi(input[i+1].c_str()); 180 } 181 else 182 { 183 if(str_input.find("-c") != string::npos) num = -1; 184 else num = -2; 185 } 186 solve(File_Name,num); 187 return 0; 188 } 189 /* 190 wf -f D:\codeblocks\wf 191 wf -f D:\codeblocks\wf -n 3 192 */
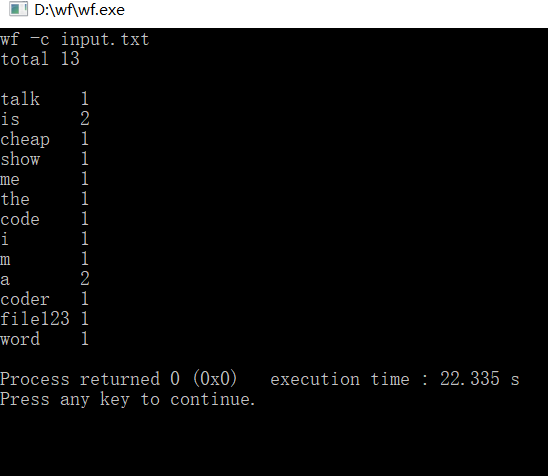
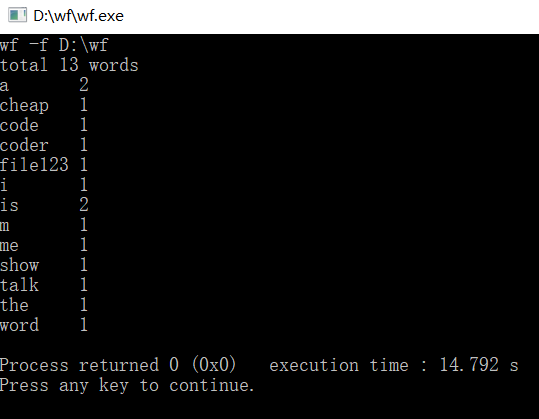
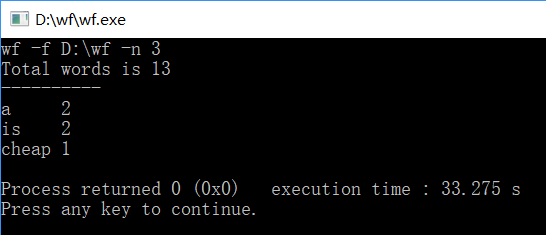
(2)功能测试:注:功能3四种输入均进行了测试
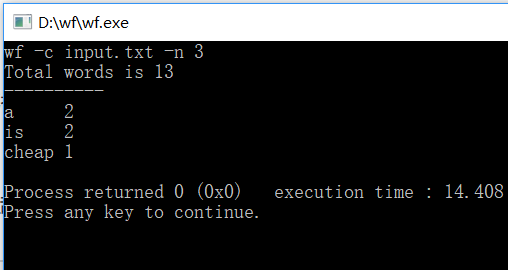
功能1:
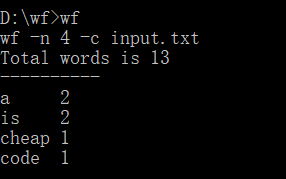
功能2:
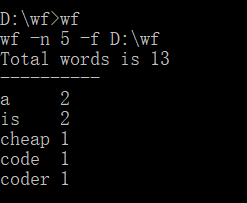
功能3:
对四种输入均进行了测试,均能实现
(3)自认为题目中的小细节
1)在输出时单词 word 后面有没有s,我注意到了这个问题,所以我对单词进行了计数,若大于1就加s。
if(total > 1) cout<<'s';
2)对单词数一列的对齐,我用一个变量维护了最大单词长度,然后在输出时对于其他单词,长度比他小几个我就补几个空格,这样就实现了对齐。
1 int Max_wordsize = 0; 2 while(ss>>str) 3 { 4 if(str[0] >= '0' && str[0] <= '9') continue; 5 Max_wordsize = Max(Max_wordsize,str.size());//寻找最长单词的长度 6 if(Map[str] == 0) Vstr.push_back(str);//把每一个单词不重复的保存起来 7 Map[str]++; 8 }
输出时
1 if(num == -1)//功能1 2 { 3 cout<<"total"<<" "<<total<<endl; 4 cout<<endl; 5 for(int i = 0;i < total;i++) 6 { 7 cout<<Vstr[i]; 8 int wordsize = Vstr[i].size(); 9 for(int j = 1; j <= Max_wordsize - wordsize;++j) cout<<" ";//补充空格 10 cout<<" "<<Map[Vstr[i]]<<endl; 11 } 12 }
(4)对于这次作业我自己的心得:
1)在这次作业的过程中我对自己比较满意的是在正式编码前将 文件打开、指定路径下文件查询、怎样用空格分开字符串,其实在这里面花费时间是最大的,我庆幸我这么做了,如果一开始就正式编码、遇到困难然后去搜寻,那么可能你已经写了很多了,然后如果对新的用法不熟悉,编译会报错,debug会很困难,而我在编码前就通过小实验熟悉了操作,所以在正式编码时debug几乎没有花费多少时间,这算我的一个收获吧!虽然这次我没有犯这个错误但我还是要打好预防针。
2)而不足就是编码前没有足够了解问题,导致频繁去看问题,浪费了不少时间。就构建之法中的软件开发流程而言就不够合格,这次让我意识到麻雀虽小但也五脏俱全,小的软件项目也应该按照流程走,这样表面上花费了时间,但是在总体来看是节省不少时间。
3)GIT并没有那么简单,本以为只要了解了那几个语句就可以了,但是在push是发生了不少错误,查了不少资料才解决。其实C++等语言学习也是一样的,那些语法学习其实是最基础的,然后就是怎样进行组合会什么功能,在升级就是对于各种报错的解决,这一点是没有捷径的,只有长时间的练习才能解决,没有学习是一蹴而就的。






