战略游戏(树形DP入门)
题目链接:here
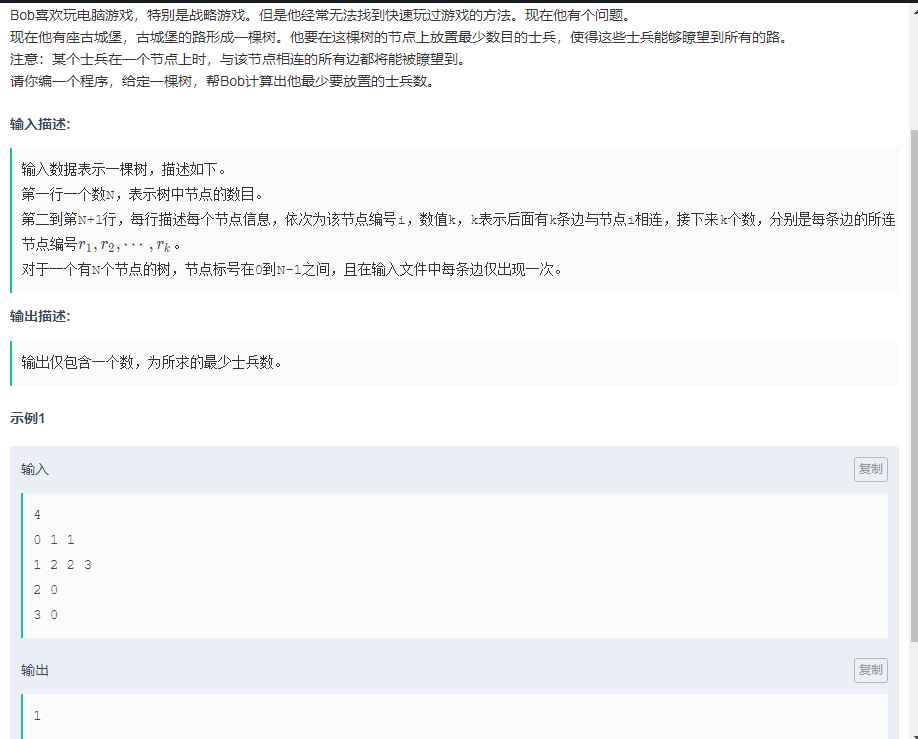
题目分析:
放置哨兵无非两种情况,放或不放,我们可以用dp[i][1]来表示第i个结点放置哨兵,dp[i][0]来表示第i个结点不放置哨兵,我们可以从上往下,从左往右来遍历树,所以这就用到了树形DP的知识,我们很容易知道,如果父亲结点没放哨兵,那么子结点肯定要放置哨兵,如果父亲放置了哨兵,那么子结点可以考虑放或者不放。所以很容易写出状态转移方程dp[v][1] += min(dp[u][1],dp[u][0]),dp[v][0] += dp[u][1]
和我的上一篇差不多:https://www.cnblogs.com/wsy107316/p/11319167.html
AC代码:
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 const int maxn = 1500+10; 5 const int mod = 1e9+7; 6 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; 7 8 9 struct node{ 10 int to,nxt; 11 }e[maxn<<1]; 12 int n; 13 int head[maxn]; 14 int tot; 15 int dp[maxn][2]; 16 17 void init(){ 18 memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); 19 tot = 0; 20 } 21 22 void addedge(int u,int v){ 23 e[tot].to=v; e[tot].nxt=head[u]; head[u]=tot++; 24 } 25 26 void dfs(int u,int fa){ 27 for(int i=head[u];~i;i=e[i].nxt){ 28 int to=e[i].to; 29 if( to==fa ) continue; 30 dfs(to,u); 31 dp[u][0] += dp[to][1]; 32 dp[u][1] += min(dp[to][1], dp[to][0]); 33 } 34 } 35 36 int main() 37 { 38 scanf("%d",&n); 39 init(); 40 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 41 int u, k; scanf("%d%d",&u,&k); 42 for(int j=0;j<k;j++){ 43 int v; scanf("%d",&v); 44 addedge(u,v); 45 addedge(v,u); 46 } 47 } 48 49 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){ 50 dp[i][0] = 0; 51 dp[i][1] = 1; 52 } 53 dfs(0,-1); 54 int minn = inf; 55 minn = min(dp[0][1], dp[0][0]); 56 printf("%d\n",minn); 57 return 0; 58 }


