Tomcat异常处理机制
声明
源码基于Spring Boot 2.3.12中依赖的Tomcat
异常例子
tomcat中返回错误页面目前主要是以下两种情况。
- 执行
servlet发生异常 - 程序中主动调用
response.sendError()方法。
下面先来看看tomcat默认的处理结果
编写以下例子触发第一种情况
@WebServlet("/exception")
public class ExceptionServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4621356333568059989L;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name");
}
}
执行结果如下图所示
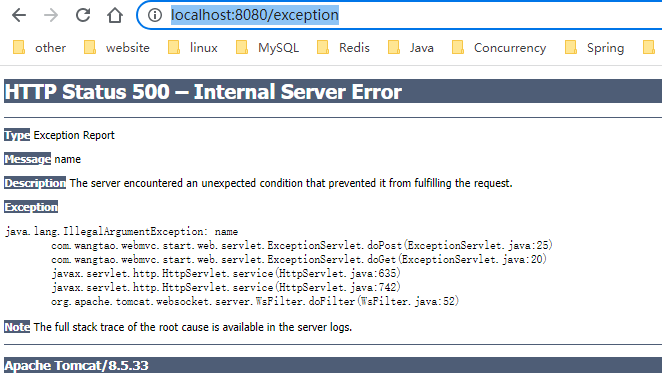
编写下面例子触发第二种情况
@WebServlet("/sendError")
public class SendErrorServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -7823675542130292567L;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 使用该属性可携带异常信息
req.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, new NullPointerException("name must not be null"));
resp.sendError(500, "system error!");
}
}
执行结果如下图所示
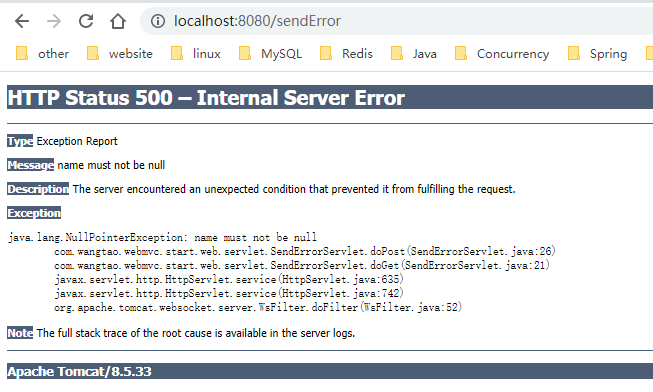
如果把代码中req.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, 'xxxx')去掉则是以下结果
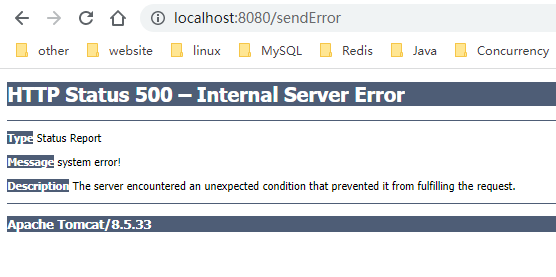
可以看到tomcat给我们返回的主要信息便是Message、Exception,其中Message的取值逻辑如下,如果有异常信息,即存在Exception,则为e.getMessage,否则便是sendError方法中指定的值。
注:
以上代码如果在Spring Boot环境中执行,需要在启动类排除掉错误处理的自动配置类,Spring Boot默认使用/error来返回错误页面。
即@SpringBootApplication(exclude = ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.class)
源码说明
首先要明确一点,sendError方法并不是在执行时就返回页面给客户端,该方法仅仅只是打了一个错误标记而已。打开源码可以看到以下片段
/**
* org.apache.catalina.connector.Response.java
*/
@Override
public void sendError(int status, String message) throws IOException {
if (isCommitted()) {
throw new IllegalStateException
(sm.getString("coyoteResponse.sendError.ise"));
}
// Ignore any call from an included servlet
if (included) {
return;
}
// 打一个错误标记,真正处理错误时会用到这个标记
setError();
// 设置返回状态码, 同时会清空message
getCoyoteResponse().setStatus(status);
// 设置错误信息
getCoyoteResponse().setMessage(message);
// Clear any data content that has been buffered
resetBuffer();
// Cause the response to be finished (from the application perspective)
setSuspended(true);
}
public boolean setError() {
// 将内部的reponse对象的errorState更新成1
return getCoyoteResponse().setError();
}
public boolean setError() {
return errorState.compareAndSet(0, 1);
}
真正执行错误页面逻辑的类是org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// ...略
// 从request对象中获取异常信息
Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
/*
* 判断是否有错误,errorState == 1
* sendError方法中会调用setError方法,更新errorState为1
*/
if (response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
AtomicBoolean result = new AtomicBoolean(false);
response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.IS_IO_ALLOWED, result);
if (result.get()) {
if (t != null) {
// 根据异常处理
throwable(request, response, t);
} else {
// 根据状态码处理
status(request, response);
}
}
}
}
protected void throwable(Request request, Response response,
Throwable throwable) {
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
return;
}
// 真实的错误
Throwable realError = throwable;
if (realError instanceof ServletException) {
// 获取cause by
realError = ((ServletException) realError).getRootCause();
if (realError == null) {
realError = throwable;
}
}
// If this is an aborted request from a client just log it and return
if (realError instanceof ClientAbortException ) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug
(sm.getString("standardHost.clientAbort",
realError.getCause().getMessage()));
}
return;
}
// 获取该异常对应的错误页面
ErrorPage errorPage = context.findErrorPage(throwable);
if ((errorPage == null) && (realError != throwable)) {
// 没有找到,再根据真实的异常再找一遍
errorPage = context.findErrorPage(realError);
}
if (errorPage != null) {
// 错误页面不为空,设置一系列的属性,
if (response.setErrorReported()) {
response.setAppCommitted(false);
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR,
errorPage.getLocation());
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR,
DispatcherType.ERROR);
// 错误码, 默认就是500
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE,
Integer.valueOf(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR));
// 错误原因
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_MESSAGE,
throwable.getMessage());
// 真实的异常信息
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION,
realError);
Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper();
if (wrapper != null) {
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_SERVLET_NAME,
wrapper.getName());
}
// 请求路径
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_REQUEST_URI,
request.getRequestURI());
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION_TYPE,
realError.getClass());
// 响应页面内容
if (custom(request, response, errorPage)) {
try {
response.finishResponse();
} catch (IOException e) {
container.getLogger().warn("Exception Processing " + errorPage, e);
}
}
}
} else {
// 根据异常没有找到错误页面,再根据错误码找,将状态码改成500
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
// The response is an error
response.setError();
// 根据状态码处理
status(request, response);
}
}
private void status(Request request, Response response) {
// 获取状态码
int statusCode = response.getStatus();
// Handle a custom error page for this status code
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
return;
}
if (!response.isError()) {
return;
}
// 根据状态码获取错误页面
ErrorPage errorPage = context.findErrorPage(statusCode);
if (errorPage == null) {
// 找不到则使用0再找一次,这点很重要, SpringBoot就是注册了一个0的错误页面
errorPage = context.findErrorPage(0);
}
if (errorPage != null && response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
response.setAppCommitted(false);
// 设置状态码
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE,
Integer.valueOf(statusCode));
// 获取错误信息,sendError方法第二个参数的值(参加该方法说明)
String message = response.getMessage();
if (message == null) {
message = "";
}
// 设置错误信息
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_MESSAGE, message);
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR,
errorPage.getLocation());
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR,
DispatcherType.ERROR);
Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper();
if (wrapper != null) {
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_SERVLET_NAME,
wrapper.getName());
}
// 设置请求路径
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_REQUEST_URI,
request.getRequestURI());
// 响应页面内容
if (custom(request, response, errorPage)) {
response.setErrorReported();
try {
response.finishResponse();
} catch (ClientAbortException e) {
// Ignore
} catch (IOException e) {
container.getLogger().warn("Exception Processing " + errorPage, e);
}
}
}
}
private boolean custom(Request request, Response response,
ErrorPage errorPage) {
if (container.getLogger().isDebugEnabled()) {
container.getLogger().debug("Processing " + errorPage);
}
try {
// Forward control to the specified location
ServletContext servletContext =
request.getContext().getServletContext();
// 根据错误页面的路径获取转发器
RequestDispatcher rd =
servletContext.getRequestDispatcher(errorPage.getLocation());
if (rd == null) {
container.getLogger().error(
sm.getString("standardHostValue.customStatusFailed", errorPage.getLocation()));
return false;
}
if (response.isCommitted()) {
// Response is committed - including the error page is the
// best we can do
rd.include(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
} else {
// Reset the response (keeping the real error code and message)
response.resetBuffer(true);
response.setContentLength(-1);
// 转发到指定页面,Spring Boot默认是/error
rd.forward(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
// If we forward, the response is suspended again
response.setSuspended(false);
}
// Indicate that we have successfully processed this custom page
return true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// Report our failure to process this custom page
container.getLogger().error("Exception Processing " + errorPage, t);
return false;
}
}
如果根据异常或者状态码找到了对应的错误页面,则会根据错误页面的配置的路径进行返回。在Spring Boot中就是配置了一个状态码为0,路径为/error的一个错误页面,而/error则对应于BasicErrorController这个处理器,用于处理所有的错误信息。当然了如果请求被全局异常处理器处理掉了,而没有走到tomcat本身的异常处理逻辑(即DispatcherServlet没有向外抛出异常,也没有调用response.sendError方法时)是不会转发到/error路径的。
默认情况下,tomcat中是没有配置任何错误页面的,因此根据异常或者状态码是找不到错误页面的,最终会执行一个默认处理,处理类为org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve,展示的内容如上面例子图片所示。
可以看到上面处理逻辑会先从request对象中获取异常信息,那么对于上文所说的第一种情况,即Servlet处理时往外抛出异常时,不难猜到tomcat内部在执行Servlet时会捕获异常,同时通过req.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, e)方法将异常信息放到request对象中,供后续异常处理时使用,具体代码见org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve类,该类会执行过滤器链以及Servlet本身逻辑。
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// ... 略
Servlet servlet = null;
try {
// 获取Servlet
servlet = wrapper.allocate();
}
// 省略了很多无关逻辑
try {
if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {
// 执行过滤器链以及Servlet
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
exception(request, response, e);
}
// ...略
}
private void exception(Request request, Response response,
Throwable exception) {
// 设置异常信息
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, exception);
// 设置状态码
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
// 设置错误标记
response.setError();
}
到这里,tomcat内部的一个错误处理机制便基本介绍完了。
配置错误页面
前文说到,tomcat会根据异常信息或者状态码去寻找对应的错误页面,如果没有找到则会使用一个默认页面返回给客户端。那么该如何配置错误页面,便是本节要说明的内容。
- 通过web.xml方式配置
<!-- 根据状态码配置 -->
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/404.html</location>
</error-page>
<!-- 状态码为0时可以匹配所有的状态码 -->
<error-page>
<error-code>0</error-code>
<location>/error.html</location>
</error-page>
<!-- 根据异常类型配置 -->
<error-page>
<exception-type>java.lang.NullPointerException</exception-type>
<location>/error.html</location>
</error-page>
- 内嵌容器编码
Spring Boot运行时一般使用内嵌容器,在org.apache.catalina.Context接口中定义了方法,可配置错误页面
public interface Context extends Container, ContextBind {
void addErrorPage(ErrorPage errorPage);
}
可以参考org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory
protected void configureContext(Context context, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) {
TomcatStarter starter = new TomcatStarter(initializers);
if (context instanceof TomcatEmbeddedContext) {
TomcatEmbeddedContext embeddedContext = (TomcatEmbeddedContext) context;
embeddedContext.setStarter(starter);
embeddedContext.setFailCtxIfServletStartFails(true);
}
context.addServletContainerInitializer(starter, NO_CLASSES);
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : this.contextLifecycleListeners) {
context.addLifecycleListener(lifecycleListener);
}
for (Valve valve : this.contextValves) {
context.getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
// 配置错误页面
for (ErrorPage errorPage : getErrorPages()) {
org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.ErrorPage tomcatErrorPage = new org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.ErrorPage();
tomcatErrorPage.setLocation(errorPage.getPath());
tomcatErrorPage.setErrorCode(errorPage.getStatusCode());
tomcatErrorPage.setExceptionType(errorPage.getExceptionName());
context.addErrorPage(tomcatErrorPage);
}
for (MimeMappings.Mapping mapping : getMimeMappings()) {
context.addMimeMapping(mapping.getExtension(), mapping.getMimeType());
}
configureSession(context);
new DisableReferenceClearingContextCustomizer().customize(context);
for (TomcatContextCustomizer customizer : this.tomcatContextCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(context);
}
}
总结
response中3个关键方法的作用
setStatus(404),设置状态码以及message,message将为空。sendError(404),设置错误标志,状态码,message为空。sendError(404, "System Error!"),设置错误标志、状态码、message。
- tomcat处理错误时,优先以异常处理,然后再是状态码处理,如果有异常,状态码固定是500,即
setStatus、sendError方法指定的状态码无效,message取e.getMessage()。如果没有异常,则状态码为sendError指定的状态码,message为sendError指定的message。响应给客户端时,会优先根据异常信息寻找配置的错误页面,找不到则会再根据状态码寻找配置的错误页面,特别的,状态码为0的错误页面可以匹配到所有的状态码,找到错误页面后,会给request对象设置一系列的值,诸如状态码,message,异常,请求路径等重要信息,然后转发到错误页面指定的路径。若没有找到错误页面,则返回一个默认的返回给客户端,包含状态码,message,异常等重要信息。 request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION)方法可以获取到Servlet执行时抛出的异常。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号