机器学习——自动生成古诗词
自动生成古诗词
一、选题背景
自动生成古诗词的初衷是想培养中小学生的传统文化,感受中华上下五千年的古诗词魅力,并培养他们的作词能力,陶冶情操
二、机器学习的实现步骤
- 从古诗词网站下载古诗,使用selenium 自动化框架进行爬取古诗词作为数据集
- 采用的是tensorflow的深度学习框架,TensorFlow™是一个基于数据流编程(dataflow programming)的符号数学系统,被广泛应用于各类机器学习(machine learning)算法的编程实现,其前身是谷歌的神经网络算法库DistBelief [1] 。
Tensorflow拥有多层级结构,可部署于各类服务器、PC终端和网页并支持GPU和TPU高性能数值计算,被广泛应用于谷歌内部的产品开发和各领域的科学研究 [1-2] 。
TensorFlow由谷歌人工智能团队谷歌大脑(Google Brain)开发和维护,拥有包括TensorFlow Hub、TensorFlow Lite、TensorFlow Research Cloud在内的多个项目以及各类应用程序接口(Application Programming Interface, API) [2] 。自2015年11月9日起,TensorFlow依据阿帕奇授权协议(Apache 2.0 open source license)开放源代码 [2] 。
- 因为计算机并不能像人类阅读文章时做到联系上下文,所以需要通过nlp神经网络模型来解决这个问题
三、机器学习的实现步骤
- 目的:培养广大的中小学生作词的能力
- 数据:通过selenium自动化框架对古诗词网站进行爬取,将爬取下来的古诗词用jieba 分词进行分词,将数据分为训练集和测试集
- 此次使用的是nlp循环神经网络模型

- 对模型的参数进行设置
- 对模型进行训练
- 使用测试集对模型进行测试,如果测试完的模型没有达到想要的效果则将其进行重新训练
1、导入需要用到的库

2诗集总数


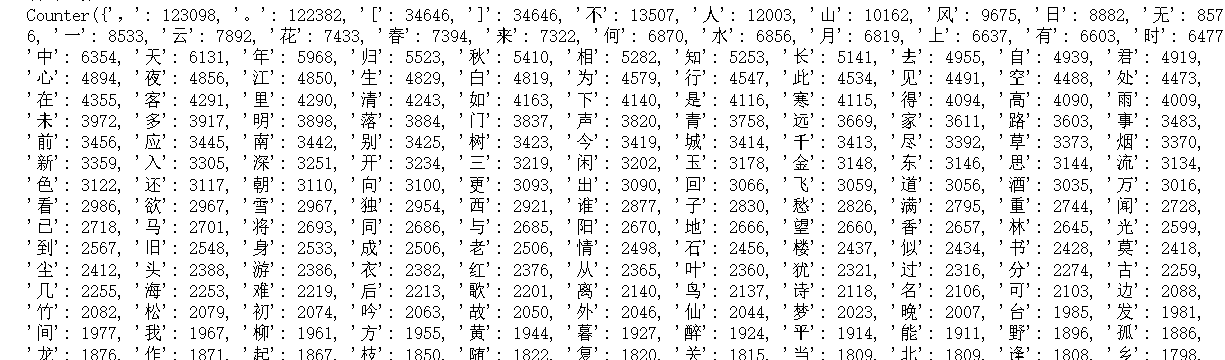
3、统计每个字出现次数


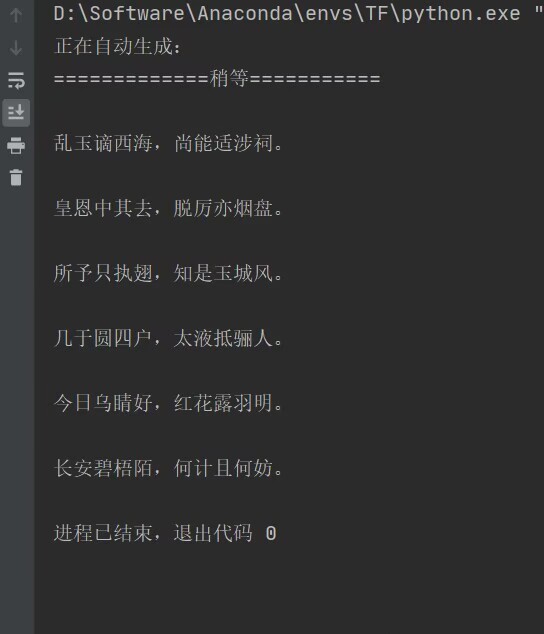
生成结果
四、总结
在训练的过程中发现总是会出现过拟合的现象,在处理的数据的时候,准备的数据还是不够多,在这个过程中,巩固了之前学习的知识,也对机器学习有了更深层次的理解。最终的训练模型达到了预期的效果。通过selenium自动化框架对古诗词网站进行爬取,将爬取下来的古诗词用jieba 分词进行分词,将数据分为训练集和测试集,经过这次的训练我深刻的意识到自己还有很多方面的不足,今后会不断地改善、加强自己对部分代码的理解。
五、完整源代码(以及输出结果)
1 #coding=utf-8 2 3 import collections 4 import numpy as np 5 import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf 6 import codecs 7 import importlib 8 #-------------------------------数据预处理---------------------------# 9 import sys 10 importlib.reload(sys) 11 12 13 14 poetry_file ='data/poetry.txt' 15 16 17 # 诗集 18 poetrys = [] 19 with codecs.open(poetry_file, "r",'utf-8') as f: 20 for line in f: 21 # print line 22 try: 23 title, content = line.strip().split(':') 24 content = content.replace(' ','') 25 if '_' in content or '(' in content or '(' in content or '《' in content or '[' in content: 26 continue 27 if len(content) < 5 or len(content) > 79: 28 continue 29 content = '[' + content + ']' 30 # print content 31 poetrys.append(content) 32 except Exception as e: 33 print (e) 34 35 # 按诗的字数排序 36 poetrys = sorted(poetrys,key=lambda line: len(line)) 37 print(u'唐诗总数: ', len(poetrys)) 38 39 # 统计每个字出现次数 40 all_words = [] 41 for poetry in poetrys: 42 all_words += [word for word in poetry] 43 counter = collections.Counter(all_words) 44 # print counter 45 count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1]) 46 # print count_pairs 47 words, _ = zip(*count_pairs) 48 #add empty char 49 words = words + (" ",) 50 # map word to id 51 # 每个字映射为一个数字ID 52 word2idmap = dict(zip(words,range(len(words)))) 53 # 把诗转换为向量形式 54 word2idfunc = lambda word: word2idmap.get(word,len(words)) 55 peorty_vecs = [list(map(word2idfunc,peotry)) for peotry in poetrys] 56 57 58 59 #batch-wise padding:do padding to the same size(sequence length) of each batch 60 batch_size = 1 61 n_batch = (len(peorty_vecs)-1) // batch_size 62 X_data,Y_data = [],[] 63 for i in range(n_batch): 64 cur_vecs = peorty_vecs[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size] 65 current_batch_max_length = max(map(len,cur_vecs)) 66 batch_matrix = np.full((batch_size,current_batch_max_length),word2idfunc(" "),np.int32) 67 for j in range(batch_size): 68 batch_matrix[j,:len(cur_vecs[j])] = cur_vecs[j] 69 x = batch_matrix 70 X_data.append(x) 71 y = np.copy(x) 72 y[:,:-1] = x[:,1:] 73 # print x 74 # print y 75 Y_data.append(y) 76 77 78 #build rnn 79 80 vocab_size = len(words)+1 81 tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution() 82 83 #input_size:(batch_size,feature_length) 84 input_sequences = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=[batch_size,None]) 85 output_sequences = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=[batch_size,None]) 86 87 88 def build_rnn(hidden_units=128,layers=2): 89 #embeding 90 with tf.variable_scope("embedding"): 91 embedding = tf.get_variable("embedding",[vocab_size,hidden_units],dtype=tf.float32) 92 #input: batch_size * time_step * embedding_feature 93 input = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding,input_sequences) 94 95 basic_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(hidden_units,state_is_tuple=True) 96 stack_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([basic_cell]*layers) 97 _initial_state = stack_cell.zero_state(batch_size,tf.float32) 98 outputs, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(stack_cell, input,initial_state=_initial_state,dtype=tf.float32) 99 outputs = tf.reshape(outputs, [-1,hidden_units]) 100 101 with tf.variable_scope("softmax"): 102 softmax_w =tf.get_variable("softmax_w",[hidden_units,vocab_size]) 103 softmax_b =tf.get_variable("softmax_b",[vocab_size]) 104 logits = tf.matmul(outputs,softmax_w)+softmax_b 105 106 probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits) 107 108 return logits, probs,stack_cell, _initial_state,state 109 110 def train(reload=True): 111 logits, probs,_,_,_ = build_rnn() 112 113 targets = tf.reshape(output_sequences,[-1]) 114 115 loss = tf.nn.seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example([logits], [targets], 116 [tf.ones_like(targets, dtype=tf.float32)],len(words)) 117 cost = tf.reduce_mean(loss) 118 119 learning_rate = tf.Variable(0.002, trainable=False) 120 tvars = tf.trainable_variables() 121 grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(cost, tvars), 5) 122 optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate) 123 train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, tvars)) 124 125 global_step = 0 126 with tf.Session() as sess: 127 sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) 128 129 saver = tf.train.Saver(write_version=tf.train.SaverDef.V2) 130 131 if reload: 132 module_file = tf.train.latest_checkpoint('.') 133 sess = saver.restore(module_file) 134 print ("reload sess") 135 136 for epoch in range(50): 137 print ("learning_rate decrease") 138 if global_step%80==0: 139 sess.run(tf.assign(learning_rate, 0.002 * (0.97 ** epoch))) 140 epoch_steps = len(zip(X_data,Y_data)) 141 for step,(x,y) in enumerate(zip(X_data,Y_data)): 142 global_step = epoch * epoch_steps + step 143 _, los = sess.run([train_op, cost], feed_dict={ 144 input_sequences:x, 145 output_sequences:y, 146 }) 147 print ("epoch:%d steps:%d/%d loss:%3f" % (epoch,step,epoch_steps,los)) 148 if global_step%100==0: 149 print ("save model") 150 saver.save(sess,"peotry",global_step=epoch) 151 152 153 def write_poem(): 154 155 def to_word(weights): 156 t = np.cumsum(weights) 157 s = np.sum(weights) 158 sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s)) 159 print ("sample:",sample) 160 print ("len Words:",len(words)) 161 return words[sample] 162 163 # 164 165 logits, probs,stack_cell, _initial_state, last_state = build_rnn() 166 with tf.Session() as sess: 167 sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) 168 saver = tf.train.Saver(write_version=tf.train.SaverDef.V2) 169 module_file = tf.train.latest_checkpoint('.') 170 print ("load:",module_file) 171 saver.restore(sess,module_file) 172 173 _state = sess.run(stack_cell.zero_state(1,dtype=tf.float32)) 174 175 x = np.array([[word2idfunc('[')]]) 176 177 prob_, _state = sess.run([probs,last_state],feed_dict={input_sequences:x,_initial_state:_state}) 178 179 word = to_word(prob_) 180 181 poem = '' 182 183 import time 184 while word != ']': 185 poem += word 186 x = np.array([[word2idfunc(word)]]) 187 [probs_, _state] = sess.run([probs, last_state], feed_dict={input_sequences: x, _initial_state: _state}) 188 word = to_word(probs_) 189 # time.sleep(1) 190 191 return poem 192 193 194 def write_head_poem(heads): 195 196 def to_word(weights): 197 #注意:以下注释代码实现了按照分布的概率进行采样,也可用在word2vec中 198 # t = np.cumsum(weights) 199 # s = np.sum(weights) 200 # sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1)*s)) 201 # print "sample:",sample 202 # print "len Words:",len(words) 203 sample = np.argmax(weights) 204 return words[sample] 205 206 logits, probs,stack_cell, _initial_state, last_state = build_rnn() 207 208 with tf.Session() as sess: 209 sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) 210 saver = tf.train.Saver(write_version=tf.train.SaverDef.V2) 211 module_file = tf.train.latest_checkpoint('.') 212 print ("load:",module_file) 213 saver.restore(sess,module_file) 214 215 _state = sess.run(stack_cell.zero_state(1,dtype=tf.float32)) 216 217 poem = '' 218 add_comma = False 219 for head in heads: 220 x = head 221 add_comma = not add_comma 222 while x!="," and x!="。" and x!=']': 223 #add current 224 poem += x 225 x = np.array([[word2idfunc(x)]]) 226 #generate next based on current 227 prob_, _state = sess.run([probs,last_state],feed_dict={input_sequences:x,_initial_state:_state}) 228 x = to_word(prob_) 229 sign = "," if add_comma else "。" 230 poem = poem + sign 231 return poem 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 # train(False) 239 print(write_poem()) 240 # print(write_head_poem(u"一二三四"))



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号