C# 预处理器指令
C# 预处理器指令
概述
预处理器指令:是编程语言中的一种特殊语法,用于在源代码编译之前对代码进行预处理。
C# 预处理器指令 与 C/C++ 预处理器指令的区别
1. C# 不支持宏定义
C# 的预处理器指令主要用于条件编译,不支持像 C/C++ 那样的宏定义。
C# 示例:
#define DEBUG using System; class Program { static void Main() { #if DEBUG Console.WriteLine("Debug mode is enabled."); #else Console.WriteLine("Release mode is enabled."); #endif } }
C/C++ 示例:
#define PI 3.14159 #define MAX(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)) int main() { double radius = 5.0; double area = PI * radius * radius; // 使用宏定义的 PI int x = 10, y = 20; int maxValue = MAX(x, y); // 使用宏定义的 MAX 函数 return 0; }
2. C# 预处理器指令必须独占一行
在 C# 中,预处理器指令必须独占一行,不能与其他代码混合在同一行。
C# 示例:
#define DEBUG int radius = 5.0;
C/C++ 示例:
#define PI 3.14159 int radius = 5.0; // 不推荐,尽管编译器可能接受
3. C# 不支持文件包含指令
C# 不支持 #include 指令,使用 using 指令来引入命名空间。
C# 示例:
using System; class Program { static void Main() { Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!"); } }
C/C++ 示例:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> int main() { std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl; std::vector<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; for (int number : numbers) { std::cout << number << std::endl; } return 0; }
4. C# 编译器直接处理
C# 编译器没有独立的预处理器,但编译器在编译过程中会直接处理预处理器指令。
在 C/C++ 中,预处理器是一个独立的工具,负责在编译之前处理源代码。
指令
可为空上下文
#nullable指令用于控制代码中的可空上下文。
1. #nullable disable
- 在此指令之后的代码中,可空性检查将被禁用
#nullable disable 会同时禁用可空性注释(annotations)和可空性警告(warnings)
#nullable disable
默认是启用可空性检查的:
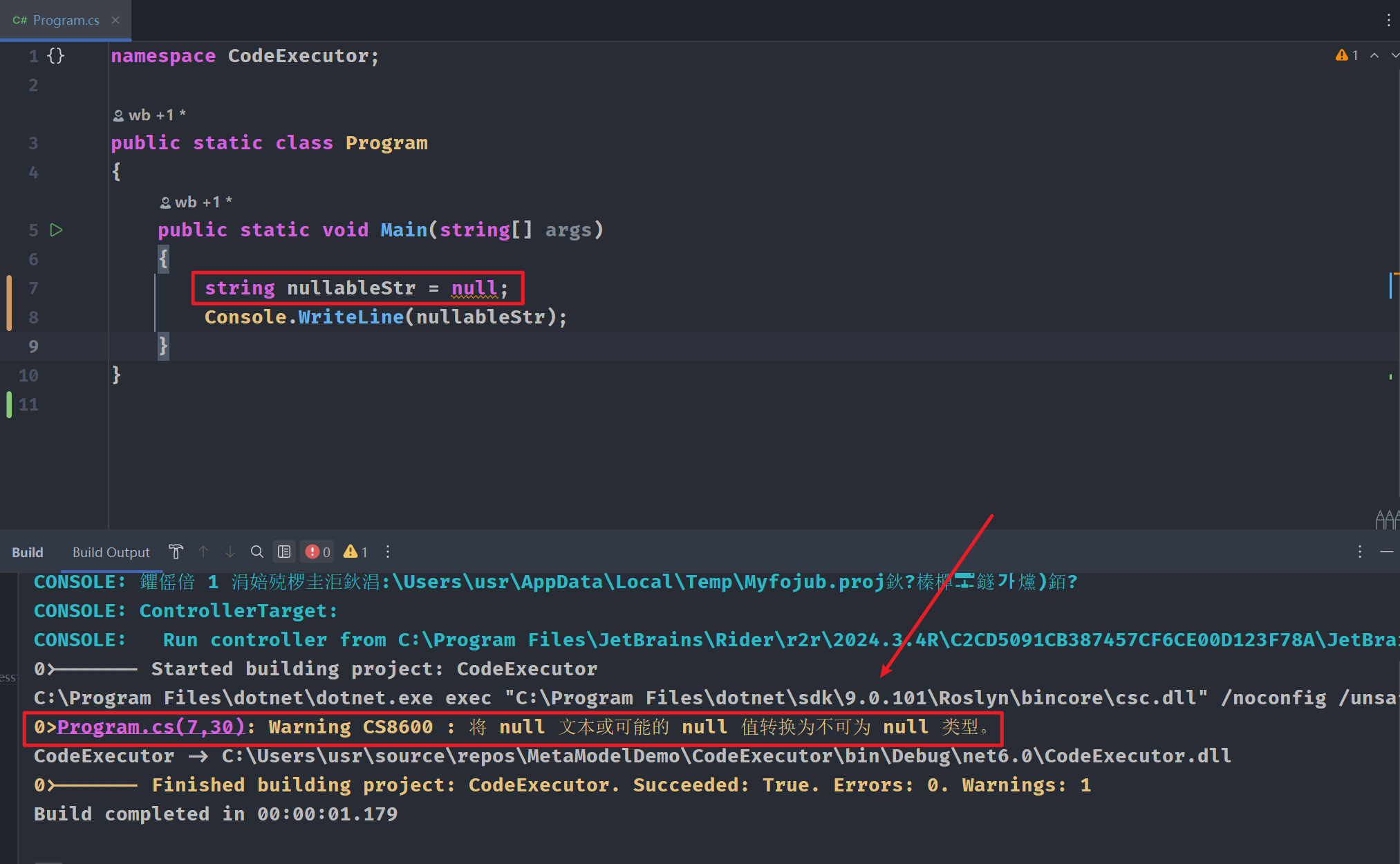
我们添加#nullable disable指令后:
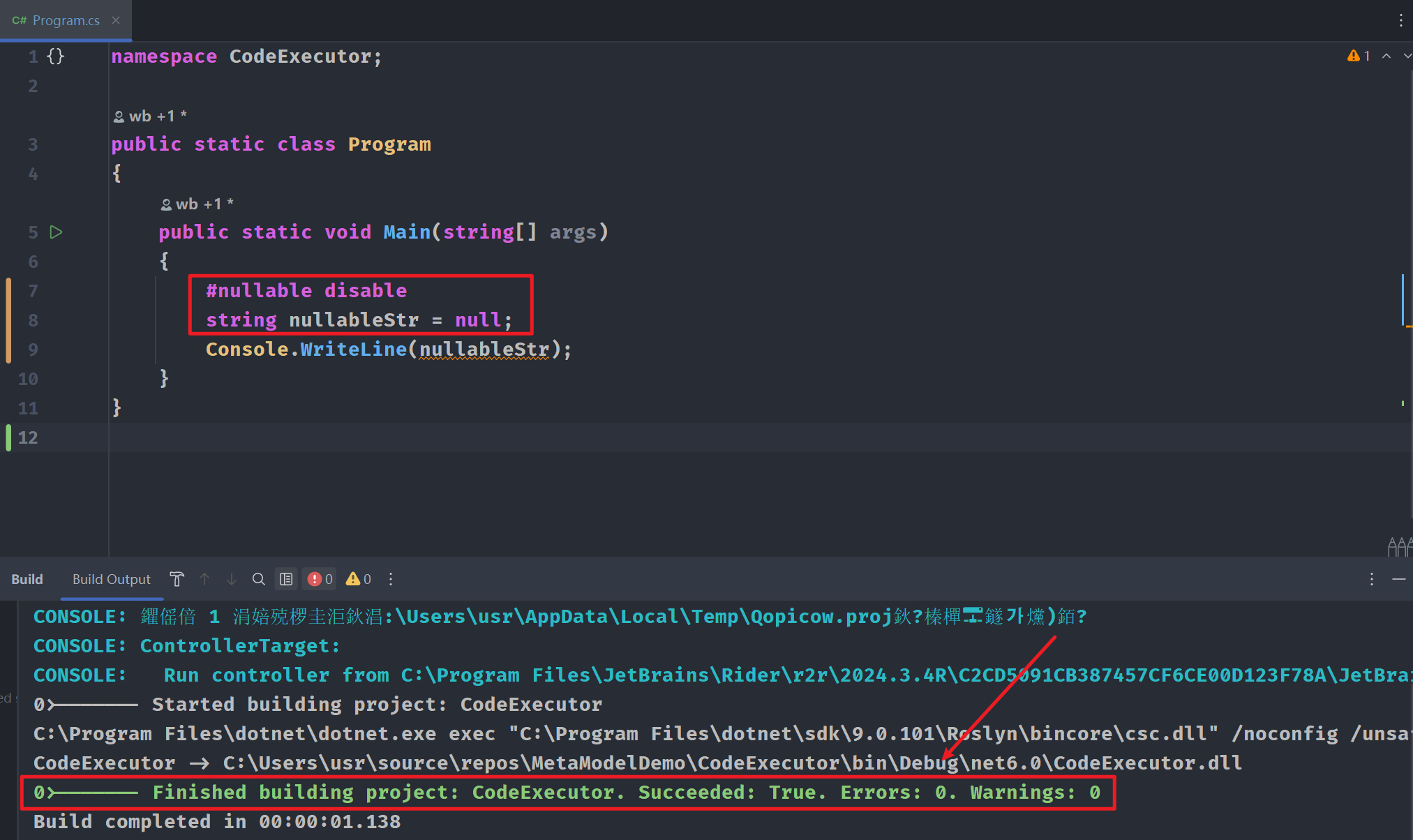
- 在此指令之后的代码中,可空注释将被忽略
#nullable disable annotations
- 在此指令之后的代码中,可空性相关的警告将被禁用
#nullable disable warnings
我们添加#nullable disable warnings指令后:
2. #nullable enable
- 在此指令之后的代码中,可空性检查将被启用
#nullable enable 会同时启用可空性注释(annotations)和可空性警告(warnings)
#nullable enable
- 在此指令之后的代码中,可空注释将被启用
#nullable enable annotations
- 在此指令之后的代码中,可空性相关的警告将被启用
#nullable enable warnings
3. #nullable resotre
- 在此指令之后的代码中,可空性检查将遵循项目的默认设置
#nullable resotre 会同时设置可空性注释(annotations)和可空性警告(warnings)遵循项目的默认设置
#nullable resotre
- 在此指令之后的代码中,可空注释将遵循项目的默认设置
#nullable resotre annotations
- 在此指令之后的代码中,可空性相关的警告将遵循项目的默认设置
#nullable resotre warnings
条件编译指令
条件编译指令有:#if、#else、#elif、#elseif、#endif、#define、#undef
-
#if- 用于开始一个条件编译块。
- 必须与
#endif配对使用,以明确结束条件编译块。
#define DEBUG #if DEBUG Console.WriteLine("DEBUG"); #endif
-
#else- 用于提供一个替代代码块,当 #if 条件不满足时执行。
- 必须紧跟在 #if 或 #elif 后面。
#if DEBUG Console.WriteLine("DEBUG"); #else Console.WriteLine("NOT DEBUG"); #endif
-
#elif- 等效于 else if,用于提供多个条件分支。
- 可以有多个 #elif,但必须紧跟在 #if 或另一个 #elif 后面。
#define VC7 #if DEBUG Console.WriteLine("DEBUG"); #elif VC7 Console.WriteLine("VC7"); #endif
-
#endif- 标记一个条件编译块的结束。
- 每个 #if 必须有一个对应的 #endif。
#define DEBUG #if DEBUG Console.WriteLine("DEBUG"); #endif
-
#define- 定义一个符号,在后续的条件编译中该符号被视为 true。
#define DEBUG
- 必须出现在文件中所有非预处理器指令之前。
#define DEBUG #undef TRACE using System; public class TestDefine { public static void Main() { #if DEBUG Console.WriteLine("DEBUG"); #endif #if TRACE Console.WriteLine("TRACE"); #endif } }
可以使用运算符 == (相等)、!= (不相等)、&&(和)、||(或)以及 !(非)运算符来计算符号是否定义。
例如:
#define VC7 using System; public class Program { public static void Main() { #if (VC7 || DEBUG) Console.WriteLine("VC7 or DEBUG is defined"); #endif } }
-
#undef- 删除一个已定义的符号,在后续的条件编译中该符号被视为 false。
#undef DEBUG
- 必须出现在文件中所有非预处理器指令之前。
#undef DEBUG using System; public class TestUndef { public static void Main() { #if DEBUG Console.WriteLine("DEBUG"); #else Console.WriteLine("NOT DEBUG"); #endif } }
代码组织指令
代码组织指令有:#region、#endregion
用于将代码逻辑分组,便于折叠和展开代码块,提高代码可读性。
#region para private static readonly int _count = 100; #endregion #region func private static void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); } #endregion
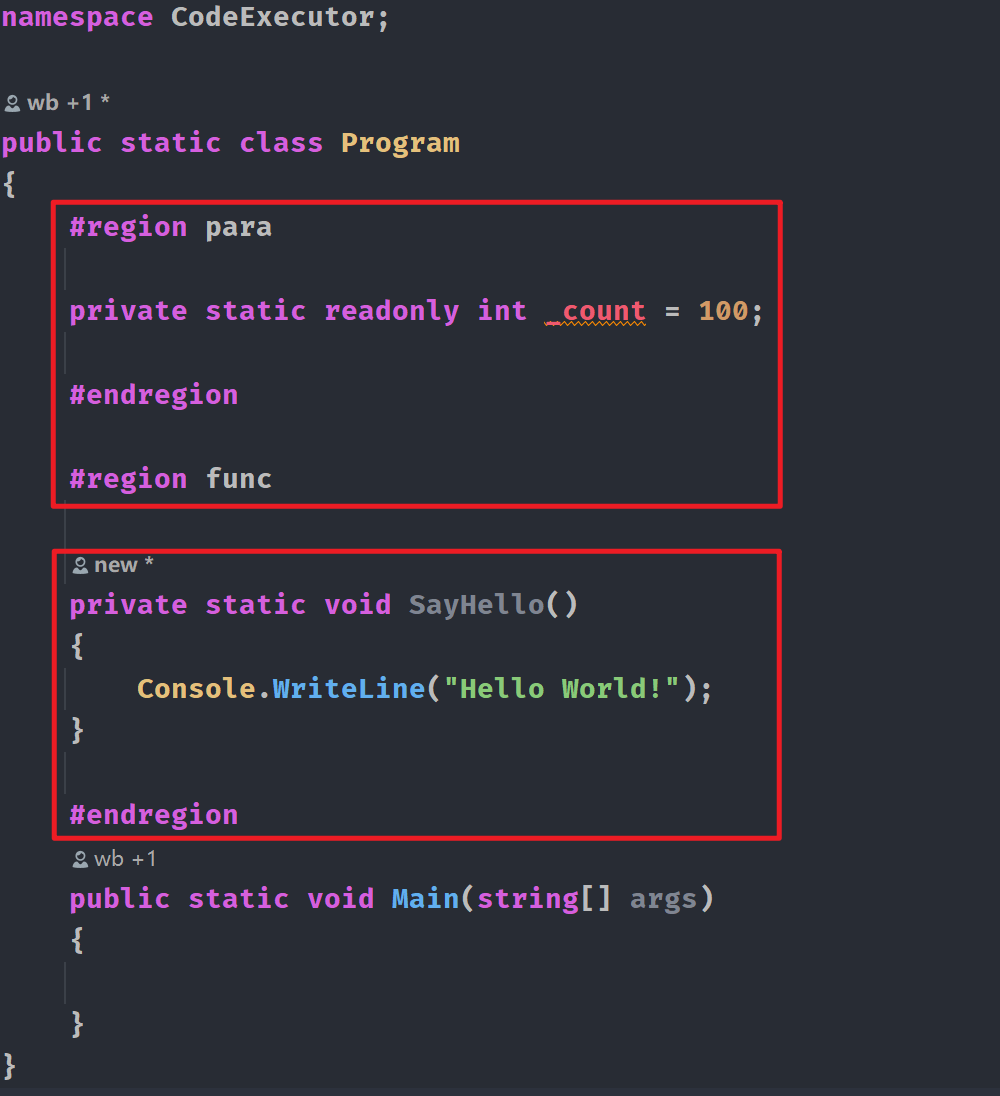
在编译器中可以折叠代码区域

警告和错误指令
警告和错误指令有:#warning、#error、#line
-
#warning- 在编译时生成警告信息。
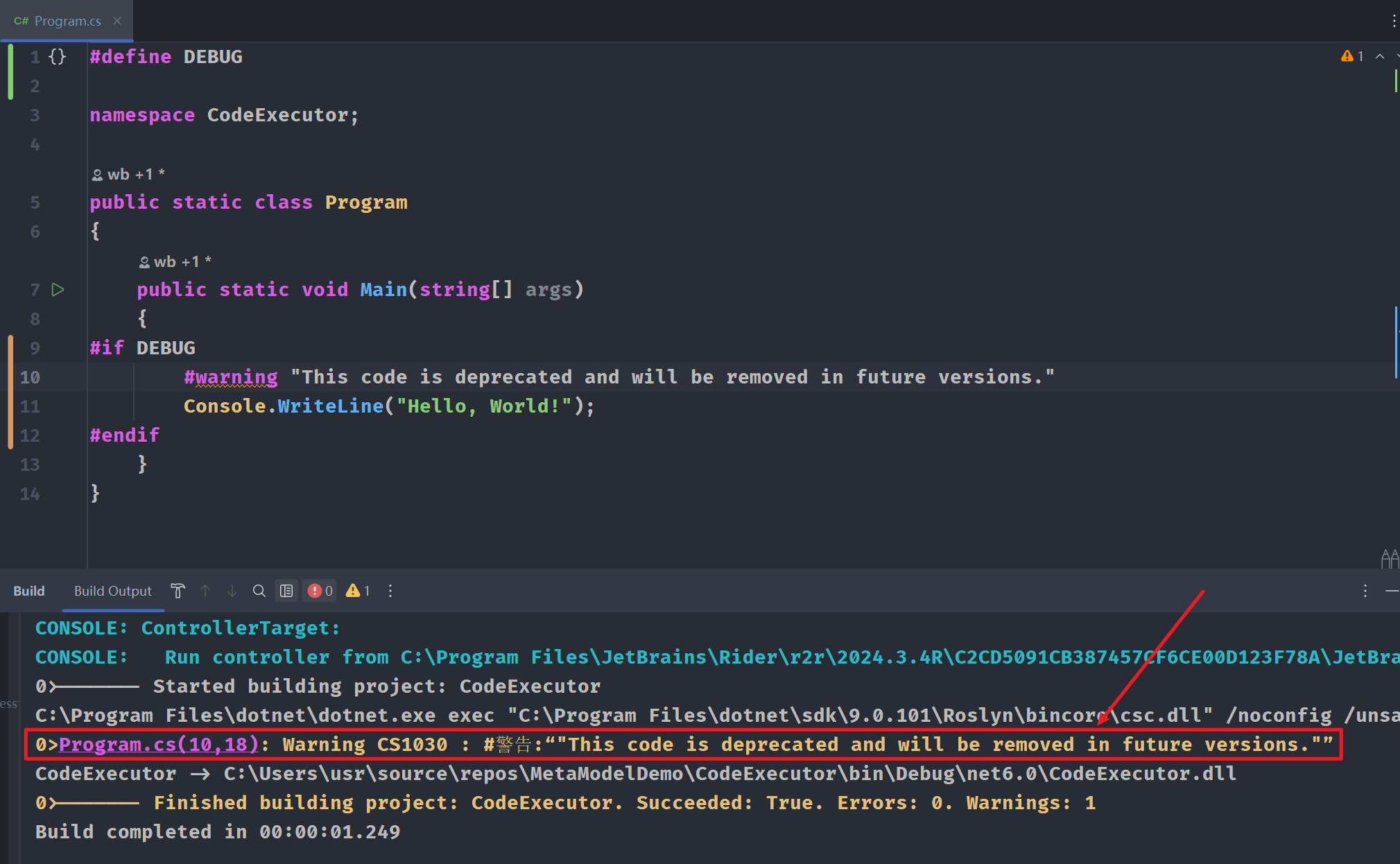
#warning "This code is deprecated and will be removed in future versions."
- 调试代码
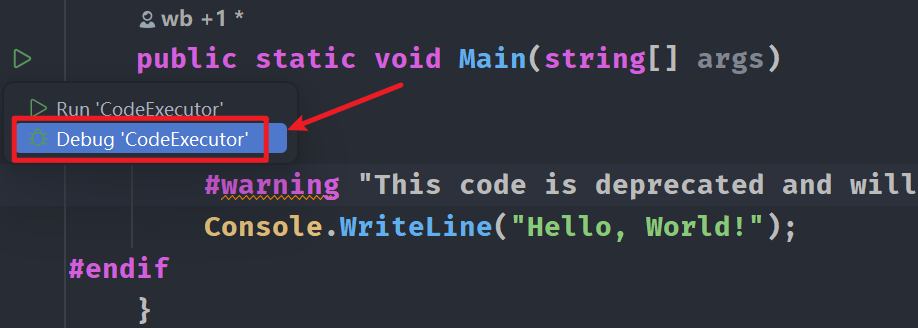
- 在构建输出窗口中给出警告信息
-
#error- 在编译时生成错误信息,阻止编译继续。
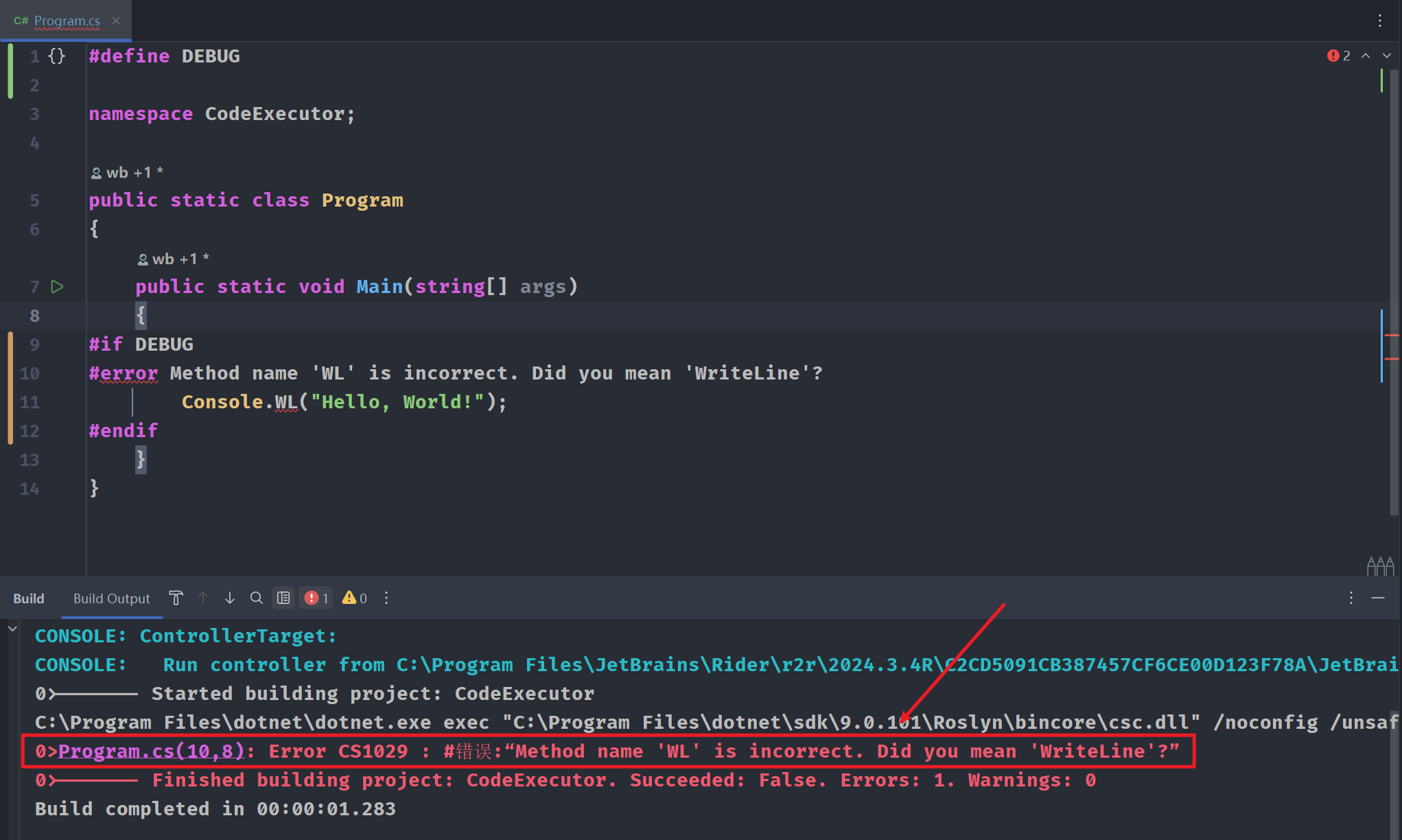
#error "This feature is not supported in this environment."
调试代码,在构建输出窗口中给出错误信息
-
#line- 用于修改调试器显示的行号信息,常用于生成代码或宏扩展。
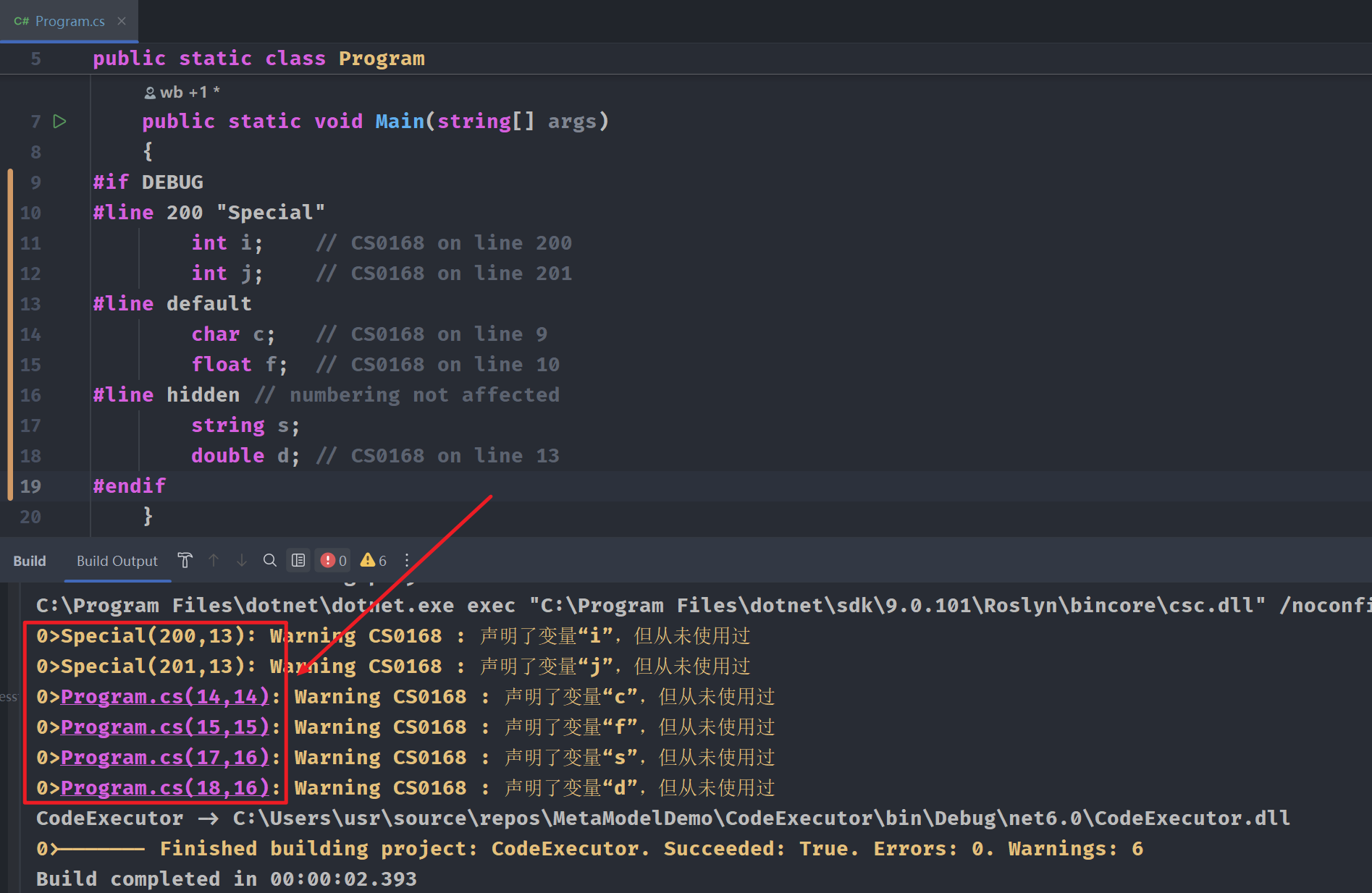
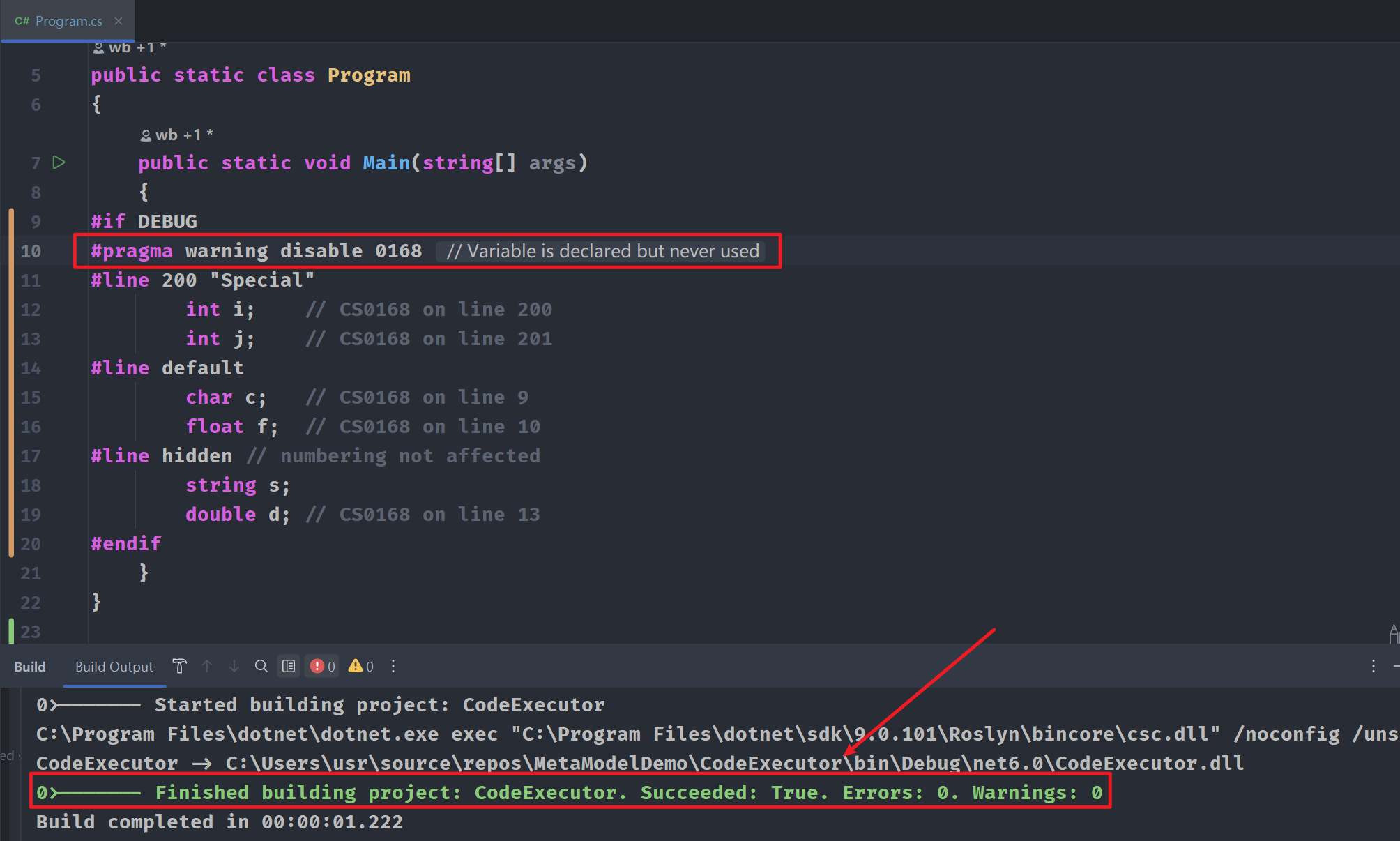
#line 200 "Special" int i; // CS0168 on line 200 int j; // CS0168 on line 201 #line default char c; // CS0168 on line 9 float f; // CS0168 on line 10 #line hidden // numbering not affected string s; double d; // CS0168 on line 13
调试代码,在构建输出窗口中给出警告信息
编译器指令
#pragma 为编译器提供特殊的指令,以说明如何编译包含杂注的文件。
Microsoft C# 编译器支持以下两个 #pragma 指令:
-
#pragma warning -
#pragma checksum
#pragma 指令的语法为:
#pragma pragma-name pragma-arguments
-
pragma-name:识别杂注的名称。warning/checksum
-
pragma-arguments:特定于杂注的参数。
#pragma warning
语法:
#pragma warning disable warning-list #pragma warning restore warning-list
参数:
warning-list // 警告编号的逗号分隔列表。只输入数字,不包括前缀 "CS"。
当没有指定警告编号时,disable 禁用所有警告,而 restore 启用所有警告。
#pragma checksum
该指令用于在编译时为源文件生成校验和信息,这些信息会被嵌入到程序数据库(PDB)文件中。校验和信息主要用于调试器,以确保调试器加载的源代码与编译时的源代码一致。
语法:
#pragma checksum "filename" "{guid}" "checksum bytes"
参数:
"filename" // 要求监视更改或更新的文件的名称。 "{guid}" // 文件的全局唯一标识符 (GUID)。 "checksum_bytes" // 十六进制数的字符串,表示校验和的字节。必须是偶数位的十六进制数。奇数位的十六进制数字会导致编译时警告,然后指令被忽略。
示例:
namespace CodeExecutor; #pragma checksum "Program.cs" "{88FBCA52-7B47-4D4B-9B9C-61F35F8E5A8C}" "4A5B6C7D" public static class Program { public static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!"); } }
源文件Program.cs编译时生成的校验和信息被嵌入.pdf文件中:

文章引用
-
微软官方文档 - C# 预处理器指令
https://learn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/csharp/language-reference/preprocessor-directives -
MSDN C# 编程指南 & 参考手册 2015 - C# 预处理器指令
https://wizardforcel.gitbooks.io/msdn-csharp/content/ref/200.html
文章声明
内容准确性: 我会尽力确保所分享信息的准确性和可靠性,但由于个人知识有限,难免会有疏漏或错误。如果您在阅读过程中发现任何问题,请不吝赐教,我将及时更正。
AI: 文章内容参考了DeepSeek、智谱清言、通义灵码大语言模型生成的内容。
posted on 2025-02-07 10:29 wubing7755 阅读(22) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现