C++ STL之set学习笔记
1.set了解:set作为一个容器也是用来存储同一数据类型的数据类型,并且能从一个数据集合中取出数据,在set中每个元素的值都唯一,而且系统能根据元素的值自动进行排序。应该注意的是set中数元素的值不能直接被改变。C++ STL中标准关联容器set, multiset, map, multimap内部采用的就是一种非常高效的平衡检索二叉树:红黑树,也成为RB树(Red-Black Tree)。RB树的统计性能要好于一般平衡二叉树,所以被STL选择作为了关联容器的内部结构,在set中查找是使用二分查找。
2.set具备的两个特点:set中的元素都是排序好的 ;set中的元素都是唯一的,没有重复的
3.常用工具:
insert(); //在集合中插入元素
begin(); // 返回指向第一个元素的迭代器
end(); // 返回指向set中的结尾,end()中是一个随便的数
clear(); // 清除所有元素
count(); // 返回某个值元素的个数,由于set中无重复元素,则count返回的就是0,1;也就是用来判断有无某个元素
empty(); // 如果集合为空,返回true
erase(); //删除集合中某个元素
find(); //返回一个指向被查找到元素的迭代器
lower_bound(); //返回指向大于(或等于)某值的第一个元素的迭代器
upper_bound(); //返回大于某个值元素的迭代器
size(); //集合中元素的数目
max_size(); //返回集合能容纳的元素的最大限值
rbegin(); //返回指向集合中最后一个元素的反向迭代器
rend(); //返回指向集合中第一个元素的反向迭代器
4.判两个set是否相等:直接用"=="判;
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <set> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 set<int>a,b; 9 a.clear(); 10 b.clear(); 11 a.insert(1); 12 a.insert(2); 13 a.insert(3); 14 b.insert(2); 15 b.insert(1); 16 b.insert(3); 17 if( a==b ) printf("a,b两个集合相同\n"); 18 else printf("a,b两个集合不相同\n"); 19 a.insert(5); 20 if( a==b ) printf("a,b两个集合相同\n"); 21 else printf("a,b两个集合不相同\n"); 22 return 0; 23 }
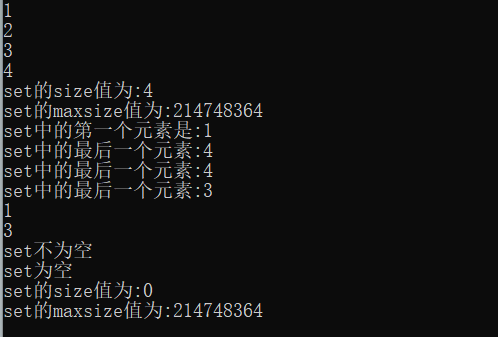
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <set> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 set<int>s; 10 set<int>::iterator it; 11 s.insert(1); 12 s.insert(2); 13 s.insert(3); 14 s.insert(4); 15 s.insert(1); 16 17 for(it=s.begin(); it!=s.end(); it++){ 18 printf("%d\n",*it); 19 } 20 21 printf("set的size值为:%d\n",s.size()); 22 printf("set的maxsize值为:%d\n",s.max_size()); 23 printf("set中的第一个元素是:%d\n",*s.begin()); 24 25 it = s.end(); 26 it--; 27 printf("set中的最后一个元素:%d\n",*it); 28 29 s.erase(2); 30 it = s.end(); 31 it--; 32 printf("set中的最后一个元素:%d\n",*it); 33 34 s.erase(4); 35 it = s.end(); 36 it--; 37 printf("set中的最后一个元素:%d\n",*it); 38 39 40 for(it=s.begin(); it!=s.end(); it++){ 41 printf("%d\n",*it); 42 } 43 if( s.empty() ) printf("set为空\n"); 44 else printf("set不为空\n"); 45 46 s.clear(); 47 if( s.empty() ) printf("set为空\n"); 48 else printf("set不为空\n"); 49 50 printf("set的size值为:%d\n",s.size()); 51 printf("set的maxsize值为:%d\n",s.max_size()); 52 return 0; 53 }
【count】
1 //count(); 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <set> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 set<int>s; 10 s.insert(1); 11 s.insert(2); 12 s.insert(3); 13 s.insert(1); 14 15 printf("set 中 1 出现的次数是 : %d\n",s.count(1)); 16 printf("set 中 5 出现的次数是 : %d\n",s.count(5)); 17 18 if( s.count(3) ) printf("set 中有 3\n"); 19 else printf("set 中没有 3\n"); 20 21 if( s.count(9) ) printf("set 中有 9\n"); 22 else printf("set 中没有 9\n"); 23 return 0; 24 }

【erase】
erase(iterator) ,删除定位器iterator指向的值
erase(first,second),删除定位器first和second之间的值,左闭右开
erase(key_value),删除键值key_value的值
1 //erase 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <set> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 set<int>s; 10 set<int>::const_iterator it; 11 set<int>::iterator first; 12 set<int>::iterator second; 13 for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){ 14 s.insert(i); 15 } 16 17 for(it=s.begin(); it!=s.end(); it++){ 18 printf("%d ",*it); 19 } 20 printf("\n"); 21 22 ///第一种删除 23 s.erase(s.begin()); 24 it = s.begin(); 25 s.erase(it); 26 27 ///第二种删除 28 first = s.begin(); 29 second = s.begin(); 30 second++; 31 second++; 32 33 printf("%d\n",*second); 34 s.erase(first,second); 35 36 ///第三种删除 37 s.erase(9); 38 39 printf("删除后 set 中的元素还剩:\n"); 40 for(it=s.begin(); it!=s.end(); it++){ 41 printf("%d ",*it); 42 } 43 printf("\n"); 44 return 0; 45 }

【find】
find() ,返回给定值值得定位器,如果没找到则返回end()。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <set> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int a[]={1,2,3}; 9 set<int> s(a,a+3); 10 set<int>::iterator it; 11 if( (it=s.find(2))!=s.end() ) printf("%d\n",*it); 12 if( (it=s.find(5))==s.end() ) printf("set 中没有 5\n"); 13 return 0; 14 }

【lower_bound+upper_bound】
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <set> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int a[]={1,5,9}; 9 set<int> s(a,a+3); 10 printf("%d\n",*s.lower_bound(1)); 11 printf("%d\n",*s.upper_bound(1)); 12 printf("%d\n",*s.lower_bound(3)); 13 printf("%d\n",*s.upper_bound(3)); 14 return 0; 15 }

【insert】
insert(key_value); 将key_value插入到set中 ,返回值是pair<set<int>::iterator,bool>,bool标志着插入是否成功,而iterator代表插入的位置,若key_value已经在set中,则iterator表示的key_value在set中的位置。
inset(first,second); 将定位器first到second之间的元素插入到set中,返回值是void.
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <set> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int a[]={1,5,9}; 9 set<int> s; 10 set<int>::iterator it; 11 s.insert(a,a+3); 12 for(it=s.begin(); it!=s.end(); it++){ 13 printf("%d ",*it); 14 } 15 printf("\n"); 16 17 pair<set<int>::iterator,bool>pr; 18 pr = s.insert(6); 19 if( pr.second ){ 20 printf("插入成功 %d\n",*pr.first); 21 } 22 pr = s.insert(5); 23 if( !pr.second ){ 24 printf("插入不成功 set 中已经有5了\n"); 25 } 26 return 0; 27 }

自定义比较函数
(1)元素不是结构体:
例:
//自定义比较函数myComp,重载“()”操作符
1 struct myComp 2 { 3 bool operator()(const your_type &a,const your_type &b) 4 [ 5 return a.data-b.data>0; 6 } 7 } 8 set<int,myComp>s; 9 ...... 10 set<int,myComp>::iterator it;
(2)如果元素是结构体,可以直接将比较函数写在结构体内。
例:
1 struct Info 2 { 3 string name; 4 float score; 5 //重载“<”操作符,自定义排序规则 6 bool operator < (const Info &a) const 7 { 8 //按score从大到小排列 9 return a.score<score; 10 } 11 } 12 set<Info> s; 13 ...... 14 set<Info>::iterator it;


